Elongation of the Aorta after Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair: A longitudinal study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. CT Scan Parameters
2.3. TEVAR Procedure
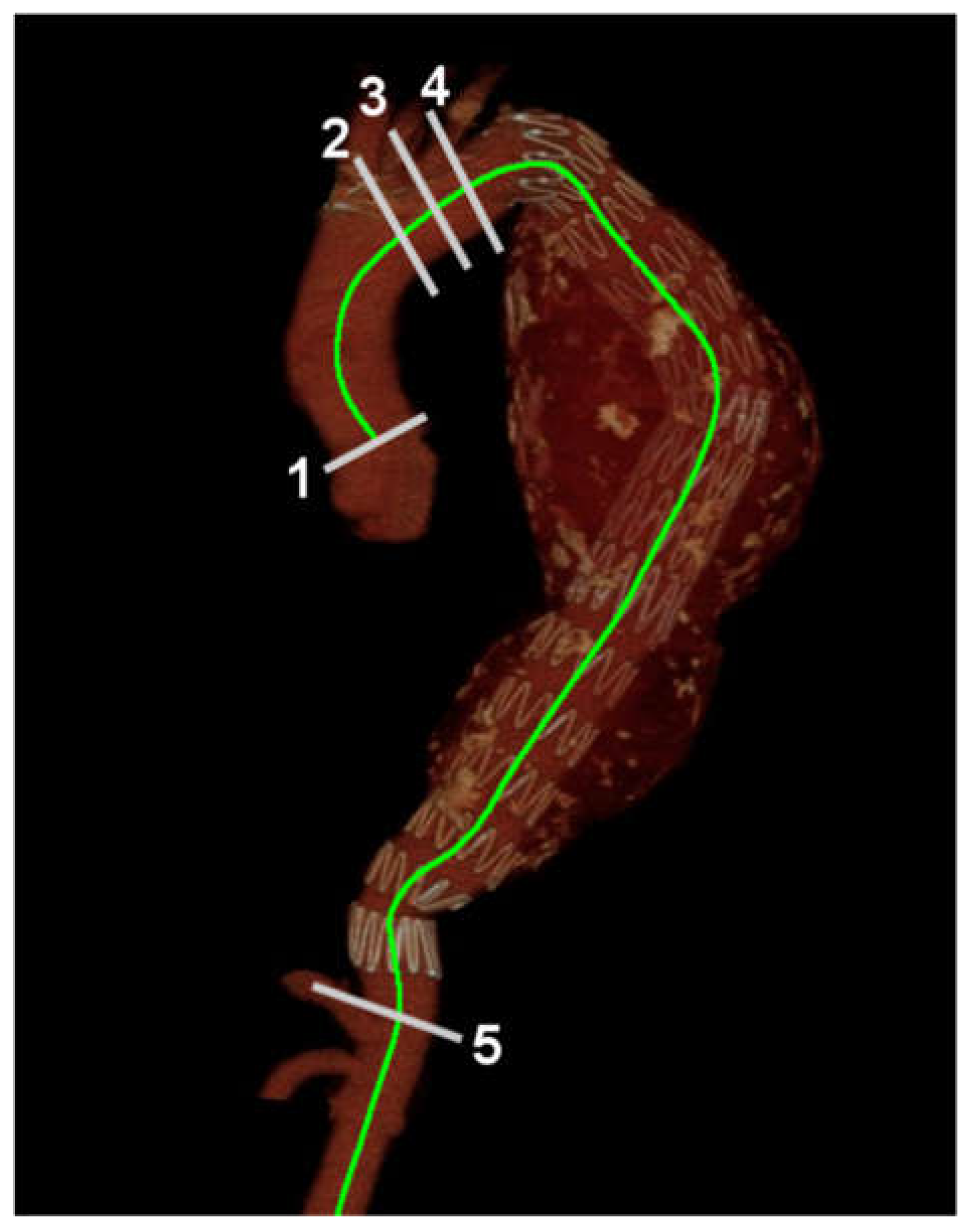
2.4. Aortic Length Measurement
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Aortic Length
3.2. Elongation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boufi, M.; Guivier-Curien, C.; Loundou, A.D.; Deplano, V.; Boiron, O.; Chaumoitre, K.; Gariboldi, V.; Alimi, Y.S. Morphological analysis of healthy aortic arch. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2017, 53, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adriaans, B.P.; Heuts, S.; Gerretsen, S.; Cheriex, E.C.; Vos, R.; Natour, E.; Maessen, J.G.; Sardari Nia, P.; Crijns, H.; Wildberger, J.E.; et al. Aortic elongation part I: The normal aortic ageing process. Heart 2018, 104, 1772–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruger, T.; Forkavets, O.; Veseli, K.; Lausberg, H.; Vohringer, L.; Schneider, W.; Bamberg, F.; Schlensak, C. Ascending aortic elongation and the risk of dissection. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2016, 50, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heuts, S.; Adriaans, B.P.; Gerretsen, S.; Natour, E.; Vos, R.; Cheriex, E.C.; Crijns, H.; Wildberger, J.E.; Maessen, J.G.; Schalla, S.; et al. Aortic elongation part II: The risk of acute type A aortic dissection. Heart 2018, 104, 1778–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigorian, A.; Spencer, D.; Donayre, C.; Nahmias, J.; Schubl, S.; Gabriel, V.; Barrios, C., Jr. National trends of thoracic endovascular aortic repair versus open repair in blunt thoracic aortic injury. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2018, 52, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Nakai, M.; Sumita, Y.; Nishimura, K.; Tazaki, J.; Kyuragi, R.; Kinoshita, Y.; Miyamoto, T.; Sakata, Y.; Nozato, T.; et al. Editor’s choice–Endovascular repair versus surgical repair for Japanese patients with ruptured thoracic and abdominal aortic aneurysms: A nationwide study. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2019, 57, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thrumurthy, S.G.; Karthikesalingam, A.; Patterson, B.O.; Holt, P.J.; Hinchliffe, R.J.; Loftus, I.M.; Thompson, M.M. A systematic review of mid-term outcomes of thoracic endovascular repair (TEVAR) of chronic type B aortic dissection. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2011, 42, 632–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daye, D.; Walker, T.G. Complications of endovascular aneurysm repair of the thoracic and abdominal aorta: Evaluation and management. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2018, 8, S138–S156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fairman, A.S.; Beck, A.W.; Malas, M.B.; Goodney, P.P.; Osborne, N.H.; Schermerhorn, M.L.; Wang, G.J. Reinterventions in the modern era of thoracic endovascular aortic repair. J. Vasc. Surg. 2020, 71, 408–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, S.; Greenberg, R.K.; Resch, T.; Bathurst, S.; Fleming, D.; Kashyap, V.; Lyden, S.P.; Clair, D. An evaluation of centerline of flow measurement techniques to assess migration after thoracic endovascular aneurysm repair. J. Vasc. Surg. 2006, 43, 1103–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisbusch, P.; Skrypnik, D.; Ante, M.; Trojan, M.; Bruckner, T.; Rengier, F.; Bockler, D. Endograft migration after thoracic endovascular aortic repair. J. Vasc. Surg. 2019, 69, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberta, H.B.; Takayama, T.; Panthofer, A.; Cambria, R.P.; Farber, M.A.; Jordan, W.D.; Matsumura, J.S. Thoracic endovascular aortic repair migration and aortic elongation differentiated using dual reference point analysis. J. Vasc. Surg. 2018, 67, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fillinger, M.F.; Greenberg, R.K.; McKinsey, J.F.; Chaikof, E.L.; Society for Vascular Surgery Ad Hoc Committee on TEVAR Reporting Standards. Reporting standards for thoracic endovascular aortic repair (TEVAR). J. Vasc. Surg. 2010, 52, 1022–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chandra, V.; Rouer, M.; Garg, T.; Fleischmann, D.; Mell, M. Aortoiliac elongation after endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2015, 29, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinella, G.; Finotello, A.; Conti, M.; Faggiano, E.; Gazzola, V.; Auricchio, F.; Chakfe, N.; Palombo, D.; Pane, B. Assessment of geometrical remodelling of the aortic arch after hybrid treatment. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2019, 55, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohyama, Y.; Redheuil, A.; Kachenoura, N.; Ambale Venkatesh, B.; Lima, J.A.C. Imaging insights on the aorta in aging. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2018, 11, e005617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farasat, S.M.; Morrell, C.H.; Scuteri, A.; Ting, C.T.; Yin, F.C.; Spurgeon, H.A.; Chen, C.H.; Lakatta, E.G.; Najjar, S.S. Pulse pressure is inversely related to aortic root diameter implications for the pathogenesis of systolic hypertension. Hypertension 2008, 51, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cronenwett, J.L.; Sargent, S.K.; Wall, M.H.; Hawkes, M.L.; Freeman, D.H.; Dain, B.J.; Cure, J.K.; Walsh, D.B.; Zwolak, R.M.; McDaniel, M.D.; et al. Variables that affect the expansion rate and outcome of small abdominal aortic aneurysms. J. Vasc. Surg. 1990, 11, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gibbons, G.H.; Dzau, V.J. The emerging concept of vascular remodeling. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 330, 1431–1438. [Google Scholar]
- Scuteri, A.; Chen, C.H.; Yin, F.C.; Chih-Tai, T.; Spurgeon, H.A.; Lakatta, E.G. Functional correlates of central arterial geometric phenotypes. Hypertension 2001, 38, 1471–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scuteri, A.; Morrell, C.H.; Orru, M.; AlGhatrif, M.; Saba, P.S.; Terracciano, A.; Ferreli, L.A.; Loi, F.; Marongiu, M.; Pilia, M.G.; et al. Gender specific profiles of white coat and masked hypertension impacts on arterial structure and function in the SardiNIA study. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 217, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Riesterer, T.; Beyersdorf, F.; Scheumann, J.; Berezowski, M.; Schrofel, H.; Kondov, S.; Czerny, M.; Rylski, B. Accuracy of deployment of the Relay non-bare stent graft in the aortic arch. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2019, 28, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lescan, M.; Czerny, M.; Berezowski, M.; Andic, M.; Bamberg, F.; Beyersdorf, F.; Schlensak, C.; Rylski, B. Morphologic performance analysis of the Relay nonbare stent graft in dissected thoracic aorta. J. Vasc. Surg. 2019, 70, 1390–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canaud, L.; Marty-Ane, C.; Ziza, V.; Branchereau, P.; Alric, P. Minimum 10-year follow-up of endovascular repair for acute traumatic transection of the thoracic aorta. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2015, 149, 825–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Characteristics | Value 1 | |
|---|---|---|
| Demographics | ||
| Age, years | 56 | (19) |
| Sex | ||
| Female | 5 | (12) |
| Male | 36 | (88) |
| Comorbidities | ||
| Hypertension | 33 | (81) |
| Diabetes Mellitus | 4 | (10) |
| Coronary artery disease | 3 | (7) |
| Congestive heart failure | 1 | (2) |
| Chronic renal failure | 1 | (2) |
| Previous stroke | 2 | (5) |
| Hyperlipidemia | 0 | (0) |
| Collagen Vascular disease | 1 | (2) |
| Aortic characteristics | ||
| Type | ||
| Aortic dissection | 21 | (51) |
| Thoracic aortic aneurysm | 15 | (37) |
| Penetrated atherosclerotic ulcer | 1 | (2) |
| Intramural hematoma | 3 | (7) |
| Blunt aortic injury | 1 | (2) |
| Complicated presentation | 17 | (42) |
| TEVAR characteristics | ||
| Stent graft number | ||
| 1 | 21 | (51) |
| 2 | 19 | (46) |
| 3 | 1 | (2) |
| Stent graft type | ||
| Stainless-steel based | 33 | (80) |
| Nitinol-based | 8 | (20) |
| Maximal stent graft diameter, mm | 36 | (4) |
| Maximal stent graft length, mm | 194 | (48) |
| Zone of repair | ||
| 1 | 10 | (24) |
| 2 | 16 | (39) |
| 3 | 15 | (37) |
| Time Interval | Aortic Segment 1 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STJ–INA | INA–CA | LCCA–CA | LSCA–CA | |||||
| Pre-TEVAR | 88 | (14) | 284 | (34) | 273 | (31) | 258 | (22) |
| Immediate post-TEVAR | 87 | (11) | 283 | (30) | 278 | (30) | 255 | (25) |
| First year | 88 | (12) | 285 | (37) | 276 | (41) | 260 | (34) |
| Second year | 88 | (11) | 289 | (42) | 279 | (40) | 264 | (29) |
| Third year | 89 | (14) | 289 | (42) | 281 | (40) | 264 | (31) |
| Fourth year | 90 | (13) | 291 | (41) | 281 | (41) | 263 | (32) |
| Fifth year | 91 | (12) | 294 | (41) | 283 | (41) | 263 | (33) |
| Time Interval | Aortic Segment 1 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STJ–INA | INA–CA | LCCA–CA | LSCA–CA | |||||
| First year | 0 | (7) | 3 | (7) | 2 | (6) | 0 | (6) |
| Second year | 2 | (7) | 4 | (10) | 2 | (9) | 2 | (8) |
| Third year | 1 | (9) | 6 | (12) | 5 | (9) | 5 | (10) |
| Fourth year | 3 | (8) | 7 | (10) | 6 | (13) | 4 | (11) |
| Fifth year | 4 | (6) | 7 | (13) | 6 | (12) | 4 | (14) |
| Segment | No. 1 | (%) |
|---|---|---|
| STJ–INA | 8 | (20) |
| INA–CA | 16 | (39) |
| LCCA–CA | 14 | (34) |
| LSCA–CA | 12 | (29) |
| Factors 1 | Group A 2 (N = 25) | Group B 3 (N = 16) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient characteristics | |||||
| Gender | 0.63 | ||||
| Female | 4 | (16) | 1 | (6) | |
| Male | 21 | (84) | 15 | (94) | |
| Age, years | 55 | (20) | 60 | (17) | <0.01 |
| Comorbidities | |||||
| Hypertension | 0.12 | ||||
| No | 7 | (28) | 1 | (6) | |
| Yes | 18 | (72) | 15 | (94) | |
| Diabetes mellitus | 0.64 | ||||
| No | 23 | (92) | 14 | (88) | |
| Yes | 2 | (8) | 2 | (12) | |
| Coronary artery disease | 0.55 | ||||
| No | 24 | (96) | 14 | (88) | |
| Yes | 1 | (4) | 2 | (12) | |
| Collagen vascular disease | 1.00 | ||||
| No | 24 | (96) | 16 | (100) | |
| Yes | 1 | (4) | 0 | (0) | |
| Congestive heart failure | 0.39 | ||||
| No | 25 | (100) | 15 | (94) | |
| Yes | 0 | (0) | 1 | (6) | |
| Aortic characteristics | |||||
| Complicated presentation | 1.00 | ||||
| No | 15 | (60) | 9 | (56) | |
| Yes | 10 | (40) | 7 | (44) | |
| Innominate artery to celiac artery length | 280 | (38) | 288 | (26) | <0.01 |
| Sinotubular junction to innominate artery | 84 | (12) | 92 | (14) | <0.01 |
| TEVAR characteristics | |||||
| Repair zone | 0.33 | ||||
| 1 | 5 | (20) | 5 | (31) | |
| 2 | 12 | (48) | 4 | (25) | |
| 3 | 8 | (32) | 7 | (44) | |
| Stent graft number | 0.85 | ||||
| 1 | 12 | (48) | 9 | (56) | |
| 2 | 12 | (48) | 7 | (44) | |
| 3 | 1 | (4) | 0 | (0) | |
| Stent graft type | 0.12 | ||||
| Nitinol-based | 7 | (28) | 1 | (6) | |
| Stainless steel-based | 18 | (72) | 15 | (94) | |
| Maximal stent graft diameter, mm | 34 | (2) | 38 | (6) | <0.01 |
| Maximal stent graft length, mm | 160 | (48) | 196 | (46) | <0.01 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, C.-K.; Chou, H.-P.; Chang, Y.-Y.; Shih, C.-C. Elongation of the Aorta after Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair: A longitudinal study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17041205
Chen C-K, Chou H-P, Chang Y-Y, Shih C-C. Elongation of the Aorta after Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair: A longitudinal study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(4):1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17041205
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Chun-Ku, Hsiao-Ping Chou, Ying-Yueh Chang, and Chun-Che Shih. 2020. "Elongation of the Aorta after Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair: A longitudinal study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 4: 1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17041205
APA StyleChen, C.-K., Chou, H.-P., Chang, Y.-Y., & Shih, C.-C. (2020). Elongation of the Aorta after Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair: A longitudinal study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(4), 1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17041205




