Evaluation of the Pre-Planned and Non-Planed Agility Performance: Comparison between Individual and Team Sports
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Procedures
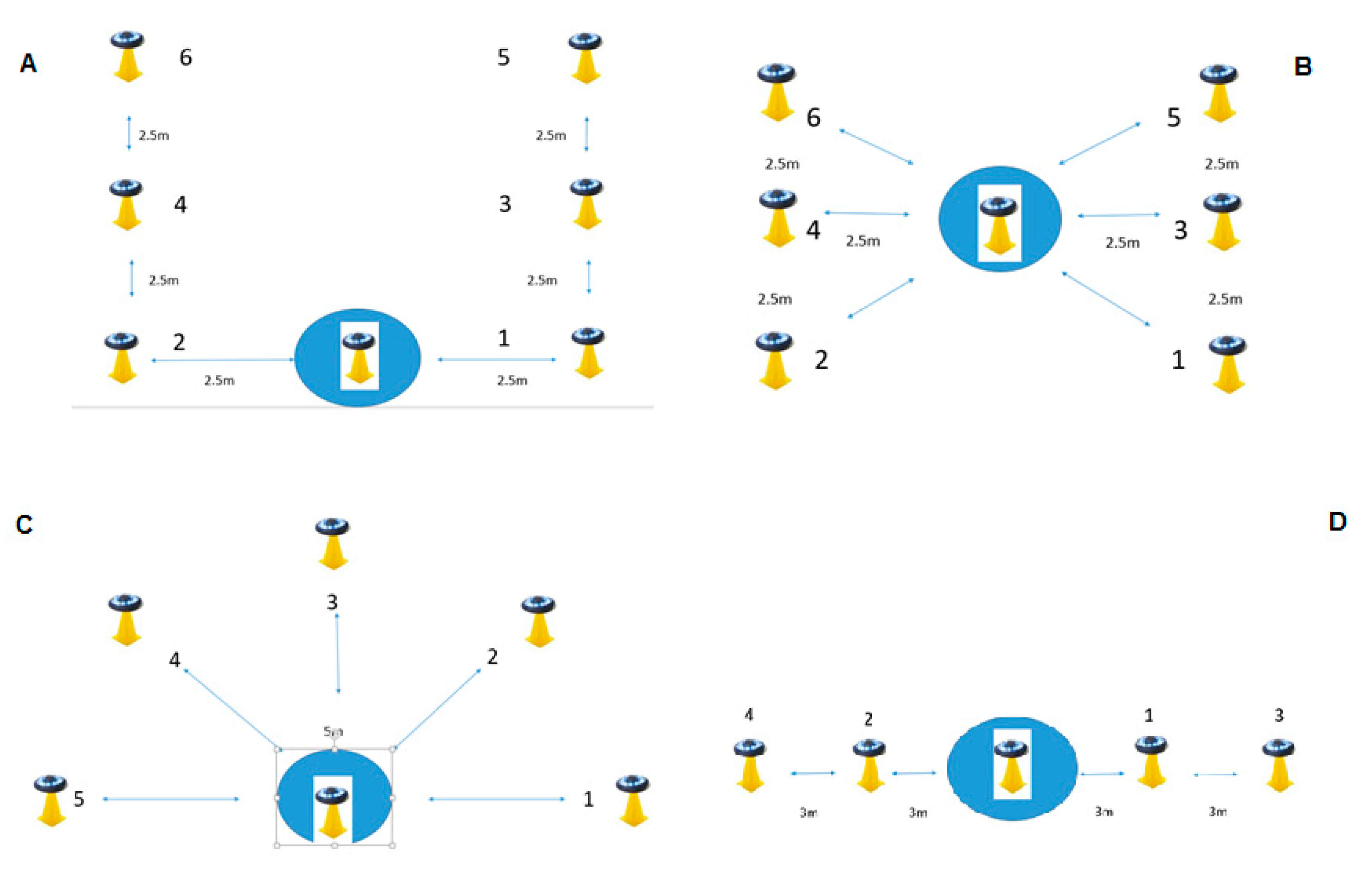
2.2.1. Agility Testing
2.2.2. Sprint and Explosive Power Testing
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Taylor, J. A conceptual model of the integration of athletic needs and sport demands in the development of competitive mental preparation strategies. Sport Psychol. 1995, 9, 339–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajbafnezhad, H.; Ahadi, H.; Heidarie, A.R.; Askarii, P.; Enayati, M.S. Difference between team and individual sports with respect to psychological skills, overall emotional intelligence and athletic success motivation in shiraz city athletes. J. Basic. Appl. Sci. Res. 2011, 1, 1904–1909. [Google Scholar]
- Mohr, M.; Krustrup, P.; Bangsbo, J. Match performance of high standard soccer players with special reference to development of fatigue. J. Sports Sci. 2003, 21, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varley, M.C.; Gabbett, T.; Aughey, R.J. Activity profiles of professional soccer, rugby league and Australian football match play. J. Sports Sci. 2014, 32, 1858–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.; McCahan, B.J. Teaching Games for Understanding as a Curriculum Model. Teaching Games for Understanding: Theory, Research, and Practice; Griffin, L., Butler, J., Eds.; Human Kinetics: Windsor, CA, USA, 2005; pp. 33–35. [Google Scholar]
- Gary, S.T. Basic Track and Field Biomechanics. 2015. Available online: https://www.slideshare.net/RonnieGary basic-track-field-biomechanics (accessed on 9 April 2019).
- Kłyszejko, W. An attempt to Systematize and Classify Sport Disciplines from the Point of View of Sport Combat; Selected Issues in Team Sports Theory (Próba usystematyzowania i klasyfikacji dyscyplin sportowych z punktu idzenia walki sportowej); AWF Publishing House: Warsaw, Poland, 1971. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Naglak, Z. Sport Training: Theory and Methodology (Trening sportowy: teoria i praktyka); Polska National Scientific Publishers: Warsaw, Poland, 1977; pp. 15–23. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Naglak, Z. Methodology of Training an Athlete (Metodyka trenowania sportowca); AWF Publishing House: Warsaw, Poland, 1999; pp. 18–21. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Verstegan, M.; Marcello., B. Agility and coordination. In High Performance Sports Conditioning; Foran, B., Ed.; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2001; pp. 139–165. [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg, P.M. Agility Training for Experienced Athletes: A Dynamical Systems Approach. Strength Cond. J. 2015, 3, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, W.B.; Dawson, B.; Henry, G.J. Agility and change of direction speed are independent skills: Implications for training for agility in invasion sports. Int. J. Sports Sci. Coach. 2015, 10, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, D.J.; Gabbett, T.J.; Nassis, G.P. Agility in team sports: Testing, training and factors affecting performance. Sports Med. 2016, 46, 421–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coh, M.; Vodicar, J.; Zvan, M.; Simenko, J.; Stodolka, J.; Rauter, S.; Mackala, K. Are change-of-direction speed and reactive agility independent skills even using the same movement pattern. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2018, 32, 1929–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, J.M.; Young, W.B. Agility literature review: Classifications, training and testing. J. Sports Sci. 2006, 24, 919–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spasic, M.; Uljevic, O.; Coh, M.; Dzelalija, M.; Sekulic, D. Predictors of early agility performance among pubescent girls. Int. J. Perform. Anal. Sport 2013, 13, 480–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakovljević, S.; Karalejić, M.; Pajić, Z.; Gardašević, B.; Mandić, R. The influence of anthropometric characteristics on the agility abilities of 14 year-old elite male basketball players. FU Phys. Ed. Sport. 2011, 9, 141–149. [Google Scholar]
- Lesinski, M.; Prieske, O.; Helm, N.; Granacher, U. Effects of soccer training on anthropometry, body composition, and physical fitness during a soccer season in female elite young athletes: A prospective cohort study. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milsom, J.; Naughton, R.; O’Boyle, A.; Iqbal, Z.; Morgans, R.; Drust, B.; Morton, J.P. Body composition assessment of English Premier League soccer players: A comparative DXA analysis of first team, U21 and U18 squads. J. Sports Sci. 2015, 33, 1799–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammami, M.A.; Ben Abderrahmane, A.; Nebigh, A.; Le Moal, E.; Ben Ounis, O.; Tabka, Z.; Zouhal, H. Effects of a soccer season on anthropometric characteristics and physical fitness in elite young soccer players. J. Sports Sci. 2013, 31, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atakan, M.M.; Unver, E.; Demirci, N.; Cinemre, A.; Bulut, S.; Turnagol, H.H. Effect of body composition on fitness performance in young male football players. J. Turkish Sport. Exerc. 2017, 19, 1–54. [Google Scholar]
- Pain, M.T.; Hibbs, A. Sprint starts and the minimum auditory reaction time. J. Sports Sci. 2007, 25, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tønnessen, E.; Haugen, T.; Shalfawi, S.A. Reaction time aspects of elite sprinters in athletic world championships. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2013, 27, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IAAF. Competition Rules 2018–2019. Available online: https://www.iaaf.org/about-iaaf/documents/rules-regulations (accessed on 11 April 2019).
- Magill, R.; Anderson, D. Motor Learning and Control: Concepts and Applications, 10th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Maćkala, K.; Michalski, R.; Stodółka, J.; Rausavljević, N.; Čoh, M. The relationship between selected motor ability determinants and anthropometric characteristicsin adolescent athletes from various sport. Coll. Antropol. 2015, 39 (Suppl. 1), 139–145. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, A.M.; Davids, K. Visual Search Strategy, Selective Attention, and Expertise in Soccer. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 1998, 69, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spierer, D.K.; Petersen, R.A.; Duffy, K. Response time to stimuli in division I soccer players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2011, 25, 1134–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuriato, M.; Lovecchio, N. Cognitive Training in Soccer: Where Is the Key Point. OALib J. 2018, 5e4333, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabbett, T.; Kelly, J.N.; Sheppard, J.M. Speed, change of direction speed, and reactive agility of rugby league players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2008, 22, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inglis, P.; Bird, S.P. Reactive agility tests-Review and practical applications. J. Aust. Strength Cond. 2016, 24, 62–69. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, J.B.; Wright, A.A.; Dischiavi, S.L.; Townsend, M.A.; Marmon, A.R. Activity Demands During Multi-Directional Team Sports: A Systematic Review. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 2533–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Per, A.F.H. Renström. In Handbook of Sports Medicine and Science, Tennis; Blackwell Science: Oxford, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Haj-Sassi, R.; Dardouri, W.; Gharbi, Z.; Chaouachi, A.; Mansour, H.; Rabhi, A.; Mahfoudhi, M. Reliability and validity of a new repeated agility test as a measure explosive of anaerobic and power. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2011, 25, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, R. Sport Psychology: Concepts and Applications, 5th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tønnessen, E.; Svendsen, I.S.; Olsen, I.C.; Guttormsen, A.; Haugen, T. Performance Development in Adolescent Track and Field Athletes According to Age, Sex and Sport Discipline. PLoS ONE 2015, 1, e0129014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackala, K.; Fostiak, M. Acute effects of plyometric intervention-performance improvement and related changes in sprinting gait variability. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2015, 29, 1956–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popowczak, M.; Rokita, A.; Świerzko, K.; Szczepan, S.; Michalski, R.; Maćkała, K. Are Linear Speed and Jumping Ability Determinants of Change of Direction Movements in Young Male Soccer Players? J. Sports Sci. Med. 2019, 8, 109–117. [Google Scholar]
- Henry, G.J.; Dawson, B.; Lay, B.S.; Young, W.B. Relationships between reactive agility movement time and unilateral, vertical, horizontal, and lateral jumps. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2016, 30, 2514–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | Group | N | Mean | SD | 95% Confidence Interval of the Mean | d | F | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||||||
| Age [years] | Individ. | 36 | 20.58 | 1.44 | 20.10 | 21.07 | 0.47 | 3.83 | 0.055 |
| Team | 34 | 21.32 | 1.72 | 20.72 | 21.92 | ||||
| Body height [cm] | Individ. | 36 | 174.08 | 8.41 | 171.24 | 176.93 | 0.54 | 4.90 | 0.030 |
| Team | 34 | 179.21 | 10.85 | 175.42 | 182.99 | ||||
| Body mass [kg] | Individ. | 36 | 68.77 | 11.34 | 64. 40 | 72.61 | 0.80 | 10.87 | 0.002 |
| Team | 34 | 78.13 | 12.39 | 73.80 | 82.45 | ||||
| Lower limb length [cm] | Individ. | 36 | 97.89 | 5.87 | 95.91 | 99.88 | 0.53 | 4.68 | 0.034 |
| Team | 34 | 101.23 | 7.02 | 98.78 | 103.68 | ||||
| Variables | Group | N | Mean | SD | 95% Confidence Interval of the Mean | F | p | d | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||||||
| FR-CODS [s] | Individ. | 36 | 16.68 | 1.77 | 16.08 | 17.28 | 1.51 | 0.223 | 0.30 |
| Team | 32 | 16.16 | 1.75 | 15.53 | 16.78 | ||||
| FR-RA [s] | Individ. | 35 | 19.08 | 1.87 | 18.44 | 19.73 | 0.97 | 0.328 | 0.25 |
| Team | 31 | 18.63 | 1.87 | 17.94 | 19.32 | ||||
| UN-CODS [s] | Individ. | 31 | 13.01 | 1.38 | 12.51 | 13.52 | 0.37 | 0.546 | 0.17 |
| Team | 25 | 13.25 | 1.53 | 12.62 | 13.88 | ||||
| UN-RA [s] | Individ. | 31 | 17.06 | 1.64 | 16.46 | 17.67 | 4.62 | 0.036 | 0.59 |
| Team | 24 | 16.02 | 1.96 | 15.19 | 16.85 | ||||
| SC-CODS [s] | Individ. | 29 | 16.81 | 1,29 | 16.32 | 17.31 | 5.18 | 0.027 | 0.62 |
| Team | 26 | 15.96 | 1.48 | 15.36 | 16.56 | ||||
| SC-RA [s] | Individ. | 28 | 18.94 | 1.19 | 18.48 | 19.40 | 2.11 | 0.153 | 0.42 |
| Team | 22 | 18.31 | 1.89 | 17.47 | 19.14 | ||||
| LA-CODS [s] | Individ. | 25 | 12.54 | 1.43 | 11.94 | 13.13 | 0.95 | 0.336 | 0.30 |
| Team | 20 | 12.12 | 1.41 | 11.46 | 12.78 | ||||
| LA-RA [s] | Individ. | 25 | 14.41 | 1.12 | 13.95 | 14.87 | 7.72 | 0.008 | 0.86 |
| Team | 19 | 13.37 | 1.37 | 12.71 | 14.03 | ||||
| Variables | Group | N | Mean | SD | 95% Confidence Interval of the Mean | Mean Square | F | p | d | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||||||
| S15m [s] | Individ. | 27 | 2.52 | 0.19 | 2.44 | 2.59 | 0.142 | 4.46 | 0.039 | 0.59 |
| Team | 27 | 2.62 | 0.16 | 2.55 | 2.68 | |||||
| F15m [s] | Individ. | 27 | 2.07 | 0.18 | 1.99 | 2.14 | 0.114 | 3.58 | 0.064 | 0.53 |
| Team | 27 | 1.98 | 0.17 | 1.91 | 2.04 | |||||
| SLJ10m–right leg [s] | Individ. | 27 | 2.69 | 0.39 | 2.54 | 2.83 | 0.789 | 5.82 | 0.020 | 0.78 |
| Team | 26 | 2.42 | 0.31 | 2.29 | 2.54 | |||||
| SLJ10m–left leg [s] | Individ. | 29 | 2.65 | 0.39 | 2.50 | 2.81 | 0.971 | 7.76 | 0.007 | 0.67 |
| Team | 26 | 2.41 | 0.34 | 2.27 | 2.55 | |||||
| Agility Performanc1 | Paired Differences | t | df | p | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | SEM | 95% Confidence Interval of the Difference | |||||||
| Lower | Upper | |||||||||
| Pair 1 | FR-CODS–FR-RA [s] | Team | −2232.52 | 1571.86 | 282.32 | −3109.08 | −1955.95 | −8.971 | 30 | 0.000 |
| Individ | –2547.68 | 1115.79 | 188.60 | –2930.95 | –2164.37 | –13.51 | 34 | |||
| Pair 2 | UN-CODS –UN-RA [s] | Team | −2929.00 | 2851.29 | 594.53 | −4161.99 | −1696.01 | −4.927 | 22 | 0.000 |
| Individ | −4048.39 | 2447.37 | 439.56 | −4946.09 | −3150.69 | −9.210 | 30 | |||
| Pair 3 | SC-CODS –SC-RA [s] | Team | −2337.41 | 1444.59 | 307.99 | −2977.90 | −1696.92 | −7.589 | 21 | 0.000 |
| Individ | −2171.50 | 1063.14 | 200.91 | −2583.74 | −1759.68 | −10.81 | 27 | |||
| Pair 4 | LA-CODS–LA-RA [s] | Team | −1314.89 | 652.67 | 149.73 | −1629.47 | −1000.32 | −8.782 | 18 | 0.000 |
| Individ | −1873.56 | 1346.79 | 269.36 | −2429.49 | −1317.63 | −6.96 | 24 | |||
| Agility Performance | Mean | SD | r | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pair 1 | FR-CODS | Team | 16.16 | 1.77 | 0.805 | 0.000 |
| Individ. | 16.68 | 1.75 | ||||
| FR-RA | Team | 18.63 | 1.87 | 0.622 | 0.000 | |
| Individ. | 19.08 | 1.87 | ||||
| Pair 2 | UN-CODS | Team | 13.25 | 1.53 | −0.308 | 0.152 |
| Individ. | 13.01 | 1.38 | ||||
| UN-RA | Team | 16.02 | 1.96 | −0.297 | 0.105 | |
| Individ. | 17.06 | 1.64 | ||||
| Pair 3 | SC-CODS | Team | 15.96 | 1.48 | 0.666 | 0.010 |
| Individ. | 16.81 | 1.29 | ||||
| SC-RA | Team | 18.31 | 1.89 | 0.636 | 0.000 | |
| Individ. | 18.94 | 1.19 | ||||
| Pair 4 | LA-CODS | Team | 12.12 | 1.41 | 0.890 | 0.010 |
| Individ. | 12.54 | 1.43 | ||||
| LA-RA | Team | 13.37 | 1.37 | 0.466 | 0.019 | |
| Individ. | 14.41 | 1.12 | ||||
| (A) | ||||||||||||||||
| Team Athletes | Variables | Individual Athletes | ||||||||||||||
| [8] | [7] | [6] | [5] | [4] | [3] | [2] | [1] | [1] | [2] | [3] | [4] | [5] | [6] | [7] | [8] | |
| 0.453 * | Body mass | –0.342 * | 0.452 * | –0.405 * | ||||||||||||
| –0.546 * | 0.401 * | Body high | –0.432 * | |||||||||||||
| –0.487 * | 0.515 * | Leg length | –0.456 * | |||||||||||||
| 0.655 * | –0.449 * | SLJ0m (LL) | 0.395 * | 0.460 * | ||||||||||||
| 0.566 * | –0.423 * | SLJ0m (RL) | 0.410 * | |||||||||||||
| 0.626 * | S15m | 0.465 * | 0.506 * | |||||||||||||
| 0.629 * | –0.491 * | F15m | ||||||||||||||
| [1] FR-CODS, [2] FR-RA, [3] UN-CODS, [4] UN-RA, [5] SC-CODS, [6] SC-RA, [7] LA-CODS, [8] LA-RA | ||||||||||||||||
| (B) | ||||||||||||||||
| Team Athletes | Variables | Individual Athletes | ||||||||||||||
| [8] | [7] | [6] | [5] | [4] | [3] | [2] | [1] | [1] | [2] | [3] | [4] | [5] | [6] | [7] | [8] | |
| 0.453 * | - | [1] FR-CODS | - | 0.373 * | ||||||||||||
| - | 0.622 * | [2] FR-RA | - | |||||||||||||
| - | [3] UNCODS | - | ||||||||||||||
| - | [4] UN-RA | 0.373 * | - | 0.483 * | ||||||||||||
| - | 0.453 * | [5] SC-CODS | - | |||||||||||||
| 0.624 * | - | [6] SC-RA | - | 0.414 * | ||||||||||||
| - | 0.606 * | [7] LA-CODS | - | 0.466 * | ||||||||||||
| - | [8] LA-RA | 0.483 * | 0.414 * | 0.466 * | - | |||||||||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mackala, K.; Vodičar, J.; Žvan, M.; Križaj, J.; Stodolka, J.; Rauter, S.; Šimenko, J.; Čoh, M. Evaluation of the Pre-Planned and Non-Planed Agility Performance: Comparison between Individual and Team Sports. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17030975
Mackala K, Vodičar J, Žvan M, Križaj J, Stodolka J, Rauter S, Šimenko J, Čoh M. Evaluation of the Pre-Planned and Non-Planed Agility Performance: Comparison between Individual and Team Sports. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(3):975. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17030975
Chicago/Turabian StyleMackala, Krzysztof, Janez Vodičar, Milan Žvan, Jožef Križaj, Jacek Stodolka, Samo Rauter, Jožef Šimenko, and Milan Čoh. 2020. "Evaluation of the Pre-Planned and Non-Planed Agility Performance: Comparison between Individual and Team Sports" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 3: 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17030975
APA StyleMackala, K., Vodičar, J., Žvan, M., Križaj, J., Stodolka, J., Rauter, S., Šimenko, J., & Čoh, M. (2020). Evaluation of the Pre-Planned and Non-Planed Agility Performance: Comparison between Individual and Team Sports. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(3), 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17030975








