Effect of Frequency of Exercise on Cognitive Function in Older Adults: Serial Mediation of Depression and Quality of Sleep
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Physical Activity as a Positive Lifestyle for Cognitive Function
1.2. Mental Health and Sleep Quality as Mediators
1.3. A Mutual Relationship between Depression and Sleep Quality
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Instruments
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive
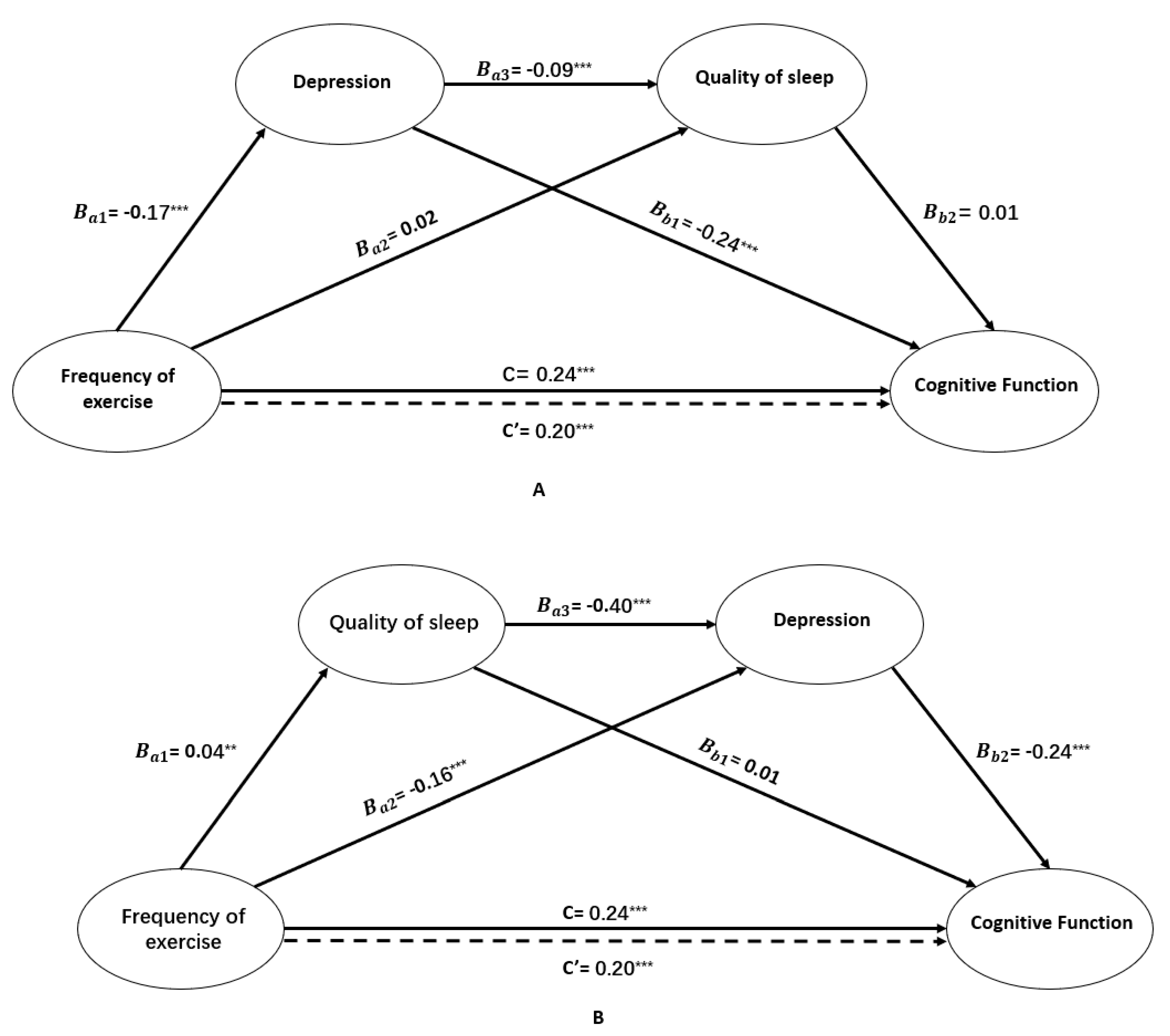
3.2. Serial Multiple Mediational Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Availability of Data and Materials
References
- Karp, A.; Paillard-Borg, S.; Wang, H.X.; Silverstein, M.; Winblad, B.; Fratiglioni, L. Mental, physical and social components in leisure activities equally contribute to decrease dementia risk. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2006, 21, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaynman, S.; Gomez-Pinilla, F. Revenge of the “sit”: How lifestyle impacts neuronal and cognitive health through molecular systems that interface energy metabolism with neuronal plasticity. J. Neurosci. Res. 2010, 84, 699–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, R.S.; Mendes de Leon, C.F.; Barnes, L.L.; Schneider, J.A.; Bienias, J.L.; Evans, D.A.; Bennett, D.A. Participation in cognitively stimulating activities and risk of incident Alzheimer disease. JAMA 2002, 287, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robitaille, A.; Muniz, G.; Lindwall, M.; Piccinin, A.M.; Hoffman, L.; Johansson, B.; Hofer, S.M. Physical activity and cognitive functioning in the oldest old: Within- and between-person cognitive activity and psychosocial mediators. Eur. J. Ageing 2014, 11, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vance, D.E.; Wadley, V.G.; Ball, K.K.; Roenker, D.L.; Rizzo, M. The effects of physical activity and sedentary behavior on cognitive health in older adults. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2005, 13, 294–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soni, M.; Orrell, M.; Bandelow, S.; Steptoe, A.; Rafnsson, S.; d’Orsi, E.; Xavier, A.; Hogervorst, E. Physical activity pre- and post-dementia: English Longitudinal Study of Ageing. Aging Ment. Health 2019, 23, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reas, E.T.; Laughlin, G.A.; Bergstrom, J.; Kritz-Silverstein, D.; Richard, E.L.; Barrett-Connor, E.; McEvoy, L.K. Lifetime physical activity and late-life cognitive function: The Rancho Bernardo study. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.K.; Etnier, J.L. The dose-response relationship between resistance exercise intensity and cognitive performance: Does heart rate mediate this effect? Int. J. Sport Psychol. 2013, 44, 37–54. [Google Scholar]
- Oberlin, L.E.; Verstynen, T.D.; Burzynska, A.Z.; Voss, M.W.; Prakash, R.S.; Chaddock-Heyman, L.; Wong, C.; Fanning, J.; Awick, E.; Gothe, N. White matter microstructure mediates the relationship between cardiorespiratory fitness and spatial working memory in older adults. Neuroimage 2016, 131, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makizako, H.; Liu-Ambrose, T.; Shimada, H.; Doi, T.; Park, H.; Tsutsumimoto, K.; Uemura, K.; Suzuki, T. Moderate-intensity physical activity, hippocampal volume, and memory in older adults with mild cognitive impairment. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2015, 70, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penedo, F.J.; Dahn, J.R. Exercise and well-being: A review of mental and physical health benefits associated with physical activity. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2005, 18, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreas, S.H. Physical activity, exercise, depression and anxiety disorders. J. Neural Transm. 2009, 116, 777–784. [Google Scholar]
- Hallgren, M.; Nguyen, T.T.; Owen, N.; Stubbs, B.; Vancampfort, D.; Lundin, A.; Dunstan, D.; Bellocco, R.; Lagerros, Y.T. Cross-sectional and prospective relationships of passive and mentally active sedentary behaviours and physical activity with depression. Br. J. Psychiatry 2019, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollak, M.J.; Milte, C.M.; van der Pligt, P.; Teychenne, M. Total physical activity but not diet quality associated with postnatal depressive symptoms amongst women living in socioeconomically disadvantaged neighborhoods. Nutr. Res. 2019, 68, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, J.L.; Brickman, A.M.; Lang, R.; Byrd, G.S.; Haines, J.L.; Pericak-Vance, M.A.; Manly, J.J. Relationship Between Depressive Symptoms and Cognition in Older, Non-demented African Americans. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2014, 20, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, P.B.; Mielke, M.M.; Xue, Q.L.; Carlson, M.C. Depressive symptoms predict incident cognitive impairment in cognitive healthy older women. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2010, 18, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClintock, S.A.; Husain, M.M.; Greer, T.L.; Cullum, C.M. Association Between Depression Severity and Neurocognitive Function in Major Depressive Disorder: A Review and Synthesis. Neuropsychology 2010, 24, 9–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Monica, C.; Johnsen, S.; Atzori, G.; Groeger, J.A.; Dijk, D.J. Rapid Eye Movement Sleep, Sleep Continuity and Slow Wave Sleep as Predictors of Cognition, Mood, and Subjective Sleep Quality in Healthy Men and Women, Aged 20-84 Years. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubitz, K.A.; Landers, D.M.; Petruzzello, S.J.; Han, M. The effects of acute and chronic exercise on sleep. A meta-analytic review. Sports Med. 1996, 21, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngstedt, S.D.; O’Connor, P.J.; Dishman, R.K. The effects of acute exercise on sleep: A quantitative synthesis. Sleep 1997, 20, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kredlow, M.A.; Capozzoli, M.C.; Hearon, B.A.; Calkins, A.W.; Otto, M.W. The effects of physical activity on sleep: A meta-analytic review. J. Behav. Med. 2015, 38, 427–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneita, Y.; Ohida, T.; Uchiyama, M.; Takemura, S.; Kawahara, K.; Yokoyama, E.; Miyake, T.; Harano, S.; Suzuki, K.; Fujita, T. The relationship between depression and sleep disturbances: A Japanese nationwide general population survey. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2006, 67, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.K.; Shi, L.; Bao, Y.P.; Sun, Y.; Shi, J.; Lu, L. The bidirectional relationship between sleep duration and depression in community-dwelling middle-aged and elderly individuals: Evidence from a longitudinal study. Sleep Med. 2018, 52, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shochat, T.; Cohen-Zion, M.; Tzischinsky, O. Functional consequences of inadequate sleep in adolescents: A systematic review. Sleep Med. Rev. 2014, 18, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, L.C.; Pignone, M.P. Screening accuracy for late-life depression in primary care: A systematic review. J. Fam. Pract. 2003, 52, 956–965. [Google Scholar]
- Yesavage, J.A.; Brink, T.L.; Rose, T.L.; Lum, O.; Huang, V.; Adey, M.; Leirer, V.O. Development and validation of a geriatric depression screening scale: A preliminary report. J. Psychiatr. Res. 1982, 17, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saczynski, J.S.; Inouye, S.K.; Guess, J.; Jones, R.N.; Fong, T.G.; Nemeth, E.; Hondara, A.; Ngo, L.; Marcantonio, E.R. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA): Creating a Crosswalk with the Mini-Mental State Examination. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2014, 63, 2370–2374. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, J.; Li, N.; Gao, J.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, B.; Du, W.; Zhang, W.; Cui, L.; Wang, Q. Optimal cutoff scores for dementia and mild cognitive impairment of the Montreal Cognitive Assessment among elderly and oldest-old Chinese population. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2015, 43, 1403–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, A. Introduction to mediation, moderation, and conditional process analysis. Journal of Educational Measurement. 2013, 51, 335–337. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, S.; Xiong, L.; Mouni, T.; Ruoyan, H.; Junchang, Y.; Chungang, L.; Kangguang, L.; Yiwen, L.; Yanlin, Z. The application of Mini-Mental State Examination and Montreal cognitive assessment for mild cognitive impairment and dementia in community survey. Chin. J. Psychiatry 2014, 5, 293–297. [Google Scholar]
- Kalak, N.; Gerber, M.; Kirov, R.; Mikoteit, T.; Yordanova, J.; Puhse, U.; Holsboer-Trachsler, E.; Brand, S. Daily morning running for 3 weeks improved sleep and psychological functioning in healthy adolescents compared with controls. J. Adolesc. Health 2012, 51, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, S.C.J.; Chang, M.Y. The Effect of Qigong on Menopausal Symptoms and Quality of Sleep for Perimenopausal Women: A Preliminary Observational Study. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2012, 18, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.C.; Liu, H.E.; Huang, H.Y.; Chiou, A.F. The effect of a simple traditional exercise programme (Baduanjin exercise) on sleep quality of older adults: A randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2012, 49, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benitez, A.; Gunstad, J. Poor sleep quality diminishes cognitive functioning independent of depression and anxiety in healthy young adults. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2012, 26, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Mendoza, J.; Shea, S.; Vgontzas, A.N.; Calhoun, S.L.; Liao, D.; Bixler, E.O. Insomnia and incident depression: Role of objective sleep duration and natural history. J. Sleep Res. 2015, 24, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joao, K.; Jesus, S.N.; Carmo, C.; Pinto, P. The impact of sleep quality on the mental health of a non-clinical population. Sleep Med. 2018, 46, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneita, Y.; Yokoyama, E.; Harano, S.; Tamaki, T.; Suzuki, H.; Munezawa, T.; Nakajima, H.; Asai, T.; Ohida, T. Associations between sleep disturbance and mental health status: A longitudinal study of Japanese junior high school students. Sleep Med. 2009, 10, 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuch, F.B.; Vancampfort, D.; Richards, J.; Rosenbaum, S.; Ward, P.B.; Stubbs, B. Exercise as a treatment for depression: A meta-analysis adjusting for publication bias. J. Psychiatry Res. 2016, 77, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakody, K.; Gunadasa, S.; Hosker, C. Exercise for anxiety disorders: Systematic review. Br. J. Sports Med. 2014, 48, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassmen, P.; Koivula, N.; Uutela, A. Physical exercise and psychological well-being: A population study in Finland. Prev. Med. 2000, 30, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paluska, S.A.; Schwenk, T.L. Physical activity and mental health: Current concepts. Sports Med. 2000, 29, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falck, R.S.; Best, J.R.; Davis, J.C.; Liu-Ambrose, T. The Independent Associations of Physical Activity and Sleep with Cognitive Function in Older Adults. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 63, 1469–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebes, R.D.; Buysse, D.J.; Halligan, E.M.; Houck, P.R.; Monk, T.H. Self-reported sleep quality predicts poor cognitive performance in healthy older adults. J. Gerontol. B Psychol. Sci. Soc. Sci. 2009, 64, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Mean | SD | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Frequency of Exercise | 2.19 | 1.82 | NA | |||
| 2. Quality of Sleep | 2.39 | 1.05 | 0.08*** | NA | ||
| 3. Depression | 1.87 | 2.22 | −0.16*** | −0.21*** | NA | |
| 4. Cognitive Function | 21.61 | 4.92 | 0.20*** | 0.08*** | −0.21*** | NA |
| Bootstrapping | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effect | Product of Coefficients | 95% BCa Confidence Interval | ||
| Point Estimate | SE | Lower | Upper | |
| Total Indirect Effect | 0.1784 | 0.0543 | 0.1038 | 0.3158 |
| FOE→DEP→CF | 0.1762 | 0.0531 | 0.1034 | 0.3143 |
| FOE→DEP→QOS→CF | 0.0009 | 0.0055 | −0.0097 | 0.0122 |
| FOE→QOS→CF | 0.0013 | 0.0084 | −0.0125 | 0.0232 |
| Bootstrapping | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effect | Product of Coefficients | 95% BCa Confidence Interval | ||
| Point Estimate | SE | Lower | Upper | |
| Total Indirect Effect | 0.0428 | 0.0091 | 0.0265 | 0.0621 |
| FOE→QOS→CF | 0.0005 | 0.0030 | -0.0053 | 0.0070 |
| FOE→QOS→DEP→CF | 0.0036 | 0.0014 | 0.0014 | 0.0069 |
| FOE→DEP→CF | 0.0387 | 0.0085 | 0.0235 | 0.0567 |
| Specific Indirect Effect Contrast Definitions | ||||
| Path 1/Path 2 | −0.0350 | 0.0082 | −0.0525 | −0.0205 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, M.; Fu, H.; Liu, R.; Fang, Y. Effect of Frequency of Exercise on Cognitive Function in Older Adults: Serial Mediation of Depression and Quality of Sleep. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 709. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17030709
Yuan M, Fu H, Liu R, Fang Y. Effect of Frequency of Exercise on Cognitive Function in Older Adults: Serial Mediation of Depression and Quality of Sleep. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(3):709. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17030709
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Manqiong, Hanhan Fu, Ruoyun Liu, and Ya Fang. 2020. "Effect of Frequency of Exercise on Cognitive Function in Older Adults: Serial Mediation of Depression and Quality of Sleep" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 3: 709. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17030709
APA StyleYuan, M., Fu, H., Liu, R., & Fang, Y. (2020). Effect of Frequency of Exercise on Cognitive Function in Older Adults: Serial Mediation of Depression and Quality of Sleep. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(3), 709. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17030709





