Effect of Natural Turf, Artificial Turf, and Sand Surfaces on Sprint Performance. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Approach to the Problem
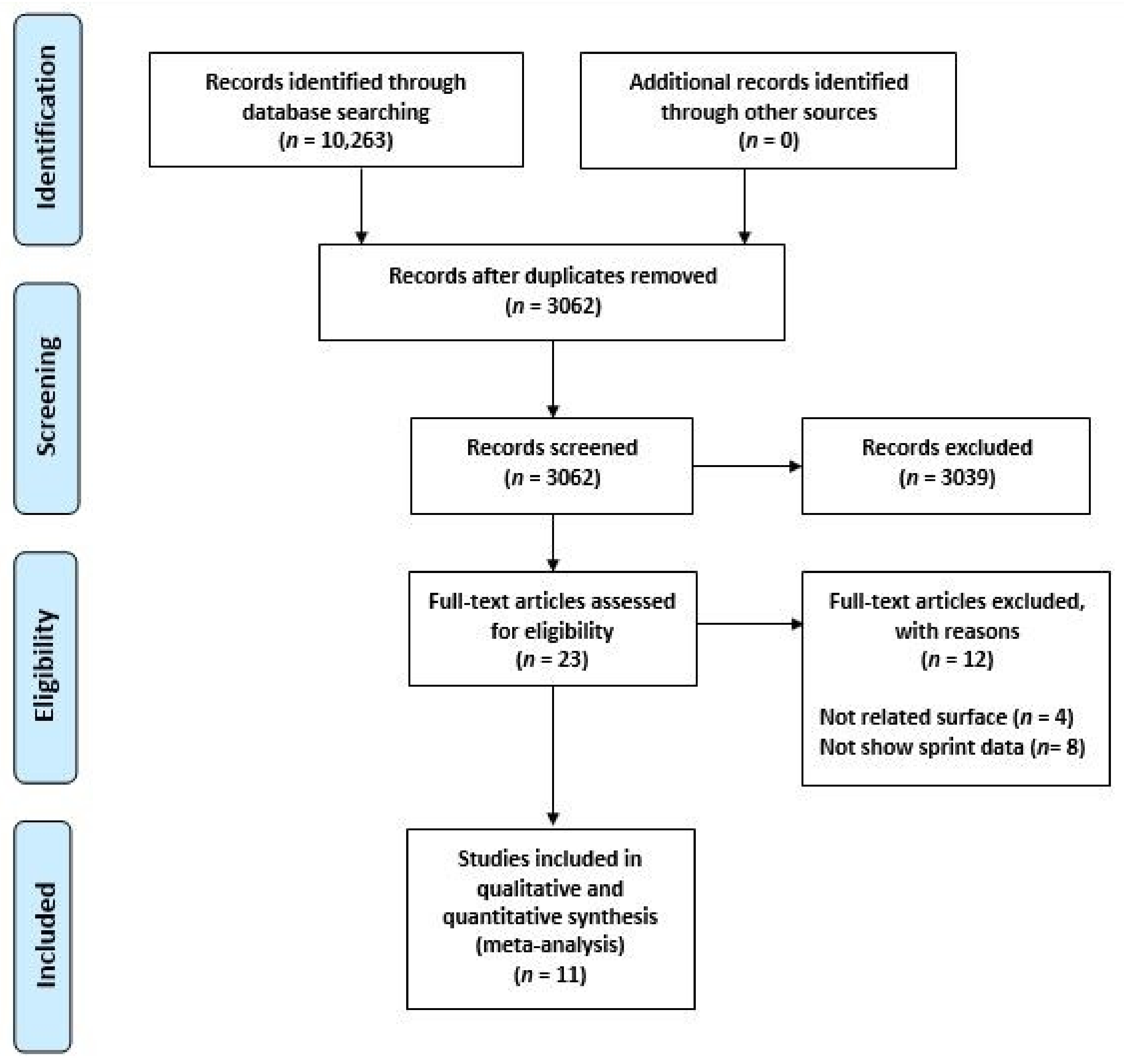
2.2. Study Selection
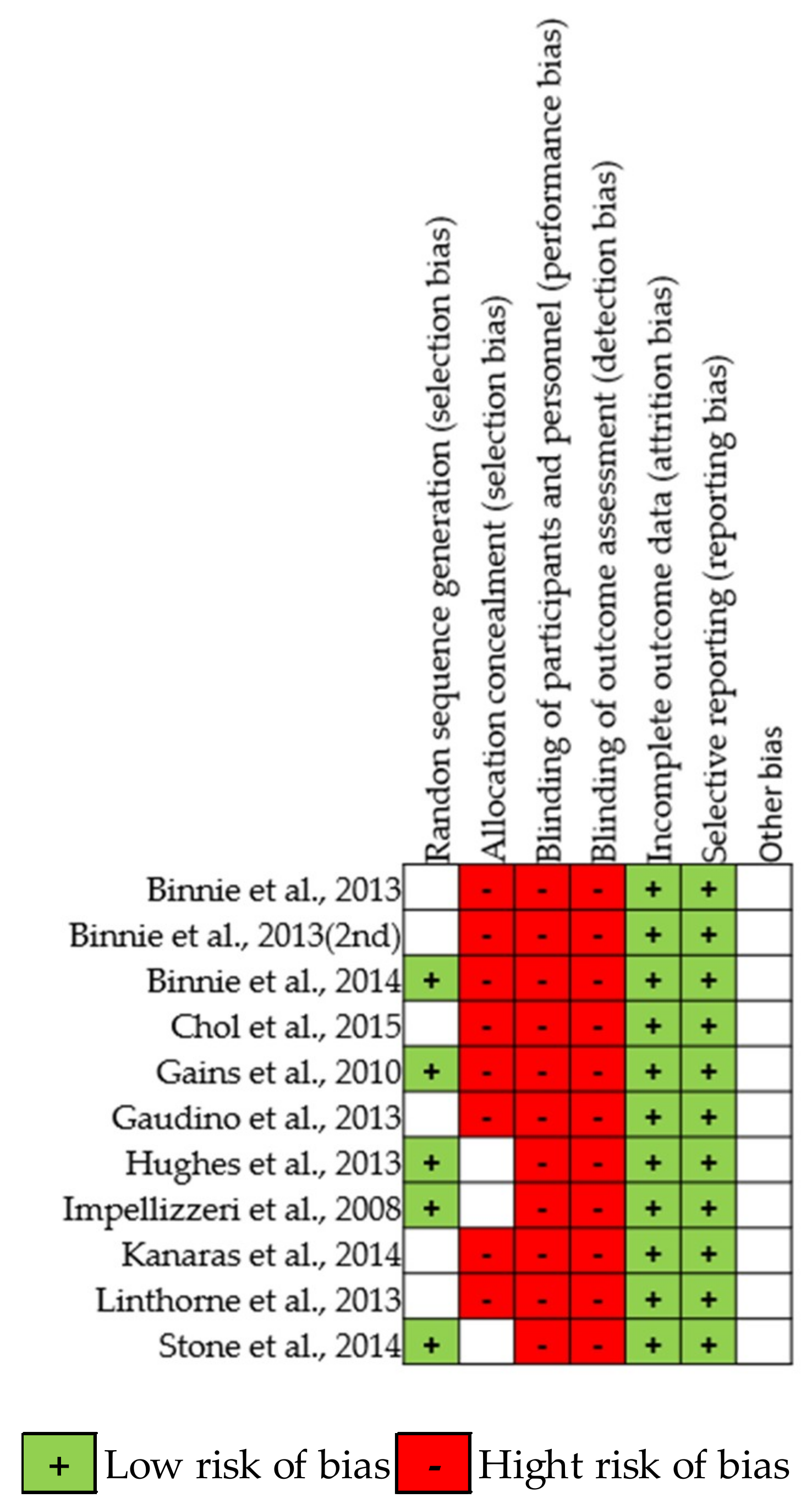
2.3. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
2.4. Data Synthesis and Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fleming, P. Artificial turf systems for sport surfaces: Current knowledge and research needs. J. Sports Eng. Technol. 2011, 225, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroud, G.; Nigg, B.; Stefanyshyn, D. Energy storage and return in sport surfaces. Sports Eng. 1999, 2, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo-Guerrero, L.; García-Tascón, M.; Burillo-Naranjo, P. New sports management software: A needs analysis by a panel of Spanish experts. J. Inf. Manag. 2008, 28, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekstrand, J.; Nigg, B.M. Surface-related injuries in soccer. Sports Med. 1989, 8, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katkat, D.; Bulut, Y.; Demir, M.; Akar, S. Effects of different sport surfaces on muscle performance. Biol. Sport. 2009, 26, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ekstrand, J.; Timpka, T.; Hägglund, M.; Karlsson, J. Risk of injury in elite football played on artificial turf versus natural grass: A prospective two-cohort study. Br. J. Sports Med. 2006, 40, 975–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuller, C.W.; Dick, R.W.; Corlette, J.; Schmalz, R. Comparison of the incidence, nature and cause of injuries sustained on grass and new generation artificial turf by male and female football players. Part 1: Match injuries. Br. J. Sports Med. 2007, 41, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Plaza-Carmona, M.; Vicente-Rodríguez, G.; Martin-Garcia, M.; Burillo, P.; Felipe, J.L.; Mata, E.; Casajús, J.; Gallardo, L.; Ara, I. Influence of hard vs. soft ground surfaces on bone accretion in prepubertal footballers. Int. J. Sports Med. 2014, 35, 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- Alcaraz, P.E.; Palao, J.M.; Elvira, J.L.; Linthorne, N.P. Effects of a sand running surface on the kinematics of sprinting at maximum velocity. Biol. Sport. 2011, 28, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Sánchez, J.; Felipe, J.L.; Burillo, P.; Del Corral, J.; Gallardo, L. Effect of the structural components of support on the loss of mechanical properties of football fields of artificial turf. J. Sports Eng. Technol. 2014, 228, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudino, P.; Gaudino, C.; Alberti, G.; Minetti, A.E. Biomechanics and predicted energetics of sprinting on sand: Hints for soccer training. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2013, 16, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Impellizzeri, F.M.; Rampinini, E.; Castagna, C.; Martino, F.; Fiorini, S.; Wisloff, U. Effect of plyometric training on sand versus grass on muscle soreness and jumping and sprinting ability in soccer players. Br. J. Sports Med. 2008, 42, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamparo, P.; Perini, R.; Orizio, C.; Sacher, M.; Ferretti, G. The energy cost of walking or running on sand. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 1992, 65, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito, J.; Krustrup, P.; Rebelo, A. The influence of the playing surface on the exercise intensity of small-sided recreational soccer games. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2012, 31, 946–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, B.; Norasteh, A.A.; Asadi, A. Neuromuscular adaptations to plyometric training: Depth jump vs. countermovement jump on sand. Sport Sci. Heal. 2013, 9, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, D. A comparison between land and sand-based tests for beach volleyball assessment. J. sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2003, 43, 418–423. [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu, S.; Fukudome, A.; Miyama, M.; Arimoto, M.; Kijima, A. Energy expenditure in maximal jumps on sand. J. Physiol. Anthropol. 2006, 25, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Binnie, M.J.; Peeling, P.; Pinnington, H.; Landers, G.; Dawson, B. Effect of surface-specific training on 20-m sprint performance on sand and grass surfaces. J Strength Cond. Res. 2013, 27, 3515–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Sánchez, J.; García-Unanue, J.; Jiménez-Reyes, P.; Gallardo, A.; Burillo, P.; Felipe, J.L.; Gallardo, L. Influence of the mechanical properties of third-generation artificial turf systems on soccer players’ physiological and physical performance and their perceptions. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brechue, W.F.; Mayhew, J.L.; Piper, F.C. Equipment and running surface alter sprint performance of college football players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2005, 19, 821. [Google Scholar]
- Gains, G.L.; Swedenhjelm, A.N.; Mayhew, J.L.; Bird, H.M.; Houser, J.J. Comparison of speed and agility performance of college football players on field turf and natural grass. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2010, 24, 2613–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassi, A.; Stefanescu, A.; Menaspà, P.; Bosio, A.; Riggio, M.; Rampinini, E. The cost of running on natural grass and artificial turf surfaces. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2011, 25, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Michele, R.; Di Renzo, A.M.; Ammazzalorso, S.; Merni, F. Comparison of physiological responses to an incremental running test on treadmill, natural grass, and synthetic turf in young soccer players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2009, 23, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maher, C.G.; Sherrington, C.; Herbert, R.D.; Moseley, A.M.; Elkins, M. Reliability of the PEDro scale for rating quality of randomized controlled trials. Phys. Ther. 2003, 83, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Binnie, M.J.; Dawson, B.; Arnot, M.A.; Pinnington, H.; Landers, G.; Peeling, P. Effect of sand versus grass training surfaces during an 8-week pre-season conditioning programme in team sport athletes. J. Sports Sci. 2014, 32, 1001–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binnie, M.J.; Dawson, B.; Pinnington, H.; Landers, G.; Peeling, P. Effect of training surface on acute physiological responses after interval training. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2013, 27, 1047–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.M.; Sum, K.-W.R.; Leung, F.L.E. Comparison between Natural Turf and Artificial Turf on Agility Performance of Rugby Union Players. Adv. Phys. Educ. 2015, 5, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hughes, M.G.; Birdsey, L.; Meyers, R.; Newcombe, D.; Oliver, J.L.; Smith, P.M.; Stembridge, M.; Stone, K.; Kerwin, D.G. Effects of playing surface on physiological responses and performance variables in a controlled football simulation. J. Sports Sci. 2013, 31, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaras, V.; Metaxas, T.I.; Mandroukas, A.; Gissis, I.; Zafeiridis, A.; Riganas, C.; Manolopoulos, E.; Vassilis, P.; Ioannis, S.V. The effect of natural and artificial grass on sprinting performance in young soccer players. Am. J. Sports Sci. 2014, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linthorne, N.P.; Cooper, J.E. Effect of the coefficient of friction of a running surface on sprint time in a sled-towing exercise. Sports Biomech. 2013, 12, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stone, K.; Hughes, M.G.; Stembridge, M.; Meyers, R.W.; Newcombe, D.J.; Oliver, J.L. The influence of playing surface on physiological and performance responses during and after soccer simulation. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2014, 16, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Connor, D.; Green, S.; Higgins, J.P. Defining the review question and developing criteria for including studies. In Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; p. 83. [Google Scholar]
- DerSimonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control. Clin. Trials 1986, 7, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maydeu-Olivares, A. Quantitative methods in psychology quantitative methods in psychology. Psychol. Bull. 1992, 112, 155–159. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, G.; Stefanyshyn, D. Identification of critical traction values for maximum athletic performance. Footwear Sci. 2011, 3, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, K.R.; Manson, N.A.; Evans, B.J.; Myer, G.D.; Gwin, R.C.; Heidt, R.S., Jr.; Hewett, T.E. Comparison of in-shoe foot loading patterns on natural grass and synthetic turf. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2006, 9, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villwock, M.R.; Meyer, E.G.; Powell, J.W.; Fouty, A.J.; Haut, R.C. Football playing surface and shoe design affect rotational traction. Am. J. Sports Med. 2009, 37, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, H.; Ekblom, B.; Krustrup, P. Elite football on artificial turf versus natural grass: Movement patterns, technical standards, and player impressions. J. Sports Sci. 2008, 26, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burillo, P.; Gallardo, L.; Felipe, J.L.; Gallardo, A.M. Artificial turf surfaces: Perception of safety, sporting feature, satisfaction and preference of football users. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2014, 14, S437–S447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felipe, J.; Gallardo, L.; Burillo, P.; Gallardo, A.; Sánchez-Sánchez, J.; Plaza-Carmona, M. Artificial turf football fields: A qualitative vision for professional players and coaches. S. Afr. J. Res. Sport Phys. Educ. Recreat. 2013, 35, 105–120. [Google Scholar]
- Sleat, W.; O’Donoghue, P.; Hughes, M.; Bezodis, I.N. The influence of natural grass surface hardness on path changes, locomotive movements and game events in soccer: A case study. Int. J. Perform. Anal. 2016, 16, 216–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potthast, W.; Verhelst, R.; Hughes, M.; Stone, K.; De Clercq, D. Football-specific evaluation of player–surface interaction on different football turf systems. Sports Technol. 2010, 3, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigg, B.M.; Wakeling, J.M. Impact forces and muscle tuning: A new paradigm. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2001, 29, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardin, E.C.; Van Den Bogert, A.J.; Hamill, J. Kinematic adaptations during running: Effects of footwear, surface, and duration. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2004, 36, 838–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pinnington, H.C.; Lloyd, D.G.; Besier, T.F.; Dawson, B. Kinematic and electromyography analysis of submaximal differences running on a firm surface compared with soft, dry sand. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005, 94, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lejeune, T.M.; Willems, P.A.; Heglund, N. Mechanics and energetics of human locomotion on sand. J. Exp. Biol. 1998, 201, 2071–2080. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pinnington, H.C.; Dawson, B. The energy cost of running on grass compared to soft dry beach sand. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2001, 4, 416–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcaraz, P.E.; Carlos-Vivas, J.; Oponjuru, B.O.; Martinez-Rodriguez, A. The effectiveness of resisted sled training (RST) for sprint performance: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2018, 48, 2143–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giatsis, G.; Kollias, I.; Panoutsakopoulos, V.; Papaiakovou, G. Volleyball: Biomechanical differences in elite beach-volleyball players in vertical squat jump on rigid and sand surface. Sports Biomech. 2004, 3, 145–158. [Google Scholar]
- Miyama, M.; Nosaka, K. Influence of surface on muscle damage and soreness induced by consecutive drop jumps. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2004, 18, 206–211. [Google Scholar]
- Bobbert, M.F. Drop jumping as a training method for jumping ability. Sports Med. 1990, 9, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nédélec, M.; McCall, A.; Carling, C.; Le Gall, F.; Berthoin, S.; Dupont, G. Physical performance and subjective ratings after a soccer-specific exercise simulation: Comparison of natural grass versus artificial turf. J. Sports Sci. 2013, 31, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsanos, K.; Kitrou, P.; Spiliopoulos, S.; Maroulis, I.; Petsas, T.; Karnabatidis, D. Comparative effectiveness of different transarterial embolization therapies alone or in combination with local ablative or adjuvant systemic treatments for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, S.; Hume, P.; Kara, S. A review of football injuries on third and fourth generation artificial turfs compared with natural turf. Sports Med. 2011, 41, 903–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Study, Year of Publication | n | ♀ (%) | Age (Years) | Sport | Level | Surface | Test | Intervention | Recorded Distance * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binnie et al. (2013a) | - | 10 | 33 | 21.15 ± 2.70 | Netball and hockey | Well-trained | Natural turf and sand | RSA 8 × 20 m | - | 20 m |
| Binnie et al. (2013b) | - | 10 | 20 | 21.40 ± 1.80 | Netball and hockey | Well-trained | Natural turf and sand | RSA 8 × 20 m | - | 20 m |
| Binnie et al. (2014) | (A) | 24 | 100 | 20.05 ± 5.70 | Netball and hockey | Well-trained | Natural turf and sand | 20 m sprint test | 8-week pre-season conditioning program | 5 m |
| (B) | 10 m | |||||||||
| (C) | 20 m | |||||||||
| Choi et al. (2015) | - | 12 | 0 | 21.20 ± 2.00 | Rugby | Semi-professional | Natural and artificial turf | 40 m sprint test | - | 40 m |
| Gains et al. (2010) | - | 24 | 0 | 18.80 ± 0.40 | American football | Elite (2nd division) | Natural and artificial turf | 40 yd sprint | - | 40 yd (36.6 m) |
| Gaudino et al. (2013) | - | 29 | 0 | 19.00 ± 1.00 | Soccer | Elite | Natural turf, artificial turf and sand | 12 m sprint | - | 12 m |
| Hughes et al. (2013) | - | 17 | 0 | 22.80 ± 2.10 | Soccer | Semi-professional | Natural and artificial turf | 60 m sprint | soccer simulation protocol (SSP) | 60 m |
| Impellizzeri et al. (2008) | (A) | 44 | 0 | 25.00 ± 4.00 | Soccer | Amateur | Natural turf and sand | 10 m sprint test | 4-week plyometric training | 10 m |
| (B) | 20 m sprint test | 20 m | ||||||||
| Kanaras et al. (2014) | (A) | 32 | 0 | 14.00 ± 0.50 | Soccer | Amateur | Natural and artificial turf | multidirectional 30 m sprint test | - | 30 m |
| (B) | (Adolescent) | 10 m | ||||||||
| (C) | 36 | 0 | 12.00 ± 0.50 | Soccer | Amateur | Natural and artificial turf | - | 30 m | ||
| (D) | (Children) | 10 m | ||||||||
| Linthorne et al. (2013) | - | 6 | 0 | 20.00 ± 2.00 | Rugby | Amateur | Natural and artificial turf | 30 m sprint test | - | 30 m |
| Stone et al. (2014) | (A) | 8 | 0 | 20.30 ± 1.40 | Soccer | Elite (1st division) | Natural and artificial turf | 60 m sprint test | soccer simulation protocol (SSP) | 60 m |
| (B) | 10 m | |||||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sanchez-Sanchez, J.; Martinez-Rodriguez, A.; Felipe, J.L.; Hernandez-Martin, A.; Ubago-Guisado, E.; Bangsbo, J.; Gallardo, L.; Garcia-Unanue, J. Effect of Natural Turf, Artificial Turf, and Sand Surfaces on Sprint Performance. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17249478
Sanchez-Sanchez J, Martinez-Rodriguez A, Felipe JL, Hernandez-Martin A, Ubago-Guisado E, Bangsbo J, Gallardo L, Garcia-Unanue J. Effect of Natural Turf, Artificial Turf, and Sand Surfaces on Sprint Performance. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(24):9478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17249478
Chicago/Turabian StyleSanchez-Sanchez, Javier, Alejandro Martinez-Rodriguez, Jose Luis Felipe, Antonio Hernandez-Martin, Esther Ubago-Guisado, Jens Bangsbo, Leonor Gallardo, and Jorge Garcia-Unanue. 2020. "Effect of Natural Turf, Artificial Turf, and Sand Surfaces on Sprint Performance. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 24: 9478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17249478
APA StyleSanchez-Sanchez, J., Martinez-Rodriguez, A., Felipe, J. L., Hernandez-Martin, A., Ubago-Guisado, E., Bangsbo, J., Gallardo, L., & Garcia-Unanue, J. (2020). Effect of Natural Turf, Artificial Turf, and Sand Surfaces on Sprint Performance. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(24), 9478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17249478










