Analysis of Gender-Dependent Personal Protective Behaviors in a National Sample: Polish Adolescents’ COVID-19 Experience (PLACE-19) Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
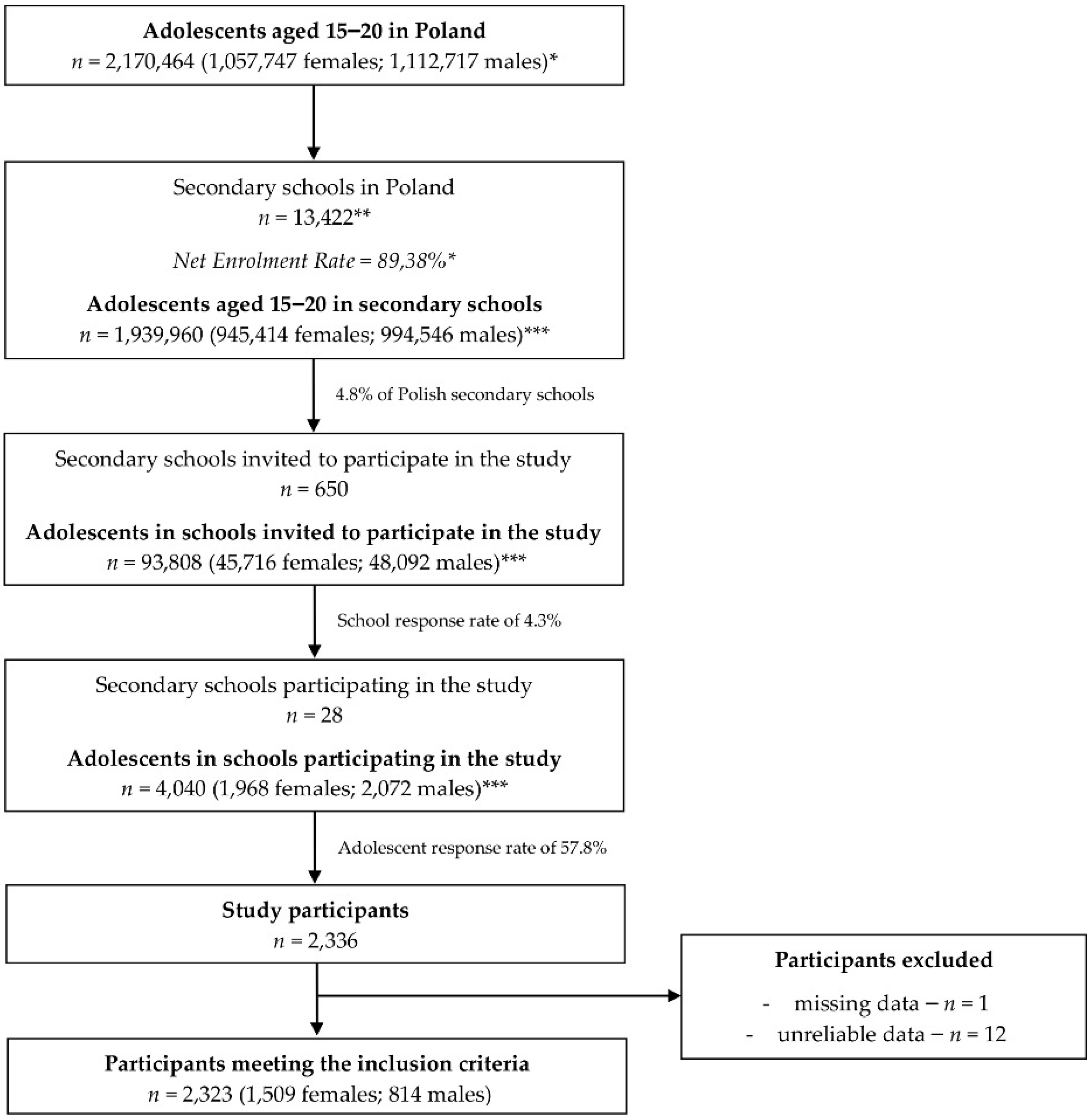
2.1. Studied Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Knowledge and Beliefs Associated with Hand Hygiene and Personal Protective Behaviors
3.2. Actual Hand Hygiene and Personal Protective Behaviors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). WHO Announces COVID-19 Outbreak a Pandemic. Available online: http://www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/health-emergencies/coronavirus-covid-19/news/news/2020/3/who-announces-covid-19-outbreak-a-pandemic (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- World Health Organization (WHO). Coronavirus Disease 2019. Strategy and Planning. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/strategies-and-plans (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- World Health Organization (WHO). Recommendation on Obligatory Hand Hygiene against Transmission of covid-19. Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/inaugural-who-partners-forum/who-interim-recommendation-on-obligatory-hand-hygiene-against-transmission-of-covid-19.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- World Health Organization (WHO). Rational Use of Personal Protective Equipment for Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) and Considerations during Severe Shortages. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications-detail/rational-use-of-personal-protective-equipment-for-coronavirus-disease-(covid-19)-and-considerations-during-severe-shortages (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- World Health Organization (WHO). Considerations for Quarantine of Individuals in the Context of Containment for Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19). Available online: https://www.who.int/publications-detail/considerations-for-quarantine-of-individuals-in-the-context-of-containment-for-coronavirus-disease-(covid-19) (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Social Distancing. Keep Your Distance to Slow the Spread. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/social-distancing.html (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- World Health Organization (WHO). WHO Guidelines on Hand Hygiene in Health Care: First Global Patient Safety Challenge Clean Care Is Safer Care; II, consensus recommendations; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK144035/ (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund. Everything You Need to Know about Washing Your Hands to Protect against Coronavirus (COVID-19). Available online: https://www.unicef.org/coronavirus/everything-you-need-know-about-washing-your-hands-protect-against-coronavirus-covid-19 (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. When and How to Wash Your Hands. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/handwashing/when-how-handwashing.html (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- World Health Organization (WHO). Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Advice for the Public: When and How to Use Masks. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/advice-for-public/when-and-how-to-use-masks (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Using Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/using-ppe.html (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- Australian Medical Association (AMA). Coronavirus (COVID-19). Available online: https://ama.com.au/article/latest-information-covid-19 (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- Jiang, S. Don’t rush to deploy COVID-19 Vaccines and Drugs without Sufficient Safety Guarantees. Nature 2020, 579, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Finset, A.; Bosworth, H.; Butow, P.; Gulbrandsen, P.; Hulsman, R.L.; Pieterse, A.H.; Street, R.; Tschoetschel, R.; van Weert, J. Effective health communication—A key factor in fighting the COVID-19 pandemic. Patient Educ. Couns. 2020, 103, 873–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-García, I.; Giménez-Júlvez, T. Characteristics of YouTube Videos in Spanish on How to Prevent COVID-19. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, M.S.; Serper, M.; Opsasnick, L.; O’Conor, R.M.; Curtis, L.M.; Benavente, J.Y.; Wismer, G.; Batio, S.; Eifler, M.; Zheng, P.; et al. Awareness, Attitudes, and Actions Related to COVID-19 Among Adults with Chronic Conditions at the Onset of the U.S. Outbreak: A Cross-sectional Survey. Ann. Int. Med. 2020, 9, M20-1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gujski, M.; Raciborski, F.; Jankowski, M.; Nowicka, P.M.; Rakocy, K.; Pinkas, J. Epidemiological Analysis of the First 1389 Cases of COVID-19 in Poland: A Preliminary Report. Med. Sci. Monit. 2020, 26, e924702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raciborski, F.; Pinkas, J.; Jankowski, M.; Sierpiński, R.; Zgliczyński, W.S.; Szumowski, Ł.; Rakocy, K.; Wierzba, W.; Gujski, M. Dynamics of COVID-19 outbreak in Poland: An epidemiological analysis of the first two months of the epidemic. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnevetsky, A.; Levy, M. Rethinking high-risk groups in COVID-19. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2020, 22, 102139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gu, Z.; Xia, S.; Shi, B.; Zhou, X.N.; Shi, Y.; Liu, J. What are the Underlying Transmission Patterns of COVID-19 Outbreak?—An Age-specific Social Contact Characterization. EClinicalMedicine 2020, 18, 100354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Q&A: Adolescents, Youth and COVID-19. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/q-a-detail/q-a-for-adolescents-and-youth-related-to-covid-19 (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- The United Nations Children’s Fund is a United Nations (UNICEF). Risk Communication & Community Engagement: Practical Tips on Engaging Adolescents and Youth in the COVID-19 Response. Available online: https://www.unicef.org/media/66761/file/Practical-Tips-on-Engaging-Adolescents-and-Youth-in-the-COVID-19-Response-2020.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- Nussbaumer-Streit, B.; Mayr, V.; Dobrescu, A.l.; Chapman, A.; Persad, E.; Klerings, I.; Wagner, G.; Siebert, U.; Christof, C.; Zachariah, C.; et al. Quarantine alone or in combination with other public health measures to control COVID-19: A rapid review. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 4, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, S.K.; Verma, N.; Saxena, S.K. Coronavirus Infection among Children and Adolescents. Coronavirus Dis. 2020, 30, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walger, P.; Heininger, U.; Knuf, M.; Exner, M.; Popp, W.; Fischbach, T.; Trapp, S.; Hübner, J.; Herr, C.; Simon, A.; et al. Children and adolescents in the CoVid-19 pandemic: Schools and daycare centers are to be opened again without restrictions. The protection of teachers, educators, carers and parents and the general hygiene rules do not conflict with this. GMS Hyg. Infect. Control. 2020, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ran, L.; Liu, Q.; Hu, Q.; Du, Q.; Tan, X. Hand hygiene, mask-wearing behaviors and its associated factors during COVID-19 epidemic: A cross-sectional study among primary school students in Wuhan, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Pan, R.; Wan, X.; Tan, Y.; Xu, L.; Ho, C.S.; Ho, R.C. Immediate Psychological Responses and Associated Factors during the Initial Stage of the 2019 Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Epidemic among the General Population in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 6, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suen, L.K.P.; So, Z.Y.Y.; Yeung, S.K.W.; Lo, K.Y.K.; Lam, S.C. Epidemiological investigation on hand hygiene knowledge and behaviour: A cross-sectional study on gender disparity. BMC Public Health 2019, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van de Mortel, T.; Bourke, R.; McLoughlin, J.; Nonu, M.; Reis, M. Gender influences handwashing rates in the critical care unit. Am. J. Infect. Control 2001, 29, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anderson, J.L.; Warren, C.A.; Perez, E.; Louis, R.I.; Phillips, S.; Wheeler, J.; Cole, M.; Misra, R. Gender and ethnic differences in hand hygiene practices among college students. Am. J. Infect. Control 2008, 36, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariwah, S.; Hampshire, K.; Kasim, A. The impact of gender and physical environment on the handwashing behaviour of university students in Ghana. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2012, 17, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Lee, E.; Yoon Park, S.; Lee, E.; Park, J.W.; Nae Yu, S.; Kim, T.; Hyok Jeon, M.; Ju Choo, E.; Hyong Kim, T. Gender Differences in Psychosocial Determinants of Hand Hygiene Among Doctors. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2019, 23, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sultana, M.; Mahumud, R.A.; Sarker, A.R.; Hossain, S.M. Hand hygiene knowledge and practice among university students: Evidence from Private Universities of Bangladesh. Risk Manag. Healthc. Policy 2016, 12, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, B.L.; Luo, W.; Li, H.M.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Liu, X.G.; Li, W.T.; Li, Y. Knowledge, attitudes, and practices towards COVID-19 among Chinese residents during the rapid rise period of the COVID-19 outbreak: A quick online cross-sectional survey. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 15, 1745–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, K.R.; Del Valle, S.Y. A meta-analysis of the association between gender and protective behaviors in response to respiratory epidemics and pandemics. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Article 35 Paragraph 1 of the Act of Educational Law from 14 December 2016; Article 70 Paragraph 1 Sentence 2 of the Polish Constitution. Dz. U. 2017 poz. 59. Available online: http://prawo.sejm.gov.pl/isap.nsf/download.xsp/WDU20170000059/T/D20170059L.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- The Central Statistical Office in Poland December. 2019. Available online: https://bdl.stat.gov.pl/BDL/dane/podgrup/temat (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- Public Administration in Poland. Towards “Glocal” Administration. Available online: https://www.ccmaresme.cat/ARXIUS/2008/SRE/SRE/GLOCAL/glocal_text_final_Poland.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2020).
- Głąbska, D.; Skolmowska, D.; Guzek, D. Population-Based Study of the Influence of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Hand Hygiene Behaviors—Polish Adolescents’ COVID-19 Experience (PLACE-19) Study. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Central Statistical Office in Poland December. 2019. Available online: http://demografia.stat.gov.pl/bazademografia/Tables.aspx (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- Polish Ministry of National Education. Available online: https://rspo.men.gov.pl/ (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- Polish Ministry of National Education. Suspension of Classes in Schools. Available online: https://www.gov.pl/web/edukacja/zawieszenie-zajec-w-szkolach (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- Ordinance of the Council of Ministers from 15 April 2020. Amending the Regulation Laying down Certain Restrictions, Orders and Prohibitions in a Relations to the Occurrence of a Pandemic Outbreak Condition. Available online: https://isap.sejm.gov.pl/isap.nsf/DocDetails.xsp?id=WDU20200000673 (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- Park, J.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, J.G. A study on the hand washing awareness and practices of Food-service employees and the load of index microorganisms on the hands. J. Environ. Health Sci. 2010, 36, 95–107. [Google Scholar]
- Jemal, S. Knowledge and Practices of Hand Washing among Health Professionals in Dubti Referral Hospital, Dubti, Afar, Northeast Ethiopia. Adv. Prev. Med. 2018, 2018, 5290797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dajaan, D.S.; Addo, H.O.; Ojo, L.; Amegah, K.E.; Loveland, F.; Bechala, B.D.; Benjamin, B.B. Hand washing knowledge and practices among public primary schools in the Kintampo Municipality of Ghana. Int. J. Community Med. Public Health 2018, 5, 2205–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Tools for Evaluation and Feedback. Available online: https://www.who.int/gpsc/5may/tools/evaluation_feedback/en/ (accessed on 7 July 2020).
- Chu, D.K.; Akl, E.A.; Duda, S.; Solo, K.; Yaacoub, S.; Schünemann, H.J.; COVID-19 Systematic Urgent Review Group Effort (SURGE) study authors. Physical distancing, face masks, and eye protection to prevent person-to-person transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2020, 31142–31149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Healthcare Providers. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/handhygiene/providers/index.html (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- Minnesota Department of Health. Which Soap Is Best? Available online: https://www.health.state.mn.us/people/handhygiene/how/bestsoap.html (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- Huang, C.; Ma, W.; Stack, S. The hygienic efficacy of different hand-drying methods: A review of the evidence. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2012, 87, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Handwashing: A Healthy Habit in the Kitchen. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/handwashing/handwashing-kitchen.html (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- World Health Organization (WHO). Hand Hygiene: Why, How & When? Available online: https://www.who.int/gpsc/5may/Hand_Hygiene_Why_How_and_When_Brochure.pdf (accessed on 2 July 2020).
- World Health Organization (WHO). WHO Save Lives: Clean Your Hands in the Context of COVID-19. Available online: https://www.who.int/infection-prevention/campaigns/clean-hands/WHO_HH-Community-Campaign_finalv3.pdf (accessed on 7 July 2020).
- Merk, H.; Kühlmann-Berenzon, S.; Linde, A.; Nyrén, O. Associations of hand-washing frequency with incidence of acute respiratory tract infection and influenza-like illness in adults: A population-based study in Sweden. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tüzün, H.; Karakaya, K.; Deniz, E.B. Turkey Handwashing Survey: Suggestion for taking the ecological model into better consideration. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2015, 20, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Üner, S.; Sevencan, F.; Başaran, E.; Balcı, C.; Bilaloğlu, B. To determine some knowledge and attitudes related to the social hand washing of individuals who apply to a primary health center. TAF Prev. Med. Bull. 2009, 8, 207–216. [Google Scholar]
- Ergin, A.; Bostanci, M.; Onal, O.; Bozkurt, A.I.; Ergin, N. Evaluation of students’ social hand washing knowledge, practices, and skills in a university setting. Cent. Eur. J. Public Health 2011, 19, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Albashtawy, M. Assessment of hand-washing habits among school students aged 6–18 years in Jordan. Br. J. Sch. Nurs. 2017, 12, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.S.; Choi, J.K.; Jeong, I.S.; Paek, K.R.; In, H.K.; Park, K.D. A Nationwide Survey on the Hand Washing Behavior and Awareness. J. Prev. Med. Public Health 2007, 40, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Proper Hygiene When around Animals. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/healthywater/hygiene/etiquette/around_animals.html (accessed on 2 July 2020).
- Musu, M.; Lai, A.; Mereu, N.M.; Galletta, M.; Campagna, M.; Tidore, M.; Piazza, M.F.; Spada, L.; Massidda, M.V.; Colombo, S.; et al. Assessing hand hygiene compliance among healthcare workers in six Intensive Care Units. J. Prev. Med. Hyg. 2017, 58, E231. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, D.R.; Braga, F.T.M.M.; Silveira, R.C.D.C.P.; Garbin, L.M. Hand hygiene: Knowledge and skill of caregivers in the hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Rev. Bras. Enferm. 2019, 72, 1653–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, M.N.; Binkert, M.E.; Mosler, H.J. Contextual and psychosocial determinants of effective handwashing technique: Recommendations for interventions from a case study in Harare, Zimbabwe. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 96, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adhikari, S.P.; Meng, S.; Wu, Y.J.; Mao, Y.P.; Ye, R.X.; Wang, Q.Z.; Sun, C.; Sylvia, S.; Rozelle, S.; Raat, H.; et al. Epidemiology, causes, clinical manifestation and diagnosis, prevention and control of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) during the early outbreak period: A scoping review. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2020, 17, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Kuwahara, K. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on children and adolescents’ lifestyle behavior larger than expected. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saurabh, K.; Ranjan, S. Compliance and Psychological Impact of Quarantine in Children and Adolescents due to Covid-19 Pandemic. Indian J. Pediatr. 2020, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- InformedHealth.org. How Can You Prevent a Coronavirus Infection? Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG): Cologne, Germany, 2006. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK555498/ (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- Hiller, J.; Schatz, K.; Drexler, H. Gender influence on health and risk behavior in primary prevention: A systematic review. Z. Gesundh. Wiss. 2017, 25, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, H.D.; Sholcosky, D.; Gabello, K.; Ragni, R.; Ogonosky, N. Sex differences in public restroom handwashing behavior associated with visual behavior prompts. Percept. Mot. Skills 2003, 97, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, A.; Vaganay-Miller, M. The Effectiveness of a Poster Intervention on Hand Hygiene Practice and Compliance When Using Public Restrooms in a University Setting. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 5036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oosterhoff, B.; Palmer, C.A.; Wilson, J.; Shook, N. Adolescents’ Motivations to Engage in Social Distancing During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Associations with Mental and Social Health. J. Adolesc. Health 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bish, A.; Michie, S. Demographic and attitudinal determinants of protective behaviours during a pandemic: A review. Br. J. Health Psychol. 2010, 15, 797–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.Y.; Lam, E.P.; Chan, C.K.; Chan, S.Y.; Chiu, M.K.; Chong, W.H.; Chu, K.W.; Hon, M.S.; Kwan, L.K.; Tsang, K.L.; et al. Practice and technique of using face mask amongst adults in the community: A cross-sectional descriptive study. BMC Public Health 2020, 16, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.S.; Wong, C.Y. Factors influencing the wearing of facemasks to prevent the severe acute respiratory syndrome among adult Chinese in Hong Kong. Prev. Med. 2004, 39, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, J.T.; Griffiths, S.; Choi, K.C.; Lin, C. Prevalence of preventive behaviors and associated factors during early phase of the H1N1 influenza epidemic. Am. J. Infect. Control 2010, 38, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Cheong, H.K.; Son, D.Y.; Kim, S.U.; Ha, C.M. Perceptions and behaviors related to hand hygiene for the prevention of H1N1 influenza transmission among Korean university students during the peak pandemic period. BMC Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fung, I.C.; Cairncross, S. How often do you wash your hands? A review of studies of handwashing practices in the community during and after the SARS outbreak in 2003. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2007, 17, 161–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.Y.; Cheng, Y.L.; Lu, Y.; Hu, Y.H.; Chen, D.F. Handwashing behaviour among Chinese adults: A cross-sectional study in five provinces. Public Health 2013, 127, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duggan, J.M.; Hensley, S.; Khuder, S.; Papadimos, T.J.; Jacobs, L. Inverse correlation between level of professional education and rate of handwashing compliance in a teaching hospital. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2008, 29, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Quintero, C.; Freeman, P.; Neumark, Y. Hand washing among school children in Bogota, Colombia. Am. J. Public Health 2009, 99, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peltzer, K.; Pengpid, S. Oral and hand hygiene behaviour and risk factors among in-school adolescents in four Southeast Asian countries. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 2780–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalçın, S.S.; Yalçın, S.; Altın, S. Hand washing and adolescents. A study from seven schools in Konya, Turkey. Int. J. Adolesc. Med. Health 2004, 16, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, Y.L.; Gralton, J.; McLaws, M.L. Face touching: A frequent habit that has implications for hand hygiene. Am. J. Infect. Control 2015, 43, 112–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.; Wang, L.; Kuo, H.D.; Shannar, A.; Peter, R.; Chou, P.J.; Li, S.; Hudlikar, R.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; et al. An Update on Current Therapeutic Drugs Treating COVID-19. Curr. Pharmacol. Rep. 2020, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, J.M. Knowledge and Behaviors toward COVID-19 among US Residents during the Early Days of the Pandemic: Cross-Sectional Online Questionnaire. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2020, 8, 19161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). N95 Respirators, Surgical Masks, and Face Masks. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/personal-protective-equipment-infection-control/n95-respirators-surgical-masks-and-face-masks (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- Statement of the President of 23 March 2020 Regarding the Update of Information Contained in the Application Regarding the Derogation from Registration Requirements Provided for Art. 55 § 1 of Regulation No. 528/2012. Available online: http://www.urpl.gov.pl/pl/komunikat-prezesa-z-dnia-23-marca-2020-roku-w-sprawie-aktualizacji-informacji-zawartych-we-wniosku (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- Curtis, V.A.; Danquah, L.O.; Aunger, R.V. Planned, motivated and habitual hygiene behaviour: An eleven country review. Health Educ. Res. 2009, 24, 655–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jumaa, P.A. Hand hygiene: Simple and complex. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 9, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willmott, M.; Nicholson, A.; Busse, H.; MacArthur, G.J.; Brookes, S.; Campbell, R. Effectiveness of hand hygiene interventions in reducing illness absence among children in educational settings: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Dis. Child. 2016, 101, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanagh, G.; Wambier, C.G. Rational hand hygiene during the coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 82, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Level | 1st Stage (31 March–14 April 2020) | 2nd Stage (15 April–29 April 2020) |
|---|---|---|
| Voivodeships | All voivodeships (n = 16) included | Voivodeships with an inadequate number of completed questionnaires with no missing data (less than 50) after the 1st stage (n = 10) included |
| Counties | Random sampling of 5 counties for each of the 16 voivodeships (n = 80) | Random sampling of 5 counties for each of the 10 voivodeships (n = 50) |
| Secondary schools | Random sampling of 5 schools for each of the 80 counties (n = 400) | Random sampling of 5 schools for each of the 50 counties (n = 250) |
| Choice of Method That Is Better for Proper Hand Hygiene and Personal Protection | Males (n = 814) | Females (n = 1509) | p ** |
|---|---|---|---|
| Not leaving home * | 542 (66.6%) | 1052 (69.7%) | 0.0521 |
| Using a face mask | 45 (5.5%) | 50 (3.3%) | |
| Behaviors are equally good | 199 (24.4%) | 364 (24.1%) | |
| Refuse answering (do not know) | 28 (3.4%) | 43 (2.8%) | |
| Handwashing * | 276 (33.9%) | 392 (26.0%) | <0.0001 |
| Using gloves | 77 (9.5%) | 108 (7.2%) | |
| Behaviors are equally good | 428 (52.6%) | 959 (63.6%) | |
| Refuse answering (do not know) | 33 (4.1%) | 50 (3.3%) | |
| Using soap * | 181 (22.2%) | 383 (25.4%) | <0.0001 |
| Using alcohol-based hand rub | 186 (22.9%) | 217 (14.4%) | |
| Behaviors are equally good | 399 (49.0%) | 852 (56.5%) | |
| Refuse answering (do not know) | 48 (5.9%) | 57 (3.8%) | |
| Using liquid soap * | 387 (47.5%) | 776 (51.4%) | 0.0001 |
| Using a soap bar | 79 (9.7%) | 74 (4.9%) | |
| Behaviors are equally good | 292 (35.9%) | 529 (35.1%) | |
| Refuse answering (do not know) | 56 (6.9%) | 130 (8.6%) | |
| Using paper towels * | 359 (44.1%) | 756 (50.1%) | 0.0441 |
| Using a hand dryer | 158 (19.4%) | 254 (16.8%) | |
| Behaviors are equally good | 194 (23.8%) | 336 (22.3%) | |
| Refuse answering (do not know) | 103 (12.7%) | 163 (10.8%) |
| Time of Handwashing | Males (n = 814) | Females (n = 1509) | p ** |
|---|---|---|---|
| Less than 5 s | 3 (0.4%) | 5 (0.3%) | <0.0001 |
| 5–10 s | 31 (3.8%) | 29 (1.9%) | |
| 11–20 s | 97 (11.9%) | 153 (10.1%) | |
| 21–40 s * | 536 (65.8%) | 1120 (74.2%) | |
| More than 40 s * | 82 (10.1%) | 144 (9.5%) | |
| Time does not matter | 37 (4.5%) | 20 (1.3%) | |
| I don’t know | 28 (3.4%) | 38 (2.5%) | |
| Wrong answers | 168 (20.6%) | 207 (13.7%) | <0.0001 |
| Proper answers | 618 (75.9%) | 1264 (83.8%) | |
| I don’t know | 28 (3.4%) | 38 (2.5%) |
| Responses by the Sample Questioned before the Implementation of the Legal Regulation * | Males (n = 452) | Females (n = 862) | p ** |
| Not leaving home | 387 (85.6%) | 788 (91.4%) | 0.0012 |
| Using a face mask | 116 (25.7%) | 300 (34.8%) | 0.0007 |
| Not touching the face | 170 (37.6%) | 396 (45.9%) | 0.0038 |
| Using gloves | 164 (36.3%) | 399 (46.3%) | 0.0005 |
| Handwashing | 428 (94.7%) | 845 (98.0%) | 0.0009 |
| Using alcohol-based hand rub | 278 (61.5%) | 667 (77.4%) | <0.0001 |
| Avoiding contact with those who may be sick | 320 (70.8%) | 677 (78.5%) | 0.0018 |
| Avoiding public places | 367 (81.2%) | 760 (88.2%) | 0.0006 |
| Taking medications or dietary supplements | 142 (31.4%) | 346 (40.1%) | 0.0019 |
| Other | 3 (0.7%) | 8 (0.9%) | 0.6171 |
| Responses by the Sample Questioned after the Implementation of the Legal Regulation * | Males (n = 362) | Females (n = 647) | p ** |
| Not leaving home | 229 (63.3%) | 480 (74.2%) | 0.0003 |
| Using a face mask | 310 (85.6%) | 575 (88.9%) | 0.1331 |
| Not touching the face | 135 (37.3%) | 280 (43.3%) | 0.0639 |
| Using gloves | 207 (57.2%) | 433 (66.9%) | 0.0021 |
| Handwashing | 339 (93.6%) | 633 (97.8%) | 0.0007 |
| Using alcohol-based hand rub | 241 (66.6%) | 497 (76.8%) | 0.0004 |
| Avoiding contact with those who may be sick | 241 (66.6%) | 502 (77.6%) | 0.0001 |
| Avoiding public places | 224 (61.9%) | 488 (75.4%) | <0.0001 |
| Taking medications or dietary supplements | 81 (22.4%) | 208 (32.1%) | 0.0010 |
| Other | 2 (0.6%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.0584 |
| Responses by Sample Questioned before the Implementation of the Legal Regulation * | Males (n = 452) | Females (n = 862) | p ** |
| Not leaving home | 350 (77.4%) | 673 (78.1%) | 0.7899 |
| Using a face mask | 210 (46.5%) | 476 (55.2%) | 0.0025 |
| Not touching the face | 211 (46.7%) | 440 (51.0%) | 0.1329 |
| Using gloves | 270 (59.7%) | 632 (73.3%) | <0.0001 |
| Handwashing | 430 (95.1%) | 835 (96.9%) | 0.1149 |
| Using alcohol-based hand rub | 336 (74.3%) | 705 (81.8%) | 0.0016 |
| Avoiding contact with those who may be sick | 330 (73.0%) | 690 (80.0%) | 0.0004 |
| Avoiding public places | 322 (71.2%) | 586 (68.0%) | 0.0257 |
| Taking medications or dietary supplements | 184 (40.7%) | 384 (44.5%) | 0.0020 |
| Other | 1 (0.2%) | 3 (0.3%) | 0.8963 |
| Responses by Sample Questioned after the Implementation of the Legal Regulation * | Males (n = 362) | Females (n = 647) | p ** |
| Not leaving home | 212 (58.6%) | 426 (65.8%) | 0.0214 |
| Using a face mask | 339 (93.6%) | 613 (94.7%) | 0.4683 |
| Not touching the face | 179 (49.4%) | 313 (48.4%) | 0.7447 |
| Using gloves | 276 (76.2%) | 552 (85.3%) | 0.0003 |
| Handwashing | 342 (94.5%) | 628 (97.1%) | 0.0408 |
| Using alcohol-based hand rub | 270 (74.6%) | 513 (79.3%) | 0.0857 |
| Avoiding contact with those who may be sick | 242 (66.9%) | 481 (74.3%) | 0.0113 |
| Avoiding public places | 198 (54.7%) | 383 (59.2%) | 0.1653 |
| Taking medications or dietary supplements | 103 (28.5%) | 257 (39.7%) | 0.0003 |
| Other | 2 (0.6%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.0584 |
| Declared Frequency | Males (n = 814) | Females (n = 1509) | p * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Not washing at all | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | <0.0001 |
| 1–2 times | 26 (3.2%) | 19 (1.3%) | |
| 3–5 times | 174 (21.4%) | 196 (13.0%) | |
| 6–10 times | 308 (37.8%) | 524 (34.7%) | |
| 11–15 times | 163 (20.0%) | 362 (24.0%) | |
| 16–20 times | 68 (8.4%) | 222 (14.7%) | |
| 21–30 times | 44 (5.4%) | 119 (7.9%) | |
| More than 30 times | 31 (3.8%) | 67 (4.4%) |
| Declared Reasons | Males (n = 814) | Females (n = 1509) | p *** |
|---|---|---|---|
| In my opinion there is no need to do it | 113 (13.9%) | 87 (5.8%) | <0.0001 |
| I don’t feel like doing it | 67 (8.2%) | 54 (3.6%) | <0.0001 |
| I have no time to do it | 37 (4.5%) | 21 (1.4%) | <0.0001 |
| I am forgetting about it | 251 (30.8%) | 334 (22.1%) | <0.0001 |
| It is constricted | 21 (2.6%) | 44 (2.9%) | 0.6398 |
| Due to side effects | 42 (5.2%) | 114 (7.6%) | 0.0278 |
| Other * | 11 (1.4%) | 18 (1.2%) | 0.7424 |
| Various reasons for not washing ** | 374 (45.9%) | 480 (31.8%) | <0.0001 |
| I always wash my hands | 440 (54.1%) | 1029 (68.2%) |
| Characteristics | Males (n = 814) | Females (n = 1509) | p * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| After coming back home | Never | 10 (1.2%) | 6 (0.4%) | <0.0001 |
| Sometimes | 113 (13.9%) | 101 (6.7%) | ||
| Always | 691 (84.9%) | 1402 (92.9%) | ||
| After handshaking | Never | 152 (18.7%) | 212 (14.0%) | 0.0041 |
| Sometimes | 330 (40.5%) | 598 (39.6%) | ||
| Always | 332 (40.8%) | 699 (46.3%) | ||
| After using public transportation | Never | 67 (8.2%) | 57 (3.8%) | <0.0001 |
| Sometimes | 164 (20.1%) | 173 (11.5%) | ||
| Always | 583 (71.6%) | 1279 (84.8%) | ||
| After money exchange | Never | 186 (22.9%) | 189 (12.5%) | <0.0001 |
| Sometimes | 257 (31.6%) | 421 (27.9%) | ||
| Always | 371 (45.6%) | 899 (59.6%) | ||
| Characteristics | Males (n = 814) | Females (n = 1509) | p * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before touching sick people | Never | 222 (27.3%) | 356 (23.6%) | 0.1156 |
| Sometime | 228 (28.0%) | 464 (30.7%) | ||
| Always | 364 (44.7%) | 689 (45.7%) | ||
| After touching sick people | Never | 43 (5.3%) | 49 (3.2%) | 0.0168 |
| Sometimes | 100 (12.3%) | 157 (10.4%) | ||
| Always | 671 (82.4%) | 1303 (86.3%) | ||
| After nose blowing | Never | 168 (20.6%) | 244 (16.2%) | 0.0004 |
| Sometimes | 369 (45.3%) | 634 (42.0%) | ||
| Always | 277 (34.0%) | 631 (41.8%) | ||
| After sneezing | Never | 145 (17.8%) | 203 (13.5%) | 0.0006 |
| Sometimes | 348 (42.8%) | 597 (39.5%) | ||
| Always | 321 (39.4%) | 709 (47.0%) | ||
| After coughing | Never | 162 (19.9%) | 241 (16.0%) | 0.0069 |
| Sometimes | 354 (43.5%) | 625 (41.4%) | ||
| Always | 298 (36.6%) | 643 (42.6%) | ||
| Characteristics | Males (n = 814) | Females (n = 1509) | p ** | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Folding sleeves | Never | 37 (4.5%) | 39 (2.6%) | 0.0045 |
| Sometimes | 166 (20.4%) | 314 (20.8%) | ||
| Always | 388 (47.7%) | 855 (56.7%) | ||
| Not applicable | 223 (27.4%) | 301 (19.9%) | ||
| Removing watches and bracelets | Never | 128 (8.5%) | 81 (10.0%) | 0.0053 |
| Sometimes | 327 (21.7%) | 128 (15.7%) | ||
| Always | 199 (13.2%) | 118 (14.5%) | ||
| Not applicable | 855 (56.7%) | 487 (59.8%) | ||
| Removing rings before or during handwashing | Never | 29 (3.6%) | 190 (12.6%) | 0.0079 |
| Sometimes | 34 (4.2%) | 132 (8.7%) | ||
| Always | 64 (7.9%) | 197 (13.1%) | ||
| Not applicable | 687 (84.4%) | 990 (65.6%) | ||
| Using soap | Never | 5 (0.6%) | 1 (0.1%) | 0.0185 |
| Sometimes | 48 (5.9%) | 70 (4.6%) | ||
| Always | 761 (93.5%) | 1438 (95.3%) | ||
| Using warm water | Never | 28 (3.4%) | 15 (1.0%) | 0.0001 |
| Sometimes | 279 (34.3%) | 498 (33.0%) | ||
| Always | 507 (62.3%) | 996 (66.0%) | ||
| Soaking hands before using soap | Never | 88 (10.8%) | 113 (7.5%) | 0.0064 |
| Sometimes | 156 (19.2%) | 259 (17.2%) | ||
| Always | 568 (69.8%) | 1136 (75.3%) | ||
| Not applicable | 2 (0.2%) | 1 (0.1%) | ||
| Spreading soap lather throughout the hands | Never | 47 (5.8%) | 52 (3.4%) | 0.0163 |
| Sometimes | 286 (35.1%) | 510 (33.8%) | ||
| Always | 480 (59.0%) | 947 (62.8%) | ||
| Not applicable | 1 (0.1%) | 0 (0.0%) | ||
| Turning the faucet off with hands * | Never | 142 (17.4%) | 363 (24.1%) | 0.0004 |
| Sometimes | 219 (26.9%) | 409 (27.1%) | ||
| Always | 453 (55.7%) | 737 (48.8%) | ||
| Drying hands with a towel | Never | 13 (1.6%) | 44 (2.9%) | 0.0120 |
| Sometimes | 114 (14.0%) | 262 (17.4%) | ||
| Always | 687 (84.4%) | 1203 (79.7%) | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guzek, D.; Skolmowska, D.; Głąbska, D. Analysis of Gender-Dependent Personal Protective Behaviors in a National Sample: Polish Adolescents’ COVID-19 Experience (PLACE-19) Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5770. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17165770
Guzek D, Skolmowska D, Głąbska D. Analysis of Gender-Dependent Personal Protective Behaviors in a National Sample: Polish Adolescents’ COVID-19 Experience (PLACE-19) Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(16):5770. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17165770
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuzek, Dominika, Dominika Skolmowska, and Dominika Głąbska. 2020. "Analysis of Gender-Dependent Personal Protective Behaviors in a National Sample: Polish Adolescents’ COVID-19 Experience (PLACE-19) Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 16: 5770. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17165770
APA StyleGuzek, D., Skolmowska, D., & Głąbska, D. (2020). Analysis of Gender-Dependent Personal Protective Behaviors in a National Sample: Polish Adolescents’ COVID-19 Experience (PLACE-19) Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(16), 5770. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17165770







