Effect of Hyaluronic Acid Filler Injection on the Interdental Papilla in a Mouse Model of Open Gingival Embrasure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal
2.2. OGE Model
2.3. Injection of HA Filler into the IDP
2.4. Tissue Preparation
2.5. Immunohistochemistry
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
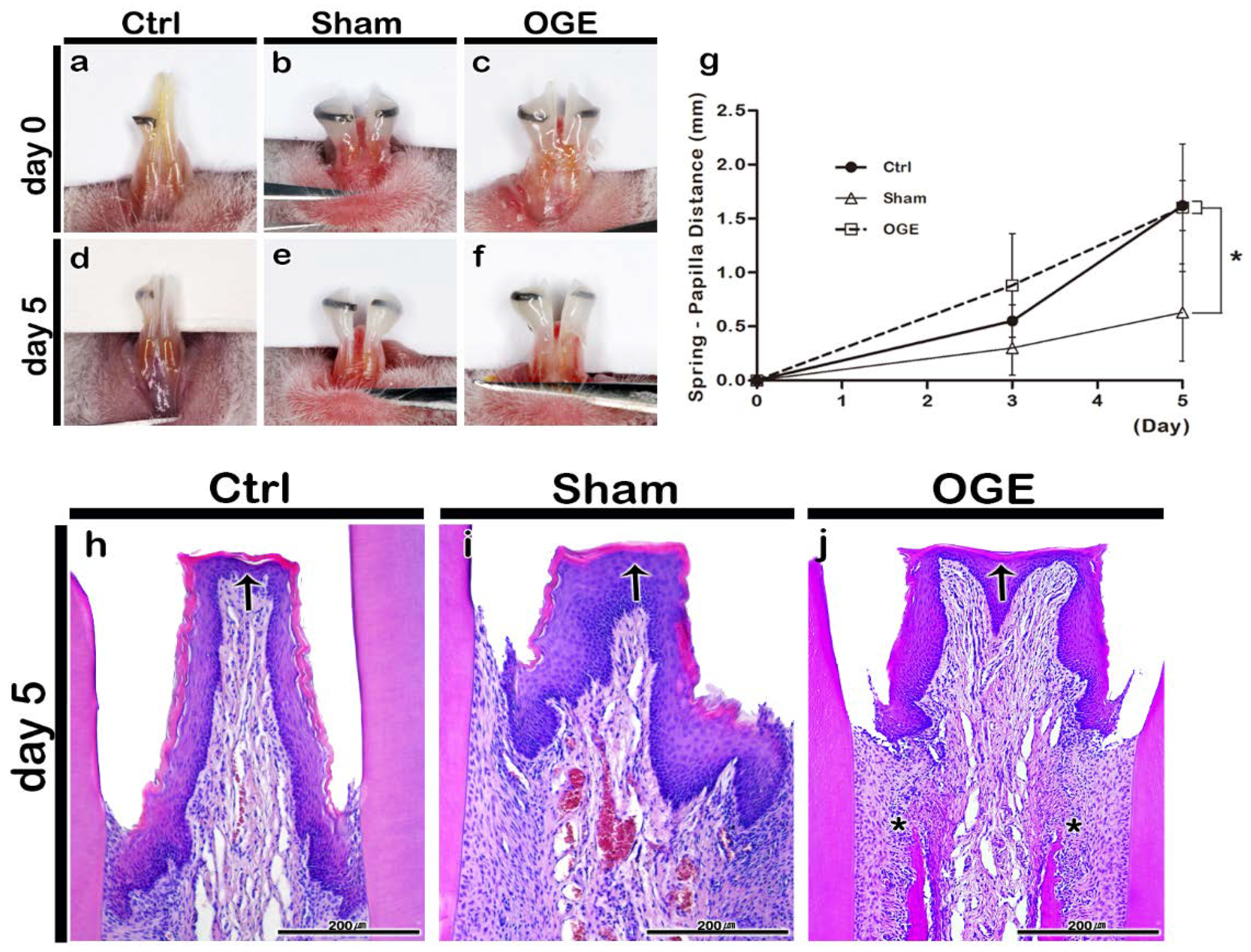
3.1. Morphological and Histological Changes in IDP after Wire Attachment
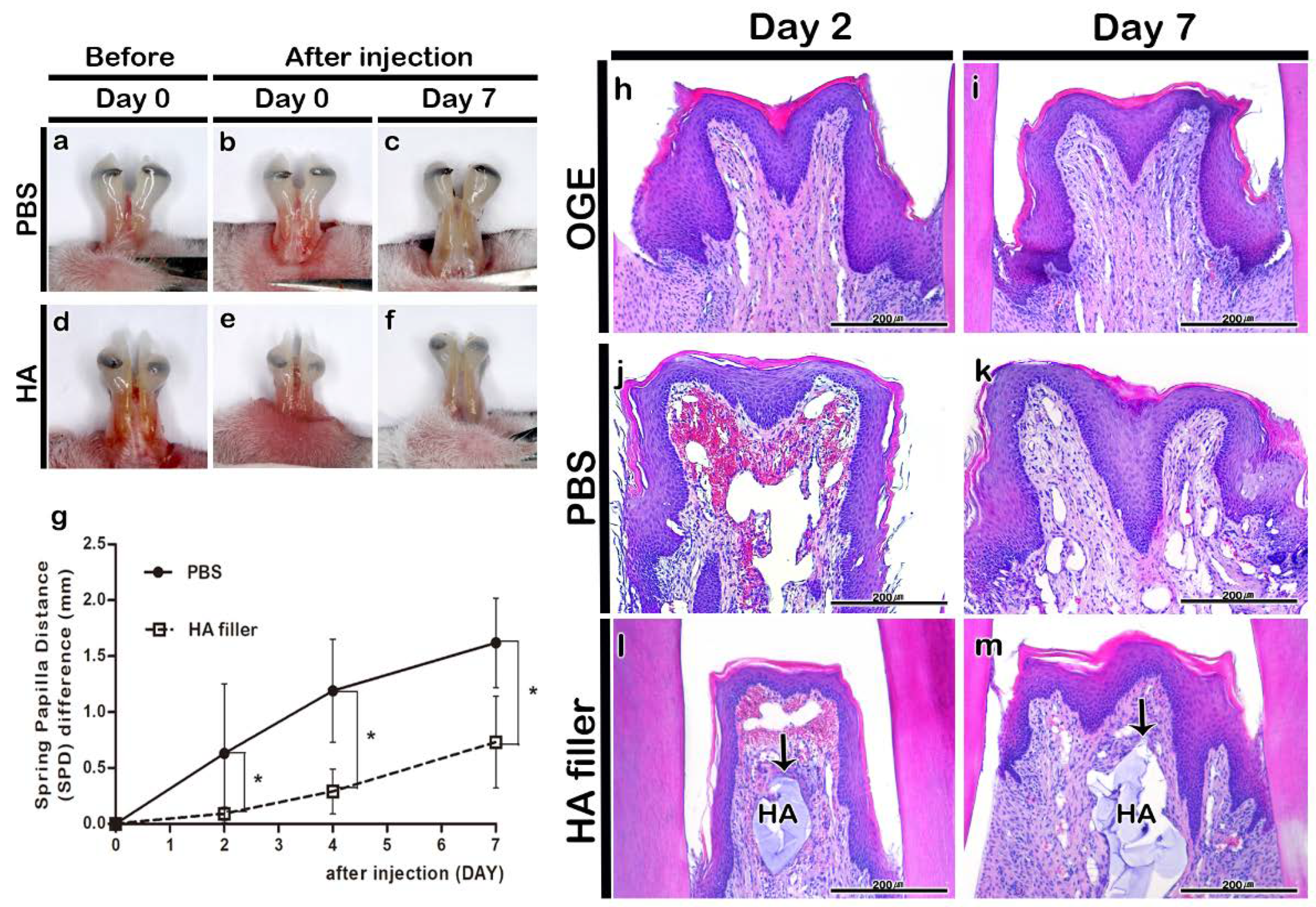
3.2. Morphological and Histological Changes in IDP after PBS or HA Filler Injection
3.3. Immunolocalization of Ki67 and Inflammatory Cytokines after PBS or HA Filler Injection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muthukumar, S.; Rangarao, S. Surgical augmentation of interdental papilla—A case series. Contemp. Clin. Dent. 2015, 6, S294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.P.; Uppoor, A.S.; Nayak, D.G.; Shah, D. Black triangle dilemma and its management in esthetic dentistry. Dent. Res. J. 2013, 10, 296–301. [Google Scholar]
- De Oliveira, J.D.; Storrer, C.M.; Sousa, A.M.; Lopes, T.R.; De Sousa Vieira, J.; Deliberador, T.M. Papillary regeneration: Anatomical aspects and treatment approaches. Rsbo Rev. Sul Bras. Odontol. 2012, 9, 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, W.; Gabitov, I.; Stepanov, M.; Kois, J.; Smidt, A.; Becker, B.E. Minimally invasive treatment for papillae deficiencies in the esthetic zone: A pilot study. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2010, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awartani, F.A.; Tatakis, D.N. Interdental papilla loss: Treatment by hyaluronic acid gel injection: A case series. Clin. Oral Investig. 2016, 20, 1775–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanwar, J.; Hungund, S.A. Hyaluronic acid: Hope of light to black triangles. J. Int. Soc. Prev. Community Dent. 2016, 6, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patel, P.; Thakkar, K.; Kikani, A.; Patel, V.; Kiran N, K.; Ahmed, S. Minimally invasive treatment for reconstruction of deficit interdental papillae: A piolt study. J. Dent. Spec. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.P.; Kim, H.J.; Yu, S.J.; Kim, B.O. Six month clinical evaluation of interdental papilla reconstruction with injectable hyaluronic acid gel using an image analysis system. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2016, 28, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelraouf, S.A.; Dahab, O.A.; Elbarbary, A.; El-Din, A.M.; Mostafa, B. Assessment of Hyaluronic Acid Gel Injection in the Reconstruction of Interdental Papilla: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 7, 1834–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fakhari, A.; Berkland, C. Applications and emerging trends of hyaluronic acid in tissue engineering, as a dermal filler and in osteoarthritis treatment. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 7081–7092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Necas, J.; Bartosikova, L.; Brauner, P.; Kolar, J. Hyaluronic acid (hyaluronan): A review. Vet. Med. 2008, 53, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casale, M.; Moffa, A.; Vella, P.; Sabatino, L.; Capuano, F.; Salvinelli, B.; Lopez, M.A.; Carinci, F.; Salvinelli, F. Hyaluronic Acid: Perspectives in Dentistry. A Systematic Review; SAGE Publications Sage UK: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesa, F.; Aneiros, J.; Cabrera, A.; Bravo, M.; Caballero, T.; Revelles, F.; Del Moral, R.G.; O’Valle, F. Antiproliferative effect of topic hyaluronic acid gel. Study in gingival biopsies of patients with periodontal disease. Histol. Histopathol. 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, R.M.; Silva, G.A.; Lima, M.F.; Calliari, M.V.; Almeida, A.P.; Alves, J.B.; Ferreira, A.J. Sodium hyaluronate accelerates the healing process in tooth sockets of rats. Arch. Oral Biol. 2008, 53, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahiya, P.; Kamal, R. Hyaluronic acid: A boon in periodontal therapy. N. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 5, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowman, M.K.; Matsuoka, S. Experimental approaches to hyaluronan structure. Carbohydr. Res. 2005, 340, 791–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, I.W. Novel and established applications of microbial polysaccharides. Trends Biotechnol. 1998, 16, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prestwich, G.D.; Kuo, J.-W. Chemically-modified HA for therapy and regenerative medicine. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2008, 9, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, H.G.; Hales, C.A. Chemistry and Biology of Hyaluronan; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, F.S.; Cazzaniga, A. Hyaluronic acid gel fillers in the management of facial aging. Clin. Interv. Aging 2008, 3, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gold, M.H. Use of hyaluronic acid fillers for the treatment of the aging face. Clin. Interv. Aging 2007, 2, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carruthers, A.; Carruthers, J. Non–animal-based hyaluronic acid fillers: Scientific and technical considerations. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2007, 120, 33S–40S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dover, J.S.; Carruthers, A.; Carruthers, J.; Alam, M. Clinical Use of RESTYLANE [published correction appears in Skin Therapy Lett. 2005 Mar;10(2):9]. Skin Ther. Lett. 2005, 105–107. [Google Scholar]
- Jordan, D.R. Soft-tissue fillers for wrinkles, folds and volume augmentation. Can. J. Ophthalmol. 2003, 38, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertl, K.; Gotfredsen, K.; Jensen, S.S.; Bruckmann, C.; Stavropoulos, A. Adverse reaction after hyaluronan injection for minimally invasive papilla volume augmentation. A report on two cases. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2017, 28, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertl, K.; Gotfredsen, K.; Jensen, S.S.; Bruckmann, C.; Stavropoulos, A. Can hyaluronan injections augment deficient papillae at implant-supported crowns in the anterior maxilla? A randomized controlled clinical trial with 6 months follow-up. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2017, 28, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, M.D.; Nedjai, B.; Hurst, T.; Pennington, D.J. Cytokines and chemokines: At the crossroads of cell signalling and inflammatory disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Res. 2014, 1843, 2563–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akdis, M.; Aab, A.; Altunbulakli, C.; Azkur, K.; Costa, R.A.; Crameri, R.; Duan, S.; Eiwegger, T.; Eljaszewicz, A.; Ferstl, R. Interleukins (from IL-1 to IL-38), interferons, transforming growth factor β, and TNF-α: Receptors, functions, and roles in diseases. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 984–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laskin, D.L.; Pendino, K.J. Macrophages and inflammatory mediators in tissue injury. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1995, 35, 655–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everse, J.; Grisham, M.B.; Everse, K.E. Peroxidases in Chemistry and Biology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1990; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Gross, S.; Gammon, S.T.; Moss, B.L.; Rauch, D.; Harding, J.; Heinecke, J.W.; Ratner, L.; Piwnica-Worms, D. Bioluminescence imaging of myeloperoxidase activity in vivo. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deby-Dupont, G.; Deby, C.; Lamy, M. Neutrophil myeloperoxidase revisited: It’s role in health and disease. Intensivmed. Notf. 1999, 36, 500–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerdes, J.; Lemke, H.; Baisch, H.; Wacker, H.-H.; Schwab, U.; Stein, H. Cell cycle analysis of a cell proliferation-associated human nuclear antigen defined by the monoclonal antibody Ki-67. J. Immunol. 1984, 133, 1710–1715. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pi, S.; Choi, Y.J.; Hwang, S.; Lee, D.W.; Yook, J.I.; Kim, K.H.; Chung, C.J. Local injection of hyaluronic acid filler improves open gingival embrasure: Validation through a rat model. J. Periodontol. 2017, 88, 1221–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charan, J.; Kantharia, N. How to calculate sample size in animal studies? J. Pharmacol. Pharmacother. 2013, 4, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- An, S.-Y.; Lee, Y.-J.; Neupane, S.; Jun, J.-H.; Kim, J.-Y.; Lee, Y.; Choi, K.-S.; An, C.-H.; Suh, J.-Y.; Shin, H.-I. Effects of vascular formation during alveolar bone process morphogenesis in mice. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 148, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liljequist, D.; Elfving, B.; Skavberg Roaldsen, K. Intraclass correlation–A discussion and demonstration of basic features. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Zarea, B.; Sghaireen, M.; Alomari, W.; Bheran, H.; Taher, I. Black triangles causes and management: A review of literature. Br. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2015, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plato Palathingal, J.M. Treatment of black triangle by using a sub-epithelial connective tissue graft. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2011, 5, 1688–1691. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.; Vandana, K.L. Use of different concentrations of hyaluronic acid in interdental papillary deficiency treatment: A clinical study. J. Indian Soc. Periodontol. 2019, 23, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, R. Comparing rat’s to human’s age: How old is my rat in people years? Nutrition 2005, 21, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drevensek, M.; Volk, J.; Sprogar, S.; Drevensek, G. Orthodontic force decreases the eruption rate of rat incisors. Eur. J. Orthod. 2009, 31, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.-Y.; Bae, S.-M.; Kyung, H.-M.; Sung, J.-H. The effects of continuous and intermittent compressive pressure on alkaline phosphatase activity of Periodontal Ligament cells. Korean J. Orthod. 1997, 27, 599–605. [Google Scholar]
- Lowney, J.J.; Norton, L.A.; Shafer, D.M.; Rossomando, E.F. Orthodontic forces increase tumor necrosis factor α in the human gingival sulcus. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1995, 108, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duranti, F.; Salti, G.; Bovani, B.; Calandra, M.; Rosati, M.L. Injectable hyaluronic acid gel for soft tissue augmentation: A clinical and histological study. Dermatol. Surg. 1998, 24, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki, M.; Aoi, N.; Gonda, K.; Hirabayashi, S.; Komuro, Y. Evaluation of the in vivo kinetics and biostimulatory effects of subcutaneously injected hyaluronic acid filler. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018, 142, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Oh, J.W.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, K.M.; Son, Y.I. Cross-linked hyaluronic acid gel injection for the patients with unilateral vocal cord paralysis. Korean J. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2005, 48, 1248–1253. [Google Scholar]
- ELSON, M.L. Soft Tissue Augmentation. Dermatol. Surg. 1995, 21, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollack, S.V. Silicone, fibrel, and collagen implantation for facial lines and wrinkles. J. Dermatol. Surg. Oncol. 1990, 16, 957–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, M.O.; Van Dyke, T.E. Natural resolution of inflammation. Periodontology 2000 2013, 63, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paliwal, S.; Fagien, S.; Sun, X.; Holt, T.; Kim, T.; Hee, C.K.; Van Epps, D.; Messina, D.J. Skin extracellular matrix stimulation following injection of a hyaluronic acid–based dermal filler in a rat model. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2014, 134, 1224–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribe, A.; Ribe, N. Neck skin rejuvenation: Histological and clinical changes after combined therapy with a fractional non-ablative laser and stabilized hyaluronic acid-based gel of non-animal origin. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2011, 13, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Garza, L.A.; Kang, S.; Varani, J.; Orringer, J.S.; Fisher, G.J.; Voorhees, J.J. In vivo stimulation of de novo collagen production caused by cross-linked hyaluronic acid dermal filler injections in photodamaged human skin. Arch. Dermatol. 2007, 143, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tecchio, C.; Micheletti, A.; Cassatella, M.A. Neutrophil-derived cytokines: Facts beyond expression. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krishnan, V.; Davidovitch, Z. Cellular, molecular, and tissue-level reactions to orthodontic force. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2006, 129, 469.e1–469.e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidovitch, Z.; Nicolay, O.F.; Ngan, P.W.; Shanfeld, J.L. Neurotransmitters, cytokines, and the control of alveolar bone remodeling in orthodontics. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 1988, 32, 411–435. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.A. Interleukin-1 and its biologically related cytokines. Adv. Immunol. 1989, 44, 153–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, C.; Carraux, P.; Micheels, P.; Kaya, G.; Salomon, D. In vivo bio-integration of three hyaluronic acid fillers in human skin: A histological study. Dermatology 2014, 228, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkhaleq, L.; Assi, M.; Abdullah, R.; Zamri-Saad, M.; Taufiq-Yap, Y.; Hezmee, M. The crucial roles of inflammatory mediators in inflammation: A review. Vet. World 2018, 11, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Antibody | Marked Cell | Localization Pattern | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBS Injection | HA Filler Injection | ||||
| Day 2 | Day 7 | Day 2 | Day 7 | ||
| Ki67 | Cell proliferation/nuclear | Basal cells of epithelium, Connective tissue around the injected material | Basal cells of epithelium | Basal cells of epithelium, Connective tissue around the injected material | Basal cells of epithelium |
| IL-1β | Macrophages/fibroblasts | Connective tissue cells | - | Connective tissue cells | - |
| IL-6 | Macrophages/fibroblasts | Very few cells in connective tissue | |||
| TNF-α | Activated macrophages | Connective tissue cells | - | Connective tissue cells | - |
| MPO | Neutrophils | Connective tissue around the injected material | - | Connective tissue around the injected material | - |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.-B.; Cho, J.; Jue, S.-S.; Park, J.H.; Kim, J.-Y. Effect of Hyaluronic Acid Filler Injection on the Interdental Papilla in a Mouse Model of Open Gingival Embrasure. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4956. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17144956
Kim S-B, Cho J, Jue S-S, Park JH, Kim J-Y. Effect of Hyaluronic Acid Filler Injection on the Interdental Papilla in a Mouse Model of Open Gingival Embrasure. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(14):4956. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17144956
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Soo-Bin, Jaehun Cho, Seong-Suk Jue, Jae Hyun Park, and Ji- Youn Kim. 2020. "Effect of Hyaluronic Acid Filler Injection on the Interdental Papilla in a Mouse Model of Open Gingival Embrasure" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 14: 4956. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17144956
APA StyleKim, S. -B., Cho, J., Jue, S. -S., Park, J. H., & Kim, J. -Y. (2020). Effect of Hyaluronic Acid Filler Injection on the Interdental Papilla in a Mouse Model of Open Gingival Embrasure. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(14), 4956. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17144956




