Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on Inflammation, Oxidative/Antioxidant Balance, and Muscle Damage after Acute Exercise in Normobaric, Normoxic and Hypobaric, Hypoxic Environments: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Anthropometric Measures and VO2max Test
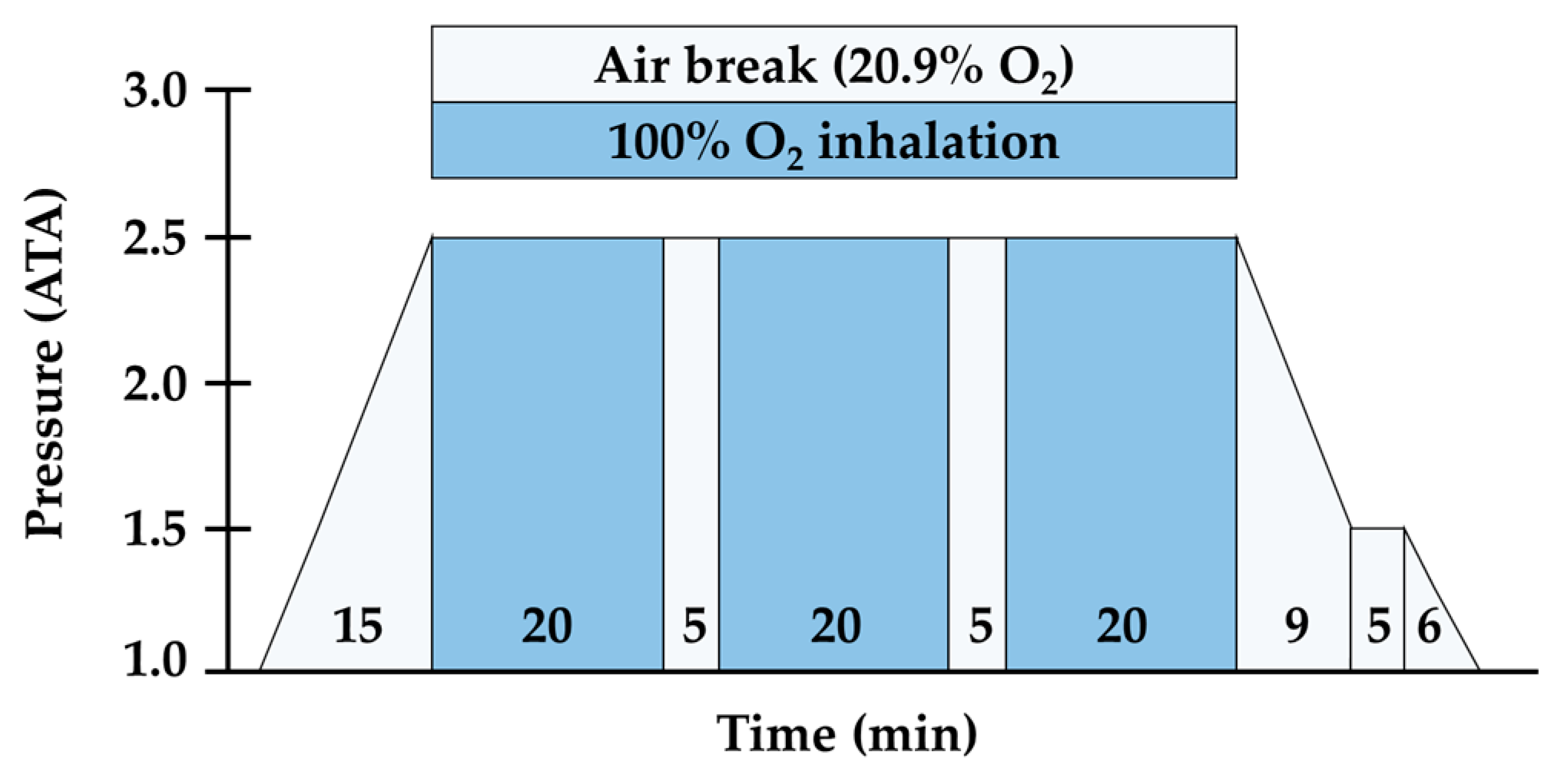
2.3. Exercise Environment Setting and HBOT Procedure Protocol
2.4. Blood Collection and Analyses
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Changes in Variables Related to Inflammation
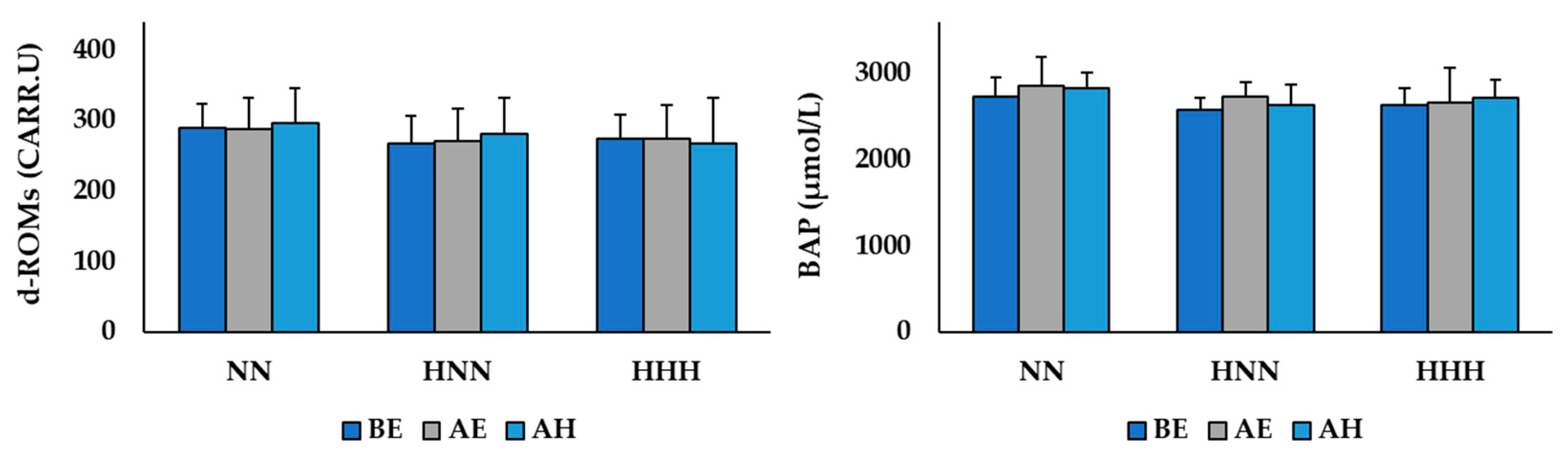
3.2. Changes in Variables Related to Oxidative/Antioxidant Balance
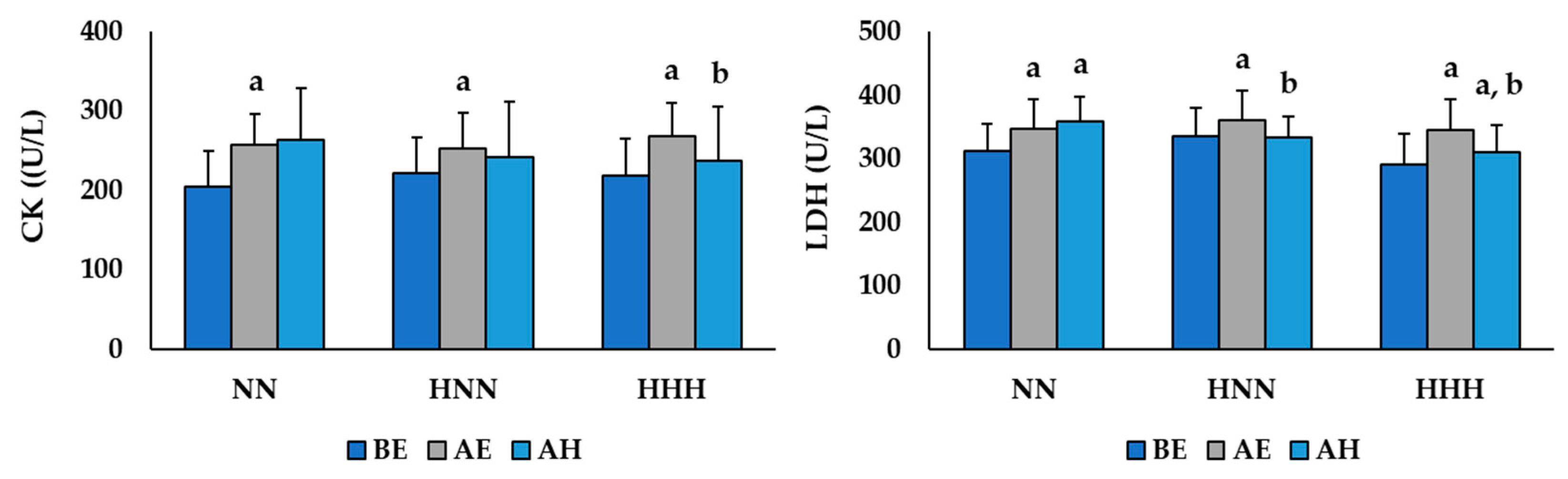
3.3. Changes in Variables Related to Muscle Damage
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Konopka, A.R.; Harber, M.P. Skeletal muscle hypertrophy after aerobic exercise training. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2014, 42, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, B.K.; Saltin, B. Exercise as medicine-evidence for prescribing exercise as therapy in 26 different chronic diseases. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2015, 25, 1–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, S.K.; Jackson, M.J. Exercise-induced oxidative stress: Cellular mechanisms and impact on muscle force production. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 1243–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, S.; Chaki, B.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Bandyopadhyay, A. High-Intensity Exercise Induced Oxidative Stress and Skeletal Muscle Damage in Postpubertal Boys and Girls: A Comparative Study. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2018, 32, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.J.; Jude, B.; Lanner, J.T. Intramuscular mechanisms of overtraining. Redox Biol. 2020, 35, 101480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liakos, C.I.; Vyssoulis, G.P.; Michaelides, A.P.; Chatzistamatiou, E.I.; Theodosiades, G.; Toutouza, M.G.; Markou, M.I.; Synetos, A.G.; Kallikazaros, I.E.; Stefanadis, C.I. The effects of angiotensin receptor blockers vs. calcium channel blockers on the acute exercise-induced inflammatory and thrombotic response. Hypertens. Res. 2012, 35, 1193–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancaccio, P.; Maffulli, N.; Buonauro, R.; Limongelli, F.M. Serum enzyme monitoring in sports medicine. Clin. Sports Med. 2008, 27, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzeo, R.S. Physiological responses to exercise at altitude: An update. Sports Med. 2008, 38, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosek, A.; Ohno, H.; Acs, Z.; Taylor, A.W.; Radak, Z. High altitude and oxidative stress. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2007, 158, 128–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltzschig, H.K.; Carmeliet, P. Hypoxia and inflammation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, S.A.; Silva, E.T.; Caris, A.V.; Lira, F.S.; Tufik, S.; Dos Santos, R.V. Vitamin E supplementation inhibits muscle damage and inflammation after moderate exercise in hypoxia. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 29, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, M.; Teixeira, V.H.; Soares, J. Dietary strategies to recover from exercise-induced muscle damage. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 65, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jówko, E.; Płaszewski, M.; Cieśliński, M.; Sacewicz, T.; Cieśliński, I.; Jarocka, M. The effect of low level laser irradiation on oxidative stress, muscle damage and function following neuromuscular electrical stimulation. A double blind, randomised, crossover trial. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2019, 11, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leeder, J.D.C.; Godfrey, M.; Gibbon, D.; Gaze, D.; Davison, G.W.; Van Someren, K.A.; Howatson, G. Cold water immersion improves recovery of sprint speed following a simulated tournament. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2019, 19, 1166–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, N.; Hieda, M.; Ramey, L.; Levine, B.D.; Guilliod, R. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Sports Musculoskeletal Injuries. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2020, 52, 1420–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Chou, W.Y.; Ko, J.Y.; Lee, M.S.; Wu, R.W. Early Recovery of Exercise-Related Muscular Injury by HBOT. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 6289380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germain, G.; Delaney, J.; Moore, G.; Lee, P.; Lacroix, V.; Montgomery, D. Effect of hyperbaric oxygen therapy on exercise-induced muscle soreness. Undersea Hyperb. Med. 2003, 30, 135–145. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, A.L.; Syrotuik, D.G.; Bell, G.J.; Jones, R.L.; Hanstock, C.C. Effects of hyperbaric oxygen on recovery from exercise-induced muscle damage in humans. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2002, 12, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godman, C.A.; Joshi, R.; Giardina, C.; Perdrizet, G.; Hightower, L.E. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment induces antioxidant gene expression. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1197, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, R.A.; Blackmon, J.R.; Jones, J.W.; Strait, G. Exercising testing in adult normal subjects and cardiac patients. 1963. Ann. Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2004, 9, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimoda, M.; Enomoto, M.; Horie, M.; Miyakawa, S.; Yagishita, K. Effects of hyperbaric oxygen on muscle fatigue after maximal intermittent plantar flexion exercise. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2015, 29, 1648–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, M.H.; Hashimoto, T.; Daoud, G.A.; Kakita, H.; Kato, S.; Goto, T.; Hibi, M.; Kato, T.; Okumura, N.; Tomishige, H.; et al. Oxidative stress after living related liver transplantation subsides with time in pediatric patients. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2011, 27, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furman, D.; Campisi, J.; Verdin, E.; Carrera-Bastos, P.; Targ, S.; Franceschi, C.; Ferrucci, L.; Gilroy, D.W.; Fasano, A.; Miller, G.W.; et al. Chronic inflammation in the etiology of disease across the life span. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1822–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boukhris, O.; Trabelsi, K.; Abdessalem, R.; Hsouna, H.; Ammar, A.; Glenn, J.M.; Bott, N.; Irandoust, K.; Taheri, M.; Turki, M.; et al. Effects of the 5-m Shuttle Run Test on Markers of Muscle Damage, Inflammation, and Fatigue in Healthy Male Athletes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupuy, O.; Douzi, W.; Theurot, D.; Bosquet, L.; Dugué, B. An Evidence-Based Approach for Choosing Post-exercise Recovery Techniques to Reduce Markers of Muscle Damage, Soreness, Fatigue, and Inflammation: A Systematic Review With Meta-Analysis. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, N.; Kojima, C.; Sumi, D.; Ikutomo, A.; Goto, K. Inflammatory, Oxidative Stress, and Angiogenic Growth Factor Responses to Repeated-Sprint Exercise in Hypoxia. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelzer, I.; Kröpfl, J.M.; Fuchs, R.; Pekovits, K.; Mangge, H.; Raggam, R.B.; Gruber, H.J.; Prüller, F.; Hofmann, P.; Truschnig-Wilders, M.; et al. Ultra-endurance exercise induces stress and inflammation and affects circulating hematopoietic progenitor cell function. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2015, 25, e442–e450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, A. Using recovery modalities between training sessions in elite athletes: Does it help? Sports Med. 2006, 36, 781–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugita, M.; Kapoor, M.P.; Nishimura, A.; Okubo, T. Influence of green tea catechins on oxidative stress metabolites at rest and during exercise in healthy humans. Nutrition 2016, 32, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martarelli, D.; Pompei, P. Oxidative stress and antioxidant changes during a 24-hours mountain bike endurance exercise in master athletes. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fitness 2009, 49, 122–127. [Google Scholar]
- Aoki, K.; Nakao, A.; Adachi, T.; Matsui, Y.; Miyakawa, S. Pilot study: Effects of drinking hydrogen-rich water on muscle fatigue caused by acute exercise in elite athletes. Med. Gas. Res. 2012, 2, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, S.K.; Radak, Z.; Ji, L.L. Exercise-induced oxidative stress: Past, present and future. J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 5081–5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American College of Sports Medicine. ACSM’s Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription, 7th ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bachi, A.L.; Sierra, A.P.; Rios, F.J.; Gonçalves, D.A.; Ghorayeb, N.; Abud, R.L.; Victorino, A.B.; Dos Santos, J.M.; Kiss, M.A.; Pithon-Curi, T.C.; et al. Athletes with higher VO2max present reduced oxLDL after a marathon race. BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2015, 1, 000014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumi, D.; Kojima, C.; Goto, K. Impact of Endurance Exercise in Hypoxia on Muscle Damage, Inflammatory and Performance Responses. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2018, 32, 1053–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervaens Costa Maia, M.; Camacho, O.F.; Pinto Marques, A.F.; Barata de Silva Coelho, P.M. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy treatment for the recovery of muscle injury induced in rats. Diving Hyperb. Med. 2013, 43, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Branco, B.H.; Fukuda, D.H.; Andreato, L.V.; Santos, J.F.; Esteves, J.V.; Franchini, E. The Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on Post-Training Recovery in Jiu-Jitsu Athletes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, B.C.; Robinson, D.; Davison, B.J.; Foley, B.; Seda, E.; Byrnes, W.C. Treatment of exercise-induced muscle injury via hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2001, 33, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable/Group | NN (n = 6) | HNN (n = 6) | HHH (n = 6) | p Value & |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 23.67 ± 3.44 | 21.67 ± 2.34 | 23.00 ± 2.76 | 0.490 |
| Height (cm) | 174.33 ± 2.89 | 173.87 ± 4.30 | 176.92 ± 5.55 | 0.450 |
| Weight (kg) | 75.63 ± 4.80 | 72.95 ± 5.23 | 74.43 ± 6.03 | 0.694 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.88 ± 1.53 | 24.12 ± 1.29 | 23.75 ± 0.68 | 0.290 |
| Body fat (%) | 22.28 ± 7.35 | 21.20 ± 5.23 | 20.97 ± 3.08 | 0.907 |
| HRrest (beats/min) | 73.33 ± 8.82 | 70.33 ± 10.75 | 66.00 ± 6.87 | 0.385 |
| HRmax (beats/min) | 196.33 ± 3.44 | 198.33 ± 2.34 | 197.00 ± 2.76 | 0.490 |
| VO2max (mL/kg/min) | 47.17 ± 2.30 | 49.15 ± 2.82 | 48.29 ± 0.87 | 0.308 |
| Fibrinogen (mg/dL) | 230.00 ± 24.92 | 231.67 ± 33.68 | 221.83 ± 39.63 | 0.862 |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 909.17 ± 136.62 | 924.47 ± 125.85 | 912.83 ± 48.01 | 0.969 |
| TNF-α (pg/mL) | 938.80 ± 8.52 | 975.46 ± 34.59 | 971.19 ± 51.42 | 0.192 |
| d-ROMs (CARR.U) | 289.67 ± 34.07 | 267.83 ± 44.21 | 274.67 ± 50.54 | 0.680 |
| BAP (μmol/L) | 2726.67 ± 220.81 | 2583.67 ± 329.77 | 2632.50 ± 186.14 | 0.619 |
| CK (U/L) | 205.85 ± 44.02 | 221.58 ± 38.27 | 218.50 ± 64.36 | 0.849 |
| LDH (U/L) | 312.83 ± 42.98 | 335.67 ± 45.91 | 291.50 ± 39.67 | 0.237 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Woo, J.; Min, J.-H.; Lee, Y.-H.; Roh, H.-T. Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on Inflammation, Oxidative/Antioxidant Balance, and Muscle Damage after Acute Exercise in Normobaric, Normoxic and Hypobaric, Hypoxic Environments: A Pilot Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7377. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17207377
Woo J, Min J-H, Lee Y-H, Roh H-T. Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on Inflammation, Oxidative/Antioxidant Balance, and Muscle Damage after Acute Exercise in Normobaric, Normoxic and Hypobaric, Hypoxic Environments: A Pilot Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(20):7377. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17207377
Chicago/Turabian StyleWoo, Jinhee, Jae-Hee Min, Yul-Hyo Lee, and Hee-Tae Roh. 2020. "Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on Inflammation, Oxidative/Antioxidant Balance, and Muscle Damage after Acute Exercise in Normobaric, Normoxic and Hypobaric, Hypoxic Environments: A Pilot Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 20: 7377. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17207377
APA StyleWoo, J., Min, J.-H., Lee, Y.-H., & Roh, H.-T. (2020). Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on Inflammation, Oxidative/Antioxidant Balance, and Muscle Damage after Acute Exercise in Normobaric, Normoxic and Hypobaric, Hypoxic Environments: A Pilot Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(20), 7377. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17207377





