The Effects of Resistance Training on Blood Pressure in Preadolescents and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources and Searches
2.2. Eligibility and Study Selection
2.3. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
2.4. Risk of Bias of Individual Studies
2.5. Data Synthesis and Satistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Literature Search and Article Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Risk of Bias Individual Studies
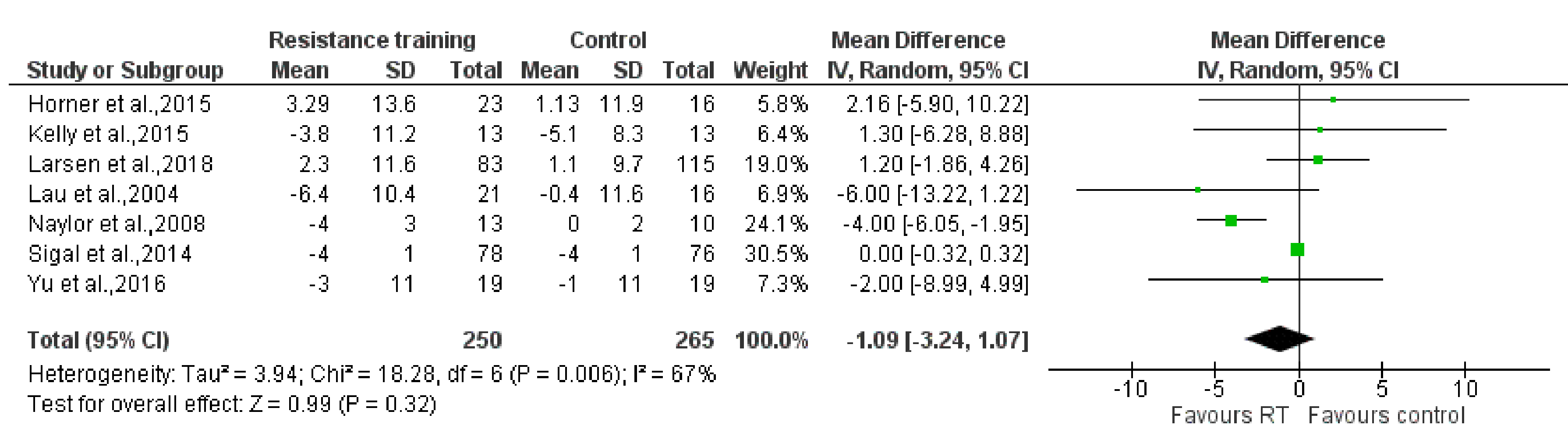
3.4. Principle Findings
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hajjar, I.; Kotchen, T.A. Trends in Prevalence, Awareness, in the United States, 1988–2000. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2003, 290, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lande, M.B.; Kupferman, J.C. Pediatric hypertension: The Year in Review. Clin. Pediatr. (Phila) 2014, 39, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornelissen, V.; Smart, N.A. Exercise Training for Blood Pressure: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chulvi, I.; Sanchis, J.; Tortosa, J.; Cortell, J.M. Exercise for hypertension. Fit. Med. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barlow, S.E. Expert committee recommendations regarding the prevention, assessment, and treatment of child and adolescent overweight and obesity: Summary report. Pediatrics 2007, 120 (Suppl. 4). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taylor-Zapata, P.; Baker-Smith, C.M.; Burckart, G.; Daniels, S.R.; Flynn, J.T.; Giacoia, G.; Green, D.; Kelly, A.S.; Khurana, M.; Li, J.S.; et al. Research gaps in primary pediatric hypertension. Pediatrics 2019, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, D.J. Pediatric hypertension: Review of updated guidelines. Pediatr. Rev. 2019, 40, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raitakari, O.; Juonala, M.; Nnemaa, T.R.; Kerblom, H.; Viikari, J. Cardiovascular risk factors in childhood as predictors of carotid artery intima-media thickness in adulthood. Atheroscler. Suppl. 2003, 4, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurray, R.G.; Ondrak, K.S. Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Children: The Importance of Physical Activity. Am. J. Lifestyle Med. 2013, 7, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkner, B.; Daniels, S.R. Summary of the fourth report on the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. Pediatrics 2004, 44, 387–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y. Tracking of Blood Pressure from Childhood to Adulthood A Systematic Review and Meta—Regression Analysis. Circulation 2008, 3171–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Law, C.M.; Shiell, A.W.; Newsome, C.A.; Syddall, H.E.; Shinebourne, E.A.; Fayers, P.M.; Martyn, C.N.; De Swiet, M. Fetal, infant, and childhood growth and adult blood pressure: A longitudinal study from birth to 22 years of age. Circulation 2002, 105, 1088–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Juonala, M.; Magnussen, C.G.; Berenson, G.S.; Venn, A.; Burns, T.L.; Sabin, M.A.; Srinivasan, S.R.; Daniels, S.R.; Davis, P.H.; Chen, W.; et al. Childhood adiposity, adult adiposity, and cardiovascular risk factors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 1876–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williams, B.; Mancia, G.; Spiering, W.; Rosei, E.A.; Azizi, M.; Burnier, M.; Clement, D.; Coca, A.; De Simone, G.; Dominiczak, A.; et al. 2018 practice guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension of the European society of cardiology and the European society of hypertension ESC/ESH task force for the management of arterial hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2018, 36, 2284–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arnett, D.K.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Albert, M.A.; Buroker, A.B.; Goldberger, Z.D.; Hahn, E.J.; Himmelfarb, C.D.; Khera, A.; Lloyd-Jones, D.; McEvoy, J.W.; et al. 2019 ACC/AHA Guideline on the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2019, 140, e596–e646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stricker, P.R.; Faigenbaum, A.D.; McCambridge, T.M. Resistance training for children and adolescents. Pediatrics 2020, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faigenbaum, A.D.; Lloyd, R.S.; Myer, G.D. Youth resistance training: Past practices, new perspectives, and future directions. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 2013, 25, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Myer, G.; Faigenbaum, A.; Chu, D.; Falkel, J.; Ford, K.; Best, T.; Hewett, T. Integrative Training for Children and Adolescents: Techniques and Practices for Reducing Sports-Related Injuries and Enhancing Athletic Performance. Phys. Sportsmed. 2011, 39, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, R.S.; Faigenbaum, A.D.; Stone, M.H.; Oliver, J.L.; Jeffreys, I.; Moody, J.A.; Brewer, C.; Pierce, K.C.; McCambridge, T.M.; Howard, R.; et al. Position statement on youth resistance training: The 2014 International Consensus. Br. J. Sports Med. 2014, 48, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hind, K.; Burrows, M. Weight-bearing exercise and bone mineral accrual in children and adolescents: A review of controlled trials. Bone 2007, 40, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardoni, B.; Thein-Nissenbaum, J.; Fast, J.; Day, M.; Li, Q.; Wang, S.; Scerpella, T. A school-based resistance intervention improves skeletal growth in adolescent females. Osteoporos. Int. 2014, 25, 1025–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishikawa, S.; Kim, Y.; Kang, M.; Morgan, D.W. Effects of weight-bearing exercise on bone health in girls: A meta-analysis. Sport. Med. 2013, 43, 875–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauersen, J.B.; Andersen, T.E.; Andersen, L.B. Strength training as superior, dose-dependent and safe prevention of acute and overuse sports injuries: A systematic review, qualitative analysis and meta-analysis. Br. J. Sports Med. 2018, 52, 1557–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collins, H.; Booth, J.N.; Duncan, A.; Fawkner, S.; Niven, A. The Effect of Resistance Training Interventions on ‘The Self’ in Youth: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Sport. Med. Open 2019, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thomas, J.; Chandler, J.; Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2009, 62, e1–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farinatti, P.; Neto, M.; Dias, I.; Cunha, F.A.; Bouskela, E.; Kraemer-Aguiar, L.G. Short-Term Resistance Training Attenuates Cardiac Autonomic Dysfunction in Obese Adolescents. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 2016, 28, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horner, K.; Barinas-Mitchell, E.; DeGroff, C.; Kuk, J.L.; Drant, S.; Lee, S. Effect of Aerobic versus Resistance Exercise on Pulse Wave Velocity, Intima Media Thickness and Left Ventricular Mass in Obese Adolescents. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 2015, 27, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, L.A.; Loza, A.; Lin, X.; Schroeder, E.T.; Hughes, A.; Kirk, A.; Knowles, A.-M. The effect of a home-based strength training program on type 2 diabetes risk in obese Latino boys. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 28, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Larsen, M.N.; Nielsen, C.M.; Madsen, M.; Manniche, V.; Hansen, L.; Bangsbo, J.; Krustrup, P.; Hansen, P.R. Cardiovascular adaptations after 10 months of intense school-based physical training for 8- to 10-year-old children. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2018, 28, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, P.W.C.; Yu, C.W.; Lee, A.; Sung, R.Y.T. The physiological and psychological effects of resistance training on Chinese obese adolescents. J. Exerc. Sci. Fit. 2004, 2, 115–120. [Google Scholar]
- Naylor, L.H.; Watts, K.; Sharpe, J.A.; Jones, T.W.; Davis, E.A.N.N.; Thompson, A.; George, K.; Ramsay, J.M.; Driscoll, G.O.; Green, D.J. Resistance Training and Diastolic Myocardial Tissue Velocities in Obese Children. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2008, 2027–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigal, R.J.; Alberga, A.S.; Goldfield, G.S.; Prud’homme, D.; Hadjiyannakis, S.; Gougeon, R.; Phillips, P.; Tulloch, H.; Malcolm, J.; Doucette, S.; et al. Effects of aerobic training, resistance training, or both on percentage body fat and cardiometabolic risk markers in obese adolescents: The healthy eating aerobic and resistance training in youth randomized clinical trial. JAMA Pediatr. 2014, 168, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.C.-W.; McManus, A.M.; So, H.-K.; Chook, P.; Au, C.-T.; Li, A.M.; Kam, J.T.-C.; So, R.C.-H.; Lam, C.W.-K.; Chan, I.H.-S.; et al. Effects of resistance training on cardiovascular health in non-obese active adolescents. World J. Clin. Pediatr. 2016, 5, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Vizcaíno, V.; Pozuelo-Carrascosa, D.P.; García-Prieto, J.C.; Cavero-Redondo, I.; Solera-Martínez, M.; Garrido-Miguel, M.; Díez-Fernández, A.; Ruiz-Hermosa, A.; Sánchez-López, M. Effectiveness of a school-based physical activity intervention on adiposity, fitness and blood pressure: MOVI-KIDS study. Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozuelo-Carrascosa, D.P.; Cavero-Redondo, I.; Herraiz-Adillo, A.; Diez-Fernandez, A.; Sanchez-Lopez, M.; Martinez-Vizcaino, V. School-based exercise programs and cardiometabolic risk factors: A meta-analysis. Pediatrics 2018, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Westcott, W.L. Resistance training is medicine: Effects of strength training on health. Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 2012, 11, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Hermoso, A.; Ramírez-Campillo, R.; Izquierdo, M. Is Muscular Fitness Associated with Future Health Benefits in Children and Adolescents? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Longitudinal Studies. Sport. Med. 2019, 49, 1079–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behringer, M.; Vom Heede, A.; Yue, Z.; Mester, J. Effects of resistance training in children and adolescents: A meta-analysis. Pediatrics 2010, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lesinski, M.; Prieske, O.; Granacher, U. Effects and dose-response relationships of resistance training on physical performance in youth athletes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Sports Med. 2016, 50, 781–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harries, S.K.; Lubans, D.R.; Callister, R. Resistance training to improve power and sports performance in adolescent athletes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2012, 15, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faigenbaum, A.D.; Kraemer-Aguiar, L.G.; Blimkie, C.J.R.; Jeffreys, I.; Micheli, L.J.; Nitka, M.; Rowland, T.W. Youth Resistance Training: Updated Position Statement Paper From the National Strength and Conditioning Association. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2009, 23, 60–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, F.B.; Ruiz, J.R.; Castillo, M.J.; Sjöström, M. Physical fitness in childhood and adolescence: A powerful marker of health. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grontved, A.; Ried-Larsen, M.; Moller, N.C.; Kristensen, P.L.; Froberg, K.; Brage, S.; Andersen, L.B. Muscle strength in youth and cardiovascular risk in young adulthood (the European Youth Heart Study). Br. J. Sports Med. 2015, 49, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cohen, D.D.; Gómez-Arbeláez, D.; Camacho, P.A.; Pinzon, S.; Hormiga, C.; Trejos-Suarez, J.; Duperly, J.; Lopez-Jaramillo, P. Low muscle strength is associated with metabolic risk factors in Colombian children: The ACFIES study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkholy, U.M.; Ahmed, I.A.; Karam, N.A.; Ali, Y.F.; Yosry, A. Assessment of left ventricular mass index could predict metabolic syndrome in obese children. J. Saudi Hear. Assoc. 2016, 28, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Korkmaz, O.; Gursu, H.A.; Karagun, B.S. Comparison of echocardiographic findings with laboratory parameters in obese children. Cardiol. Young 2016, 26, 1060–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, K.; Jones, T.W.; Davis, E.A.; Green, D. Exercise training in obese children and adolescents: Current concepts. Sport. Med. 2005, 35, 375–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, M.A.; Gutin, B.; Owens, S.; Barbeau, P.; Tracy, R.P.; Litaker, M. Effects of physical training and its cessation on the hemostatic system of obese children. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 69, 1130–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watts, K.; Beye, P.; Siafarikas, A.; O’Driscoll, G.; Jones, T.W.; Davis, E.A.; Green, D.J. Effects of exercise training on vascular function in obese children. J. Pediatr. 2004, 144, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cote, A.T.; Harris, K.C.; Panagiotopoulos, C.; Sandor, G.G.S.; Devlin, A.M. Childhood Obesity and Cardiovascular Dysfunction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loaiza-Betancur, A.F.; Pérez Bedoya, E.; Montoya Dávila, J.; Chulvi-Medrano, I. Effect of Isometric Resistance Training on Blood Pressure Values in a Group of Normotensive Participants: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Sports Health 2020, 12, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loaiza-Betancur, A.F.; Chulvi-Medrano, I. Is Low-Intensity Isometric Handgrip Exercise an Efficient Alternative in Lifestyle Blood Pressure Management? A Systematic Review. Sports Health 2020, 12, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Source | Population | Intervention Description | BP Assessment Method | Frequency (D/WK) | Intensity | Volume (Sets × REPS) | Study Length (WKS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Farinatti et al., 2016 [27] | Enrolled: N = 44 Completers: N = 44 44 F; Age: 13–17 Resistance group: N = 24. Obese | RT = chest and leg press, low row, leg extension, upper back, leg and arm curls, leg abduction/adduction, triceps ext. | Semi-automatic sphyngomanometer | 3 | 1–2 Wks: 50–70% 10 RM 3–6 Wks: 60–80% 10 RM 7–12 Wks: 70–85% 10 RM | 1 × 15 2 × 8–12 3 × 6–10 | 12 |
| Control group: N = 20. Non-obese | |||||||
| Horner et al., 2015 [28] | Enrolled N = 81; Completers N = 66 41 M; 40 F; Age: 12–18 Resistance group: N = 27; 14 M 13 F; Age: 14.6 (1.9) | RT = Body exercises | automated sphygmomanometer | 3 | Not report | 2 × 12 | 12 |
| Control group: 24 N = 24; 12 M 12 F; Age: 14.9 (1.8) | |||||||
| Kelly et al., 2015 [29] | Enrolled N = 26; Completers N = 26 26 M; Age = 14–18 Obese Resistance group: N = 13; Age: 15.4 (0.9) | RT = day 1 consisted of compound lower body exercises and isolated upper body exercises and day 2 included com- pound upper body exercises and isolated lower body exercises. | Not report | 2 | 1–4 Wks: light to moderate intensity 5–10 Wks: mod to high intensity) 11–16 Wks: mod to high intensity | 1 × 10–15 2–3 × 13–15 3–4 × 8–12 | 16 |
| Control group: N = 13; Age: 15.6 (0.96) | |||||||
| Larsen et al., 2018 [30] | Enrolled N = 83; Completers N = 83 Age = 8–10 Resistance group: N = 83 | CST = Plyometric and dynamic strength exercises using upper and lower body. | automated sphygmomanometer | 3 | Not report | 30-s all-out exercise periods with 45-s rest periods with 6–10 stations | 40 |
| Control group: N = 115 | |||||||
| Lau et al., 2004 [31] | Enrolled N = 36; Completers N = 36 24 M; 12 F; Age = 10–17 Obese. Resistance group: N = 21 | RT = Lat pull-down, shoulder press, leg press, leg extension, leg curl, heel raise, biceps curl, triceps extension, push-up. | standard mercury sphyngomanometer | 3 | 75–85% RM | 1 × 5 | 6 |
| Control group: N = 16 | |||||||
| Naylor et al., 2008 [32] | Enrolled N = 23; Completers N = 23 11 M; 12 F; Age = 12–14 Obese. Resistance group: N = 13; 7 M; 6 F Age: 12.2 (0.4) | RT = weight-stack machines. | Not report | 3 | 75–90% RM | 2 × 8 | 8 |
| Control group: N = 10; 4 M; 6 F; Age: 13.6 (0.4) | |||||||
| Sigal et al., 2014 [33] | Enrolled N = 304; Completers N = 229 91 M; 213 F; Age = 14–18 Obese Resistance group: N = 78; 23 M; 55 F; Age: 15.9 (1.5) | RT = weight machines | Not report | 4 | 65–85% RM | 2 × 15 | 24 |
| Control group: N = 76; 24 M; 52 F; Age: 15.6 (1.3) | |||||||
| Yu et al., 2016 [34] | Enrolled N = 38; Completers N = 38 25 M; 13 F; Age = 11–13 Non-obese. Resistance group: N = 19; Age: 12.3 (0.42) | RT = Elbow extension, elbow flexion, trunk extension, trunk flexion, shoulder press, knee extension, knee flexion, push-up, squats, incline dip and hip abd | standard sphygmomanometer | 2 | 12 RM | 3 × 12 | 10 |
| Control group: N = 19; Age: 12.1 (0.3) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guillem, C.M.; Loaiza-Betancur, A.F.; Rebullido, T.R.; Faigenbaum, A.D.; Chulvi-Medrano, I. The Effects of Resistance Training on Blood Pressure in Preadolescents and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7900. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17217900
Guillem CM, Loaiza-Betancur AF, Rebullido TR, Faigenbaum AD, Chulvi-Medrano I. The Effects of Resistance Training on Blood Pressure in Preadolescents and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(21):7900. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17217900
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuillem, Carles Miguel, Andrés Felipe Loaiza-Betancur, Tamara Rial Rebullido, Avery D. Faigenbaum, and Iván Chulvi-Medrano. 2020. "The Effects of Resistance Training on Blood Pressure in Preadolescents and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 21: 7900. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17217900
APA StyleGuillem, C. M., Loaiza-Betancur, A. F., Rebullido, T. R., Faigenbaum, A. D., & Chulvi-Medrano, I. (2020). The Effects of Resistance Training on Blood Pressure in Preadolescents and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(21), 7900. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17217900








