Use of Neurodynamic or Orthopedic Tension Tests for the Diagnosis of Lumbar and Lumbosacral Radiculopathies: Study of the Diagnostic Validity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
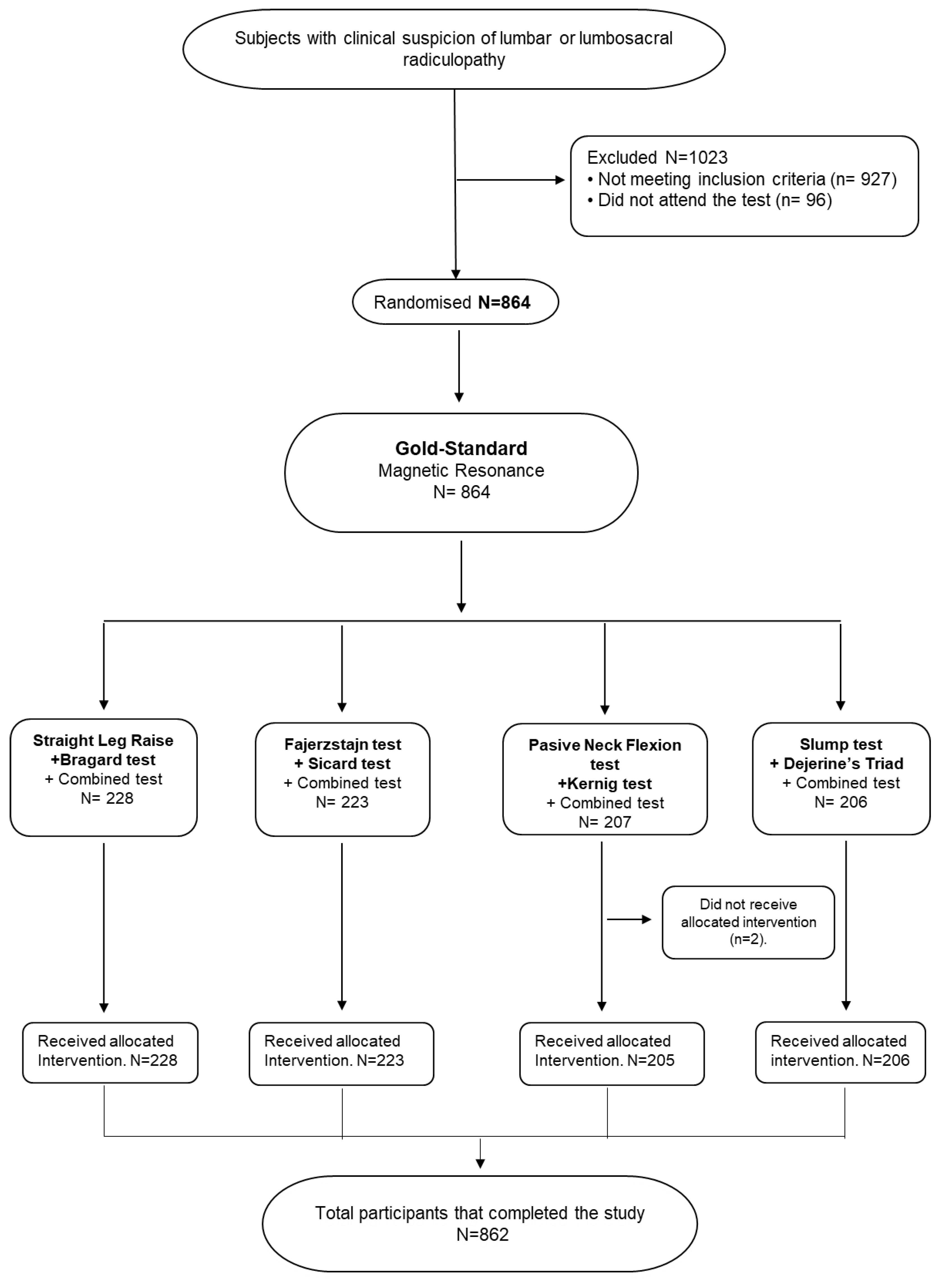
2.2. Recruitment Process
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Testing Procedure
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
Participants
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sánchez, S.D.; Calderón, M.M.; García Leoni, M.E.; Palazuelos, M.V. Dolores musculoesqueléticos. Radiculopatías. Afectación de partes blandas. Artritis aguda. Medicine 2011, 10, 6023–6040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latka, D.; Miekisiak, G.; Jarmuzek, P.; Lachowski, M.; Kaczmarczyk, J. Treatment of lumbar disc herniation with radiculopathy. Clinical practice guidelines endorsed by The Polish Society of Spinal Surgery. Neurol Neurochir. Pol. 2016, 50, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochoa Sangrador, C.; González de Dios, J.; Buñuel Álvarez, J.C. Evaluación de artículos científicos sobre pruebas diagnósticas. Evid. Pediatr. 2007, 3, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Zamora, J.; Abraira, V. Análisis de la calidad de los estudios de evaluación de pruebas diagnósticas. Nefrología 2008, 28, 42–45. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, D.R.; Hurwitz, E.L. A theoretical model for the development of a diagnosis based clinical decision rule for the management of patients with spinal pain. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2007, 8, 60–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.R.; Hurwitz, E.L.; Gerrard, J.K.; Clary, R. Pain patterns and descriptions in patients with radicular pain: Does the pain necessarily follow a specific dermatome? Chiropr. Osteopat. 2009, 17, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larraguibel Salas, F. Síndrome lumbociático. Rev. Med. Clin. Condes. 2006, 17, 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- Umaña Giraldo, H.; Henao Zuluaga, C.; Castillo Berrio, C. Semiología del dolor lumbar. Rev. Med. Risaralda 2010, 16, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-García, P.L.; Rodríguez-Pupo, L.; Rodríguez-García, D. Técnicas clínicas para el examen físico neurológico. III. Función sensitiva. Rev. Neurol. 2004, 39, 966–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, D.S. Movilización del Sistema Nervioso; Paidotribo: Barcelona, Spain, 2002; pp. 131–134. [Google Scholar]
- Hilal, K.; Sajjad, Z.; Sayani, R.; Khan, D. Utility of Limited Protocol Magnetic Resonance Imaging Lumbar Spine for Nerve Root Compression in a Developing Country, Is It Accurate and Cost Effective? Asian Spine J. 2013, 7, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trainor, K.; Pinnington, M.A. Reliability and diagnostic validity of the slump knee bend neurodynamic test for upp.er/mid lumbar nerve root compression: A pilot study. Physiotherapy 2011, 97, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, D.S.; Anderson, I.B.; Carson, M.G.; Elkins, C.L.; Stuckey, L.B. Upper Limb Neural Tension and Seated Slump Tests: The false positive rate among healthy young adults without cervical or lumbar symptoms. J. Man. Manip. Ther. 2008, 16, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shacklock, M.; Donoso, G.; Lucha López, M. Hacia un enfoque en el diagnóstico con test neurodinámicos (tensión neural). Rev. Fisioter. 2007, 29, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, R.; Gemmell, H. Accuracy of spinal orthopaedic tests: A systematic review. Chiropr. Osteopat. 2006, 14, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camino Willhuber GO, P.N. Straight Leg Raise Test. In Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Natalio Firpo, C.A. Manual de Ortopedia y Traumatología, 1st ed.; Carlos Natalio Firpo: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2010; pp. 120–150. [Google Scholar]
- Fransoo, P. Examen Clínico del Paciente con Lumbalgia; Paidotribo: Barcelona, Spain, 2003; pp. 100–204. [Google Scholar]
- Ricard, F. Tratamiento Osteopático de las Lumbalgias y Lumbociáticas por Hernias Discales; Médica Panamericana: Madrid, Spain, 2003; pp. 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, M.A.; Greenwood, T.M.; Kumar, D.R.; Mazza, J.J.; Yale, S.H. Josef Brudzinski and Vladimir Mikhailovich Kernig: Signs for diagnosing Meningitis. Clin. Med. Res. 2010, 8, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitland, G.D. The Slump Test: Examination and treatment. Aust. J. Physiother. 1985, 31, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.F.; Korevaar, D.A.; Altman, D.G.; Bruns, D.E.; Gatsonis, C.A.; Hooft, L.; Irwig, L.; Levine, D.; Reitsma, J.B.; De Vet, H.C.W.; et al. STARD 2015 guidelines for reporting diagnostic accuracy studies: Explanation and elaboration. BMJ Open 2016, 6, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossuyt, P.M.; Reitsma, J.B.; Bruns, D.E.; Gatsonis, C.A.; Glasziou, P.P.; Irwig, L.M. STARD 2015: An updated list of essential items for reporting diagnostic accuracy studies. BMJ 2015, 351, h5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asociación Médica Mundial. Declaración de Helsinki de la Asociación Médica Mundial. Principios éticos para las investigaciones médicas en seres humanos. An. Sist. Sanit. Navar. 2001, 24, 209–212. [Google Scholar]
- UE. Reglamento (UE) 2016/679 del Parlamento Europeo y del Consejo, de 27 de abril de 2016, Relativo a la Protección de las Personas Físicas en lo que Respecta al Tratamiento de datos Personales y a la Libre Circulación de estos Datos y por el que se Deroga la Directiva 95/46/CE (Reglamento General de Protección de datos); Diario Oficial de la Unión Europea: Madrid, Spain, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Comuñas, F. Dolor radicular. Rev. Soc. Esp. Dolor 2000, 7 (Suppl. 2), 36–48. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, K.J. Physical assessment of lower extremity radiculopathy and sciatica. J. Chiropr. Med. 2007, 6, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesa, J.C.; García, O.; Lillo, J.; Mascaró, F.; Arruga, J. Oftalmología basada en pruebas: Evaluación crítica de la literatura sobre pruebas diagnósticas. Arch. Soc. Esp. Oftalmol. 2008, 83, 639–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerda, L.J.; Cifuentes, A.L. Uso de tests diagnósticos en la práctica clínica (Parte 1). Análisis de las propiedades de un test diagnóstico. Rev. Chil. Infect. 2010, 27, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupérez, F. Validez de los Elementos Diagnósticos en Endometriosis. Aplicación al Análisis de Decisión Clínica. Ph.D. Thesis, Departamento de Cirugía, Ciencias Médicas y Sociales-Universidad de Alcalá, Madrid, Spain, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Epidemiología General y Demografía Sanitaria, 2010–2011. Open Course Ware (16633). Epidat: Pruebas Diagnósticas. Available online: https://goo.gl/UfAwMe (accessed on 1 May 2014).
- Ortín Ortín, E.; Sánchez Sánchez, J.A.; Menárguez Puche, J.F.; Hidalgo García, I.M. Lectura crítica de un artículo sobre diagnóstico. In Atención Sanitaria Basada en la Evidencia: Su Aplicación a la Práctica Clínica; Sánchez Sánchez, J.A., Ed.; Consejería de Sanidad: Murcia, Spain, 2007; pp. 233–578. [Google Scholar]
- Hervás Angulo, A.; Lacosta Ramírez, U.; Brugarolas Brufau, C.; Díez Espino, J. Aplicabilidad en una comunidad (validez externa) de los estudios de prevención primaria de hipercolesterolemia. Aten. Primaria 2003, 32, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva Fuente-Alba, C.; Molina Villagra, M. Likelihood ratio (razón de verosimilitud): Definición y aplicación en Radiología. Rev. Argent. Radiol. 2017, 81, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donis, J.H. Assessment of the validity and reliability of a diagnostic test. Avan. Biomed. 2012, 1, 73–81. [Google Scholar]
- Camila Medina, M. Generalidades de las pruebas diagnósticas, y su utilidad en la toma de decisiones médicas. Rev. Colomb. Psiquiat. 2011, 40, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa Sangrador, C.; Molina Arias, M. Evaluación de la precisión de las pruebas diagnósticas (1). Variables discretas. Evid. Pediatr. 2017, 13, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Cortés-Reyes, E.T.; Rubio-Romero, A.J.; Gaitán-Duarte, H. Statistical methods for evaluating diagnostic test agreement and reproducibility. Rev. Colomb. Obstet. Ginecol. 2009, 61, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Windt, D.; Simons, E.; Riphagen, I.I.; Ammendolia, C.; Verhagen, A.P.; Laslett, M.; Deville, W.; Deyo, R.A.; Bouter, L.M.; de Vet, H.C.; et al. Physical examination for lumbar radiculopathy due to disc herniation in patients with low-back pain. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011, 1–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabin, A.; Gerszten, P.C.; Karausky, P.; Bunker, C.H.; Potter, D.M.; Welch, W.C. The sensitivity of the Seated Straight-Leg Raise Test compared with the Supine Straight-Leg Raise Test in patients presenting with Magnetic Resonance Imaging evidence of lumbar nerve root compression. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2007, 88, 840–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iversen, T.; Solberg, T.K.; Romner, B.; Wilsgaard, T.; Nygaard, Ø.; Waterloo, K.; Brox, J.I.; Ingebrigtsen, T. Accuracy of physical examination for chronic lumbar radiculopathy. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2013, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suri, P.; Rainville, J.; Katz, J.N.; Jouve, C.; Hartigan, C.; Limke, J.; Pena, E.; Li, L.; Swaim, B.; Hunter, D.J. The accuracy of the Physical Examination for the diagnosis of Midlumbar and Low Lumar Nerve Root Impingement. Spine 2011, 36, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poiraudeau, S. Value of the bell test and the hyperextension test for diagnosis in sciatica associated with disc herniation: Comparison with Lasegue’s sign and the crossed Lasegue’s sign. Rheumatology 2001, 40, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majlesi, J.; Togay, H.; Ünalan, H.; Toprak, S. The sensitivity and specificity of the slump and the straight leg raising tests in patients with lumbar disc herniation. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2008, 14, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cecin, H.A. Sinal de Cecin (Sinal “X”): Um aprimoramento no diagnóstico de compressão radicular por hérnias discais lombares. Rev. Bras. Reumatol. 2010, 50, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capra, F.; Vanti, C.; Donati, R.; Tombetti, S.; O’Reilly, C.; BScPhysio(hons); Pillastrini, P. Validity of the straight-leg raise test for patients with sciatic pain with or without lumbar pain using magnetic resonance imaging results as a reference standard. J. Manipulative Physiol. Ther. 2011, 34, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaia, V.; Baxter, D.; Cook, C. The pain provocation-based Straight Leg Raise Test for diagnosis of lumbar disc herniation, lumbar radiculopathy, and/or sciatica: A systematic review of clinical utility. J. Back Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 2012, 25, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekedahl, H.; Jönsson, B.; Annertz, M. Accuracy of clinical tests in detecting disk herniation and nerve root compression in subjects with lumbar radicular symptoms. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2018, 99, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekedahl, H.; Jönsson, B. Fingertip-to-floor test and straight leg raising test: Validity, responsiveness, and predictive value in patients with acute/subacute low back pain. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2012, 93, 2210–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vroomen, P.C.; De Krom, M.C.; Knottnerus, J.A. Consistency of history taking and physical examination in patients with suspected lumbar nerve root involvement. Spine 2000, 25, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreiner, D.S.; Hwang, S.W.; Easa, J.E.; Resnick, D.K.; Baisden, J.L.; Bess, S. An evidence-based clinical guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of lumbar disc herniation with radiculopathy. Spine J. 2014, 14, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, J.; Inez Silva, L.; Liberali, M.; Yumi Kiara, P.; Marcelo Pilatti, C. Concordância entre o teste de distensão dural na posição sentada (slump test) e o teste de lasègue no diagnóstico fisioterapêutico de lombociatalgia. FIEP Bull. 2013, 83, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Homayouni, K.; Jafari, S.; Yari, H. Sensitivity and specificity of Modified Bragard Test in patients with lumbosacral rediculopathy using electrodiagnosis as a reference standard. J. Chiropr. Med. 2018, 17, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vroomen, P.C.; De Krom, M.C.; Knottnerus, J.A. Diagnostic value of history and physical examination in patients suspected of sciatica due to disc herniation: A systematic review. J. Neurol. 1999, 246, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurie, J.D. What diagnostic tests are useful for low back pain? Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2005, 19, 557–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devillé, W.; van der Windt, D.; Dzaferagić, A.; Bezemer, P.; Bouter, L. The test of Lasègue: Systematic review of the accuracy in diagnosing herniated discs. Spine 2000, 25, 1140–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koes, B.; Van Tulder, M.; Peul, W. Diagnosis and treatment of sciatica. Br. Med. J. 2007, 334, 1313–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’kumbuzi, V.R.P.; Ntawukuriryayo, J.T.; Haminana, J.D.; Munyandamutsa, J.; Nzakizwanimana, E. Accuracy of straight leg raise and slump tests in detecting lumbar disc herniation: A pilot study. Cent. Afr. J. Med. 2012, 58, 5–11. [Google Scholar]
- Urban, L.; MacNeil, B. Diagnostic Accuracy of the Slump Test for Identifying Neuropathic Pain in the Lower Limb. J. Orthop. Sport. Phys. Ther. 2015, 45, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Group | Starting Date | Finishing Date | Tests Performed |
|---|---|---|---|
| SLR 1-B 2 | 7 July 2014 | 11 November 2014 | Straight Leg Raise [14] |
| Bragard test [17] | |||
| F 3-S 4 | 13 November 2014 | 10 July 2015 | Fajersztajn test [18] |
| Sicard test [19] | |||
| PNFT 5-K 6 | 13 July 2015 | 23 March 2016 | Passive Neck Flexion test [10] |
| Kernig test [20] | |||
| ST 7-DT 8 | 28 March 2016 | 25 August 2016 | Slump test [21] |
| Dejerine’s triad [19] |
| Group | Gender (%) | L1 (%) | L2 (%) | L3 (%) | L4 (%) | L5 (%) | S1 (%) | S2 (%) | S3 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLR 1-B 2 | Male 21.05 | 0 | 0 | 3.07 | 7.01 | 8.77 | 7.89 | 0 | 0 |
| 5.70% Right-6.57% Left-3.94% Bilateral-10.52% Lost | |||||||||
| Female 18.42 | 0 | 0.43 | 1.31 | 6.14 | 8.33 | 7.89 | 0 | 0 | |
| 9.21% Right-6.57% Left-0.87% Bilateral-7.45% Lost | |||||||||
| F 3-S 4 | Male 27.80 | 0 | 0 | 4.03 | 8.96 | 12.55 | 8.52 | 0 | 0 |
| 8.07% Right-11.21% Left-13% Bilateral-1.79% Lost | |||||||||
| Female 19.28 | 0 | 0.44 | 1.34 | 7.17 | 6.72 | 7.62 | 0 | 0 | |
| Right 8.07%-Left 8.96%-Bilateral 4.03%-Lost 2.24% | |||||||||
| PNFT 5-K 6 | Male 23.90 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6.82 | 12.19 | 9.6 | 0 | 0 |
| 7.80% Right-12.68% Left-7.31% Bilateral-0.48% Lost | |||||||||
| Female 30.24 | 0.48 | 0.97 | 4.39 | 9.26 | 13.17 | 11.70 | 0.48 | 0.48 | |
| 13.65% Right-15.60% Left-9.75% Bilateral-2.43% Lost | |||||||||
| ST 7-DT 8 | Male 26.21 | 0 | 0 | 1.94 | 6.31 | 13.59 | 11.65 | 0.48 | 0.48 |
| 9.70% Right-12.13% Left-12.62% Bilateral-0% Lost | |||||||||
| Female 28.64 | 0 | 0 | 5.82 | 15.53 | 13.59 | 4.85 | 0 | 0 | |
| 8.73% Right-16.01% Left-14.56% Bilateral-0.48% Lost | |||||||||
| Test | Sens 9 (%) | Spec 10 (%) | PV+ 11 (%) | PV− 12 (%) | LR+ 13 | LR− 14 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLR 1 | 83.33 | 74.24 | 70.18 | 85.96 | 3.24 | 0.22 |
| B 2 | 84.38 | 73.48 | 69.83 | 86.61 | 3.18 | 0.21 |
| Combined test SLR 1 + B 2 | 83.38 | 72.73 | 69.23 | 86.49 | 3.09 | 0.21 |
| Multiple parallel SLR 1 and B 2 | 97.40 | 54.55 | 60.92 | 96.64 | 2.14 | 0.05 |
| F 3 | 43.12 | 80.70 | 68.12 | 59.74 | 2.23 | 0.70 |
| S 4 | 66.06 | 68.42 | 66.67 | 67.83 | 2.09 | 0.50 |
| Combined test F 3 + S 4 | 46.79 | 78.07 | 67.11 | 60.54 | 2.13 | 0.68 |
| Multiple parallel F 3 and S 4 | 80.69 | 55.21 | 63.27 | 74.94 | 1.80 | 0.35 |
| PNFT 5 | 31.53 | 95.74 | 89.74 | 54.22 | 7.41 | 0.72 |
| K 6 | 61.26 | 70.21 | 70.83 | 60.55 | 2.06 | 0.55 |
| Combined test PNFT 5 + K 6 | 64.86 | 68.09 | 70.59 | 62.14 | 2.03 | 0.52 |
| Multiple parallel PNFT 5 and K 6 | 73.47 | 67.22 | 72.58 | 68.21 | 2.24 | 0.39 |
| ST 7 | 80.17 | 77.78 | 82.30 | 75.27 | 3.61 | 0.25 |
| DT 8 | 19.83 | 96.67 | 88.46 | 48.33 | 5.95 | 0.83 |
| Combined test ST 7 + DT 8 | 93.97 | 77.78 | 84.50 | 90.91 | 4.23 | 0.08 |
| Multiple parallel ST 7 and DT 8 | 84.10 | 75.19 | 81.37 | 78.58 | 3.39 | 0.21 |
| Test | Cohen’s Kappa Index |
|---|---|
| SLR 1 | 0.974 |
| B 2 | 0.974 |
| F 3 | 0.929 |
| S 4 | 0.674 |
| PNFT 5 | 0.386 |
| K 6 | 0.942 |
| S 7 | 0.841 |
| DT 8 | 0.159 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
González Espinosa de los Monteros, F.J.; Gonzalez-Medina, G.; Ardila, E.M.G.; Mansilla, J.R.; Expósito, J.P.; Ruiz, P.O. Use of Neurodynamic or Orthopedic Tension Tests for the Diagnosis of Lumbar and Lumbosacral Radiculopathies: Study of the Diagnostic Validity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17197046
González Espinosa de los Monteros FJ, Gonzalez-Medina G, Ardila EMG, Mansilla JR, Expósito JP, Ruiz PO. Use of Neurodynamic or Orthopedic Tension Tests for the Diagnosis of Lumbar and Lumbosacral Radiculopathies: Study of the Diagnostic Validity. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(19):7046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17197046
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzález Espinosa de los Monteros, Francisco Javier, Gloria Gonzalez-Medina, Elisa Maria Garrido Ardila, Juan Rodríguez Mansilla, José Paz Expósito, and Petronila Oliva Ruiz. 2020. "Use of Neurodynamic or Orthopedic Tension Tests for the Diagnosis of Lumbar and Lumbosacral Radiculopathies: Study of the Diagnostic Validity" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 19: 7046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17197046
APA StyleGonzález Espinosa de los Monteros, F. J., Gonzalez-Medina, G., Ardila, E. M. G., Mansilla, J. R., Expósito, J. P., & Ruiz, P. O. (2020). Use of Neurodynamic or Orthopedic Tension Tests for the Diagnosis of Lumbar and Lumbosacral Radiculopathies: Study of the Diagnostic Validity. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(19), 7046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17197046






