Contamination Level, Ecological Risk, and Source Identification of Heavy Metals in the Hyporheic Zone of the Weihe River, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of Study Area
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Quality Control and Quality Assurance
2.4. Analysis of Samples
2.5. Calculation of Pollution Levels
2.5.1. Geo-Accumulation Index (Igeo)
2.5.2. Enrichment Factor (EF)
2.5.3. Contamination Factor (CF)
2.6. Potential Ecological Risk and Risk Index
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Estimation of Heavy Metals in the Sediments of the Weihe River
3.2. Contamination Level
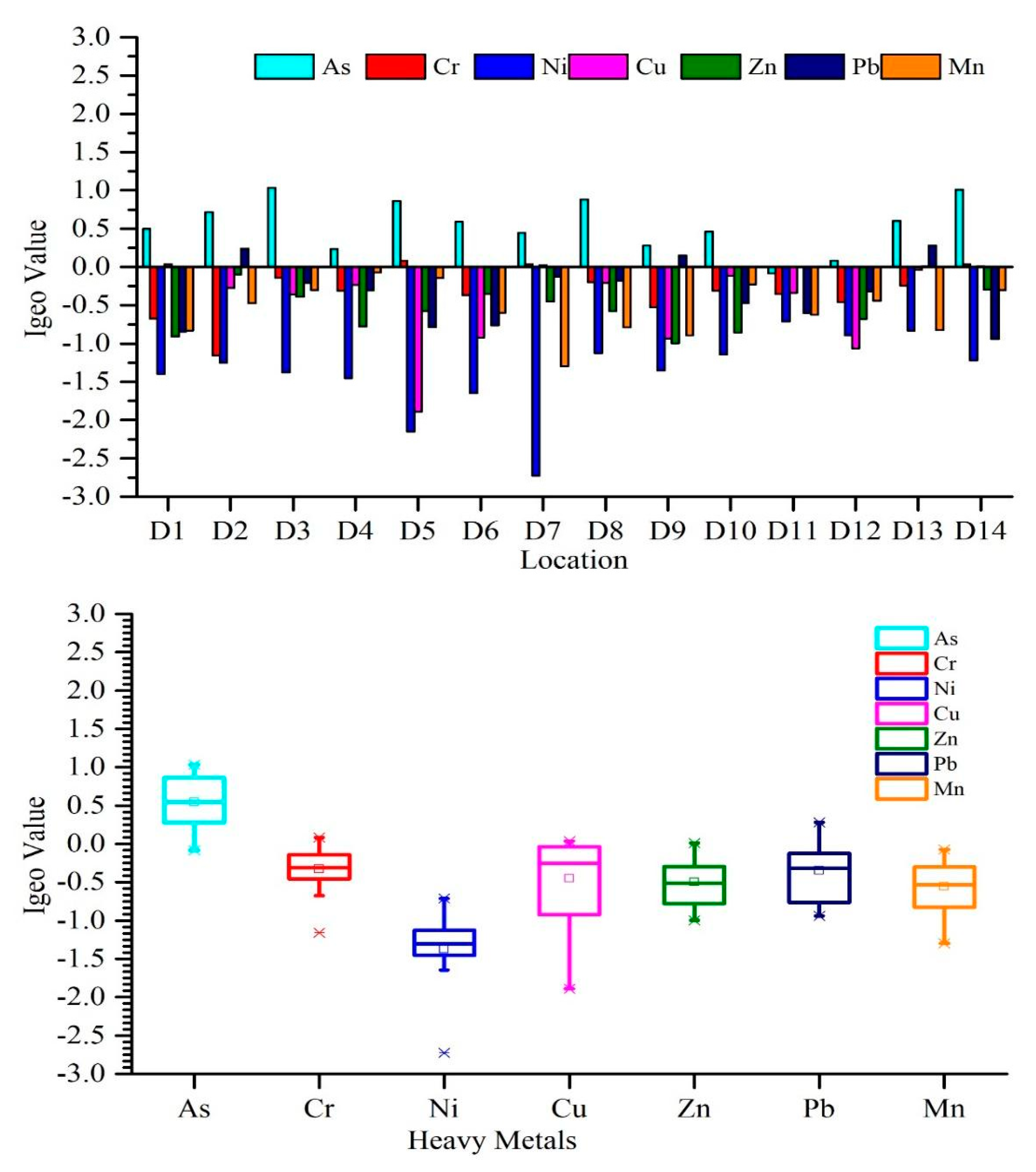
3.2.1. Geo-Accumulation Index (Igeo)
3.2.2. Enrichment Factor (EF)
3.2.3. Contamination Factor (CF)
3.3. Potential Ecological Risk and Risk Index
3.4. Correlation among Heavy Metals
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, J.; Long, Y.; Zhang, Y. Assessing the variability of heavy metal concentrations in liquid-solid two-phase and related environmental risks in the weihe river of Shaanxi province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 8243–8262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butturini, A.; Bernal, S.; Sabater, S.; Sabater, F. The influence of riparian-hyporheic zone on the hydrological responses in an intermittent stream. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 6, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ocampo-Duque, W.; Osorio, C.; Piamba, C.; Schuhmacher, M.; Domingo, J.L. Water quality analysis in rivers with non-parametric probability distributions and fuzzy inference systems: Application to the Cauca River, Colombia. Environ. Int. 2013, 52, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, P.J.; Jacobson, K.M. Hydrologic controls of physical and ecological processes in Namib Desert ephemeral rivers: Implications for conservation and management. J. Arid Environ. 2013, 93, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayllón, D.; Almodóvar, A.; Nicola, G.G.; Parra, I.; Elvira, B. Modelling carrying capacity dynamics for the conservation and management of territorial Salmonids. Fish. Res. 2012, 134–136, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilin, J.; Moreira, L.B.; Aguiar, J.E.; Marins, R.; Moledo de Souza Abessa, D.; Monteiro da Cruz Lotufo, T.; Costa-Lotufo, L.V. Sediment quality assessment in a tropical estuary: The case of Ceará River, Northeastern Brazil. Mar. Environ. Res. 2013, 91, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, N.; Wu, J.; Xiang, D.; Cheng, S.; Zhou, Q. A field study on seed bank and its potential applications in vegetation restoration of a polluted urban river in China. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 60, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Zhao, C.; Luo, Y.Y.; Liu, C.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Luo, Y.Y.; Zhao, D.; An, S.; Zhu, H. Heavy metals in surface sediments of the Jialu River, China: Their relations to environmental factors. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 270, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, K.; Kim, J.; Lee, M.; Park, S.; Kwon, H.J.; Cheong, H.K.; Jang, J.Y.; Kim, D.S.; Yu, S.; Kim, Y.W.; et al. Assessment of exposure to heavy metals and health risks among residents near abandoned metal mines in Goseong, Korea. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 178, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastami, K.D.; Bagheri, H.; Kheirabadi, V.; Zaferani, G.G.; Teymori, M.B.; Hamzehpoor, A.; Soltani, F.; Haghparast, S.; Harami, S.R.M.; Ghorghani, N.F.; et al. Distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments along southeast coast of the Caspian Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 81, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Bai, J.; Lu, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Gao, Z.; Wen, X.; Liu, X. Fractionation, transfer, and ecological risks of heavy metals in riparian and ditch wetlands across a 100-year chronosequence of reclamation in an estuary of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 517, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, G.; Ramasamy, V.; Sundarrajan, M.; Paramasivam, K. Spatial and vertical distributions of heavy metals and their potential toxicity levels in various beach sediments from high-background-radiation area, Kerala, India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 91, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duman, F.; Aksoy, A.; Demirezen, D. Seasonal variability of heavy metals in surface sediment of Lake Sapanca, Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 133, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deniseger, J.; Roch, M.; Clark, M.J.R. The effects of decreasing heavy metal concentrations on the biota of Buttle Lake. Water Res. 1990, 24, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Ansari, A.A.; Müller, G.; Singh, I.B. Heavy metals in freshly deposited sediments of the Gomati River (a tributary of the Ganga River) effects of human activities. Environ. Geol. 1997, 29, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calmano, W.; Ahlf, W.; Förstner, U. Exchange of Heavy Metals Between Sediment Components and Water. In Metal Speciation in the Environment; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1990; pp. 503–522. [Google Scholar]
- Batley, G.E. Trace Element Specification: Analytical Methods and Problems; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000; ISBN 9780849347122. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Wang, Z.; Shan, J.; Chen, J.; Tang, C.; Yi, M.; Zhao, X. Distribution characteristics and sources of trace metals in sediment cores from a trans-boundary watercourse: An example from the Shima River, Pearl River Delta. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 134, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.M.; Ali, M.L.; Islam, M.S.; Rahman, M.Z. Preliminary assessment of heavy metals in water and sediment of Karnaphuli River, Bangladesh. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2016, 5, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malvandi, H. Preliminary evaluation of heavy metal contamination in the Zarrin-Gol River sediments, Iran. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 117, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.F.; Song, Y.H.; Yuan, P.; Cui, X.Y.; Qiu, G.L. The remediation of heavy metals contaminated sediment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Wu, M.; Liao, S.; Zhang, D.; Pan, B. The sorption of heavy metals on thermally treated sediments with high organic matter content. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 160, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Mou, X.; Tong, C.; Wang, C.; Xie, Z.; Song, H.; Sun, W.; Lv, Y. Spatial variations and bioaccumulation of heavy metals in intertidal zone of the Yellow River estuary, China. Catena 2015, 126, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, S.; Shah, M.T.; Khan, S. Heavy metal concentrations in soil and wild plants growing around Pb-Zn sulfide terrain in the Kohistan region, northern Pakistan. Microchem. J. 2011, 99, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altın, A.; Filiz, Z.; Iscen, C.F. Assessment of seasonal variations of surface water quality characteristics for Porsuk Stream. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 158, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damian, F.; Damian, G.; Lǎcǎtuşu, R.; Iepure, G. Heavy metals concentration of the soils around Zlatna and Copşa Micǎ Smelters Romania. Carpathian J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2008, 3, 65–82. [Google Scholar]
- Pekey, H.; Karakaş, D.; Bakoǧlu, M. Source apportionment of trace metals in surface waters of a polluted stream using multivariate statistical analyses. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 49, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, A.; Zhai, S.; Matthias, Z.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, F. Heavy metals in Changjiang estuarine and offshore sediments: Responding to human activities. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2012, 31, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Feng, C.; Wang, D.; Liu, Y.; Shen, Z. Salinity increases the mobility of Cd, Cu, Mn, and Pb in the sediments of Yangtze Estuary: Relative role of sediments’ properties and metal speciation. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 977–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olawoyin, R.; Oyewole, S.A.; Grayson, R.L. Potential risk effect from elevated levels of soil heavy metals on human health in the Niger delta. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 85, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeel, M.; Lee, J.Y.; Zain, M.; Rizwan, M.; Nawab, A.; Ahmad, M.A.; Shafiq, M.; Yi, H.; Jilani, G.; Javed, R.; et al. Cryptic footprints of rare earth elements on natural resources and living organisms. Environ. Int. 2019, 127, 785–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejna, M.; Gottardo, D.; Baldi, A.; Dell’Orto, V.; Cheli, F.; Zaninelli, M.; Rossi, L. Review: Nutritional ecology of heavy metals. Animal 2018, 12, 2156–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, J.; Wang, Y.; Istanbulluoglu, E.; Bai, T.; Huang, Q.; Yang, D.; Huang, S. Impact of climate change and human activities on runoff in the Weihe River Basin, China. Quat. Int. 2015, 380–381, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Xu, Z.; Hui, Y.; Li, H.; Li, Q. Instream flow requirements for sediment transport in the lower Weihe River. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 3547–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Gao, B.; Xu, D.; Peng, W.; Lu, J. Multiple assessments of trace metals in sediments and their response to the water level fluctuation in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varol, M. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Tigris River (Turkey) using pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 195, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekaran, A.; Ravisankar, R.; Harikrishnan, N.; Satapathy, K.K.; Prasad, M.V.R.; Kanagasabapathy, K.V. Multivariate statistical analysis of heavy metal concentration in soils of Yelagiri Hills, Tamilnadu, India - Spectroscopical approach. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 137, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhuiyan, M.A.H.; Parvez, L.; Islam, M.A.; Dampare, S.B.; Suzuki, S. Heavy metal pollution of coal mine-affected agricultural soils in the northern part of Bangladesh. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 173, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohiuddin, K.M.; Zakir, H.M.; Otomo, K.; Sharmin, S.; Shikazono, N. Geochemical distribution of trace metal pollutants in water and sediments of downstream of an urban river. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 7, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santos Bermejo, J.C.; Beltrán, R.; Gömez Ariza, J.L. Spatial variations of heavy metals contamination in sediments from Odiel river (Southwest Spain). Environ. Int. 2003, 29, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turekian, K.K.; Wedepohl, K.H. Distribution of some major elements of the Earth’s crust. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1961, 72, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Uría, A.; López-Mateo, C.; Roca, E.; Fernández-Marcos, M.L. Source identification of heavy metals in pastureland by multivariate analysis in NW Spain. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinex, S.A.; Helz, G.R. Regional geochemistry of trace elements in Chesapeake Bay sediments. Environ. Geol. 1981, 3, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, K.; Ram Mohan, V.; Szefer, P. Evaluation of metal contamination in coastal sediments of the Bay of Bengal, India: Geochemical and statistical approaches. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 49, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayadi, M.H.; Sayyed, M.R.G.; Kumar, S. Short-term accumulative signatures of heavy metals in river bed sediments in the industrial area, Tehran, Iran. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 162, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salati, S.; Moore, F. Assessment of heavy metal concentration in the Khoshk River water and sediment, Shiraz, Southwest Iran. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 164, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, B.; Ismail, A.; Arshad, A.; Yap, C.K.; Kamarudin, M.S. Anthropogenic impacts on heavy metal concentrations in the coastal sediments of Dumai, Indonesia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 148, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loska, K.; Wiechula, D.; Barska, B.; Cebula, E.; Chojnecka, A. Assessment of arsenic enrichment of cultivated soils in Southern Poland. Polish J. Environ. Stud. 2003, 12, 187–192. [Google Scholar]
- Birch, G.F.; Olmos, M.A. Sediment-bound heavy metals as indicators of human influence and biological risk in coastal water bodies. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2008, 65, 1407–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakan, S.M.; Dordević, D.S.; Manojlović, D.D.; Predrag, P.S. Assessment of heavy metal pollutants accumulation in the Tisza river sediments. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 3382–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. Stress testing and the new technetium-99m cardiac imaging agents. Am. J. Card. Imaging 1979, 5, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Pejman, A.; Nabi Bidhendi, G.; Ardestani, M.; Saeedi, M.; Baghvand, A. A new index for assessing heavy metals contamination in sediments: A case study. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 58, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, L.; Li, H.; Yang, Z.; Min, X.; Liao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Men, S.; Yan, Y.; Xu, J. Heavy metals and metalloids in the surface sediments of the Xiangjiang River, Hunan, China: Distribution, contamination, and ecological risk assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, X.; Gui, S.; Huang, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Guo, W. Ecological risk assessment and source identification for heavy metals in surface sediment from the Liaohe River protected area, China. Chemosphere 2017, 175, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, J.; Xiong, K.; Huang, X.; Duan, S. Distribution of Heavy Metals in Core Sediments from Baihua Lake. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 16, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alyazichi, Y.M.; Jones, B.G.; McLean, E.; Pease, J.; Brown, H. Geochemical Assessment of Trace Element Pollution in Surface Sediments from the Georges River, Southern Sydney, Australia. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 72, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, L.; Yang, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, L. Source identification and risk assessment of heavy metal contaminations in urban soils of Changsha, a mine-impacted city in Southern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 17058–17066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohiuddin, K.M.; Otomo, K.; Ogawa, Y.; Shikazono, N. Seasonal and spatial distribution of trace elements in the water and sediments of the Tsurumi River in Japan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanif, N.; Eqani, S.A.M.A.S.; Ali, S.M.; Cincinelli, A.; Ali, N.; Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Tanveer, Z.I.; Bokhari, H. Geo-accumulation and enrichment of trace metals in sediments and their associated risks in the Chenab River, Pakistan. J. Geochem. Explor. 2016, 165, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karageorgis, A.; Nikolaidis, N.; Karamanos, H.; Skoulikidis, N. Water and sediment quality assessment of the Axios River and its coastal environment. Cont. Shelf Res. 2003, 23, 1929–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, A.; Erratico, C.; Viganò, L. Assessment of the environmental significance of heavy metal pollution in surficial sediments of the River Po. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson-Edwards, K.A.; Macklin, M.G.; Taylor, M.P. 2000 years of sediment-borne heavy metal storage in the Yorkshire Ouse basin, NE England, UK. Hydrol. Process. 1999, 13, 1087–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yin, P.; Chen, B.; Gao, F.; Song, H.; Li, M. Distribution and contamination assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of the Luanhe River Estuary, northwest of the Bohai Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 109, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.; Wu, F.; Mo, C.; Liu, B.; Zhu, J.; Deng, Q.; Liao, H.; Zhang, Y. Bioaccumulation of antimony, arsenic, and mercury in the vicinities of a large antimony mine, China. Microchem. J. 2011, 97, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Li, H.; Tu, Y.; Liu, B.; Yang, Z. Assessment of heavy metal contamination, distribution and source identification in the sediments from the Zijiang River, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Niu, J.; Tang, Z. Distribution and speciation of heavy metals in sediments from the mainstream, tributaries, and lakes of the Yangtze River catchment of Wuhan, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 1186–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.C.; Xu, J.; Liu, C.C.; Zhang, P.; Dai, M. Heavy metals in the surface sediments in Lanzhou Reach of Yellow River, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 82, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Ahmed, M.K.; Raknuzzaman, M.; Habibullah -Al- Mamun, M.; Islam, M.K. Heavy metal pollution in surface water and sediment: A preliminary assessment of an urban river in a developing country. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.P.; Malik, A.; Sinha, S.; Singh, V.K.; Murthy, R.C. Estimation of Source of Heavy Metal Contamination in Sediments of Gomti River (India) using Principal Component Analysis. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2005, 166, 321–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares-Rieumont, S.; de la Rosa, D.; Lima, L.; Graham, D.W.; D’Alessandro, K.; Borroto, J.; Martínez, F.; Sánchez, J. Assessment of heavy metal levels in Almendares River sediments—Havana City, Cuba. Water Res. 2005, 39, 3945–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rifaat, A.E. Major controls of metals distribution in sediments of the Nile Delta, Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2005, 31, 16–28. [Google Scholar]
- Heiny, J.S.; Tate, C.M. Concentration, Distribution, and Comparison of Selected Trace Elements in Bed Sediment and Fish Tissue in the South Platte River Basin, USA, 1992–1993. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1997, 32, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbassi, A.R.; Monavari, S.M.; Nabi Bidhendi, G.R.; Nouri, J.; Nematpour, K. Metal pollution assessment of sediment and water in the Shur River. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 147, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maanan, M.M.; Saddik, M.; Maanan, M.M.; Chaibi, M.; Assobhei, O.; Zourarah, B. Environmental and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Nador lagoon, Morocco. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, G.; Ramasamy, V.; Meenakshisundaram, V.; Venkatachalapathy, R.; Ponnusamy, V. Influence of mineralogical and heavy metal composition on natural radionuclide concentrations in the river sediments. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2011, 69, 1466–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, N.; Laursen, J.; Viksna, A.; Pind, N.; Holm, P.E. Multi-elemental EDXRF mapping of polluted soil from former horticultural land. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Su, P.; Lin, Q.; Song, J.; Sun, H.; Cheng, D.; Wang, S.; Peng, J.; Fu, J. Distribution, assessment and coupling relationship of heavy metals and macroinvertebrates in sediments of the Weihe River Basin. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 50, 101665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facetti, J.; Dekov, V.M.; Van Grieken, R. Heavy metals in sediments from the Paraguay river: A preliminary study. Sci. Total Environ. 1998, 209, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paine, A.J. Mechanisms of chromium toxicity, carcinogenicity and allergenicity: Review of the literature from 1985 to 2000. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2001, 20, 439–451. [Google Scholar]
- Bhuiyan, M.A.H.; Suruvi, N.I.; Dampare, S.B.; Islam, M.A.; Quraishi, S.B.; Ganyaglo, S.; Suzuki, S. Investigation of the possible sources of heavy metal contamination in lagoon and canal water in the tannery industrial area in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 175, 633–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazarika, N.; Srivastava, A.; Das, A. Quantification of particle bound metallic load and PAHs in urban environment of Delhi, India: Source and toxicity assessment. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 29, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, C.L. Riverine composition and estuarine geochemistry of particulate metals in China—Weathering features, anthropogenic impact and chemical fluxes. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2002, 54, 1051–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezgin, N.; Ozcan, H.K.; Demir, G.; Nemlioglu, S.; Bayat, C. Determination of heavy metal concentrations in street dusts in Istanbul E-5 highway. Environ. Int. 2004, 29, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Igeo | EF | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Igeo Classes | Sediment quality | EF Class | Sediment quality |
| No pollution | No pollution | ||
| No to moderate pollution | Very small pollution | ||
| Moderate pollution | Deficiency to small pollution | ||
| Moderate to heavy pollution | Moderate to high pollution | ||
| Heavy pollution | High pollution | ||
| Heavy to extreme pollution | Very high pollution | ||
| Extreme pollution | Exceptionally high pollution | ||
| ER Level | Value of ER | Risk | Value of RI | Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Low | Low | ||
| 1 | Moderate | Moderate | ||
| 2 | Considerable | Considerable | ||
| 3 | High | Very High | ||
| 4 | Very High |
| Location | As | Cr | Ni | Cu | Zn | Pb | Mn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | 27.55 | 84.64 | 38.76 | 69.34 | 75.84 | 16.72 | 716.34 |
| D2 | 31.98 | 60.54 | 42.83 | 55.77 | 133.27 | 35.42 | 918.44 |
| D3 | 39.93 | 122.66 | 39.28 | 52.63 | 108.65 | 25.94 | 1036.63 |
| D4 | 22.89 | 108.79 | 37.28 | 57.44 | 82.98 | 24.25 | 1212.79 |
| D5 | 35.43 | 142.93 | 22.98 | 18.23 | 95.75 | 17.46 | 1152.61 |
| D6 | 29.38 | 104.74 | 32.63 | 35.53 | 111.45 | 17.68 | 842.41 |
| D7 | 26.62 | 138.67 | 15.43 | 68.40 | 104.27 | 27.57 | 519.25 |
| D8 | 35.98 | 117.87 | 46.68 | 58.47 | 95.64 | 26.49 | 738.43 |
| D9 | 23.69 | 93.78 | 39.98 | 35.39 | 71.32 | 33.30 | 686.94 |
| D10 | 26.88 | 108.67 | 46.24 | 62.43 | 78.74 | 21.63 | 1088.73 |
| D11 | 18.43 | 105.67 | 62.38 | 53.45 | 141.83 | 19.75 | 828.73 |
| D12 | 20.67 | 98.46 | 54.94 | 32.30 | 88.87 | 23.99 | 940.64 |
| D13 | 29.59 | 113.87 | 57.46 | 65.94 | 143.64 | 36.39 | 718.64 |
| D14 | 39.24 | 138.37 | 43.76 | 67.93 | 116.28 | 15.62 | 1035.43 |
| Minimum | 18.43 | 60.54 | 15.43 | 18.23 | 71.32 | 15.62 | 519.25 |
| Maximum | 39.93 | 142.93 | 62.38 | 69.34 | 143.64 | 36.39 | 1212.79 |
| Average | 29.16 | 109.98 | 41.47 | 52.37 | 103.47 | 24.44 | 888.29 |
| River | Cu | As | Cr | Ni | Zn | Mn | Pb | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weihe River, Xian, China | 18.23–69.34 | 18.43–39.93 | 60.54–142.93 | 15.43–62.38 | 71.32–143.64 | 519.25–1212.79 | 15.62–36.39 | This Study |
| Zijiang River, Hunan, China | 18.37–59.01 | 6.90–74.34 | 48.47–95.32 | 21.50–52.29 | 42.41–251.61 | 570.75–2106.73 | 12.70–104.32 | [65] |
| Yangtze River, China | 129 | 29.90 | 205 | NA | 1142 | NA | 98 | [66] |
| Jialu River, China | 8.82–107.61 | 2.39–14.57 | 40.04–96.39 | 19.75–80.26 | 42.39–210.00 | NA | 14.79–51.17 | [64] |
| Luanhe River, China | NA | 3.4–13.5 | 9.6–35.6 | 3.5–35.8 | NA | NA | 22.6–43.7 | [63] |
| Yellow River, China | 30–102 | 14–48 | 41–128 | NA | NA | NA | 26–78 | [67] |
| Korotoa River, Bangladesh | 76 | 25 | 109 | 95 | NA | NA | 58 | [68] |
| Axios River, Greece | 93 | 40 | 180 | 188 | 271 | NA | 140 | [60] |
| River Po, Italy | 90.1 | NA | NA | 16198.5 | 645 | NA | 98.5 | [61] |
| Gomti River, India | 245.33 | NA | 88.7 | 76.08 | 343.47 | 834.7 | 156.2 | [69] |
| Chenab River, Pakistan | 5.80–9.40 | NA | NA | NA | 11.7–50.5 | 245–851 | 2.4–32.4 | [59] |
| Almendares River, Cuba | 420.8 | NA | 23.4 | NA | 708.8 | NA | 189 | [70] |
| Nile River Egypt | 81 | NA | 274 | 112 | 221 | 2810 | 23.2 | [71] |
| South Platte River, USA | 480 | 31 | 71 | NA | 3700 | 6700 | 270 | [72] |
| Tees River, UK | 76.9 | NA | NA | NA | 1920 | 5240 | 6880 | [62] |
| As | Cr | Ni | Cu | Zn | Pb | Mn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | 1 | ||||||
| Cr | 0.389 * | 1 | |||||
| Ni | −0.289 | −0.380 ** | 1 | ||||
| Cu | 0.092 ** | −0.032 | 0.157 | 1 | |||
| Zn | 0.146 | 0.008 * | 0.361 ** | 0.203 ** | 1 | ||
| Pb | −0.083 | −0.367 | 0.170 * | 0.120 | 0.242 ** | 1 | |
| Mn | 0.214 ** | 0.132 | 0.046 | −0.286 * | −0.132 | −0.365 ** | 1 |
| Metals | Components | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| As | 0.805 | −0.049 | 0.164 |
| Cr | 0.788 | −0.157 | −0.153 |
| Ni | −0.510 | −0.112 | 0.741 |
| Cu | 0.205 | 0.551 | 0.352 |
| Zn | 0.164 | 0.218 | 0.810 |
| Pb | −0.308 | 0.623 | 0.213 |
| Mn | 0.126 | −0.868 | 0.140 |
| Eigenvalue | 2.093 | 1.421 | 1.171 |
| % Total variance | 29.898 | 20.203 | 16.725 |
| Cumulative % variance | 29.898 | 50.201 | 66.926 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahamad, M.I.; Song, J.; Sun, H.; Wang, X.; Mehmood, M.S.; Sajid, M.; Su, P.; Khan, A.J. Contamination Level, Ecological Risk, and Source Identification of Heavy Metals in the Hyporheic Zone of the Weihe River, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1070. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17031070
Ahamad MI, Song J, Sun H, Wang X, Mehmood MS, Sajid M, Su P, Khan AJ. Contamination Level, Ecological Risk, and Source Identification of Heavy Metals in the Hyporheic Zone of the Weihe River, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(3):1070. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17031070
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhamad, Muhammad Irfan, Jinxi Song, Haotian Sun, Xinxin Wang, Muhammad Sajid Mehmood, Muhammad Sajid, Ping Su, and Asif Jamal Khan. 2020. "Contamination Level, Ecological Risk, and Source Identification of Heavy Metals in the Hyporheic Zone of the Weihe River, China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 3: 1070. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17031070
APA StyleAhamad, M. I., Song, J., Sun, H., Wang, X., Mehmood, M. S., Sajid, M., Su, P., & Khan, A. J. (2020). Contamination Level, Ecological Risk, and Source Identification of Heavy Metals in the Hyporheic Zone of the Weihe River, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(3), 1070. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17031070





