A Multicenter, Prospective, Observational, Open-Label Study of the Safety and Comfort of Gensulin® Delivery Device Use in a Large Cohort of Adult and Elderly Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
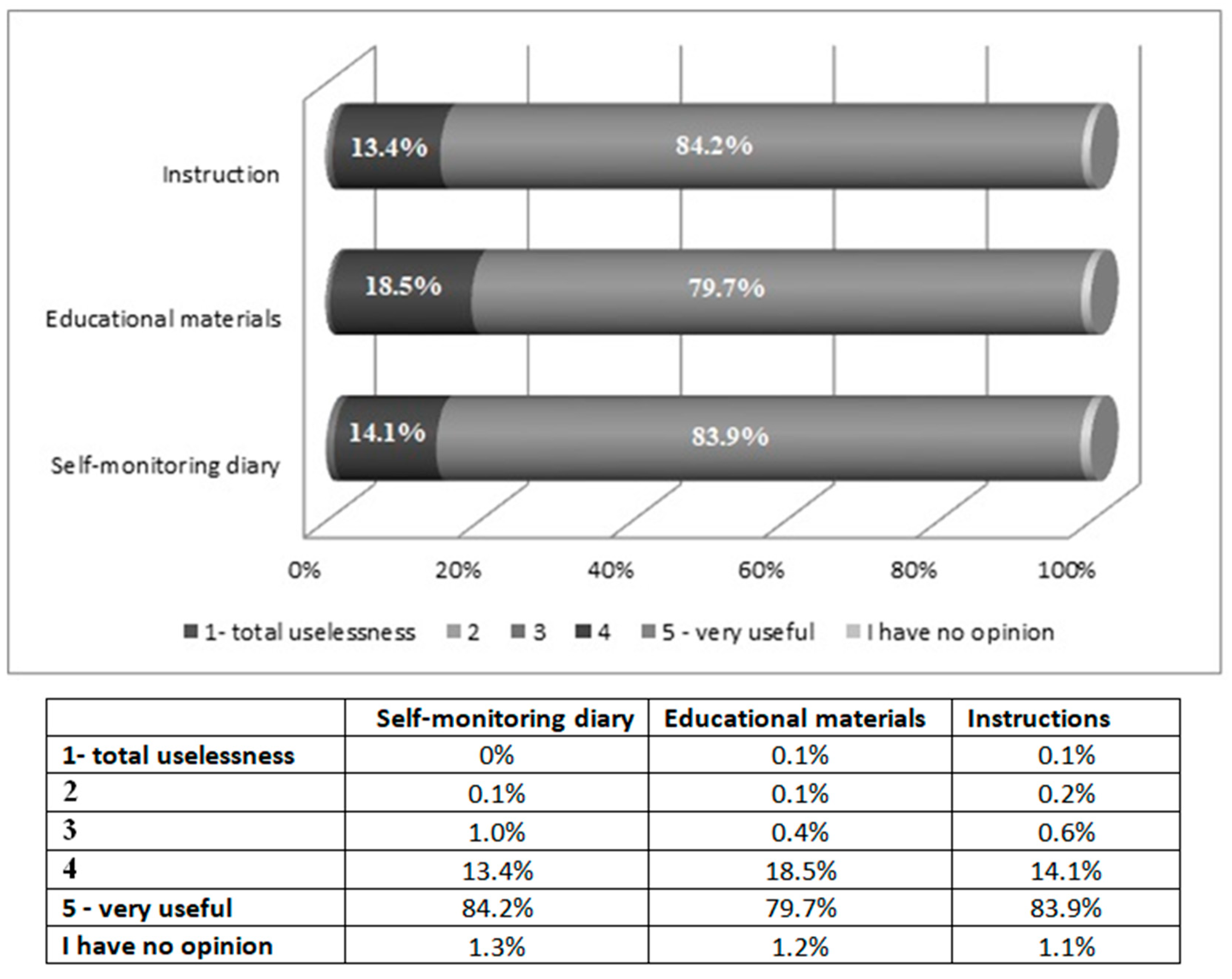
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 9th ed.; IDF: Brussels, Belgium, 2019; Available online: https://www.diabetesatlas.org (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Turner, R.C.; Cull, C.A.; Frighi, V.; Holman, R.R. Glycemic control with diet, sulfonylurea, metformin, or insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Progressive requirement for multiple therapies (UKPDS 49). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. JAMA 1999, 281, 2005–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, S.; Yudkin, J.S.; Kehlenbrink, S.; Davies, J.I.; Wild, S.H.; Lipska, K.J.; Sussman, J.B.; Beran, D. Estimation of global insulin use for type 2 diabetes, 2018–2030: A microsimulation analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rex, J.; Jensen, K.H.; Lawton, S.A. A review of 20 years’ experience with the NovoPen family of insulin injection devices. Clin. Drug Investig. 2006, 26, 367–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perfetti, R. Reusable and disposable insulin pens for the treatment of diabetes: Understanding the global differences in user preference and an evaluation of inpatient insulin pen use. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2010, 12 (Suppl. 1), S79–S85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, K.H.; Szeinbach, S.L.; Lenox, S.M. Preference for insulin delivery systems among current insulin users and nonusers. Clin. Ther. 2004, 26, 1498–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fendler, W.; Roman-Liu, D.; Tokarski, T.; Romanczuk, R.; Mlynarski, W. Trigger matters: An ergonomy analysis of insulin pens. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2015, 17, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papanas, N.; Maltezos, E. The diabetic hand: A forgotten complication? J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2010, 24, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Definition of an Older or Elderly Person. Available online: http://www.who.int/healthinfo/survey/ageingdefnolder/en/ (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- IDF ATLAS, FACT and Figures about Diabetes. Available online: https://www.idf.org/aboutdiabetes/what-is-diabetes/facts-figures.html (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Cho, N.H.; Shaw, J.E.; Karuranga, S.; Huang, Y.; da Rocha Fernandes, J.D.; Ohlrogge, A.W.; Malanda, B. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 138, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohannon, N.J.; Ohannesian, J.P.; Burdan, A.L.; Holcombe, J.H.; Zagar, A. Patient and physician satisfaction with the Humulin/Humalog Pen, a new 3.0-mL prefilled pen device for insulin delivery. Clin. Ther. 2000, 22, 1049–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancu, N.; Czupryniak, L.; Genestin, E.; Sourij, H. A Pan-European and Canadian prospective survey to evaluate patient satisfaction with the SoloSTAR insulin injection device in type 1 and type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2011, 5, 1224–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adolfsson, P.; Veijola, R.; Huot, C.; Hansen, H.D.; Lademann, J.B.; Phillip, M. Safety and patient perception of an insulin pen with simple memory function for children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes--the REMIND study. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2012, 28, 1455–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marathe, P.H.; Gao, H.X.; Close, K.L. American Diabetes Association Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes 2017. J. Diabetes 2017, 9, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. BMJ (Clin. Res. Ed.) 2007, 335, 806–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AADE position statement. Individualization of diabetes self-management education. Diabetes Educ. 2007, 33, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhafiz, A.H.; Rodriguez-Manas, L.; Morley, J.E.; Sinclair, A.J. Hypoglycemia in older people—A less well recognized risk factor for frailty. Aging Dis. 2015, 6, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, J. Management of hypoglycemia in older adults with type 2 diabetes. Postgrad. Med. 2019, 131, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ligthelm, R.J.; Borzi, V.; Gumprecht, J.; Kawamori, R.; Wenying, Y.; Valensi, P. Importance of observational studies in clinical practice. Clin. Ther. 2007, 29, 1284–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahay, B.K.; Seshiah, V. Importance of observational studies in understanding regional clinical practice: Rationale and design of the A1chieve study. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2013, 61, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

| Complaint | Number of Patients n = 258 (2.5%) |
|---|---|
| The insulin injection was too fast or too slow | 2.3% |
| The set dose was higher than intended | 0.7% |
| The wrong dose was delivered | 2.1% |
| The patient did not know the insulin injection technique | 44% |
| Difficult to operate | 0.04% |
| Pen got stuck | 0.04% |
| Needles were getting broken | 0.16% |
| Too heavy | 0.08% |
| Too small | 0.04% |
| Too lose in setting the dose | 0.08% |
| Leaky case | 0.19% |
| The number on the scale too small to read | 0.08% |
| Numbers on the scale clashed | 2.8% |
| Broken case | 0.4% |
| Broken spring | 0.2% |
| Problems with correcting the dose | 0.2% |
| Cartridge too small | 0.04% |
| Left marks on the skin | 0.04% |
| The sheath did not open properly | 0.04% |
| Question Rate | Very Good | Good | Sufficient | Poor | Very Poor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Setting and correcting the dose | 87.8% | 10.0% | 1.7% | 0.3% | 0.2% |
| Information confirming that the dose was administrated successfully | 92.0% | 4.7% | 1.3% | 0.6% | 1.4% |
| Trigger location | 80.9% | 11.6% | 2.2% | 2.0% | 3.3% |
| Force needed to insulin administration | 75.0% | 17.2% | 3.1% | 2.1% | 2.6% |
| Question Rate | Better | The Same | Worse |
|---|---|---|---|
| Setting and correcting the dose | 34.1% | 56.5% | 9.4% |
| Information confirming that the dose was administrated correctly | 79.8% | 12.7% | 7.5% |
| Trigger location | 26.3% | 27.2% | 46.5% |
| Force needed to insulin administration | 50.0% | 32.7% | 17.3% |
| Adverse Event | Number of Patients n = 65 (0.6%) |
|---|---|
| Headache | 3.2% |
| Tremor | 17.7% |
| Difficulty breathing | 4.8% |
| Tingle of hands and feet | 4.8% |
| Weakness | 9.7% |
| Swelling | 1.6% |
| Sweating | 14.5% |
| Somnolence | 1.6% |
| High blood pressure | 1.6% |
| Feeling bad | 4.8% |
| Dizziness | 8.1% |
| Fingernails changed color | 1.6% |
| Palpitation | 1.6% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Masierek, M.; Nabrdalik, K.; Kwiendacz, H.; Sawczyn, T.; Gumprecht, J. A Multicenter, Prospective, Observational, Open-Label Study of the Safety and Comfort of Gensulin® Delivery Device Use in a Large Cohort of Adult and Elderly Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7587. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17207587
Masierek M, Nabrdalik K, Kwiendacz H, Sawczyn T, Gumprecht J. A Multicenter, Prospective, Observational, Open-Label Study of the Safety and Comfort of Gensulin® Delivery Device Use in a Large Cohort of Adult and Elderly Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(20):7587. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17207587
Chicago/Turabian StyleMasierek, Małgorzata, Katarzyna Nabrdalik, Hanna Kwiendacz, Tomasz Sawczyn, and Janusz Gumprecht. 2020. "A Multicenter, Prospective, Observational, Open-Label Study of the Safety and Comfort of Gensulin® Delivery Device Use in a Large Cohort of Adult and Elderly Patients with Type 2 Diabetes" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 20: 7587. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17207587
APA StyleMasierek, M., Nabrdalik, K., Kwiendacz, H., Sawczyn, T., & Gumprecht, J. (2020). A Multicenter, Prospective, Observational, Open-Label Study of the Safety and Comfort of Gensulin® Delivery Device Use in a Large Cohort of Adult and Elderly Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(20), 7587. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17207587





