Pyrethroid-Induced Organ Toxicity and Anti-Oxidant-Supplemented Amelioration of Toxicity and Organ Damage: The Protective Roles of Ascorbic Acid and α-Tocopherol
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of the Vitamin Solutions and Experimental Animals
2.2. Toxicant Concentrations, Time-Bound Inhalations, and Exposures
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Sample Collections and Histopathological Examinations
2.5. Data Scoring and Statistical Significance
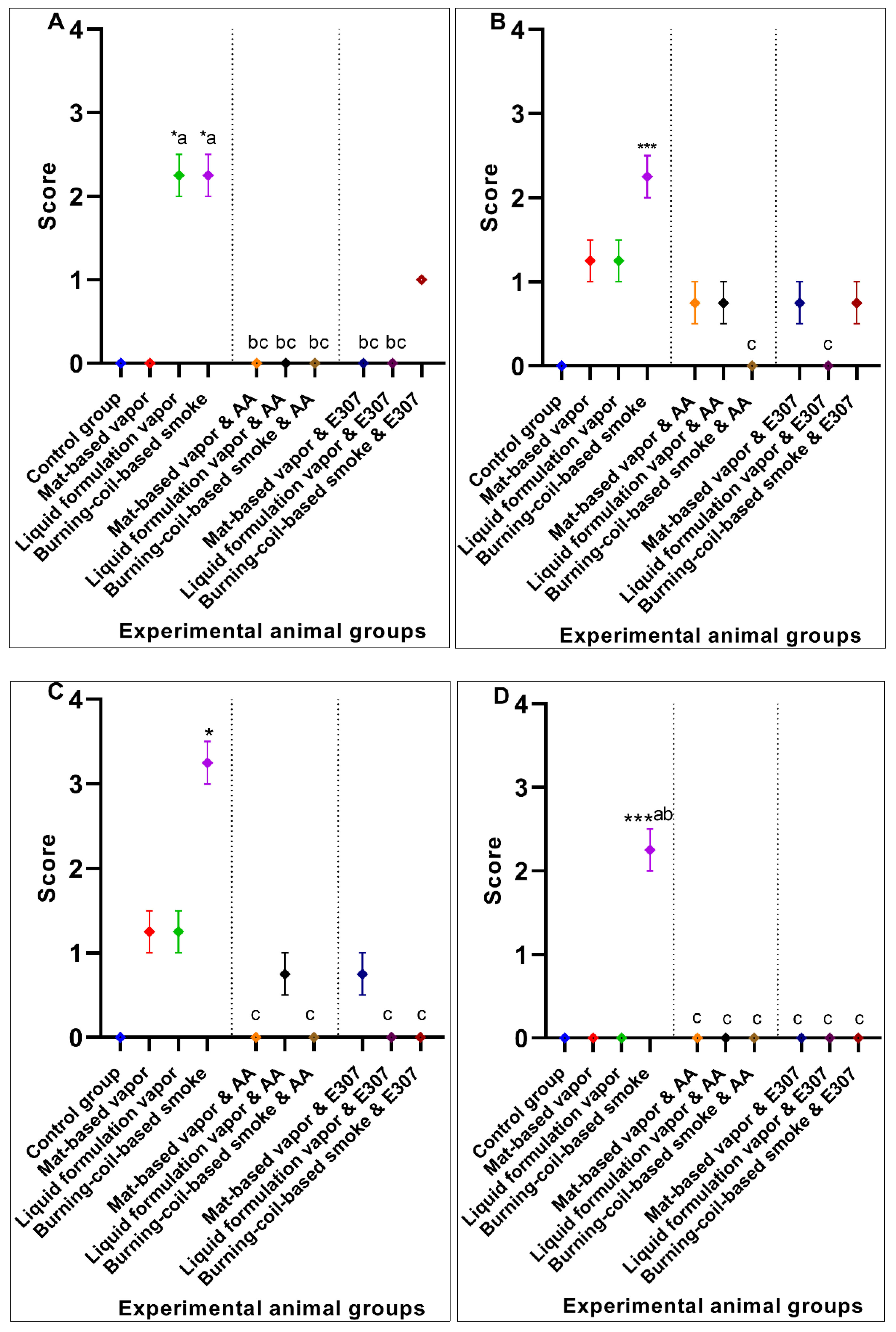
3. Results
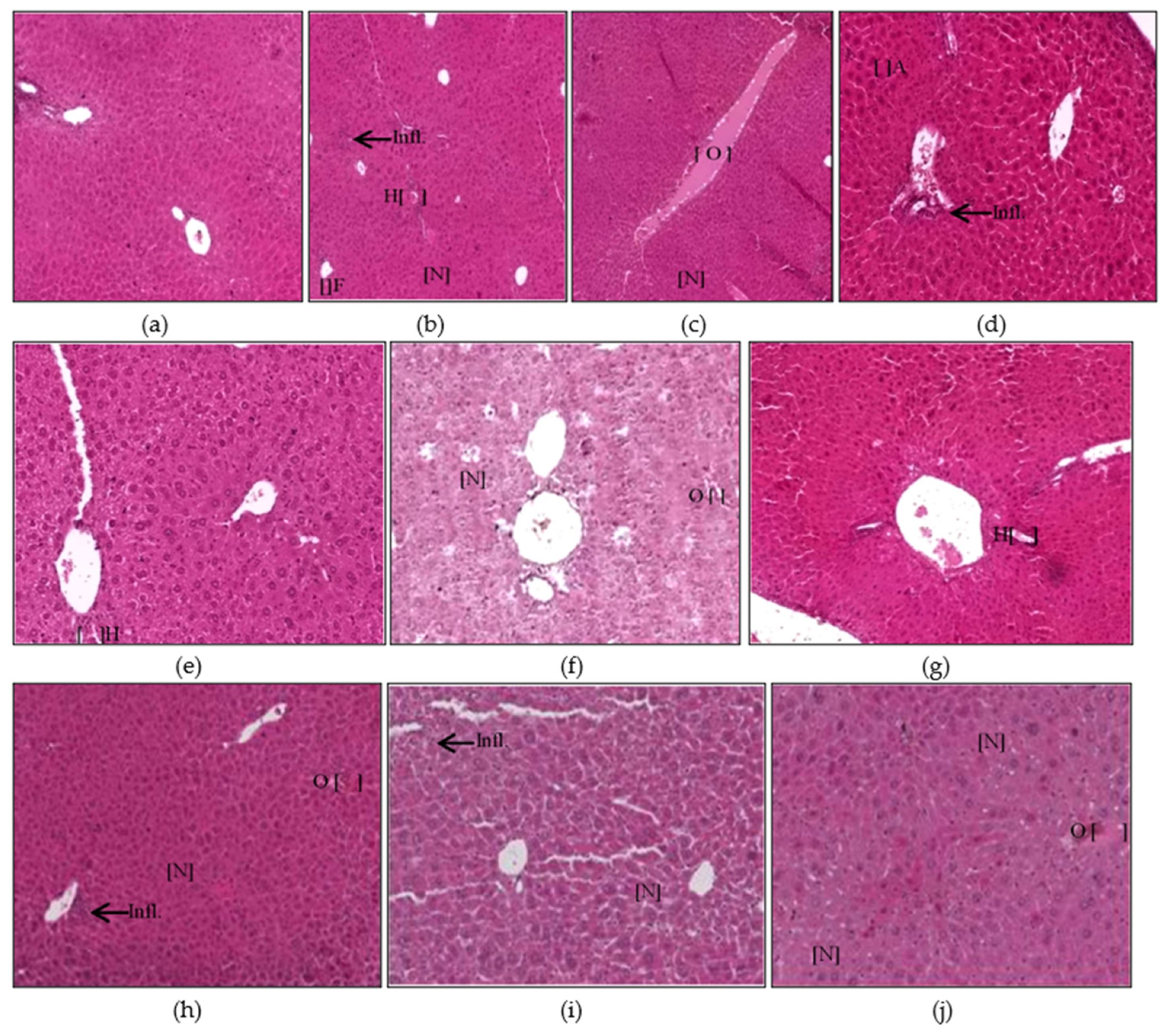
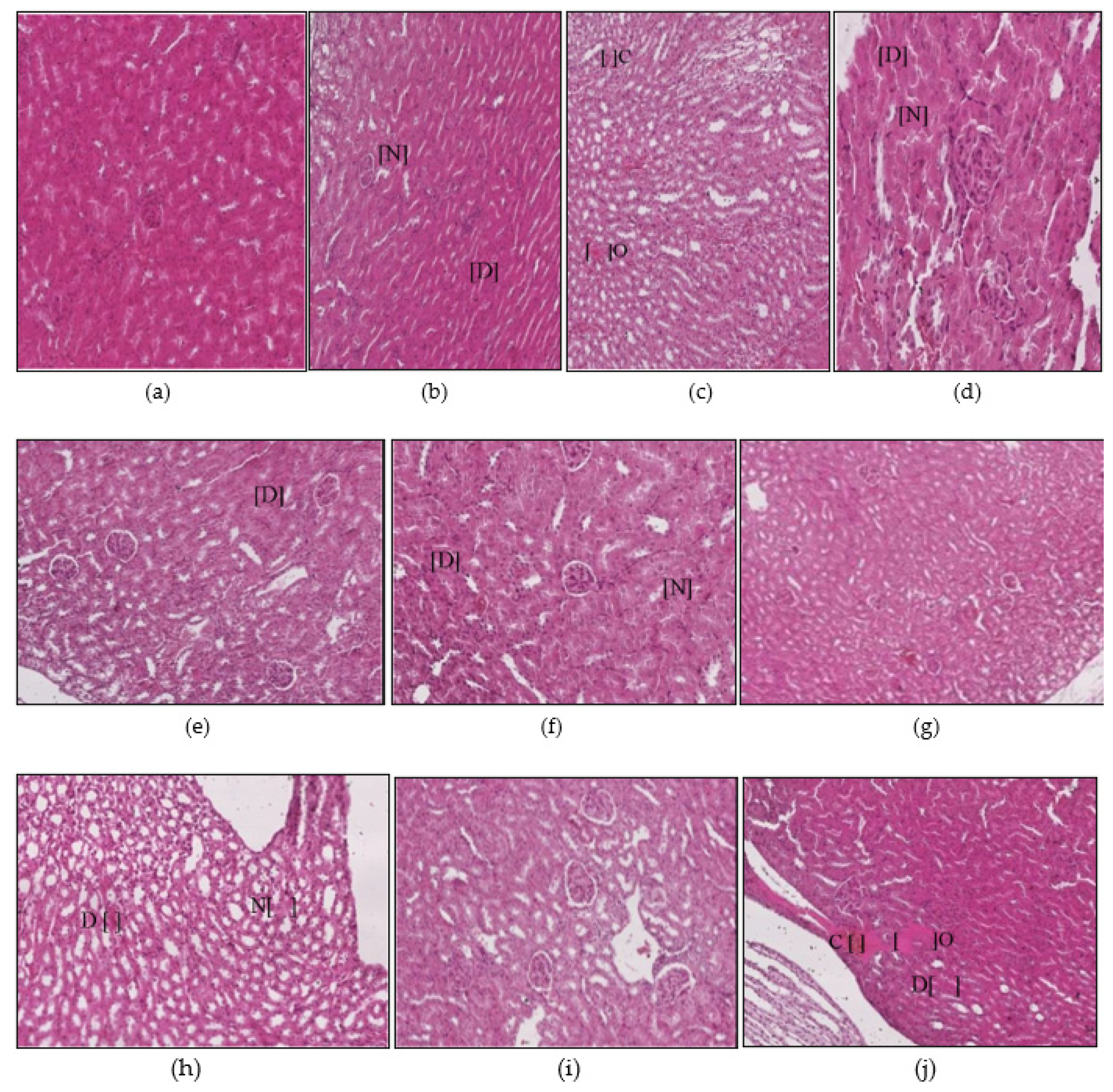
3.1. Histopathological Findings
3.1.1. Liver Histopathology
3.1.2. Heart Histopathology
3.1.3. Kidney Histopathology
3.1.4. Lungs Histopathology
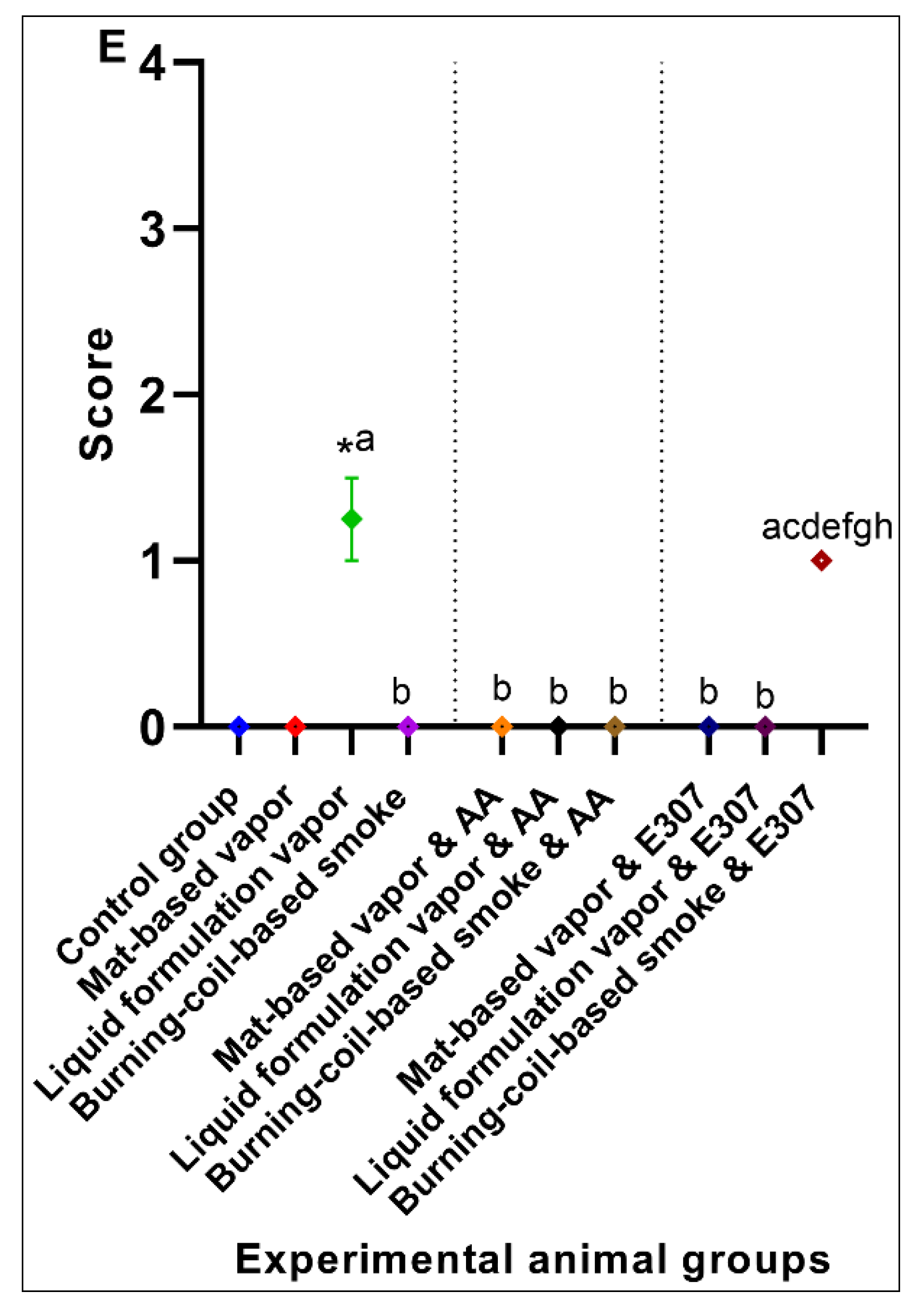
3.1.5. Brain Histopathology
3.2. Significant Effects of AA and E307 on the Experimental Animals’ Tissues
4. Discussion
4.1. Pyrethroid Toxicity, Treatment, and Role of Ascorbic Acid and α-Tocopherol: Histopathological Examinations
4.2. Molecular Mechanism: A Plausible Biomechanics Outline Proposed for Toxicity Generation, and Its Amelioration
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bordoni, L.; Nasuti, C.; Fedeli, D.; Galeazzi, R.; Laudadio, E.; Massaccesi, L.; López-Rodas, G.; Gabbianelli, R. Early impairment of epigenetic pattern in neurodegeneration: Additional mechanisms behind pyrethroid toxicity. Exp. Gerontol. 2019, 124, 110629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, P.; Singh, N. Synthetic pyrethroid pesticide toxicity in Caenorhabditis elegans to analyze physiological changes. Int. J. Res. Anal. Rev. 2018, 5, 757–766. [Google Scholar]
- Garba, S.H.; Shehu, M.M.; Adelaiye, A.B. Toxicological Effects of Inhaled Mosquito Coil Smoke on the Rat Spleen: A Haematological and Histological Study. J. Med. Sci. 2007, 7, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baugh, P.J. A Review of Pyrethroid and Mitin Analysis in Environmental Matrices by Sample Extraction & Preparation, ELISAs with a Unique Focus on GC/NICI-MS. Curr. Trends Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 3, 125–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Wu, Z.; Li, L.; Huang, M.; Xu, S.; Yan, D. Pyrethroid pesticide residues in the global environment: An overview. Chemosphere 2018, 191, 990–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhan, H. Biodegradation of Synthetic Pyrethroid Insecticides. In Microbial Metabolism of Xenobiotic Compounds; Series Microorganisms for Sustainability; Arora, P.K., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; Volume 10, pp. 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulla, M.S.; Thavara, U.; Tawatsin, A.; Kong-Ngamsuk, W.; Chompoosri, J. Mosquito burden and impact on the poor: Measures and costs for personal protection in some communities in Thailand. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 2001, 17, 153–159. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, M.A.I. Biochemical and Molecular Biological Studies on the Action of Formamidines in Synergizing Insecticidal Action of Pyrethroids and Neonicotinoids in Aedes Aegypti Mosquitoes; University of California: Davis, CA, USA, 2011; ISBN 1267238151. [Google Scholar]
- Thirumurugan, P.; Selvan, S.; Yamini Priya, V.; Dhanasekar, L. Impact of Hemidesmus indicus on mosquito coil exposed rat. J. Med. Plants 2015, 3, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- ATSDR—Public Health Statement: Pyrethrins and Pyrethroids. Available online: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/phs/pyrethrinsandpyrethroids (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention -The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (CDC-NIOSH). Pyrethrum. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/npg/npgd0685.html (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- Wakeling, E.N.; Neal, A.P.; Atchison, W.D. Pyrethroids and their effects on ion channels. In Pesticides—Advances in Chemical and Botanical Pesticides; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 39–66. [Google Scholar]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (US-EPA). Available online: https://www.epa.gov/ingredients-used-pesticide-products/pyrethrins-and-pyrethroids (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- United States Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. Toxicological Profile for Pyrethrins and Pyrethroids. 2003. Available online: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp155.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- Vallero, D.A. Environmental Biotechnology: A Biosystems Approach; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; ISBN 0124078974. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Gan, J.; Hunter, W.; Spurlock, F. Effect of suspended solids on bioavailability of pyrethroid insecticides. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. Int. J. 2006, 25, 1585–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu-Chen, C.; Ruey-Hong, W.; Li-Jie, S.; Ming-Chih, C.; Huei, L. Exposure to mosquito coil smoke may be a risk factor for lung cancer in Taiwan. J. Epidemiol. 2008, 18, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, M.R.; Ghose, D.K.; Rahman, M.F.; Hossain, M.T.; Rahman, M.R.; Rahman, M.A.; Islam, R. Evidence of health complications caused by mosquito coil smoke inhalation in a mouse model. J Adv. Biotech. Exp. Ther. 2020, 3, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayorinde, A.; Oboh, B.; Oduola, A.; Otubanjo, O. The insecticide susceptibility status of Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) in farm and nonfarm sites of Lagos State, Nigeria. J. Insect Sci. 2015, 15, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayorinde, A.; Oboh, B.; Otubanjo, O.; Alimba, A.; Odeigah, P. Some toxicological effects of a commonly used mosquito repellent in Lagos State, Nigeria. Res. J. Environ. Toxicol. 2014, 8, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullahi, S.N.; Dahiru, M.M.; Rabiu, D.H.; Mohammed, J.M. Toxicological Effect of Inhaled Mosquito Incense Sticks Smoke on the Histology and Biochemical Responses in Experimental Rats. FUDMA J. Sci. 2020, 4, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, M.; Rehman, N.; Nazam Ansari, M.; Kamal, M.; Ganaie, M.A.; Awaad, A.S.; Alqasoumi, S.I. Comparative study of subchronic toxicities of mosquito repellents (coils, mats and liquids) on vital organs in Swiss albino mice. Saudi Pharm. J. 2019, 27, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iribhogbe, O.I.; Agbaje, E.O.; Oreagba, I.A.; Aina, O.O.; Ota, A.D. Oxidative stress and micronutrient therapy in malaria: An in vivo study in Plasmodium berghei infected mice. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 16, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Hashim, J.H.; Jalaludin, J.; Hashim, Z.; Goldstein, B.D. Mosquito coil emissions and health implications. Environ. Health Perspect. 2003, 111, 1454–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, N.; Javed, S.; Asmatullah, A.; Ahmad, K.R.; Abbas, T.; Iqbal, J. Histological changes in the lung and liver tissues in mice exposed to pyrethroid inhalation. Walailak J. Sci. Technol. 2014, 11, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson-Corley, K.N.; Olivier, A.K.; Meyerholz, D.K. Principles for valid histopathologic scoring in research. Vet. Pathol. 2013, 50, 1007–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klopfleisch, R. Multiparametric and semi-quantitative scoring systems for the evaluation of mouse model histopathology—A systematic review. BMC Vet. Res. 2013, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taiwo Idowu, E.; Aimufua, O.J.; Yomi-Onilude, E.; Akinsanya, B.; Adetoro Otubanjo, O. Toxicological Effects of Prolonged and Intense Use of Mosquito Coil Emission in Rats and its Implications on Malaria Control. Rev. Biol. Trop. 2013, 61, 1463–1473. [Google Scholar]
- Taiwo, V.O.; Nwagbara, N.D.; Suleiman, R.; Angbashim, J.E.; Zarma, M.J. Clinical signs and organ pathology in rats exposed to graded doses of pyrethroids- containing mosquito coil smoke and aerosolized insecticidal sprays. Afr. J. Biomed. Res. 2010, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, N.; Nazir, S.; Jabeen, R. Mosquito Coil Smoke Inhalation Effects on Interstitium of Kidney of Albino Rats. Pak J. Med. Health Sci. 2015, 9, 672. Available online: https://www.pjmhsonline.com/2015/apr_june/ (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- Grewal, K.K.; Sandhu, G.S.; Kaur, R.; Brar, R.S.; Sandhu, H.S. Toxic impacts of cypermethrin on behavior and histology of certain tissues of albino rats. Toxicol. Int. 2010, 17, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feulgren, R.; Rossenbeck, H. Mikroskopisch-chemischer Nachweis einer Nucleinsäure vom Typus der Thymonucleinsäure und die- darauf beruhende elektive Färbung von Zellkernen in mikroskopischen Präparaten. Hoppe-Seyler’s Z. Physiol. Chem. 1924, 135, 203–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houston, D.K.; Johnson, M.A. Does vitamin C intake protect against lead toxicity? Nutr. Rev. 2000, 58, 73–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samitz, M.H. Ascorbic acid in the prevention and treatment of toxic effects from chromates. Acta Derm. Venereol. 1970, 50, 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- Head, K.A. Estriol: Safety and efficacy. Altern. Med. Rev. J. Clin. Ther. 1998, 3, 101–113. [Google Scholar]
- Chambial, S.; Dwivedi, S.; Shukla, K.K.; John, P.J.; Sharma, P. Vitamin C in disease prevention and cure: An overview. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2013, 28, 314–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathaswamy, A.H.M.; Wangikar, U.; Koti, B.C.; Thippeswamy, A.H.M.; Ronad, P.M.; Manjula, D.V. Cardioprotective effect of ascorbic acid on doxorubicin-induced myocardial toxicity in rats. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2011, 43, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galuppi, A.; Perrone, A.M.; La Macchia, M.; Santini, D.; Medoro, S.; Maccarini, L.R.; Strada, I.; Pozzati, F.; Rossi, M.; De Iaco, P. Local α-Tocopherol for Acute and Short-Term Vaginal Toxicity Prevention in Patients Treated with Radiotherapy for Gynecologic Tumors. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2011, 21, 1708–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misirlioglu, C.H.; Demirkasimoglu, T.; Kucukplakci, B.; Sanri, E.; Altundag, K. Pentoxifylline and α-tocopherol in prevention of radiation-induced lung toxicity in patients with lung cancer. Med. Oncol. 2007, 24, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascoe, G.A.; Reed, D.J. Vitamin E protection against chemical-induced cell injury. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1987, 256, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annual Review of Cosmetic Ingredient Safety Assessments—2001/2002. Int. J. Toxicol. 2003, 22, 1–3. [CrossRef]
- Galal, M.K.; Khalaf, A.A.A.; Ogaly, H.A.; Ibrahim, M.A. Vitamin E attenuates neurotoxicity induced by deltamethrin in rats. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousef, M.I.; Awad, T.I.; Mohamed, E.H. Deltamethrin-induced oxidative damage and biochemical alterations in rat and its attenuation by Vitamin E. Toxicology 2006, 227, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwata, N.; Okazaki, M.; Xuan, M.; Kamiuchi, S.; Matsuzaki, H.; Hibino, Y. Orally Administrated Ascorbic Acid Suppresses Neuronal Damage and Modifies Expression of SVCT2 and GLUT1 in the Brain of Diabetic Rats with Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion. Nutrients 2014, 6, 1554–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.I.; Begum, M.; Chowdhury, R.; Rahman, M.M.; Asaduzzaman, M. Synergistic Hepatoprotective Interaction between α-Tocopherol and Ascorbic Acid on Paracetamol Induced Liver Damage in Rats. Preprints 2020, 2020060122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Califima, D. Histologic Examination of the Protective Effect of Vitamin E and C in Cisplatin-Induced Hepatotoxicity. Trakya Universitesi Tip Fakultesi Dergisi. 2005, 22, 124–131. [Google Scholar]
- Adikwu, E.; Deo, O. Hepatoprotective Effect of Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid). Pharmacol. Pharm. 2013, 4, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.P. Cellular defenses against damage from reactive oxygen species. Physiol. Rev. 1994, 74, 139–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uttara, B.; Singh, A.V.; Zamboni, P.; Mahajan, R.T. Oxidative stress and neurodegenerative diseases: A review of upstream and downstream antioxidant therapeutic options. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2009, 7, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Sun, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, D. Oxidative stress, mitochondrial damage and neurodegenerative diseases. Neural Regen. Res. 2013, 8, 2003–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobo, V.; Patil, A.; Phatak, A.; Chandra, N. Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: Impact on human health. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2010, 4, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weydert, C.J.; Cullen, J.J. Measurement of superoxide dismutase, catalase and glutathione peroxidase in cultured cells and tissue. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, B.; Gutteridge, J.M.C. Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2015; ISBN 9780198717478. [Google Scholar]
- Sies, H. Oxidative stress: Oxidants and antioxidants. Exp. Physiol. 1997, 82, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacher, P.; Beckman, J.S.; Liaudet, L. Nitric oxide and peroxynitrite in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 315–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Q.; Lin, C.-L.G. Oxidative damage to RNA: Mechanisms, consequences, and diseases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 1817–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aseervatham, G.S.B.; Sivasudha, T.; Jeyadevi, R.; Arul Ananth, D. Environmental factors and unhealthy lifestyle influence oxidative stress in humans—An overview. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 4356–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, A.; Lilley, E. Superoxide anions, free-radical scavengers, and nitrergic neurotransmission. Gen. Pharmacol. Vasc. Syst. 1997, 28, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auscher, C.; Amory, N.; van der Kemp, P.; Delbarre, F. Xanthine Oxidase Activity in Human Intestines. Histochemical and Radiochemical Study. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1979, 122B, 197–201. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, T.P.; Rao, N.V.; Hopkins, C.; Pennington, L.; Tolley, E.; Hoidal, J.R. Role of reactive oxygen species in reperfusion injury of the rabbit lung. J. Clin. Investig. 1989, 83, 1326–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granger, D.N.; Kvietys, P.R. Reperfusion injury and reactive oxygen species: The evolution of a concept. Redox Biol. 2015, 6, 524–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dröge, W. Free Radicals in the Physiological Control of Cell Function. Physiol. Rev. 2002, 82, 47–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martindale, J.L.; Holbrook, N.J. Cellular response to oxidative stress: Signaling for suicide and survival. J. Cell. Physiol. 2002, 192, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, L.C.; LeVine, H. The cerebral proteopathies. Neurobiol. Aging 2000, 21, 559–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danial, N.N.; Korsmeyer, S.J. Cell Death. Cell 2004, 116, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.T.; Beal, M.F. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Nature 2006, 443, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohal, R.S.; Sohal, B.H.; Orr, W.C. Mitochondrial superoxide and hydrogen peroxide generation, protein oxidative damage, and longevity in different species of flies. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1995, 19, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, J.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Zhang, X.; Shen, Y.; Gao, Y.-J. Repetitive Hyperbaric Oxygen Treatment Attenuates Complete Freund’s Adjuvant-Induced Pain and Reduces Glia-Mediated Neuroinflammation in the Spinal Cord. J. Pain 2013, 14, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzanetakou, I.P.; Doulamis, I.P.; Korou, L.-M.; Agrogiannis, G.; Vlachos, I.S.; Pantopoulou, A.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Patsouris, E.; Vlachos, I.; Perrea, D.N. Water Soluble Vitamin E Administration in Wistar Rats with Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Open Cardiovasc. Med. J. 2012, 6, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





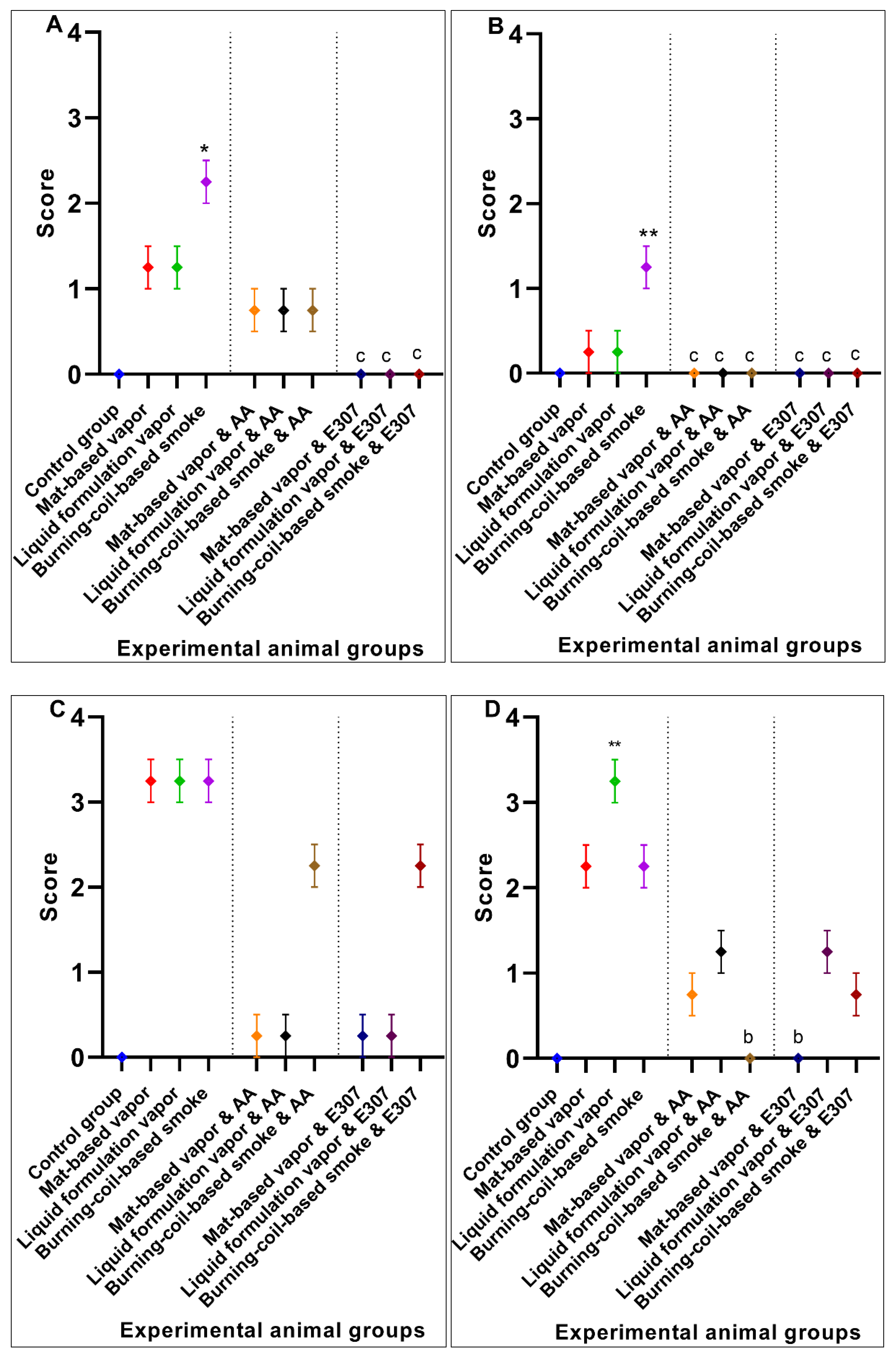






| Organ | The Group with Significant Recovery | Significant Compound |
|---|---|---|
| Liver | AA-treated mat-based-vapor exposure | AA (Ascorbic Acid) |
| AA-treated burning-coil-based smoke exposure | AA | |
| Heart | AA-treated liquid formulation vapor exposure | AA |
| Kidneys | AA-treated mat-based vapor exposure | AA |
| AA-treated burning-coil-based smoke exposure | AA | |
| E307-treated liquid formulation vapor exposure | E307 (α-Tocopherol) | |
| Lungs | E307-treated liquid formulation vapor exposure | E307 |
| Brain | AA-treated mat-based vapor exposure | AA |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Omar, M.S.; Naz, M.; Mohammed, S.A.A.; Mansha, M.; Ansari, M.N.; Rehman, N.U.; Kamal, M.; Mohammed, H.A.; Yusuf, M.; Hamad, A.M.; et al. Pyrethroid-Induced Organ Toxicity and Anti-Oxidant-Supplemented Amelioration of Toxicity and Organ Damage: The Protective Roles of Ascorbic Acid and α-Tocopherol. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17176177
Al-Omar MS, Naz M, Mohammed SAA, Mansha M, Ansari MN, Rehman NU, Kamal M, Mohammed HA, Yusuf M, Hamad AM, et al. Pyrethroid-Induced Organ Toxicity and Anti-Oxidant-Supplemented Amelioration of Toxicity and Organ Damage: The Protective Roles of Ascorbic Acid and α-Tocopherol. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(17):6177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17176177
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Omar, Mohsen S., Mamuna Naz, Salman A. A. Mohammed, Momina Mansha, Mohd N. Ansari, Najeeb U. Rehman, Mehnaz Kamal, Hamdoon A. Mohammed, Mohammad Yusuf, Abubaker M. Hamad, and et al. 2020. "Pyrethroid-Induced Organ Toxicity and Anti-Oxidant-Supplemented Amelioration of Toxicity and Organ Damage: The Protective Roles of Ascorbic Acid and α-Tocopherol" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 17: 6177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17176177
APA StyleAl-Omar, M. S., Naz, M., Mohammed, S. A. A., Mansha, M., Ansari, M. N., Rehman, N. U., Kamal, M., Mohammed, H. A., Yusuf, M., Hamad, A. M., Akhtar, N., & Khan, R. A. (2020). Pyrethroid-Induced Organ Toxicity and Anti-Oxidant-Supplemented Amelioration of Toxicity and Organ Damage: The Protective Roles of Ascorbic Acid and α-Tocopherol. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(17), 6177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17176177










