The Comparison of Perfectionism and Commitment between Professional and Amateur Golfers and the Association between Perfectionism and Commitment in the Two Groups
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Design and Subjects
2.2. Measurements
2.2.1. Multidimensional Perfectionism Scale (MPS)-Korean
2.2.2. Expansion of Sports Commitment Model (ESCM)-Korean
2.2.3. Golf Handicap
2.3. Analysis and Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Psychological Characteristics
3.1.1. Testing for Normality of Data
3.1.2. Comparison of Demographic Data between Professional Golfers and Amateur Golfers
3.1.3. Comparison of Perfectionism and Commitment between Professional Golfers and Amateur Golfers
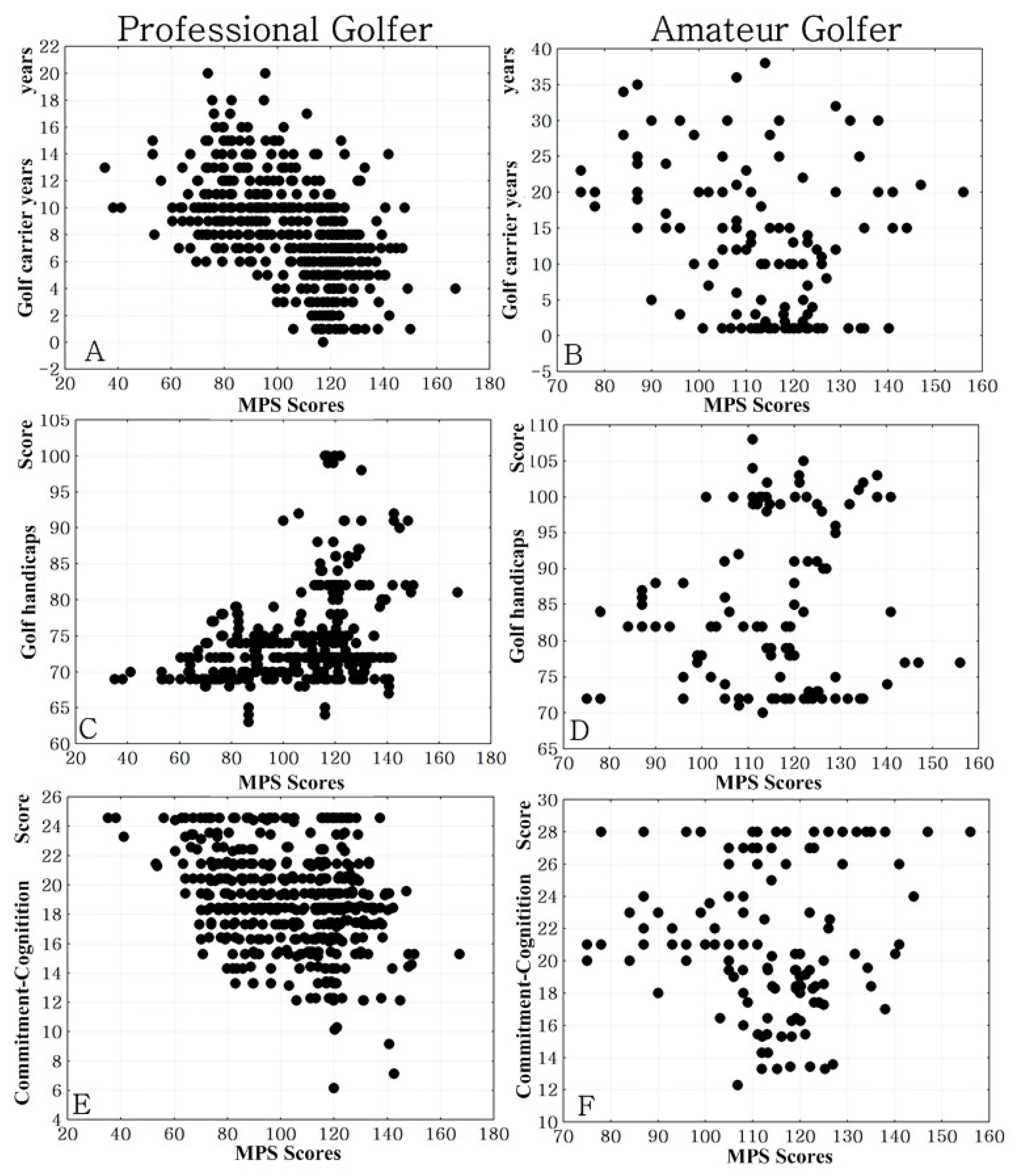
3.2. Correlation between Perfectionism, Commitment, Golf Handicap and Golf Career Length
3.2.1. Correlation between Perfectionism and Commitment
3.2.2. Correlation between Perfectionism, Golf Handicap and Golf Career Length
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stoeber, J.; Otto, K.; Pescheck, E.; Becker, C.; Stoll, O. Perfectionism and competitive anxiety in athletes: Differentiating striving for perfection and negative reactions to imperfection. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2007, 42, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K.; Kim, T. The relationship between perfectionism and motivational climate in competitive athletes. J. Digit. Converg. 2019, 17, 369–376. [Google Scholar]
- Bum, C.H.; Yoo, C.K.; Jung, C.K. A convergence study on the relationship between perfectionism, stress, and burnout among college golf athletes. J. Korea Converg. Soc. 2017, 8, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Madigan, D.J.; Curran, T.; Stoeber, J.; Hill, A.P.; Smith, M.M.; Passfield, L. Development of perfectionism in junior athletes: A three-sample study of coach and parental pressure. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2019, 31, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, K.D.; Hannon, J.C.; Harveson, A.; Lee, J.W.; Nam, J.J.; Han, D.H. Perfectionism and burnout in women professional golfers. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2016, 56, 1077–1085. [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson, A.E.; Nias, D.K.; White, P.D. Is perfectionism associated with fatigue? J. Psychosom. Res. 1996, 44, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flett, G.L.; Hewitt, P.L. The perils of perfectionism in sports and exercise. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2005, 14, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, R.J.; Carlat, D.J.; Millon, T.; Millon, C.M.; Meagher, S.; Grossman, S. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders; American Psychiatric Association Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin, G.M. The overlap between anxiety, depression, and obsessive-compulsive disorder. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 2015, 17, 249–260. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Wee, N.J.; Ramsey, N.F.; Jansma, J.M.; Denys, D.A.; van Megen, H.J.; Westenberg, H.M.; Kahn, R.S. Spatial working memory deficits in obsessive compulsive disorder are associated with excessive engagement of the medial frontal cortex. Neuroimage Clin. 2003, 20, 2271–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, A.F.; Hale, S. Processing speed, working memory, and fluid intelligence: Evidence for a developmental cascade. Psychol. Sci. 1996, 7, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kail, R.; Salthouse, T.A. Processing speed as a mental capacity. Acta Psychol. 1994, 86, 199–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyllonen, P.C.; Christal, R.E. Reasoning ability is (little more than) working-memory capacity?! Intelligence 1990, 14, 389–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salthouse, T.A. The processing-speed theory of adult age differences in cognition. Psychol. Rev. 1996, 103, 403–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamond, A. Attention-deficit disorder (attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder without hyperactivity): A neurobiologically and behaviorally distinct disorder from attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (with hyperactivity). Dev. Psychol. 2005, 17, 807–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gathercole, S.E.; Alloway, T.P.; Kirkwood, H.J.; Elliott, J.G.; Holmes, J.; Hilton, K.A. Attentional and executive function behaviours in children with poor working memory. Learn. Individ. Differ. 2008, 18, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeau, L.; Boivin, M.; Tessier, R.; Lefebvre, F.; Robaey, P. Mediators of behavioral problems in 7-year-old children born after 24 to 28 weeks of gestation. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatr. 2001, 22, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, L.M.; Bruce, J.M.; Bruce, A.S.; Lynch, S.G. Processing speed and working memory training in multiple sclerosis: A double-blind randomized controlled pilot study. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2015, 37, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, W.M. Applying the Sport Commitment Model to Sport Injury Rehabilitation. J. Sport Rehabil. 2020, 29, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, W.M.; Weiss, M.R. Attraction- and entrapment-based commitment among competitive female gymnasts. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2003, 25, 229–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.A.; Thomas, P.R.; Marsh, H.W.; Smethurst, C.J. Relationships between flow, self-concept, psychological skills, and performance. Int. J. Sport Psychol. 2001, 13, 129–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swann, C.; Keegan, R.; Piggott, D.; Crust, L.; Smith, M.F. Exploring flow occurrence in elite golf. Athl. Insight 2012, 4, 171–186. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplánová, A. Financial awards and their effect on football players’ anxiety and coping skills. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutcliffe, J.H.; Greenberger, P.A. Identifying psychological difficulties in college athletes. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2020, 8, 2216–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, S.; Jenkins, D.; Rynne, S.; Halson, S.L.; Kelly, V. What is mental fatigue in elite sport? Perceptions from athletes and staff. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2019, 19, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewitt, P.L.; Flett, G.L. Perfectionism in the self and social contexts: Conceptualization, assessment, and association with psychopathology. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1991, 60, 456–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.Y. The Multidimensional Perfectionism: Concept, Measurement and Relationship of Maladjustment. Master’s Thesis, University of Korea, Seoul, Korea, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, H.Y.; Shon, J.H. The relationship between leisure sports activity and Multi-dimensional Perfectionism. J. Sport Leis. Stud. 2009, 38, 1127–1136. [Google Scholar]
- Scanlan, T.K.; Carpenter, P.J.; Schmidt, G.W.; Simons, J.P.; Keeler, B. An introduction to the Sport Commitment Model. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 1993, 15, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.G. Validity verification of Sport Commitment Behavior Scale. J. Korean Sport Psychol. 2004, 15, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Kobriger, S.L.; Smith, J.; Hollman, J.H.; Smith, A.M. The contribution of golf to daily physical activity recommendations: How many steps does it take to complete a round of golf? Mayo Clin. Proc. 2006, 81, 1041–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Hippel, P.T. Mean, median, and skew: Correcting a textbook rule. J. Stat. Educ. 2005, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westfall, P.H. Kurtosis as peakedness, 1905–2014. R.I.P. Am. Stat. 2014, 68, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, D.; Mallery, M. SPSS for Windows Step by Step: A Simple Guide and Reference, 17.0 Update, 10th ed.; Pearson: Boston, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Cramér, H. Mathematical Methods of Statistics, 1st ed.; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1946; p. 282. [Google Scholar]
- Bakeman, R. Recommended effect size statistics for repeated measures designs. Behav. Res. Methods 2005, 37, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, P.L.; Flett, G.L. Personality traits and the coping process. In Handbook of Coping: Theory, Research, Applications; Zeidner, M., Endler, N.S., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 410–433. [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama, T.; Inomata, K. Qualitative examination of flow experience among top Japanese athletes. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2005, 100, 969–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, E.J. Flow in sport: A study of college athletes. Imagin. Cogn. Personal. 2008, 28, 69–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anshel, M.H.; Mansouri, H. Influences of perfectionism on motor performance, affect, and causal attributions in response to critical information feedback. J. Sport Behav. 2005, 28, 99–124. [Google Scholar]
- Flett, G.L.; Hewitt, P.L.; Blankstein, K.R.; Koledin, S. Dimensions of perfectionism and irrational thinking. J. Ration. Emot. Cogn. Behav. Ther. 1991, 9, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamachek, D.E. Psychodynamics of normal and neurotic perfectionism. Psychol. J. Hum. Behav. 1978, 15, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt, P.L.; Flett, G.L. Perfectionism and depression: A multidimensional analysis. J. Soc. Behav. Personal. 1990, 5, 423–438. [Google Scholar]
- Terry-Short, L.A.; Owens, R.G.; Slade, P.D.; Dewey, M.E. Positive and negative perfectionism. Personal. Individ. Differ. 1995, 18, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashby, J.S.; Bruner, L.P. Multidimensional perfectionism and obsessive-compulsive behaviors. J. Coll. Couns. 2005, 8, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philp, M.; Egan, S.; Kane, R. Perfectionism, over commitment to work, and burnout in employees seeking workplace counselling. Aust. J. Psychol. 2012, 64, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coles, K.; Tomporowski, P.D. Effects of acute exercise on executive processing, short-term and long-term memory. J. Sports Sci. 2008, 26, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontifex, M.; Hillman, C.; Fernhall, B.; Thompson, K.; Valentini, T. The effect of acute aerobic and resistance exercise on working memory. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, A.R.; Kane, M.J.; Engle, R.W. Working memory capacity and its relation to general intelligence. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2003, 7, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psych Central. Key to Greatness Is Working Memory, Not Practice. Available online: http://psychcentral.com/news/2011/10/06/key-to-greatness-is-working-memory-not-practice/30110.html (accessed on 6 June 2011).
- Bois, J.; Sarrazin, P.; Southon, J.; Southon, J.; Boiché, J. Psychological characteristics and their relation to performance in professional golfers. Sport Psychol. 2009, 23, 252–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohn, P.J. An exploratory study on peak performance in golf. Sport Psychol. 1991, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, H.; Feldman, P.; Bilker, W.; Gur, R.C. Working memory deficit as a core neuropsychological dysfunction in schizophrenia. Am. J. Psychiatry 2014, 160, 1809–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matser, E.J.; Kessels, A.G.; Lezak, M.D.; Jordan, B.D.; Troost, J. Neuropsychological impairment in amateur soccer players. JAMA 1999, 282, 971–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, A.E.; Cox, D.N.; Whitfield, K.; Fouladi, R.T. Cumulative concussion exposure in rugby players: Neurocognitive and symptomatic outcomes. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2008, 30, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, A. All or none hypothesis: A global-default mode that characterizes the brain and mind. Dev. Psychopathol. 2009, 45, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontani, G.; Lodi, L.; Felici, A.; Migliorini, S.; Corradeschi, F. Attention in athletes of high and low experience engaged in different open skill sports. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2006, 102, 791–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, P. Cognitions, emotions and golf performance. In Optimising Performance in Golf; Thomas, P.R., Ed.; Australian Academic Press: Brisbane, Australia, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Naito, K.; Kato, T.; Fukuda, T. Expertise and position of line of sight in golf putting. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2004, 99, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, M.; Saf, A.D.; Vosoughi, A.; Tebbenouri, G.; Zarnagh, H.G. Effectiveness of the mindfulness-acceptance-commitment-based approach on athletic performance and sports competition anxiety: A randomized clinical trial. Electron. Physician 2018, 10, 6749–6755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Professional Golfers (n = 486) | Amateur Golfers (n = 233) | Percentage of Change | Statistics | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) † | 22.1 ± 3.0 | 44.8 ± 10.2 | 102.7 | t = 45.9, p < 0.01, ES = 3.012 |
| Sex (male/female) § | 233/253 | 103/130 | χ2 = 0.8, p = 0.34, ES = 0.035 | |
| Golf career (years) † | 8.1 ± 3.5 | 12.6 ± 10.2 | 55.6 | t = 8.7, p < 0.01, ES = 0.592 |
| Training time (hours/day) † | 6.5 ± 2.6 | 3.2 ± 2.5 | 50.7 | t = 13.3, p < 0.01, ES = 1.293 |
| Golf handicap † | 73.7 ± 5.8 | 84.0 ± 11.1 | 13.9 | t = 15.1, p < 0.01, ES = 1.308 |
| MPS total †† | 107.7 ± 20.9 | 112.8 ± 15.6 | 4.7 | F = 4.8, p = 0.02, ES = 0.560 |
| MPS Self-oriented †† | 38.9 ± 6.5 | 42.0 ± 9.0 | 10.3 | F = 8.9, p < 0.01, ES = 0.598 |
| MPS Others-oriented †† | 33.3 ± 7.5 | 34.4 ± 7.9 | 3.2 | F = 3.7, p = 0.06, ES = 0.587 |
| MPS Socially prescribed †† | 34.4 ± 10.2 | 34.8 ± 7.9 | 1.2 | F = 0.7, p = 0.41, ES = 0.069 |
| Commitment-Cognition †† | 21.4 ± 4.5 | 18.9 ± 3.4 | 12.6 | F = 9.4, p < 0.01, ES = 0.691 |
| Commitment-Behavior †† | 17.4 ± 3.8 | 15.8 ± 2.8 | 9.4 | F = 4.6, p = 0.03, ES = 0.479 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nam, J.J.; Han, D.H. The Comparison of Perfectionism and Commitment between Professional and Amateur Golfers and the Association between Perfectionism and Commitment in the Two Groups. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5657. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17165657
Nam JJ, Han DH. The Comparison of Perfectionism and Commitment between Professional and Amateur Golfers and the Association between Perfectionism and Commitment in the Two Groups. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(16):5657. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17165657
Chicago/Turabian StyleNam, Jae Jun, and Doug Hyun Han. 2020. "The Comparison of Perfectionism and Commitment between Professional and Amateur Golfers and the Association between Perfectionism and Commitment in the Two Groups" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 16: 5657. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17165657
APA StyleNam, J. J., & Han, D. H. (2020). The Comparison of Perfectionism and Commitment between Professional and Amateur Golfers and the Association between Perfectionism and Commitment in the Two Groups. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(16), 5657. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17165657





