Abstract
Haemaphysalis longicornis Neumann, 1901 is a vector of many pathogens of public and veterinary health importance in its native range in East Asia and introduced range in Oceania. In North America, this tick was first detected in New Jersey in 2017. Currently, this tick has been reported from 15 states of the United States. In this study, we modeled the habitat suitability of H. longicornis using the MaxEnt modeling approach. We separated occurrence records from the published literature from four different geographical regions in the world and developed MaxEnt models using relevant environmental variables to describe the potential habitat suitability of this tick in North America. The predictive accuracy of the models was assessed using the U.S. county locations where this tick species has been reported. Our best model predicted that the most suitable North American areas for geographic expansion of H. longicornis are from Arkansas–South Carolina to the south of Quebec–Nova Scotia in the east, and from California to the coast of British Columbia in the west. Enhanced surveillance and further investigation are required to gain a better understanding of the role that this tick might play in the transmission of diseases to humans and animals in North America.
1. Introduction
Haemaphysalis longicornis Neumann, 1901 (Acari, Ixodidae), the Asian longhorned tick, is a three-host, tropical tick whose native range includes Japan, China, eastern Russia, and Korea [1]. It has also become established in Australia, New Zealand, and the western Pacific islands (New Caledonia, Fiji, Western Samoa, Tonga, Vanuatu) [1,2,3]. In East Asia, H. longicornis is the main vector for transmission of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus (SFTSV) in humans [4]. This emerging zoonotic disease caused by a novel bunyavirus was first identified in China in 2009 [5] and then in South Korea and Japan in 2013 [6,7]. Genetically, SFTSV is closely related to the heartland virus (HRTV), which has been isolated in the United States [8,9,10]. In Japan, H. longicornis is also considered a vector of Rickettsia japonica, which causes Japanese spotted fever in humans [11]. In Australia and New Zealand, this tick species is a vector for the protozoan parasite Theileria orientalis Ikeda that causes bovine theileriosis [3,12,13]. Theileriosis can lead to severe and life-threatening anemia in cattle [3]. Haemaphysalis longicornis is also a competent vector for other bovine disease organisms such as Babesia ovata, B. major, and Anaplasma bovis in New Zealand [13], and the DNA of Ehrlichia and Borrelia spp. has been detected in ticks collected from its native range in East Asia [14,15].
In North America, H. longicornis was first detected on a sheep in New Jersey in August 2017 [16]. Retrospective investigations have revealed that this tick has actually been present in the United States since 2010 [17], but it was initially misidentified as the native rabbit tick, Haemaphysalis leporispalustris (Packard, 1869) [18]. Since then, this tick has been reported in 118 counties in 15 states of the United States [19]. So far, there has not been any detection of this tick in Canada [20,21]. To our knowledge, there has not been any human pathogen detected in field-collected H. longicornis in the United States; however, there is a concern that this tick has the potential to transmit endemic pathogens such as Anaplasma, Babesia, and Rickettsia species [20]. The first human bite case by H. longicornis tick in the United States was reported from New York state in 2018 [22]. This tick species has parthenogenetic, bisexual, and aneuploid populations [23]. The parthenogenetic population is capable of asexual reproduction, whereby females can lay eggs without fertilization by the males [21]. In New Jersey, among more than the 1100 ticks collected from the index site, only one male specimen was found, indicating that the invasive population was parthenogenetic [16]. This was supported by a genetic analysis, which indicated H. longicornis ticks in the United States are more similar to those of parthenogenetic populations than those of bisexual populations [24]. The parthenogenetic populations are distributed in Australia, New Zealand, New Caledonia, Fiji, New Hebrides, Tonga, northeastern Russia, northern Japan, Kyushu and Yakushima in southern Japan, and Sichuan and Shanghai in China [1,25,26]. Modeling has indicated areas along the Gulf and Atlantic coast of eastern North America as the potential geographical range of H. longicornis expansion [27]. Other modeling studies have indicated the potential expansion and distribution of this tick species in eastern North America from southern Canada to the Gulf coast, and in a small temperate area on the west coast [28], and the southeastern United States, the Pacific Northwest, and central and southern Mexico [29].
In this study, we used the H. longicornis presence data from Rochlin (2018) [28] augmented with data from Zhang et al. (2019) [30] with MaxEnt [31] to model the habitat suitability of H. longicornis in North America. We separated the H. longicornis presence data into native range and introduced range and then built MaxEnt models for each of them to compare the habitat suitability predictions for North America. The objectives of this study were to (1) separate the global H. longicornis occurrence data for different regions in the world and build competing models using environmental predictors identified by Rochlin (2018) [28], (2) build competing models for different regions using environmental variables from WorldClim [32] and ENVIREM [33], and (3) compare habitat suitability predictions for North America by these competing models and subsequently select the two best models to describe the potential distribution and expansion of H. longicornis in North America. The findings from this study will help develop cost-effective surveillance programs, targeting areas within the predicted range of H. longicornis occurrence under the current environment.
2. Materials and Methods
We used the H. longicornis presence data containing 261 occurrence points from Rochlin (2018) [28] and 146 occurrence points at China’s county-level from Zhang et al. (2019) [30]. The environmental predictors used were bio 1 (annual mean temperature), bio 5 (maximum temperature of the warmest month), and bio 12 (annual precipitation) downloaded from WorldClim (https://www.worldclim.org/) [32] at 2.5 min spatial resolution and Global Ecological Zone (GEZ) (http://www.fao.org/geonetwork/srv/en/main.home#ecology) based on Rochlin (2018) [28]. GEZ was rasterized at the same 2.5 min spatial resolution. The other 12 WorldClim variables and 3 of the ENVIREM [33] variables, i.e., annual potential evapotranspiration (annualPET), Thornthwaite aridity index, and continentality, were also considered at 2.5 min resolution. For North America, 97 occurrence records were obtained by georeferencing the coordinates of the centroids of the counties that have reported the presence of H. longicornis in the United States as of April 2020 [19]. Data preparation was done using ArcGIS® (v 10.6.1) software by ESRI (Toronto, Canada) and R (R Core Team, Vienna, Austria) [34] with the raster [35] and rgdal packages [36].
As the occurrence records were of presence-only data, maximum entropy distribution modeling, or MaxEnt modeling was used to create habitat suitability maps of H. longicornis in North America. Statistical modeling was done by running MaxEnt (New York, U.S.A.) [31] in R [34] within Dismo [37], MIAmaxent [38], and ENMeval [39] packages. The raster stack containing the environmental predictors was separated into four geographic areas of interest: (1) the current range of H. longicornis in both East Asia and Oceania (entire distribution), (2) the native range of H. longicornis in East Asia (East Asia), (3) the introduced range of H. longicornis in Oceania (Oceania), and (4) the parthenogenetic range of H. longicornis in East Asia (native parthenogenetic). The approximate occurrence locations where parthenogenetic populations are reported in the literature [1,25,26] were delineated from the native range and used as the parthenogenetic range data. For each area of interest, the environmental values were extracted at the occurrence locations. Random background points (around 1000) were generated from the area of unsuitable habitat modeled from the “BIOCLIM” algorithm (a classic presence-only climate envelope model) [37] for each region to be used as pseudo-absence points [40], and their corresponding environmental values were extracted. The environmental data for all four areas of interest were compared using box plots. The frequency of observed presence (FOP) plots [38] for the predictors of interest were also analyzed to determine whether the patterns of occurrence specific to the study area were compatible with the ecological knowledge of the H. longicornis (Figure S1).
We used a two-step strategy to predict the habitat suitability of H. longicornis in North America. For the first modeling step, we used the same environmental predictors as Rochlin (2018) [28], i.e., bio 1, bio 5, bio 12, and GEZ, to develop a series of candidate MaxEnt models (Table S1) with a variety of settings. Random 5-fold partitioning of the presence and absence data (80% training, 20% testing) was used to assess each area of interest to find the best model based primarily on the corrected Akaike Information Criteria (AICc) [41,42]. The modeled relationships of the original predictor variables (i.e., the “feature classes” and “regularization multiplier”) for each best MaxEnt model are presented in Table S1. The contribution and permutation importance of the environmental variables of the best models generated for each area of interest were assessed from the MaxEnt output. These models were then projected into North America to identify areas of greatest predicted habitat suitability. The predicted maps of the final models were compared for niche similarity [43], and the predictive accuracy of the models was ranked using the known presence locations in the United States based on both the correlation of the predicted and observed data and the AICc [44]. Further, the H. longicornis habitat suitability in North America was mapped into 5 classes (0–0.2, very low; 0.2–0.4, low; 0.4–0.6, moderate; 0.6–0.8, high; 0.8–1.0, very high) following the classification of Zuliani et al. [44].
For the second modeling step, we used 12 bioclimatic variables from WorldClim Version 2 [32] and 3 variables (i.e., annualPET, Thornthwaite aridity index, and continentality) from ENVIREM [33]. These variables were used to find the best subsets of predictors for MaxEnt modeling using a forward stepwise selection process [38]. Using the subsets of predictors identified, a series of candidate MaxEnt models (Table S2) were developed using the same methodology described for the first modeling step. Then, the two best MaxEnt models from the second step were identified using both correlation and AICc to predict habitat suitability for the H. longicornis in North America.
3. Results
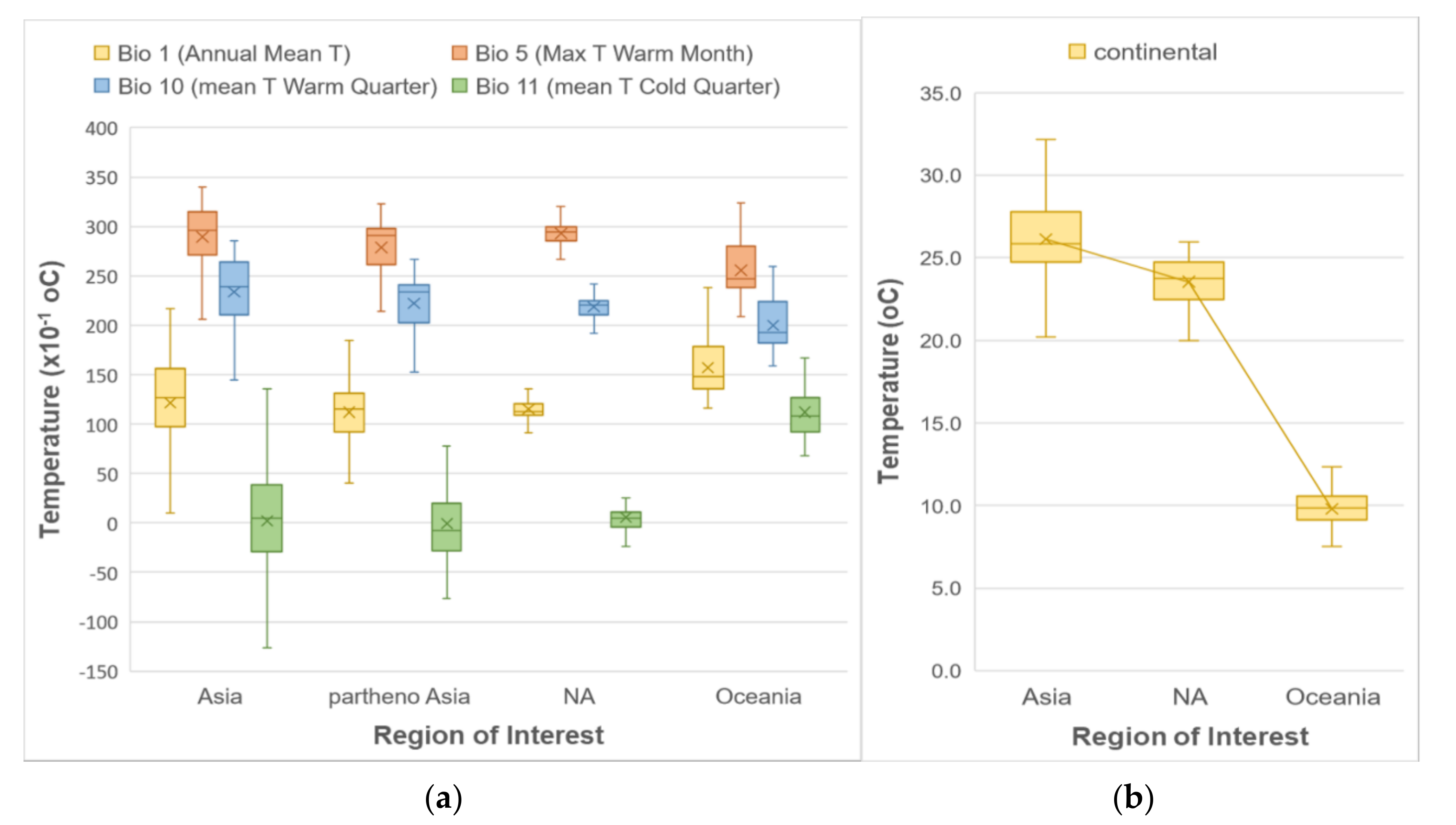
For the first step of our analysis, we looked at whether using all occurrences from the entire known geographic distribution of H. longicornis, occurrences from only its native range, as well as its native parthenogenetic range, or occurrences from only its introduced range would make a difference in determining its habitat suitability prediction in North America as the analysis of the climatic predictors showed some differences and similarities depending on regions of interest (Figure 1). Examination of the boxplots in Figure 1 showed that predictors for the North America region follow a similar temperature pattern as the native and parthenogenetic range in East Asia (both for means—represented by the crosses in box plots—and medians) to a greater extent than the ones from the introduced range in Oceania. Precipitation patterns did not vary much among the different regions, and hence they are not included in this figure.
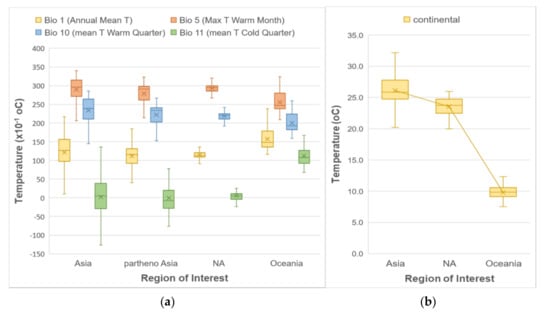
Figure 1.
Boxplots of different temperature predictors, (a) WorldClim and (b) ENVIREM, showing the distribution of their values at the H. longicornis presence locations according to the geographic region.
Four competing MaxEnt models were generated based on the environmental predictors from Rochlin [28]. The relative importance of the environmental predictors on the models generated was assessed using MaxEnt’s permutation importance for each model (Table 1). The best features (linear–quadratic (LQ)) and their corresponding beta-multipliers (rm) were selected (Table S1). The relative importance of the environmental predictors varied depending on the geographic region. For the entire distribution range and East Asia range, the two most important predictors were bio 1 (annual mean temperature) at 77.6% and 41.2%, respectively, followed by GEZ—global ecozones—at 10.3% and 33.6%, respectively. For Oceania, the most important were bio 5 (max temperature of warmest month) at 74.8%, followed by bio 12 (annual precipitation) at 13.7%; for the native parthenogenetic range, it was bio 1 at 51.48%, followed by GEZ at 26.54%.

Table 1.
Permutation importance of the environmental predictors applied by Rochlin (2018) [28] in competitive MaxEnt models, as applied to the geographic areas of interest of H. longicornis occurrences.
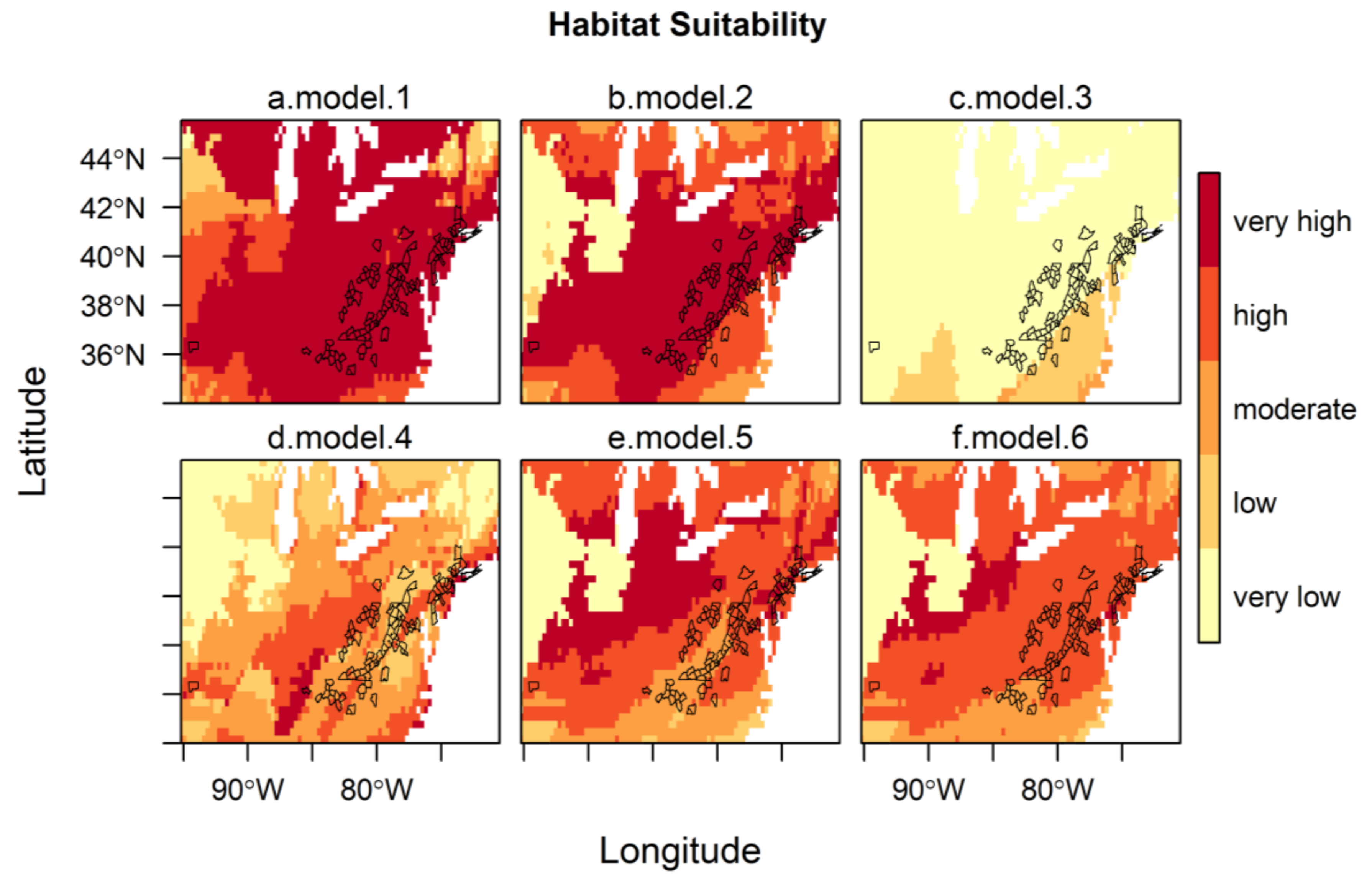
These models were projected onto North America to indicate regions of predicted habitat suitability for H. longicornis, and the predictions were assessed based on AUC, correlation, and AICc, using the known occurrences of H. longicornis in the eastern United States (Table 2). The four corresponding maps of the habitat suitability for the eastern United States, along with the counties with reported H. longicornis occurrences, are shown in Figure 2a–d. The maps show the changes in the level of suitability according to the zone of influence chosen for developing the models, i.e., ranging from very high suitability almost everywhere (model 1) to almost all unsuitable (model 3). All models present good predictability since their AUC values are between 0.83 and 0.97, with a preference for models developed on the entire range and East Asia (AUC > 0.95). However, the model developed on the native zone of occurrences (East Asia) was the best model to predict the habitat suitability of H. longicornis in North America, as shown by both correlation (0.68) and AICc.

Table 2.
AUC, correlation, corrected AIC, delta (Δ) Akaike, and the number of parameters for each model predicting North America’s habitat suitability using the predictors from Rochlin (2018) (models 1–4) and WorldClim and ENVIREM (models 5–6). The two best models are highlighted.
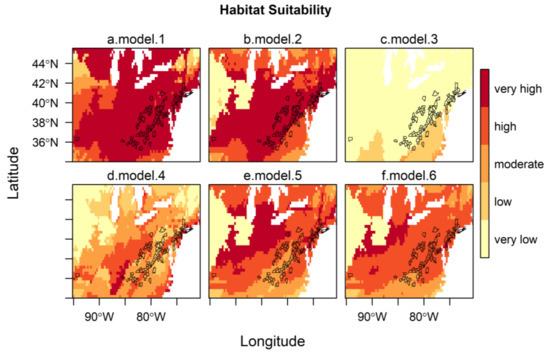
Figure 2.
Habitat suitability of H. longicornis under current climatic and environmental conditions in the eastern United States, with outlines of U.S. counties with reported H. longicornis occurrences [19]. The habitat suitability of all models is represented by 5 classes (0–0.2, very low; 0.2–0.4, low; 0.4–0.6, moderate; 0.6–0.8, high; 0.8–1.0, very high) following the classification of Zuliani et al. [44]. Models with bio 1, bio 5, bio 12, and (Global Ecological Zone) GEZ using H. longicornis occurrence locations from (a) the entire range, (b) the native range, (c) Oceania, (d) parthenogenetic range; and (e) model with bio 1, GEZ, continentality and f. model with bio 10, bio 11, and GEZ using H. longicornis occurrence locations from the native range.
For the second step of our analysis, we looked at whether using different climatic predictors would improve the predictability of MaxEnt modeling for North America. Only the two best models, i.e., the models applied to the East Asia zone (models 5 and 6), are presented in this paper. The results of the predictor selection are presented in Table S2. Table 3 displays the relative importance of the environmental predictors to each model, while Table 2 presents the assessment of the predictability of each model in North America.

Table 3.
Permutation importance of different environmental predictors used for MaxEnt modeling applied to the East Asia zone of H. longicornis occurrences.
For model 5, GEZ was the most important predictor at 45.4%, followed by bio 1 (annual mean temperature) at 27.7% and continentality (the difference between the mean temperature of warmest month and the mean temperature of the coldest month) at 26.8%, showing that bio 1 and continentality had a similar importance to the model. For model 6, bio 11 (mean temperature of coldest quarter) at 46.4% was the most important predictor, followed by GEZ at 43.0% and bio 10 (mean temperature of warmest quarter) at 10.6%. Both models, as shown in Table 2, had good predictability with an AUC greater than 0.95. The best model of the two is model 6, considering both the correlation (0.64) and AICc (2418.7) metrics. Figure 2d–e presents the corresponding two maps of the habitat suitability for the eastern United States, along with the U.S. counties with reported H. longicornis occurrences. It shows that the level of suitability changes according to the model chosen, from high (model 6) to a mixture of moderate and high suitability (model 5). When comparing these two models and the four preceding models from the first modeling step, model 2 was the best model based on both correlation and AICc metrics.
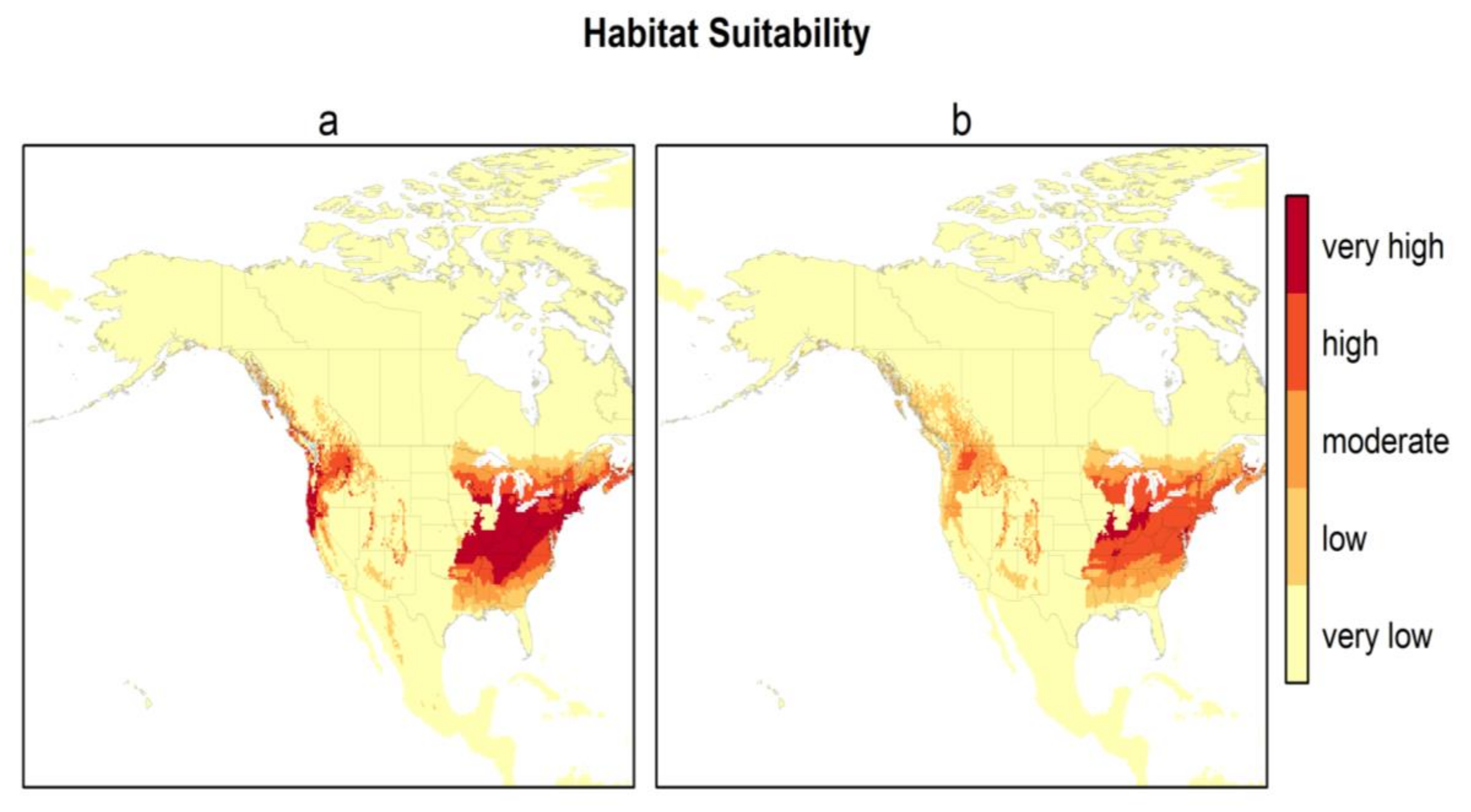
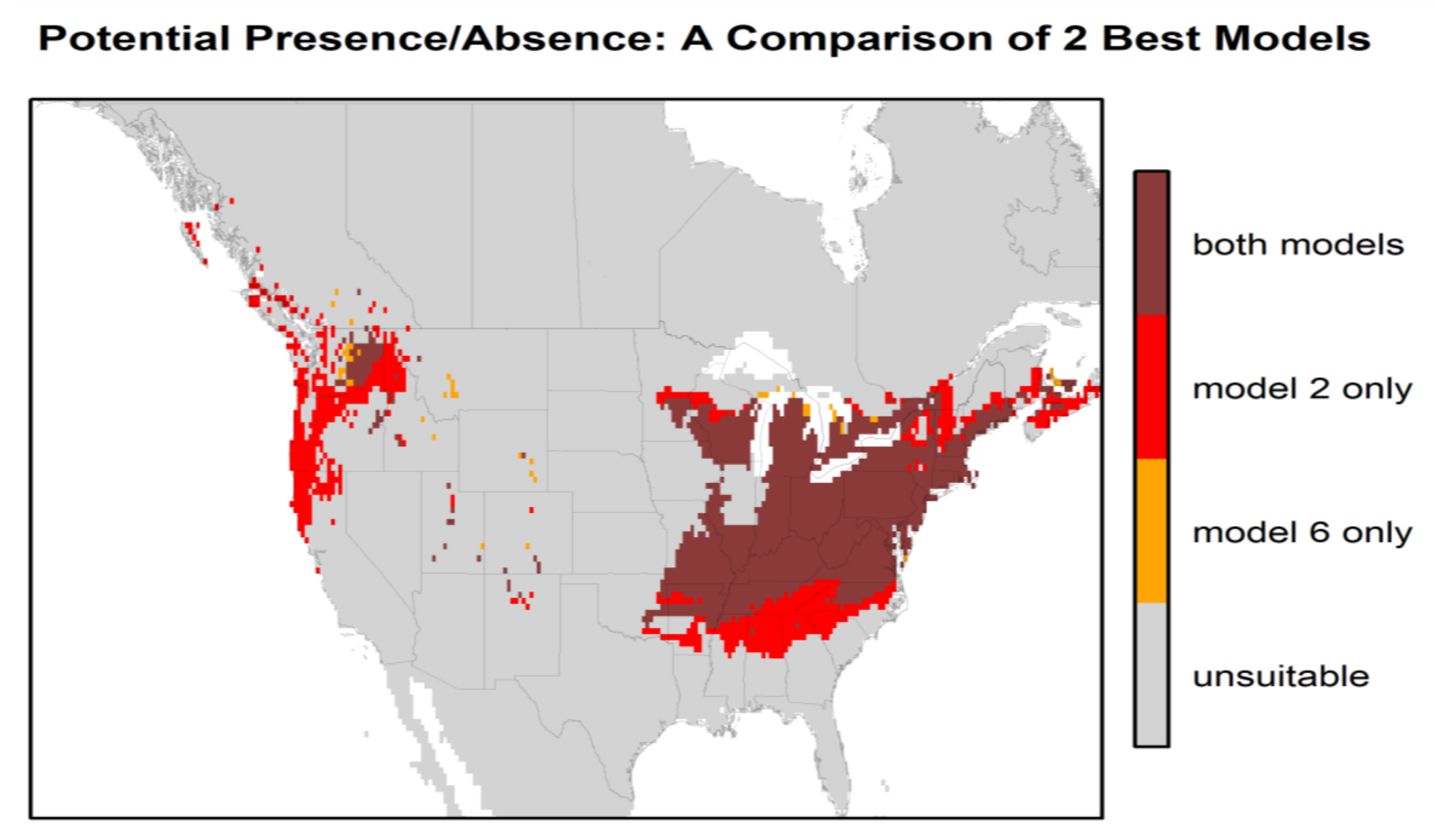
Figure 3 presents the habitat suitability maps for North America from the two best models (models 2 and 6). Based on these maps, the most suitable areas in North America are found within the temperate zones, i.e., the east, and a narrower area in the west between the Rocky Mountains and the Pacific coast. The difference in North American habitat suitability prediction by the 2 best models is illustrated in Figure 4. The east zone goes from Arkansas–South Carolina to the south of Quebec–Nova Scotia for model 2 and from Tennessee–North Carolina to New York–south of Maine for model 6; the west zone goes from California to the coast of British Columbia for model 2 and encompasses just a small zone east of Washington State for model 6. There is an overlap of 88.4% between these two maps. Model 2 predicts a greater area of “very high” suitability habitat (p > 0.8), while Model 6 predicts more areas as “high” suitability habitat (0.6 < p < 0.8) for the same area in the east.
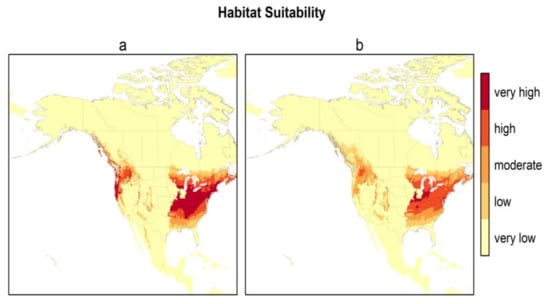
Figure 3.
Habitat suitability of H. longicornis under current climatic and environmental conditions for North America for the two best models ((a) model 2—bio 1, bio 5, bio 12, and (Global Ecological Zone) GEZ using H. longicornis occurrence locations from the native range, Asia; (b) model 6—bio 10, bio 11, and GEZ using H. longicornis occurrence locations from the native range, Asia).
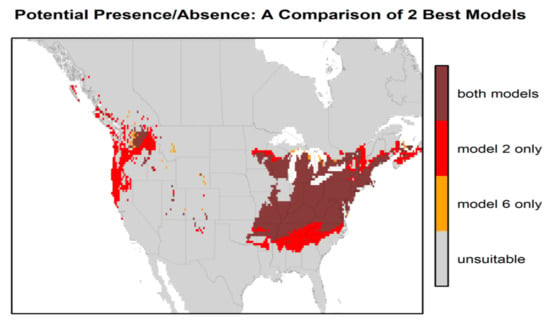
Figure 4.
Comparison of the habitat suitability of H. longicornis in North America between the 2 best models (model 2 (bio 1, bio 5, bio 12, and GEZ) and model 6 (bio 10, bio 11, and GEZ) for the high suitability probabilities (≥ 0.6).
4. Discussion
The establishment and potential expansion of H. longicornis in North America has been of public health and veterinary concern, particularly in the United States and Canada. Globally, this tick species is associated with at least 59 pathogens, of which 30 are potentially pathogenic to humans [45]. The most noted human pathogen transmitted by the H. longicornis in its native range in East Asia is the SFTSV [4]. Since its discovery in 2009, cases of SFTSV have been increasingly reported in East Asia [46]. In November 2019, the first case of SFTSV was reported from Taiwan [47], and cases have also occurred in Vietnam [48], suggesting that the SFTSV is expanding its range in Asia. Since H. longicornis plays an important role in maintaining and transmitting SFTSV, the possibility of this disease in North America should not be neglected.
To our knowledge, there has been no evidence of any human pathogen transmitted by H. longicornis in North America [22,49]. However, there is a concern that this tick might be capable of transmitting Rickettsia rickettsii, which causes Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Under laboratory conditions, H. longicornis larvae and nymphs, from a colony derived from females collected in New York, were able to acquire and transmit this pathogen [50], further increasing the public health concern. Recently, Theileria orientalis Ikeda, a protozoan parasite transmitted by H. longicornis in East Asia, New Zealand, and Australia, has been detected in cattle in Virginia, and this has prompted further concerns that this tick species might play a role in the continued transmission of the pathogen causing Theileria-associated bovine infectious anemia [17]. In Australia, it is estimated that T. orientalis infection has been associated with a loss of AUD 19.6 million per annum for the red meat industry [51]. Therefore, the potential role of this tick in transmitting these pathogens in humans and animals in North America cannot be ignored.
Currently, all published models of H. longicornis distribution use climatic variables to predict distribution [27,28,29,45]. Ecological zones have also been included as these can represent a complex of interacting abiotic and biotic variables [28]. The distribution of potential host species was not considered in our work as this is unlikely to limit the distribution of this tick. All stages have been found on a variety of domestic animals including cattle, horses, and dogs [3]. Moreover, all stages of this tick have been collected from white-tailed deer, Odocoileus virginianus (Zimmermann, 1780), a widely distributed wildlife species [52], and a variety of other wildlife in the United States [53]. The wide host range of H. longicornis may facilitate dispersion over short and long distances. Globally, 77 species of animals are hosts for this tick species [45]. In the United States, the H. longicornis has been isolated from 21 species of domestic and wild animals and also from humans [19]. Migratory birds might play an important role in the dispersal of this tick to a new area [29,45]. Further, the parthenogenetic ability of H. longicornis is particularly concerning in the context of its potential expansion [29]. A single engorged female can reproduce without mating and establish a population in a new area with suitable environmental conditions [3].
Temperature and precipitation are the most important climatic factors that influence the distribution of H. longicornis in both the native (East Asia) and the introduced (Oceania) regions [54,55]. Annual mean temperature greater than 12 °C, mean coldest monthly temperature less than 2 °C, and annual rainfall above 1000 mm are considered to be optimum for H. longicornis range expansion in New Zealand [54]. H. longicornis tolerates a wide range of temperatures (−2 to 40 °C), but the warm and moist temperate conditions are known to be preferred [3]. Humidity is the limiting factor for the establishment of H. longicornis populations, as the threshold for survival and host-seeking activity is 85% relative humidity [3,45]. In our models (models 2 and 6), the most important environmental variables influencing the distribution of H. longicornis were bio 1 (annual mean temperature) and GEZ for model 2, and GEZ and bio 11 (mean temperature of coldest quarter) for model 6. In both models, these variables explained more than 70% of the contribution to the model. Our finding that the bio 1 and GEZ are important variables for H. longicornis expansion corroborates the findings from the previously published MaxEnt modeling studies [28,45].
We also analyzed the patterns of temperature and precipitation variables in different regions where H. longicornis is found. There was a similar pattern of temperature between North America and East Asia, and this might explain why H. longicornis habitat suitability in North America was better predicted by the model developed with data from its native range of East Asia alone. A separate model for parthenogenetic H. longicornis within its native range was also developed [1,3]. This was done mainly in an attempt to improve the predictive accuracy in North America, as the H. longicornis population in North America is also parthenogenetic. We assumed that the parthenogenetic populations might have a different geographical range with different environmental requirements than bisexual populations, which (if true) can improve the predictive accuracy of the models. However, this process did not improve the predictive accuracy of the model, probably because relatively few occurrence records of parthenogenetic H. longicornis within its native range were available, and their distribution overlaps that of the bisexual populations.
In our study, we predicted that the most suitable areas for the H. longicornis in North America were found within the east zone, i.e., from Arkansas–South Carolina to south of Quebec–Nova Scotia for model 2 and from Tennessee–North Carolina to New York–south of Maine for model 6. In the west zone, the most potentially suitable areas were from California to the coast of British Columbia for model 2 and just a small zone east of Washington State for model 6. The findings are largely in agreement with previous studies that have used the MaxEnt approach [28,29]. However, unlike the predicted distribution from Raghavan et al. (2019) [29], central and southern Mexico were not predicted to be highly suitable areas in our models. This difference in potential prediction could have been due to using a different number of occurrence points and locations or the use of different environmental variables for model calibration. The other MaxEnt modeling study by Zhao et al. (2020) [45], conducted at the global scale, predicted the western coast to be more suitable than the eastern coast in the United States for H. longicornis. The use of a relatively low number of occurrence points (249 points) by Zhao et al. (2020) [45] could have affected the predictive accuracy of the models. Further, discrepancies in results among different MaxEnt modeling studies could also occur as a result of using different sources of occurrence data and model settings (i.e., features and regularization in MaxEnt). In our study, the accuracy of habitat suitability predictions for North America was assessed using the 97 known occurrences from the U.S. counties (Figure 2). All 97 locations that have reported the presence of the H. longicornis corresponded to the areas predicted as a “very high” suitability by model 2 and predominantly “high” suitability areas by model 6. Most of the potentially suitable areas in the east and west zones correspond to the humid temperate zone and coastal areas, respectively, where humidity may not be the limiting factor.
Reliable presence data is critical for the predictive accuracy of species distribution models. For instance, there was no accurate description of the H. longicornis range for parthenogenetic and bisexual populations in the literature; however, we attempted to delineate these ranges and looked at the predictive response of the models. Further, the 97 location records of H. longicornis occurrences in the United States were derived from the centroids of positive counties. More accurate publicly available presence and absence data would improve the predictive accuracy of the models. This would facilitate a more cost-effective targeted surveillance for early detection and subsequent tick control response. As H. longicornis is a threat to human and animal health, there is a need to embrace a one health approach for its monitoring and control by ensuring timely data sharing and engaging interdisciplinary expertise.
5. Conclusions
Haemaphysalis longicornis is currently distributed in 118 counties in 15 states of the United States [19]. Previously, specimens of H. longicornis were misidentified as the native rabbit tick, Haemaphysalis leporispalustris [18], resulting in a delay in an appropriate response to the incursion of this exotic tick. Haemaphysalis longicornis has most likely come to North America from East Asia [24]. Companion animals (particularly dogs) entering the United States are thought to be the source [24]. Based on our habitat suitability models, the geographic distribution of the H. longicornis will likely continue to expand in North America. Due to the ability of this tick to transmit pathogens, the potential threat of this tick to public and veterinary health should not be ignored. Enhanced tick surveillance to determine the expanding geographical distribution of the H. longicornis in North America should be continued. There is also a need for human and animal health monitoring systems to work together to determine the potential role this tick might play in the transmission of diseases to humans and animals in North America. Effective control methods for this tick in North America should be determined using a collaborative one health approach.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/17/21/8285/s1. Figure S1: Frequency of Observed Presence (FOP) plots for the predictors of interest (WorldClim bio1—annual mean temperature; bio5—max temperature of warmest month; bio12—annual precipitation; bio10—mean temperature of warmest month; and bio11—mean temperature of coldest month (temperature in °C*10 and precipitation in mm); GEZ—global ecozone; ENVIREM continentality (in °C) for the East Asia region with 325 presences and 980 background points. These plots were created via the R package MIAmaxent [38], where the dots are the values of the predictors at the given locations, the red line a smoother regression line, and the background distribution approximate the data density; Table S1: Results of estimating the best MaxEnt model features and regularization (rm) for each geographic area of interest using the ENMeval R package [39]. Results are based on the random 5-fold method for data partitioning, where background points were randomly selected from the area of unsuitable habitat modeled from the BIOCLIM algorithm (a classic presence-only climate envelope model), and settings that primarily minimize AICc (i.e., ΔAIcc = 0) were selected for our best models (in bold); however, the AUC metrics and OR (threshold-based omission rates for test localities) metrics were calculated to select less complex models (when compared to Frequency of Observed Presence plots) and lowest number of parameters if those were giving similar or higher AUC and lowest OR because a low OR indicates less overfitting. [L: linear, Q: Quadratics, H: hinge]; Table S2: Results of the nested MaxEnt-type models built during the forward DV selection using the MIAmaxent R package [38], where DV is the derived variables from the original ones using a specified transformation [Linear, Quadratics, Monotonous, Forward or Reverse Hinge, or Threshold for Continuous variable and binary for Categorical variable] that balance complexity of model with its fitness. Alpha = 0.005 was used to set the threshold for the amount of variation a DV must explain to be kept, i.e., P < alpha. The selected original variables (highlighted in grey) were then entered into the ENMeval algorithm to find the best model features and regularization. The response curves for both MIAmaxent and ENMeval algorithms were compared to their corresponding Frequency of Observed Presence plot for a quick assessment.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.N., I.C., T.J.L., and S.C.C.; methodology, I.C., J.N., T.J.L., S.J.D., and S.C.C.; software, I.C.; validation, S.J.D., T.J.L., and S.C.C.; formal analysis, I.C., and J.N.; investigation, I.C., and J.N.; resources, S.J.D., T.J.L., and S.C.C.; data curation, I.C.; writing—original draft preparation, J.N.; writing—review and editing, J.N., I.C., T.J.L., S.J.D., and S.C.C.; visualization, J.N., I.C., and S.C.C.; supervision, S.C.C.; project administration, S.C.C.; funding acquisition, S.C.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the One Health Graduate Training award, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Calgary (J.N) and the Public Health Agency Canada (PHAC), Infectious Disease & Climate Change Fund (I.C) The views expressed herein do not necessarily represent the views of the Public Health Agency of Canada.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge Joel Hutcheson, former Research Scientist, Centre for Vector-borne Disease, National Centre for Animal Diseases, Canadian Food Inspection Agency, Lethbridge, Alberta, Canada, for his insights and guidance for this work. The authors would also like to thank reviewers for their comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Hoogstraal, H.; Roberts, F.H.S.; Kohls, G.M.; Tipton, V.J. Review of Haemaphysalis (Kaiseriana) longicornis Neumann (Resurrected) of Australia, New Zealand, New Caledonia, Fiji, Japan, Korea, and Northeastern China and USSR, and Its Parthenogenetic and Bisexual Populations (Ixodoidea, Ixodidae). J. Parasitol. 1968, 54, 1197–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jongejan, F.; Uilenberg, G. The global importance of ticks. Parasitology 2004, 129, S3–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heath, A.C.G. Biology, ecology and distribution of the tick, Haemaphysalis longicornis Neumann (Acari: Ixodidae) in New Zealand. N. Z. Vet. J. 2016, 64, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Shin, W.-J.; Jung, J.U. Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus NSs Interacts with TRIM21 To Activate the p62-Keap1-Nrf2 Pathway. J. Virol. 2020, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.-J.; Liang, M.-F.; Zhang, S.-Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.-D.; Sun, Y.-L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.-F.; Popov, V.L.; Li, C.; et al. Fever with Thrombocytopenia Associated with a Novel Bunyavirus in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.-H.; Yi, J.; Kim, G.; Choi, S.J.; Jun, K.I.; Kim, N.-H.; Choe, P.G.; Kim, N.-J.; Lee, J.-K.; Oh, M. Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome, South Korea, 2012. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1892–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, T.; Maeda, K.; Suzuki, T.; Ishido, A.; Shigeoka, T.; Tominaga, T.; Kamei, T.; Honda, M.; Ninomiya, D.; Sakai, T.; et al. The First Identification and Retrospective Study of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome in Japan. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 209, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.-W.; Ryou, J.; Choi, W.-Y.; Han, M.-G.; Lee, W.-J. Epidemiological and Clinical Features of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome during an Outbreak in South Korea, 2013–2015. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 95, 1358–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brault, A.C.; Savage, H.M.; Duggal, N.K.; Eisen, R.J.; Staples, J.E. Heartland Virus Epidemiology, Vector Association, and Disease Potential. Viruses 2018, 10, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMullan, L.K.; Folk, S.M.; Kelly, A.J.; MacNeil, A.; Goldsmith, C.S.; Metcalfe, M.G.; Batten, B.C.; Albarino, C.G.; Zaki, S.R.; Rollin, P.E.; et al. A New Phlebovirus Associated with Severe Febrile Illness in Missouri. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahara, F. Japanese spotted fever: Report of 31 cases and review of the literature. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1997, 3, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammer, J.F.; Emery, D.; Bogema, D.R.; Jenkins, C. Detection of Theileria orientalis genotypes in Haemaphysalis longicornis ticks from southern Australia. Parasit. Vectors 2015, 8, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, K.E.; Summers, S.R.; Heath, A.C.G.; McFadden, A.M.J.; Pulford, D.J.; Tait, A.B.; Pomroy, W.E. Using a rule-based envelope model to predict the expansion of habitat suitability within New Zealand for the tick Haemaphysalis longicornis, with future projections based on two climate change scenarios. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 243, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.; Jiang, B.-G.; Liu, W.; Zhao, Q.-M.; Wu, X.-M.; Zhang, P.-H.; Zhan, L.; Yang, H.; Cao, W.-C. Presence of pathogenic Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in ticks and rodents in Zhejiang, south-east China. J. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 57, 980–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Sun, J.; Yan, J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Han, H.; Tong, Z.; Liu, M.; Wu, Y.; et al. Detection of a Novel Ehrlichia Species in Haemaphysalis longicornis Tick from China. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2016, 16, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainey, T.; Occi, J.L.; Robbins, R.G.; Egizi, A. Discovery of Haemaphysalis longicornis (Ixodida: Ixodidae) Parasitizing a Sheep in New Jersey, United States. J. Med. Entomol. 2018, 55, 757–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oakes, V.J.; Yabsley, M.J.; Schwartz, D.; LeRoith, T.; Bissett, C.; Broaddus, C.; Schlater, J.L.; Todd, S.M.; Boes, K.M.; Brookhart, M.; et al. Theileria orientalis Ikeda Genotype in Cattle, Virginia, USA. Emerg. Infect. Dis. J. 2019, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, A.T.; Dominguez, K.; Cleveland, C.A.; Dergousoff, S.J.; Doi, K.; Falco, R.C.; Greay, T.; Irwin, P.; Lindsay, L.R.; Liu, J.; et al. Molecular Characterization of Haemaphysalis Species and a Molecular Genetic Key for the Identification of Haemaphysalis of North America. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USDA National Haemaphysalis longicornis (Asian Longhorned Tick) Situation Report, U.S. Department of Agriculture’s Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service. 2020. Available online: https://www.aphis.usda.gov/animal_health/animal_diseases/tick/downloads/longhorned-tick-sitrep.pdf (accessed on 23 October 2020).
- Hutcheson, H.J.; Dergousoff, S.J.; Lindsay, L.R. Haemaphysalis longicornis: A tick of considerable veterinary importance, now established in North America. Can. Vet. J. 2019, 60, 27–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Public Health Ontario. The Asian Longhorned Tick: Assessing Public Health Implications for Ontario; Ontario Agency for Health Protection and Promotion (Public Health Ontario): Toronto, ON, Canada, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wormser, G.P.; McKenna, D.; Piedmonte, N.; Vinci, V.; Egizi, A.M.; Backenson, B.; Falco, R.C. First Recognized Human Bite in the United States by the Asian Longhorned Tick, Haemaphysalis longicornis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 70, 314–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, J.H.; Tanaka, K.; Sawada, M. Cytogenetics of ticks (Acari: Ixodoidea). Chromosoma 1973, 42, 269–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egizi, A.; Bulaga-Seraphin, L.; Alt, E.; Bajwa, W.I.; Bernick, J.; Bickerton, M.; Campbell, S.R.; Connally, N.; Doi, K.; Falco, R.C.; et al. First glimpse into the origin and spread of the Asian longhorned tick, Haemaphysalis longicornis, in the United States. Zoonoses Public Health 2020, 67, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrin, C.S.; Oliver Jr, J.H. Numerical taxonomic studies of parthenogenetic and bisexual populations of Haemaphysalis longicornis and related species (Acari: Ixodidae). J. Parasitol. 1974, 1025–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yang, X.; Bu, F.; Yang, X.; Liu, J. Morphological, biological and molecular characteristics of bisexual and parthenogenetic Haemaphysalis longicornis. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 189, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magori, K. Preliminary prediction of the potential distribution and consequences of Haemaphysalis longicornis using a simple rule-based climate envelope model. bioRxiv 2018, 389940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochlin, I. Modeling the Asian Longhorned Tick (Acari: Ixodidae) Suitable Habitat in North America. J. Med. Entomol. 2018, 56, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, R.K.; Barker, S.C.; Cobos, M.E.; Barker, D.; Teo, E.J.M.; Foley, D.H.; Nakao, R.; Lawrence, K.; Heath, A.C.G.; Peterson, A.T. Potential Spatial Distribution of the Newly Introduced Long-horned Tick, Haemaphysalis longicornis in North America. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Zheng, D.; Ian, Y.T.; Li, S. A dataset of distribution and diversity of ticks in China. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S.J.; Anderson, R.P.; Schapire, R.E. Maximum entropy modeling of species geographic distributions. Ecol. Model. 2006, 190, 231–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijmans, R.J.; Cameron, S.E.; Parra, J.L.; Jones, P.G.; Jarvis, A. Very high resolution interpolated climate surfaces for global land areas. Int. J. Climatol. 2005, 25, 1965–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Title, P.O.; Bemmels, J.B. ENVIREM: An expanded set of bioclimatic and topographic variables increases flexibility and improves performance of ecological niche modeling. Ecography 2018, 41, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hijmans, R.J. {raster: Geographic Data Analysis and Modeling}, R package version 3.1-5; 2020; Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=raster (accessed on 4 November 2020).
- Bivand, R.; Keitt, T.; Rowlingson, B. rgdal: Bindings for the “Geospatial” Data Abstraction Library, R package version 1.4-8; 2019; Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=rgdal (accessed on 4 November 2020).
- Hijmans, R.J.; Phillips, S.; Leathwick, J.; Elith, J. dismo: Species Distribution Modeling, R package version 1.1-4; 2017; Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=dismo (accessed on 4 November 2020).
- Vollering, J.; Halvorsen, R.; Mazzoni, S. The MIAmaxent R package: Variable transformation and model selection for species distribution models. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 12051–12068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muscarella, R.; Galante, P.J.; Soley-Guardia, M.; Boria, R.A.; Kass, J.M.; Uriarte, M.; Anderson, R.P. ENMeval: An R package for conducting spatially independent evaluations and estimating optimal model complexity for Maxent ecological niche models. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2014, 5, 1198–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elith, J.; Phillips, S.J.; Hastie, T.; Dudík, M.; Chee, Y.E.; Yates, C.J. A statistical explanation of MaxEnt for ecologists. Divers. Distrib. 2019, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, K.P.; Anderson, D.R. Multimodel Inference: Understanding AIC and BIC in Model Selection. Sociol. Methods Res. 2004, 33, 261–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, D.L.; Seifert, S.N. Ecological niche modeling in Maxent: The importance of model complexity and the performance of model selection criteria. Ecol. Appl. 2011, 21, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, D.L.; Glor, R.E.; Turelli, M. Environmental Niche Equivalency Versus Conservatism: Quantitative Approaches to Niche Evolution. Evolution 2008, 62, 2868–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuliani, A.; Massolo, A.; Lysyk, T.; Johnson, G.; Marshall, S.; Berger, K.; Cork, S.C. Modelling the Northward Expansion of Culicoides sonorensis (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) under Future Climate Scenarios. PLoS ONE 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Li, J.; Cui, X.; Jia, N.; Wei, J.; Xia, L.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, X.; et al. Distribution of Haemaphysalis longicornis and associated pathogens: Analysis of pooled data from a China field survey and global published data. Lancet Planet. Health 2020, 4, e320–e329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, D.; Dai, K.; Zhao, G.-P.; Li, X.-L.; Shi, W.-Q.; Zhang, J.S.; Yang, Y.; Liu, W.; Fang, L.-Q. Mapping the global potential transmission hotspots for severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome by machine learning methods. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.-H.; Yang, S.-L.; Tang, S.-E.; Wang, T.-C.; Hsu, T.-C.; Su, C.-L.; Chen, M.-Y.; Shimojima, M.; Yoshikawa, T.; Shu, P.-Y. Human Case of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus Infection, Taiwan, 2019. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1612–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, X.C.; Yun, Y.; Van An, L.; Kim, S.-H.; Thao, N.T.P.; Man, P.K.C.; Yoo, J.R.; Heo, S.T.; Cho, N.-H.; Lee, K.H. Endemic Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome, Vietnam. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 1029–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Beard, C.; Occi, J.; Bonilla, D.L.; Egizi, A.M.; Fonseca, D.M.; Mertins, J.W.; Backenson, B.P.; Bajwa, W.I.; Barbarin, A.M.; Bertone, M.A.; et al. Multistate Infestation with the Exotic Disease-Vector Tick Haemaphysalis longicornis - United States, August 2017-September 2018. Mmwr-Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2018, 67, 1310–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, H.M.; Ford, S.L.; Snellgrove, A.N.; Hartzer, K.; Smith, E.B.; Krapiunaya, I.; Levin, M.L. The Ability of the Invasive Asian Longhorned Tick Haemaphysalis longicornis (Acari: Ixodidae) to Acquire and Transmit Rickettsia rickettsii (Rickettsiales: Rickettsiaceae), the Agent of Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever, Under Laboratory Conditions. J. Med. Entomol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, K.E.; Lawrence, B.L.; Hickson, R.E.; Hewitt, C.A.; Gedye, K.R.; Fermin, L.M.; Pomroy, W.E. Associations between Theileria orientalis Ikeda type infection and the growth rates and haematocrit of suckled beef calves in the North Island of New Zealand. N. Z. Vet. J. 2019, 67, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tufts, D.M.; VanAcker, M.C.; Fernandez, M.P.; DeNicola, A.; Egizi, A.; Diuk-Wasser, M.A. Distribution, Host-Seeking Phenology, and Host and Habitat Associations of Haemaphysalis longicornis Ticks, Staten Island, New York, USA. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 792–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.A.; Bevins, S.N.; Ruder, M.G.; Shaw, D.; Vigil, S.L.; Randall, A.; Deliberto, T.J.; Dominguez, K.; Thompson, A.T.; Mertins, J.W.; et al. Surveys for ticks on wildlife hosts and in the environment at Asian longhorned tick (Haemaphysalis longicornis)-positive sites in Virginia and New Jersey, 2018. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neilson, F.J.A. An investigation into the ecology, biology, distribution and control of Haemaphysalis longicornis Neumann, 1901: A thesis presented in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the degree ofMaster of Veterinary Science at Massey University. Master’s Thesis, Massey University, Palmerston North, New Zealand, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, L.; Yang, X.; Liu, J. Seasonal abundance and activity of the hard tick Haemaphysalis longicornis (Acari: Ixodidae) in North China. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2012, 56, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).