Validity of Bioimpedance Spectroscopy in the Assessment of Total Body Water and Body Composition in Wrestlers and Untrained Subjects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. D2O Dilution Method
2.3. Bioimpedance Spectroscopy (BIS)
2.4. Body Composition
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Subject Characteristics
3.2. Body Resistance, Total Water Content
3.3. Body Composition
3.4. Regression and CCC Analysis
3.5. Bland–Altman Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kyle, U.G.; Bosaeus, I.; De Lorenzo, A.D.; Deurenberg, P.; Elia, M.; Gómez, J.M.; Heitmann, B.L.; Kent-Smith, L.; Melchior, J.-C.; Pirlich, M.; et al. Bioelectrical impedance analysis--part I: Review of principles and methods. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 23, 1226–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Marken Lichtenbelt, W.D.; Westerterp, K.R.; Wouters, L.; Luijendijk, S.C. Validation of bioelectrical-impedance measurements as a method to estimate body-water compartments. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1994, 60, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seoane, F.; Abtahi, S.; Abtahi, F.; Ellegard, L.; Johannsson, G.; Bosaeus, I.; Ward, L.C. Mean expected error in prediction of total body water: A true accuracy comparison between bioimpedance spectroscopy and single frequency regression equations. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 656323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox-Reijven, P.L.; Soeters, P.B. Validation of bio-impedance spectroscopy: Effects of degree of obesity and ways of calculating volumes from measured resistance values. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2000, 24, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagayama, H.; Yamada, Y.; Ichikawa, M.; Kondo, E.; Yasukata, J.; Tanabe, Y.; Higaki, Y.; Takahashi, H. Evaluation of fat-free mass hydration in athletes and non-athletes. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2020, 120, 1179–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lorenzo, A.; Andreoli, A.; Matthie, J.; Withers, P. Predicting body cell mass with bioimpedance by using theoretical methods: A technological review. J. Appl. Physiol. 1997, 82, 1542–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moissl, U.M.; Wabel, P.; Chamney, P.W.; Bosaeus, I.; Levin, N.W.; Bosy-Westphal, A.; Korth, O.; Muller, M.J.; Ellegard, L.; Malmros, V.; et al. Body fluid volume determination via body composition spectroscopy in health and disease. Physiol. Meas. 2006, 27, 921–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiterio, A.L.; Silva, A.M.; Minderico, C.S.; Carnero, E.A.; Fields, D.A.; Sardinha, L.B. Total body water measurements in adolescent athletes: A comparison of six field methods with deuterium dilution. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2009, 23, 1225–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, A.; Slater, G.; Byrne, N.; Chaseling, J. Validation of bioelectrical impedance spectroscopy to measure total body water in resistance-trained males. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2015, 25, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, C.N.; Judice, P.B.; Santos, D.A.; Magalhaes, J.P.; Minderico, C.S.; Fields, D.A.; Sardinha, L.B.; Silva, A.M. Suitability of bioelectrical based methods to assess water compartments in recreational and elite athletes. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2016, 35, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, H.; Yamashita, D.; Arimitsu, T.; Sakae, K.; Shimizu, S. Anthropometric Characteristics of Elite Japanese Female Wrestlers. Int. J. Wrestl. Sci. 2015, 5, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, H.; Fukunaga, T. Profiles of musculoskeletal development in limbs of college Olympic weightlifters and wrestlers. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1999, 79, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, Y.; Masuo, Y.; Yokoyama, K.; Hashii, Y.; Ando, S.; Okayama, Y.; Morimoto, T.; Kimura, M.; Oda, S. Proximal electrode placement improves the estimation of body composition in obese and lean elderly during segmental bioelectrical impedance analysis. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 107, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagayama, H.; Yoshimura, E.; Yamada, Y.; Ichikawa, M.; Ebine, N.; Higaki, Y.; Kiyonaga, A.; Tanaka, H. Effects of rapid weight loss and regain on body composition and energy expenditure. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2014, 39, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, Y.; Yokoyama, K.; Noriyasu, R.; Osaki, T.; Adachi, T.; Itoi, A.; Naito, Y.; Morimoto, T.; Kimura, M.; Oda, S. Light-intensity activities are important for estimating physical activity energy expenditure using uniaxial and triaxial accelerometers. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 105, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, Y.; Hashii-Arishima, Y.; Yokoyama, K.; Itoi, A.; Adachi, T.; Kimura, M. Validity of a triaxial accelerometer and simplified physical activity record in older adults aged 64-96 years: A doubly labeled water study. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2018, 118, 2133–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagayama, H.; Jikumaru, Y.; Hirata, A.; Yamada, Y.; Yoshimura, E.; Ichikawa, M.; Hatamoto, Y.; Ebine, N.; Kiyonaga, A.; Tanaka, H.; et al. Measurement of body composition in response to a short period of overfeeding. J. Physiol. Anthropol. 2014, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, K.S.; Cole, R.H. Dispersion and absorption in dielectrics I. Alternating current characteristics. J. Chem. Phys. 1941, 9, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, Y.; Watanabe, Y.; Ikenaga, M.; Yokoyama, K.; Yoshida, T.; Morimoto, T.; Kimura, M. Comparison of single- or multifrequency bioelectrical impedance analysis and spectroscopy for assessment of appendicular skeletal muscle in the elderly. J. Appl. Physiol. 2013, 115, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiose, K.; Yamada, Y.; Motonaga, K.; Sagayama, H.; Higaki, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Takahashi, H. Segmental extracellular and intracellular water distribution and muscle glycogen after 72-h carbohydrate loading using spectroscopic techniques. J. Appl. Physiol. 2016, 121, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouchi, M.; Mochimaru, M. AIST Anthropometric Database. H16PRO 287; 2005. Available online: https://www.airc.aist.go.jp/dhrt/91-92/index.html (accessed on 27 July 2020).
- Siri, W.E. Body composition from fluid spaces and density: Analysis of methods. In Techniques for Measuring Body Composition; Brozek, J., Henschel, A., Eds.; National Academy of Sciences: Washington, DC, USA, 1961; pp. 223–244. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.I. A concordance correlation coefficient to evaluate reproducibility. Biometrics 1989, 45, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, J.R.; Tobkin, S.E.; Roberts, M.D.; Dalbo, V.J.; Kerksick, C.M.; Bemben, M.G.; Cramer, J.T.; Stout, J.R. Total body water estimations in healthy men and women using bioimpedance spectroscopy: A deuterium oxide comparison. Nutr. Metab. 2008, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, C.C.; Churchill, T.; Clauser, C.E.; Bradtmiller, B.; McConville, J.T.; Tebbetts, I.; Walker, R.A. Anthropometric Survey of US Army Personnel: Summary Statistics, Interim Report for 1988; Anthropology Research Project Inc.: Yellow Springs, OH, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Wulan, S.N.; Westerterp, K.R.; Plasqui, G. Ethnic differences in body composition and the associated metabolic profile: A comparative study between Asians and Caucasians. Maturitas 2010, 65, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rush, E.C.; Freitas, I.; Plank, L.D. Body size, body composition and fat distribution: Comparative analysis of European, Maori, Pacific Island and Asian Indian adults. Br. J. Nutr. 2009, 102, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBride, G. A Proposal for Strength-of-Agreement Criteria for Lin’s Concordance Correlation Coefficient; NIWA Client Report: HAM2005-062; NIWA: Auckland, New Zealand, 2005; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Matias, C.N.; Santos, D.A.; Gonçalves, E.M.; Fields, D.A.; Sardinha, L.B.; Silva, A.M. Is bioelectrical impedance spectroscopy accurate in estimating total body water and its compartments in elite athletes? Ann. Hum. Biol. 2013, 40, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, C.; Noujeimi, F.; Sardinha, L.; Teixeira, V.; Silva, A. Total body water and water compartments assessment in athletes: Validity of multi-frequency bioelectrical impedance. Sci. Sports 2018, 34, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
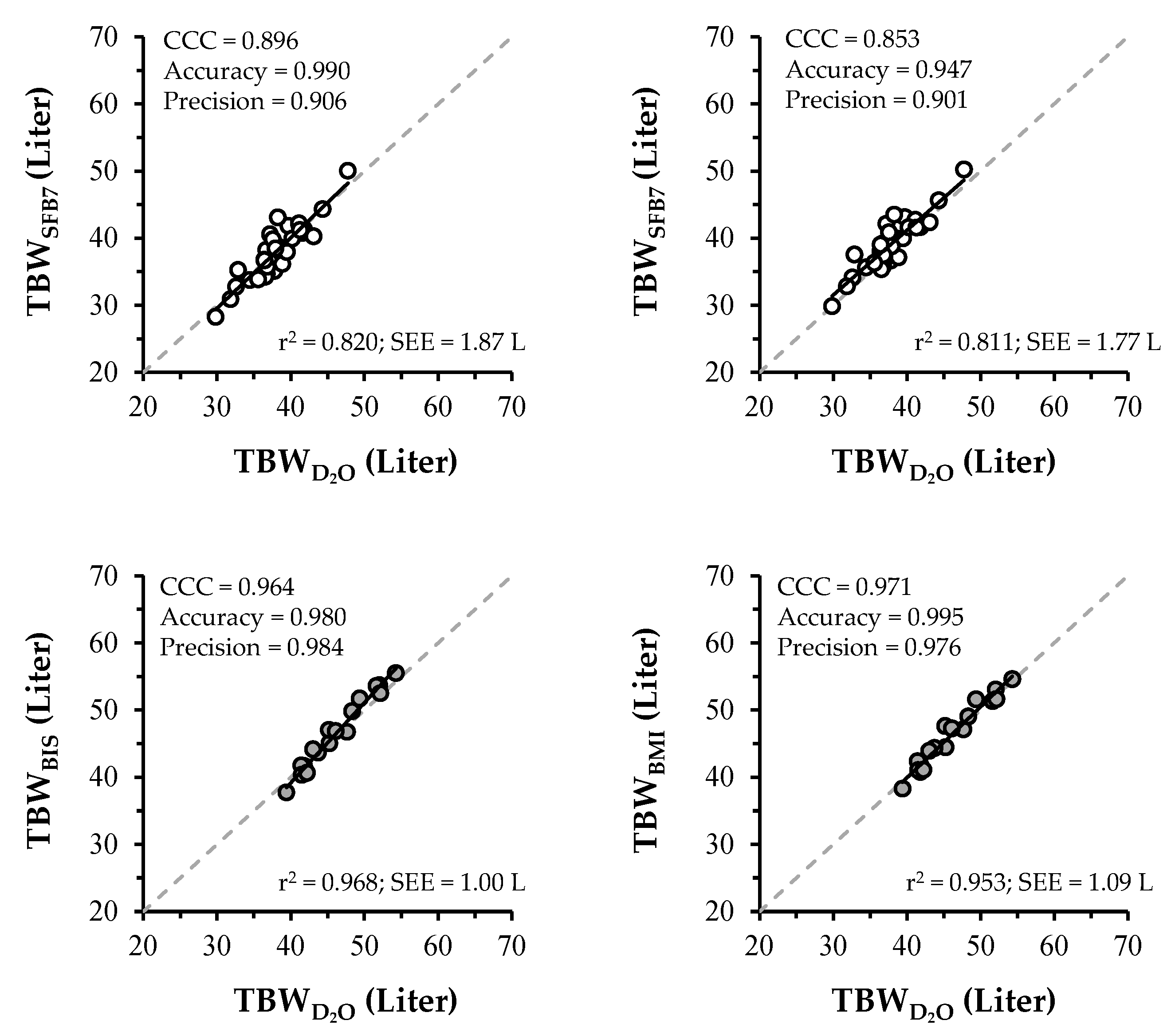
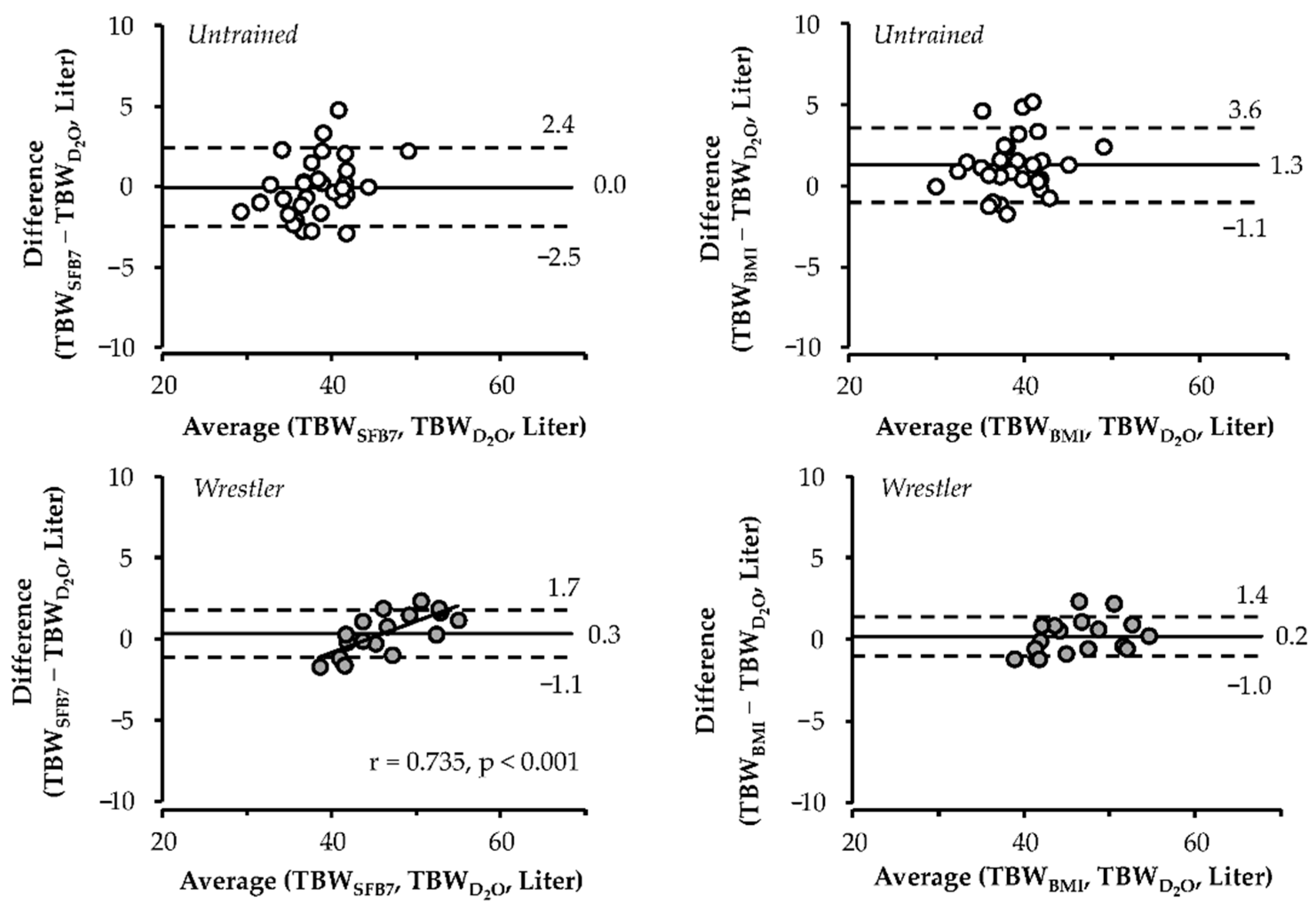
| Variable | Unit | Untrained (n = 31) | Wrestlers (n = 18) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | year | 23 | ± | 4 | (20–37) | 21 | ± | 1 † | (19–22) |
| Height | cm | 173.4 | ± | 6.5 | (161.3–192.1) | 167.8 | ± | 3.7 † | (160.4–173.4) |
| Weight | kg | 63.9 | ± | 6.2 | (50.3–82.4) | 72.2 | ± | 8.3 †† | (62.9–91.6) |
| BMI | kg/m2 | 21.2 | ± | 1.7 | (18.0–25.1) | 25.6 | ± | 2.1 †† | (22.6–31.4) |
| Db | g/mL | 1.065 | ± | 0.009 | (1.049–1.083) | 1.074 | ± | 0.011 † | (1.037–1.086) |
| Variable | Unit | Untrained (n = 31) | Wrestlers (n =18) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Re | Ohm | 642 | ± | 71 | 506 | ± | 45 †† |
| Ri | Ohm | 1226 | ± | 213 | 852 | ± | 111 †† |
| TBWD2O | Liter | 38.1 | ± | 3.8 | 46.0 | ± | 4.5 †† |
| TBWSFB7 | Liter | 38.1 | ± | 4.3 | 46.3 | ± | 5.4 †† |
| ECWSFB7 | Liter | 16.0 | ± | 1.9 | 18.6 | ± | 2.1 †† |
| ICW SFB7 | Liter | 22.1 | ± | 2.7 | 27.6 | ± | 3.5 †† |
| TBWBMI | Liter | 39.4 | ± | 4.0 ** | 46.2 | ± | 4.9 †† |
| ECWBMI | Liter | 15.6 | ± | 1.8 | 18.1 | ± | 2.0 †† |
| ICWBMI | Liter | 23.8 | ± | 2.5 | 28.1 | ± | 3.1 †† |
| Variable | Unit | Untrained (n = 31) | Wrestlers (n = 18) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FFM3C | kg | 53.0 | ± | 5.1 | 63.3 | ± | 5.8 †† |
| %Fat3C | % | 16.9 | ± | 3.5 | 12.1 | ± | 4.3 †† |
| FFMSFB7 | kg | 52.8 | ± | 6.0 | 64.0 | ± | 7.5 †† |
| %FatSFB7 | % | 17.3 | ± | 4.7 | 11.3 | ± | 4.6 †† |
| FFMBMI | kg | 54.6 | ± | 5.6 ** | 63.9 | ± | 6.7 †† |
| %FatBMI | % | 14.4 | ± | 4.9 ** | 11.3 | ± | 5.1 † |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shiose, K.; Kondo, E.; Takae, R.; Sagayama, H.; Motonaga, K.; Yamada, Y.; Uehara, Y.; Higaki, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Tanaka, H. Validity of Bioimpedance Spectroscopy in the Assessment of Total Body Water and Body Composition in Wrestlers and Untrained Subjects. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9433. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17249433
Shiose K, Kondo E, Takae R, Sagayama H, Motonaga K, Yamada Y, Uehara Y, Higaki Y, Takahashi H, Tanaka H. Validity of Bioimpedance Spectroscopy in the Assessment of Total Body Water and Body Composition in Wrestlers and Untrained Subjects. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(24):9433. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17249433
Chicago/Turabian StyleShiose, Keisuke, Emi Kondo, Rie Takae, Hiroyuki Sagayama, Keiko Motonaga, Yosuke Yamada, Yoshinari Uehara, Yasuki Higaki, Hideyuki Takahashi, and Hiroaki Tanaka. 2020. "Validity of Bioimpedance Spectroscopy in the Assessment of Total Body Water and Body Composition in Wrestlers and Untrained Subjects" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 24: 9433. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17249433
APA StyleShiose, K., Kondo, E., Takae, R., Sagayama, H., Motonaga, K., Yamada, Y., Uehara, Y., Higaki, Y., Takahashi, H., & Tanaka, H. (2020). Validity of Bioimpedance Spectroscopy in the Assessment of Total Body Water and Body Composition in Wrestlers and Untrained Subjects. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(24), 9433. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17249433







