Comprehensive Assessment of Water Quality and Pollution Source Apportionment in Wuliangsuhai Lake, Inner Mongolia, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Chemical Analytical Procedures
2.2. Multivariate Statistical Analyses
2.2.1. PCA
2.2.2. HCA
2.3. Improved Nemerow Pollution Exponential Method and Comprehensive Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Descriptive Statistics of Water Quality Factors in Wuliangsuhai Lake
3.2. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) for Irrigation and Non-Irrigation Periods
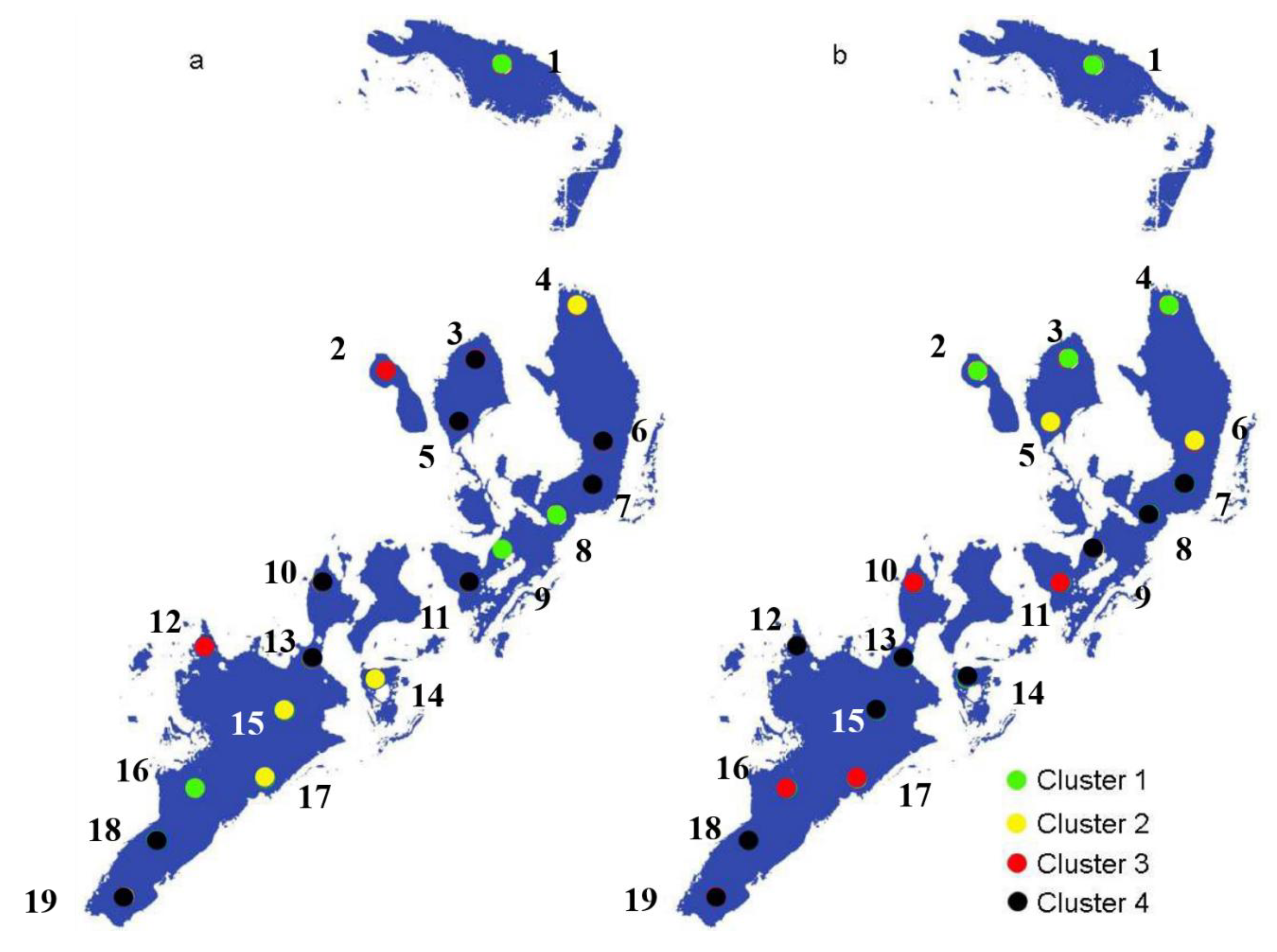
3.3. Hierarchical Cluster Analysis (HCA) for Irrigation and Non-Irrigation Periods
3.4. Possible Sources of Pollutants and Comprehensive Evaluation of Wuliangsuhai Lake
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giri, S.; Qiu, Z. Understanding the relationship of land uses and water quality in Twenty First Century: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 173, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artemyeva, A.A. Analytical chemistry in water quality monitoring during manned space missions. Acta Astronaut. 2016, 126, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Xia, C.; Xu, M.; Guo, J.; Sun, G. Application of modified water quality indices as indicators to assess the spatial and temporal trends of water quality in the Dongjiang River. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 66, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, S.J.; Cabral, J.A.; Bastos, R.; Cortes, R.; Vicente, J.; Eitelberg, D.; Yu, H.; Honrado, J.; Santos, M. A stochastic dynamic model to assess land use change scenarios on the ecological status of fluvial water bodies under the Water Framework Directive. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepage, M.; Harrison, T.; Breine, J.; Cabral, H.; Coates, S.; Galván, C.; García, P.; Jager, Z.; Kelly, F.; Mosch, E.C.; et al. An approach to intercalibrate ecological classification tools using fish in transitional water of the North East Atlantic. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 67, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobeyn, S.; Bennetsen, E.; Van Echelpoel, W.; Everaert, G.; Goethals, P.L.M. Impact of abundance data errors on the uncertainty of an ecological water quality assessment index. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 60, 746–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisi, O.; Ay, M. Comparison of Mann–Kendall and innovative trend method for water quality parameters of the Kizilirmak River, Turkey. J. Hydrol. 2014, 513, 362–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandel, P.; Maurel, M.; Chenu, D. Better understanding of water quality evolution in water distribution networks using data clustering. Water Res. 2015, 87, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Hou, Z.; Liao, J.; Fu, L.; Peng, Q. Influences of the land use pattern on water quality in low-order streams of the Dongjiang River basin, China: A multi-scale analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 551, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomer, D.B.; MacQuarrie, K.T.B.; Al, T.A. Using permutational and multivariate statistics to understand inorganic well water chemistry and the occurrence of methane in groundwater, southeastern New Brunswick, Canada. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 675, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustaoğlu, F.; Tepe, Y.; Taş, B. Assessment of stream quality and health risk in a subtropical Turkey river system: A combined approach using statistical analysis and water quality index. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 113, 105815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unda-Calvo, J.; Ruiz-Romera, E.; Martínez-Santos, M.; Vidal, M.; Antigüedad, I. Multivariate statistical analyses for water and sediment quality index development: A study of susceptibility in an urban river. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 135026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.Y.; Lee, K.L.; Im, T.H.; Lee, I.J.; Kim, S.; Han, K.Y.; Ahn, J.M. Evaluation of water quality for the Nakdong River watershed using multivariate analysis. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2016, 5, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koebbing, J.F.; Patuzzi, F.; Baratieri, M.; Beckmann, V.; Thevs, N.; Zerbe, S. Economic evaluation of common reed potential for energy production: A case study in Wuliangsuhai Lake (Inner Mongolia, China). Biomass Bioenergy 2014, 70, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, C.W.; He, J.; Liang, Y.; Mao, H.F.; Liu, H.L.; Wang, F.J. Temporal and spatial distribution of biogenic silica and its significance in the Wuliangsuhai Lake and Daihai Lake. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2010, 30, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Teng, F.; Yang, W.; Wang, F.; Yu, L. Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Pollution Assessment of Ice-water Pollutants During the Ice-sealing Period in Wuliangsuhai. J. Irrig. Drain. 2020, 39, 122. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, R.F.; Hu, Y.Y.; Zhang, S.Y.; Wu, R.R.; Guo, X.T. Microplastics in the surface water of Wuliangsuhai Lake, northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 723, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.P.; Xing, Y.X.; Wei, C.L.; Li, Y.Y.; Liu, Y.M.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Y. Distribution and Assessment of Heavy Metals in the Overlying Water-Sediment-Plant-Fish System in the Wuliangsuhai Lake by Using Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2019, 39, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.-J.; He, L.-s.; Li, Q.; Yuan, D.-h.; Deng, Y. Investigating the spatial variability of dissolved organic matter quantity and composition in Lake Wuliangsuhai. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 62, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, J.Y.; Wang, G.Q.; Wang, X.J.; Wu, J.W. Impact of changes in water management on hydrology and environment: A case study in North China. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2020, 28, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, D.; Li, C.; Shi, X.; Zhao, S.; Quan, D.; Yang, Z. Seasonal changes of nutritional status of lake Wuliangsuhai. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2019, 33, 186–192. [Google Scholar]
- Ba, D. Characterization of Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Environmental Factors of Wuliangsuhai Lake and Evaluation of its Eutrophication. Trans. Oceanol. Limnol. 2019, 4, 108–114. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Shi, X.H.; Li, C.Y.; Zhao, S.N.; Pen, F.; Green, T.R. Simulation of Hydrology and Nutrient Transport in the Hetao Irrigation District, Inner Mongolia, China. Water 2017, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, C.Y.; Zhang, C.F.; Shi, X.H.; Bourque, C.P.A.; Zhao, S.N. Evaluation of the applicability of the SWAT model in an arid piedmont plain oasis. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 73, 1341–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, L.; Lu, C.W.; He, J.; Wang, W.Y.; Yan, D.H. Impacts of Microorganisms on Degradation and Release Characteristics of Organic Phosphorus in Lake Sediments During Freezing Season. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2015, 36, 4501–4508. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.L.; Wei, J.X.; Bai, N.; Cha, H.; Cao, C.; Zheng, K.X.; Liu, Y. The phosphorus fractions and adsorption-desorption characteristics in the Wuliangsuhai Lake, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 20648–20661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerschbaumer, L.; Kobbing, J.F.; Ott, K.; Zerbe, S.; Thevs, N. Development scenarios on Hetao irrigation area (China): A qualitative analysis from social, economic and ecological perspectives. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 815–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.N.; Ryan, M.C.; Sun, B.; Li, C.Y. The influence of irrigation and Wuliangsuhai Lake on groundwater quality in eastern Hetao Basin, Inner Mongolia, China. Hydrogeol. J. 2014, 22, 1101–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotomayor, G.; Hampel, H.; Vázquez, R.F.; Goethals, P.L.M. Multivariate-statistics based selection of a benthic macroinvertebrate index for assessing water quality in the Paute River basin (Ecuador). Ecol. Indic. 2020, 111, 106037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuc, M.; Cieslik-Boczula, K.; Rospenk, M. Influence of inhalation anesthetics on the chain-melting phase transition of DPPC liposomes. Near-infrared spectroscopy studies supported by PCA analysis. Vib. Spectrosc. 2016, 85, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armano, G.; Farmani, M.R. Multiobjective clustering analysis using particle swarm optimization. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 55, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Li, F.; Li, J.; Liu, Q. Distribution and Contamination Risk Assessment of Dissolved Trace Metals in Surface Waters in the Yellow River Delta. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2013, 19, 1514–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, M.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Su, C. Arsenic and Heavy Metal Accumulation and Risk Assessment in Soils around Mining Areas: The Urad Houqi Area in Arid Northwest China as an Example. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, N.; Liu, W.; Xie, H.; Gao, L.; Han, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, H. Distribution and assessment of heavy metals in the surface sediment of Yellow River, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 39, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xia, X.H.; Yang, Z.F.; Wang, F. Assessment of water quality in Baiyangdian Lake using multivariate statistical techniques. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 13, 1213–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.Q.; Fan, D.J.; Zhang, X.X.; Chen, J.; Li, C.F.; Cao, C.G. Deep placement of nitrogen fertilizers reduces ammonia volatilization and increases nitrogen utilization efficiency in no-tillage paddy fields in central China. Field Crop. Res. 2015, 184, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Huo, S.; Xi, B.; Zhang, J.; Wu, F. Heavy metal contamination in sediments from typical lakes in the five geographic regions of China: Distribution, bioavailability, and risk. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 81, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Shi, R.; Chen, J.; Li, H. Distribution pattern of antibiotic resistance genes and bacterial community in agricultural soil samples of Wuliangsuhai watershed. China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 295, 106884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Item * | Analysis Method | Testing Instrument | The Lowest Detection Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | Glass electrode method | pH meter | 0.1 |
| NH3–N | Nessler’s reagent spectrophotometry | SK-100AR Ammonia nitrogen analyzer | 0.025 mg/L |
| DO | Iodine quantity method | Laboratory glassware for titration | 0.2mg/L |
| BOD | Dilution and inoculation method | Biochemical incubator | 2 mg/L |
| Turbidity | Turbidity meter method | Portable turbidimeter | |
| Salinity | Weight method | Electronic balance | 2 mg/L |
| Transparency | Plug’s plate method | Plug’s plate | 10mm |
| Chlorophyll a | Acetone extraction—spectrophotometric method | Spectrophotometer | 0.04mg/L |
| Anionic surfactant | The methylene blue spectrophotometric method | Spectrophotometer | 0.05 mg/L |
| Suspended matter | Weight method | Electronic balance | 4 mg/L |
| Cyanide | The isonicotinic acid-barbituric acid spectrophotometry | Flow injection analyzer (FIA) | 0.001 mg/L |
| TN | Peroxide potassium sulfate-ultraviolet spectrophotometry | Spectrophotometer | 0.05 mg/L |
| TP | Mo-Sb anti-spectrophotometer | Spectrophotometer | 0.01 mg/L |
| KMnO4 | Acid electric process | Laboratory glassware for titration | 0.5 mg/L |
| Petroleum | Infrared spectrophotometry | Infrared oil content analyzer | 0.018 mg/L |
| Volatile phenol | 4-aminoantipyrene spectrophotometric method | Flow injection analysis (FIA) | 0.001 mg/L |
| Sulfide | The amino dimethyl aniline photometric method | 0.02 mg/L | |
| Fluoride | Ion selective electrode potentiometry | Fluoride ion selective electrode | 0.05 mg/L |
| Cr6+ | 1,5-diphenylcarbazide spectrophotometry | Spectrophotometer | 0.004 mg/L |
| COD | Potassium dichromate method | Laboratory glassware for titration | 30 mg/L |
| Se | Atomic fluorescence spectrometry | Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometer (AFS) - 830 | 0.002 mg/L |
| Zn | Flame atomic absorption spectrophotometry | 0.005 mg/L | |
| Cu | Graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry | NovAA-400PGraphite furnace | 0.01 mg/L |
| Pb | 0.001 mg/L | ||
| Cd | 0.0001 mg/L | ||
| Hg | Atomic fluorescence spectrophotometry | Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometer (AFS) -830 | 6.00 × 10−6 mg/L |
| As | 6.00 × 10−5 mg/L | ||
| Coliform bacteria | Multi-tube zymolytic method | Incubator | 10 most probable number/L |
| Grade | Comprehensive Pollution Index (Ptotal) | Level |
|---|---|---|
| I | ≤0.20 | Cleanness |
| II | 0.21–0.40 | Sub-cleanness |
| III | 0.41–1.00 | Slight pollution |
| IV | 1.01–2.0 | Moderate pollution |
| V | ≥2.01 | Severe pollution |
| Item | Range | Min | Max | Mean | Median | Standard Deviation | Variation Coefficient | Nation Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1.42 | 7.89 | 9.31 | 8.43 | 8.41 | 0.27 | 0.03 | 6–9 |
| Turbidity | 64.00 | 3.00 | 67.00 | 14.11 | 11.50 | 10.21 | 0.72 | ≤19 |
| Total Suspended solids(TSS) | 97.00 | 4.00 | 101.00 | 18.72 | 14.00 | 15.51 | 0.83 | None |
| Salinity | 5128.00 | 696.00 | 5824.00 | 1902.25 | 1849.00 | 853.32 | 0.45 | None |
| Transparency | 180.00 | 10.00 | 190.00 | 87.18 | 90.00 | 41.73 | 0.48 | None |
| Chlorophyll a | 0.12 | 0.01 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.94 | ≤0.01 |
| DO | 6.10 | 2.90 | 9.00 | 5.74 | 5.81 | 1.36 | 0.24 | ≥5 |
| KMnO4 | 8.50 | 3.80 | 12.30 | 8.10 | 7.93 | 2.01 | 0.25 | ≤6 |
| BOD | 9.50 | 2.00 | 11.50 | 3.40 | 2.95 | 1.48 | 0.43 | ≤4 |
| CODMn | 97.00 | 16.00 | 113.00 | 41.12 | 38.7 | 16.21 | 0.39 | ≤20 |
| TN | 4.57 | 0.97 | 5.54 | 1.72 | 1.54 | 0.78 | 0.45 | ≤1 |
| NH3–N | 1.64 | 0.03 | 1.67 | 0.19 | 0.15 | 0.20 | 1.05 | ≤1 |
| TP | 0.2050 | 0.0170 | 0.2220 | 0.0792 | 0.0076 | 0.0385 | 0.49 | ≤0.2 |
| Oil | 0.0490 | Ld * | 0.0490 | 0.0037 | Ld * | 0.0100 | 2.70 | ≤0.05 |
| Fluoride | 0.7800 | 0.3100 | 1.0900 | 0.5746 | 0.5505 | 0.1331 | 0.23 | ≤1.0 |
| Anionic Surfactants | 0.1550 | Ld * | 0.1550 | 0.0189 | Ld * | 0.0391 | 2.06 | ≤0.2 |
| As | 0.0086 | 0.0008 | 0.0093 | 0.0025 | 0.0022 | 0.0015 | 0.58 | ≤0.05 |
| Hg | 0.0001 | Ld * | 0.0001 | 0.00001 | 0.00003 | 0.00001 | 0.40 | ≤0.0001 |
| Pb | 0.0436 | Ld * | 0.0436 | 0.0038 | 0.0021 | 0.0054 | 1.43 | ≤0.05 |
| Cu | 0.0216 | Ld * | 0.0216 | 0.0037 | 0.0020 | 0.0044 | 1.20 | ≤1.0 |
| Zn | 0.3480 | Ld * | 0.3480 | 0.0331 | 0.0180 | 0.0528 | 1.60 | ≤1.0 |
| Cd | 0.0010 | Ld * | 0.0010 | 0.0002 | 0.0002 | 0.0002 | 0.87 | ≤0.050 |
| Se | 0.0030 | Ld * | 0.0030 | 0.0002 | 0.0001 | 0.0004 | 1.86 | ≤0.01 |
| Coliform Bacteria | 328.00 | 2.00 | 330.00 | 46.56 | 20.00 | 67.88 | 1.46 | ≤1000 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, R.; Zhao, J.; Shi, W.; Song, S.; Wang, C. Comprehensive Assessment of Water Quality and Pollution Source Apportionment in Wuliangsuhai Lake, Inner Mongolia, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5054. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17145054
Shi R, Zhao J, Shi W, Song S, Wang C. Comprehensive Assessment of Water Quality and Pollution Source Apportionment in Wuliangsuhai Lake, Inner Mongolia, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(14):5054. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17145054
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Rui, Jixin Zhao, Wei Shi, Shuai Song, and Chenchen Wang. 2020. "Comprehensive Assessment of Water Quality and Pollution Source Apportionment in Wuliangsuhai Lake, Inner Mongolia, China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 14: 5054. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17145054
APA StyleShi, R., Zhao, J., Shi, W., Song, S., & Wang, C. (2020). Comprehensive Assessment of Water Quality and Pollution Source Apportionment in Wuliangsuhai Lake, Inner Mongolia, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(14), 5054. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17145054





