Process Mining-Supported Emergency Room Process Performance Indicators †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Process Mining in Emergency Rooms
2.2. Process Performance Measurement
3. Method
3.1. Preliminaries
3.1.1. Devil’s Quadrangle
3.1.2. ER Clinical Event Logs
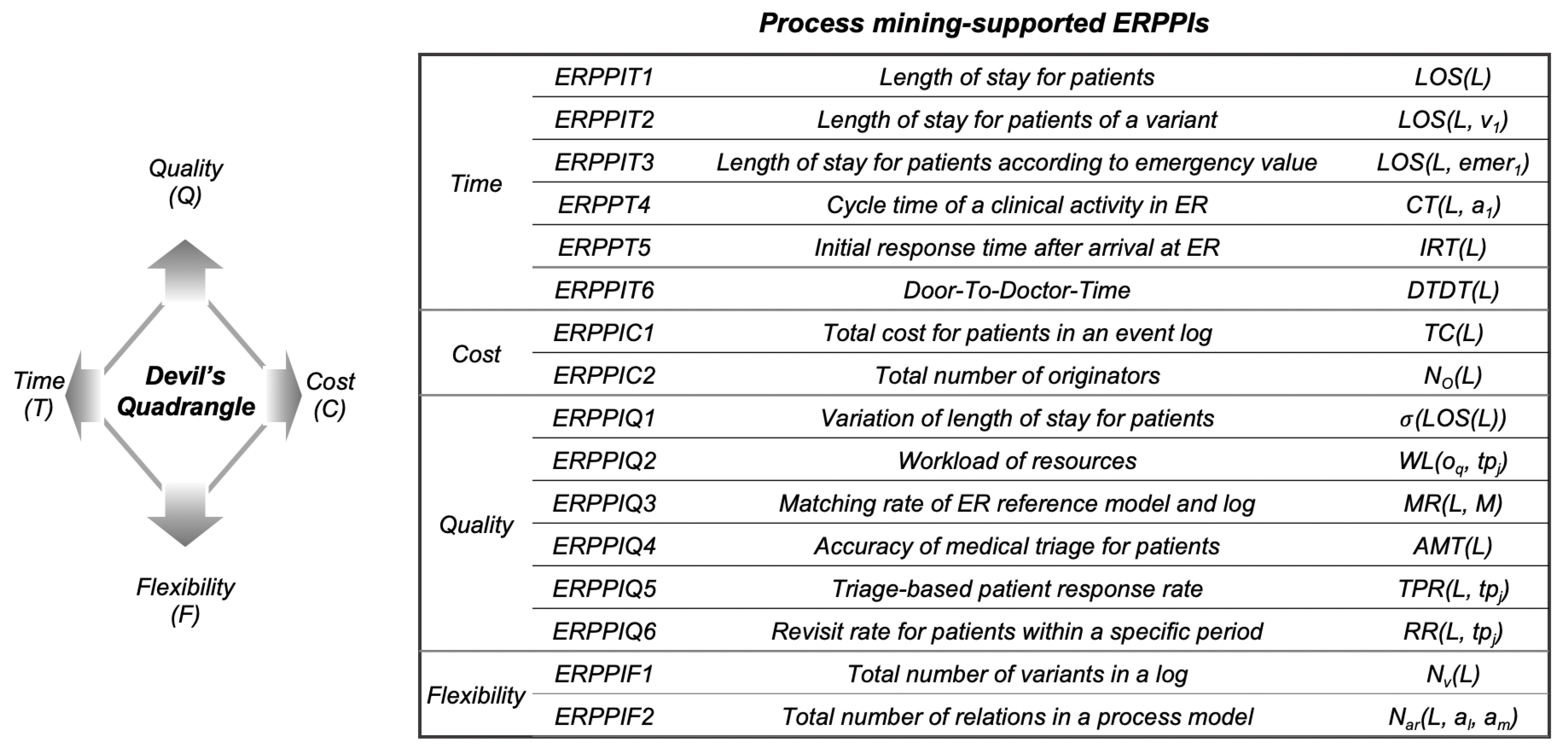
3.2. A Framework for Emergency Room Process Performance Indicators
3.3. Time-Related ERPPIs
3.4. Cost-Related ERPPIs
3.5. Quality-Related ERPPIs
3.6. Flexibility-Related ERPPIs
4. Case Study
4.1. Context
4.2. Results
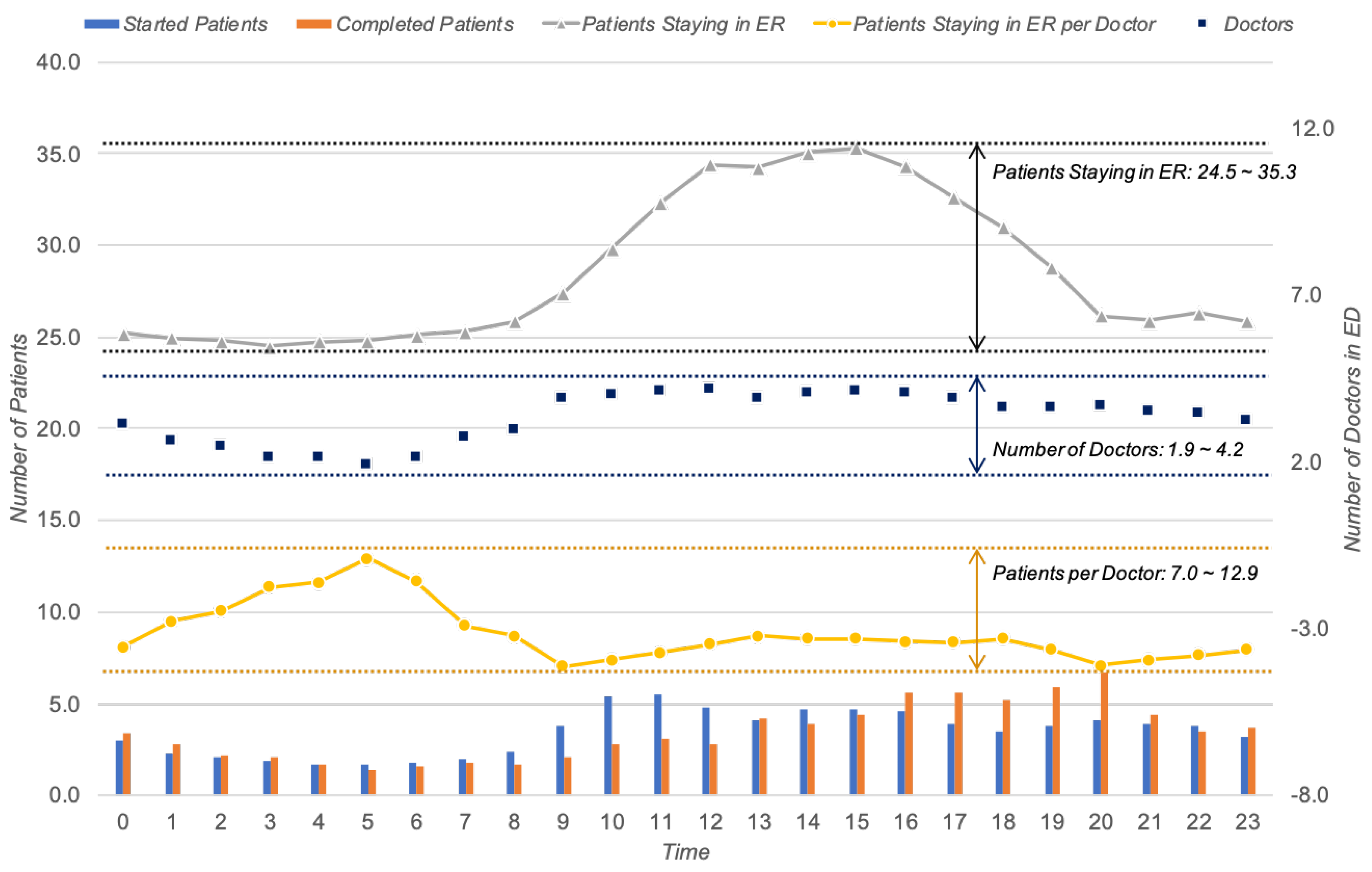
4.2.1. Time Perspective
4.2.2. Cost Perspective
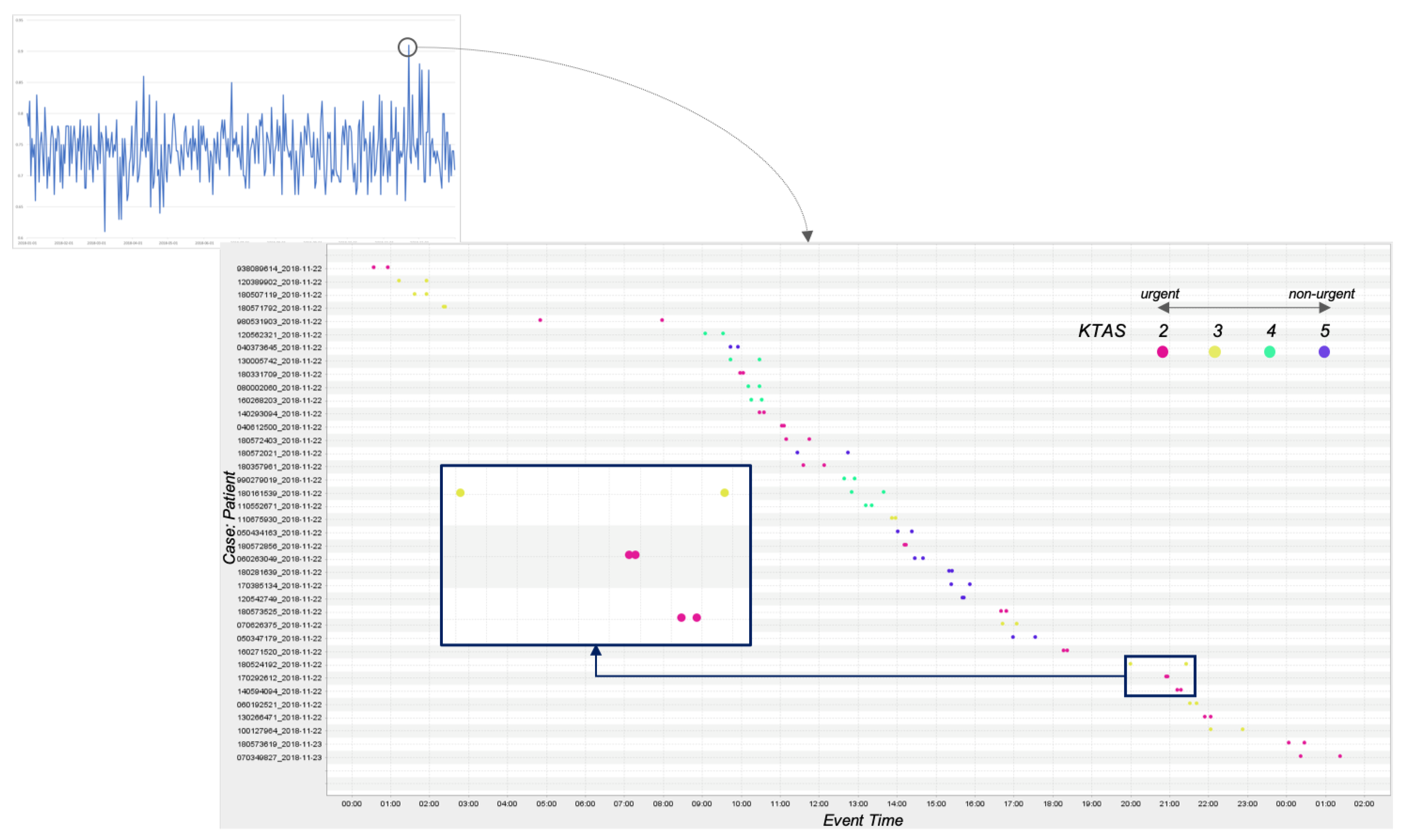
4.2.3. Quality Perspective
4.2.4. Flexibility Perspective
5. Discussion
5.1. Discussion with ER Experts
5.2. Further Applications of ERPPIs
5.3. Contributions and Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leu, J.D.; Huang, Y.T. An application of business process method to the clinical efficiency of hospital. J. Med. Syst. 2011, 35, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mans, R.S.; van der Aalst, W.M.; Vanwersch, R.J. Process Mining in Healthcare: Evaluating and Exploiting Operational Healthcare Processes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mans, R.S.; Schonenberg, M.H.; Song, M.; van der Aalst, W.M.P.; Bakker, P.J.M. Application of Process Mining in Healthcare—A Case Study in a Dutch Hospital; Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies; Fred, A., Filipe, J., Gamboa, H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 425–438. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, H.; Cho, M.; Kim, S.; Hwang, H.; Song, M.; Yoo, S. Analysis of length of hospital stay using electronic health records: A statistical and data mining approach. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derlet, R.W.; Richards, J.R. Overcrowding in the nation’s emergency departments: Complex causes and disturbing effects. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2000, 35, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumas, M.; La Rosa, M.; Mendling, J.; Reijers, H.A. Fundamentals of Business Process Management; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, J.A.M. Evidence-Based Healthcare and Public Health: How to Make Decisions about Health Services and Public Health; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Berner, E.S. Clinical Decision Support Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 233. [Google Scholar]
- Rojas, E.; Sepúlveda, M.; Munoz-Gama, J.; Capurro, D.; Traver, V.; Fernandez-Llatas, C. Question-driven methodology for analyzing emergency room processes using process mining. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stefanini, A.; Aloini, D.; Benevento, E.; Dulmin, R.; Mininno, V. Performance analysis in emergency departments: A data-driven approach. Meas. Bus. Excell. 2018, 22, 130–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.; Song, M.; Comuzzi, M.; Yoo, S. Evaluating the effect of best practices for business process redesign: An evidence-based approach based on process mining techniques. Decis. Support Syst. 2017, 104, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, E.; Munoz-Gama, J.; Sepúlveda, M.; Capurro, D. Process mining in healthcare: A literature review. J. Biomed. Inf. 2016, 61, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, E.; Cifuentes, A.; Burattin, A.; Munoz-Gama, J.; Sepúlveda, M.; Capurro, D. Performance Analysis of Emergency Room Episodes Through Process Mining. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rovani, M.; Maggi, F.M.; de Leoni, M.; van der Aalst, W.M. Declarative process mining in healthcare. Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 9236–9251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rojas, E.; Sepúlveda, M.; Munoz-Gama, J.; Capurro, D.; Seret, A. Calculating emergency room metrics through process mining. In Proceedings of the 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Perimal-Lewis, L.; Teubner, D.; Hakendorf, P.; Horwood, C. Application of process mining to assess the data quality of routinely collected time-based performance data sourced from electronic health records by validating process conformance. Health Inform. J. 2016, 22, 1017–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebuge, Á.; Ferreira, D.R. Business process analysis in healthcare environments: A methodology based on process mining. Inf. Syst. 2012, 37, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandez-Llatas, C.; Ibanez-Sanchez, G.; Celda, A.; Mandingorra, J.; Aparici-Tortajada, L.; Martinez-Millana, A.; Munoz-Gama, J.; Sepúlveda, M.; Rojas, E.; Gálvez, V.; et al. Analyzing Medical Emergency Processes with Process Mining: The Stroke Case. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Business Process Management, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 9–14 September 2018; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 214–225. [Google Scholar]
- Ibanez-Sanchez, G.; Fernandez-Llatas, C.; Martinez-Millana, A.; Celda, A.; Mandingorra, J.; Aparici-Tortajada, L.; Valero-Ramon, Z.; Munoz-Gama, J.; Sepúlveda, M.; Rojas, E.; et al. Toward value-based healthcare through interactive process mining in emergency rooms: The stroke case. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perimal-Lewis, L.; De Vries, D.; Thompson, C.H. Health intelligence: Discovering the process model using process mining by constructing start-to-end patient journeys. In Proceedings of the Seventh Australasian Workshop on Health Informatics and Knowledge Management, Auckland, New Zealand, 20–23 January 2014; Volume 153, pp. 59–67. [Google Scholar]
- Ceglowski, A.; Churilov, L.; Wassertheil, J. Knowledge discovery through mining emergency department data. In Proceedings of the 38th Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Big Island, HI, USA, 6 January 2005; p. 142c. [Google Scholar]
- Partington, A.; Wynn, M.; Suriadi, S.; Ouyang, C.; Karnon, J. Process Mining for Clinical Processes: A Comparative Analysis of Four Australian Hospitals. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. 2015, 5, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delias, P.; Doumpos, M.; Grigoroudis, E.; Manolitzas, P.; Matsatsinis, N. Supporting healthcare management decisions via robust clustering of event logs. Knowl. Based Syst. 2015, 84, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duma, D.; Aringhieri, R. An ad hoc process mining approach to discover patient paths of an Emergency Department. Flex. Serv. Manuf. J. 2020, 32, 6–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rismanchian, F.; Lee, Y.H. Process Mining–Based Method of Designing and Optimizing the Layouts of Emergency Departments in Hospitals. HERD Health Environ. Res. Des. J. 2017, 10, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, R.S.; Norton, D.P. Linking the balanced scorecard to strategy. Calif. Manag. Rev. 1996, 39, 53–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, R.S.; Norton, D.P. Having trouble with your strategy? Then map it. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2000, 78, 167–176. [Google Scholar]
- Haffey, M.K.D.; Duffy, A.H.B. Process performance measurement support: A critical analysis. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Engineering Design (ICED 01), Glasgow, UK, 21–23 August 2001; IMechE Professional Engineering Publishing: London, UK, 2001; pp. 561–568. [Google Scholar]
- Kueng, P. Process performance measurement system: A tool to support process-based organizations. Total Qual. Manag. 2000, 11, 67–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glykas, M. Fuzzy cognitive strategic maps in business process performance measurement. Expert Syst. Appl. 2013, 40, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neely, A.; Mills, J.; Platts, K.; Richards, H.; Gregory, M.; Bourne, M.; Kennerley, M. Performance measurement system design: Developing and testing a process-based approach. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2000, 20, 1119–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekaran, A.; Kobu, B. Performance measures and metrics in logistics and supply chain management: A review of recent literature (1995–2004) for research and applications. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2007, 45, 2819–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakarian, A.; Wickett, P.; Siradeghyan, Y. Quantitative model for evaluating the quality of an automotive business process. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2006, 44, 1055–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.Y. Constructing a strategy map for banking institutions with key performance indicators of the balanced scorecard. Eval. Program Plan. 2012, 35, 303–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vom Brocke, J. Service portfolio measurement: Evaluating financial performance of service-oriented business processes. Int. J. Web Serv. Res. 2007, 4, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hinrichs, N.; Barke, E. Applying performance management on semiconductor design processes. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management, Singapore, 8–11 December 2008; pp. 278–281. [Google Scholar]
- Wetzstein, B.; Ma, Z.; Leymann, F. Towards measuring key performance indicators of semantic business processes. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Business Information Systems, Innsbruck, Austria, 5–7 May 2008; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 227–238. [Google Scholar]
- Popova, V.; Sharpanskykh, A. Modeling organizational performance indicators. Inf. Syst. 2010, 35, 505–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del-Río-Ortega, A.; Resinas, M.; Cabanillas, C.; Ruiz-Cortés, A. On the definition and design-time analysis of process performance indicators. Inf. Syst. 2013, 38, 470–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwon, H.; Kim, Y.J.; Jo, Y.H.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.; Hwang, J.E.; Jeong, J.; Choi, Y.J. The Korean Triage and Acuity Scale: Associations with admission, disposition, mortality and length of stay in the emergency department. Int. J. Qual. Health Care 2019, 31, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leemans, S.J.; Syring, A.F.; van der Aalst, W.M. Earth movers’ stochastic conformance checking. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Business Process Management, Vienna, Austria, 1–6 September 2019; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 127–143. [Google Scholar]
- Suriadi, S.; Andrews, R.; ter Hofstede, A.H.; Wynn, M.T. Event log imperfection patterns for process mining: Towards a systematic approach to cleaning event logs. Inf. Syst. 2017, 64, 132–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günther, C.W.; Rozinat, A. Disco: Discover Your Processes. BPM (Demos) 2012, 940, 40–44. [Google Scholar]
- PuzzleData. ProDiscovery. Available online: https://www.puzzledata.com/product/ (accessed on 15 March 2020).
- Verbeek, H.; Buijs, J.; Van Dongen, B.; van der Aalst, W.M. Prom 6: The process mining toolkit. Proc. BPM Demonstr. Track 2010, 615, 34–39. [Google Scholar]
- van der Aalst, W.M. Data science in action. In Process Mining; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 3–23. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, M.; Song, M.; Yoo, S.; Reijers, H.A. An Evidence-Based Decision Support Framework for Clinician Medical Scheduling. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 15239–15249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| CaseID | Activity | Timestamp | Type | Resource | Emergency | PatientID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Entry | 01/02/2018 19:05 | Complete | John | 3 | P1 |
| 1 | Treatment | 01/02/2018 19:17 | Complete | Jane | 3 | P1 |
| 1 | Consultation | 01/02/2018 19:20 | Start | Tom | 3 | P1 |
| 2 | Entry | 01/02/2018 19:21 | Complete | John | 1 | P2 |
| 2 | Treatment | 01/02/2018 19:36 | Complete | Jane | 1 | P2 |
| ERPPI | Type | Average | Median |
|---|---|---|---|
| ERPPIT1 () | – | 8.4 h | 4.8 h |
| ERPPIT2 () | length of stay with hospitalization | 11.5 h | 7.5 h |
| length of stay with discharge | 5.4 h | 3.4 h | |
| ERPPIT3 () | Severe (i.e., 1 and 2 of KTAS) | 11.8 h | 6.6 h |
| Moderate (i.e., 3 of KTAS) | 8.9 h | 5.3 h | |
| Mild (i.e., 4 and 5 of KTAS) | 6.0 h | 3.5 h | |
| ERPPIT4 () | Consultation | 17.2 m | 8.0 m |
| Basic Treatment | 27.2 m | 6.0 m | |
| First-aid Treatment | 9.4 m | 3.0 m | |
| Diagnostic Test | 10.5 m | 2.0 m | |
| Decision on Hospitalization or Discharge | 50.7 m | 24.0 m | |
| Discharge | 27.1 m | 5.0 m | |
| Hostpitalization | 114.5 m | 68.0 m | |
| ERPPIT5 () | – | 8.0 m | 19.6 m |
| Classification Method | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline (Rule-based) | 0.4442 | 0.4400 | 0.3741 | 0.3329 |
| Regression-based Classifier | 0.7056 | 0.6985 | 0.5997 | 0.6370 |
| Decision Tree | 0.7578 | 0.7236 | 0.6158 | 0.6509 |
| Random Forest | 0.7509 | 0.7749 | 0.5580 | 0.6122 |
| SVM-based Classifier | 0.6654 | 0.5685 | 0.5905 | 0.5761 |
| Multi-Perceptron Neural Net | 0.7607 | 0.7548 | 0.6430 | 0.6812 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, M.; Song, M.; Park, J.; Yeom, S.-R.; Wang, I.-J.; Choi, B.-K. Process Mining-Supported Emergency Room Process Performance Indicators. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17176290
Cho M, Song M, Park J, Yeom S-R, Wang I-J, Choi B-K. Process Mining-Supported Emergency Room Process Performance Indicators. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(17):6290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17176290
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Minsu, Minseok Song, Junhyun Park, Seok-Ran Yeom, Il-Jae Wang, and Byung-Kwan Choi. 2020. "Process Mining-Supported Emergency Room Process Performance Indicators" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 17: 6290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17176290
APA StyleCho, M., Song, M., Park, J., Yeom, S.-R., Wang, I.-J., & Choi, B.-K. (2020). Process Mining-Supported Emergency Room Process Performance Indicators. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(17), 6290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17176290





