Physical and Physiological Profiles of Aerobic and Anaerobic Capacities in Young Basketball Players
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Instruments and Equipment
2.5. Variables
- i.1) Shots: It is the total number of shots the player makes during the duration of the test.
- i.2) Scores: It is the number of scored shots.
- i.3) Efficacy (%): It is the value (expressed in %) calculated of the product between Scores and Number of Shots.
- ii.1) Heart Rate Maximum (HR Max): Maximum value of beats per minute reached by the athlete during the test.
- ii.2) Heart Rate Medium (HR Med): Average value of beats per minute during the test.
- ii.3) % Heart Rate Maximum (% HR Max): It is an indicator of the intensity of the physical-physiological effort of the athlete during the test. This value is calculated taking into account the HR Max.
- ii.4) Heart Rate Recovery (HR Rec): Value of beats per minute after two minutes of the end of the test. The athlete must do a passive recovery at the end of the tests [15].
- iii.1) Part of Circuit: Number of circuit fragments made by the player during the duration of the test. In the aerobic test, each circuit is made up of 12 fractions, whereas in the anaerobic test, each circuit is made up of 4 fractions.
- iii.2) Distance (m): The number of meters travelled during the test. In the aerobic test, each fraction has an approximate distance of 15 m and in the anaerobic test, each fraction has an approximate distance of 7.5 m [5].
- iv.1) Accelerations: Positive increase in speed made during the game, total and per minute.
- iv.2) Decelerations: Negative increase in speed made during the game, total and per minute.
- v.1) Impacts: They are measured through the force that the musculoskeletal structures support in relation to gravitational force (g-force).
- v.2) PlayerLoad: It is a vectorial magnitude derived from triaxial accelerometry data that quantifies the movement at a high resolution. Accelerations and decelerations are used to construct a cumulative measure of the rate of change in acceleration. A cumulative measure (PL) and a measure of intensity (PL · min−1) are used and can then indicate the stress rate at which players subject their body for a certain period of time. As a unit load, it has a moderate-high degree of reliability and validity [25,26].
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Aerobic Capacity
4.2. Anaerobic Capacity
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zarić, I.; Dopsaj, M.; Marković, M. Match performance in young female basketball players: Relationship with laboratory and field tests. Int. J. Perform. Anal. Sport 2018, 18, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, N.M.; Kilding, A.E. Aerobic conditioning for team sport athletes. Sports Med. 2009, 39, 615–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latzel, R.; Hoos, O.; Stier, S.; Kaufmann, S.; Fresz, V.; REim, D.; Beneke, R. Energetic profile of the basketball exercise simulation test in junior elite players. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2018, 13, 810–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zupan, M.F.; Arata, A.W.; Dawson, L.H.; Wile, A.L.; Payn, T.L.; Hannon, M.E. Wingate anaerobic test peak power and anaerobic capacity classifications for men and women intercollegiate athletes. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2009, 23, 2598–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibáñez, S.J.; Reina, M.; Mancha-Triguero, D.; García-Rubio, J. Evaluación de la capacidad aeróbica y anaeróbica de jugadores de baloncesto en edades de formación. In Baloncesto Formativo. La Preparación Física II, Camino Hacia El Alto Rendimiento, 1st ed.; Esper Di Cesare, P.A., Ed.; Autores de Argentina: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2019; pp. 365–388. [Google Scholar]
- Bompa, T.O. Periodización Del Entrenamiento Deportivo; Editorial Paidotribo: Barcelona, Spain, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wilmore, J.H.; Costill, D.L. Physiology of Sport and Exercise, 3rd ed.; Human Kinetics: Hong Kong, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ibáñez, S.J.; Sampaio, J.; Feu, S.; Lorenzo, A.; Gómez, M.A.; Ortega, E. Basketball game-related statistics that discriminate between teams’ season-long success. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2008, 8, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reina, M.; García-Rubio, J.; Feu, S.; Ibáñez, S.J. Training and Competition Load Monitoring and Analysis of Women’s Amateur Basketball by Playing Position: Approach Study. Front. Psychol. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdelkrim, N.B.; El Fazaa, S.; El Ati, J. Time-motion analysis and physiological data of elite under 19-year-old basketball players during competition. Br. J. Sports Med. 2007, 41, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reina, M.; Mancha-Triguero, D.; García-Santos, D.; García-Rubio, J.; Ibáñez, S.J. Comparación de tres métodos de cuantificación de la carga de entrenamiento en baloncesto. Ricyde. Rev. Int. Cienc. Deporte. 2019, 15, 368–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erculj, F.; Dezman, B.; Vuckovic, G.; Pers, J.; Perse, M.; Kristan, M. An analysis of basketball players’ movements in the Slovenian Basketball League play-offs using the Sagit Tracking System. J. Phys. Educ. 2008, 6, 75–84. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelkrim, N.B.; Castagna, C.; Jabri, I.; Battikh, T.; El Fazaa, S.; El Ati, J. Activity profile and physiological requirements of junior elite basketball players in relation to aerobic-anaerobic fitness. J. Strength Cond Res. 2010, 24, 2330–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köklü, Y.; Alemdaroğlu, U.; Koçak, F.; Erol, A.; Fındıkoğlu, G. Comparison of chosen physical fitness characteristics of Turkish professional basketball players by division and playing position. J. Hum. Kinet. 2011, 30, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancha-Triguero, D.; García-Rubio, J.; Ibáñez, S.J. SBAFIT: A field-based test battery to assess physical fitness in basketball players. J. Sports Sci. 2019, 15, 107–126. [Google Scholar]
- Doma, K.; Leicht, A.; Sinclair, W.; Schumann, M.; Damas, F.; Burt, D.; Woods, C. The impact of exercise-induced muscle damage on physical fitness qualities in elite female basketball players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2018, 32, 1731–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Štrumbelj, B.; Vuckovic, G.; Jakovljevic, S.; Milanovic, Z.; James, N.; Erculj, F. Graded shuttle run performance by playing positions in elite female basketball. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2015, 29, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancha-Triguero, D.; García-Rubio, J.; Calleja-González, J.; Ibáñez, S.J. Physical fitness in basketball players: A systematic review. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2019, 59, 1513–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bompa, T.O.; Buzzichelli, C. Periodization: Theory and Methodology of Training; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- McGill, S.M.; Andersen, J.T.; Horne, A.D. Predicting performance and injury resilience from movement quality and fitness scores in a basketball team over 2 years. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2012, 26, 1731–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ato, M.; López-García, J.J.; Benavente, A. Un sistema de clasificación de los diseños de investigación en psicología. An. Psicol. 2013, 29, 1038–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibáñez, S.J.; Sáenz-López, P.; Gutiérrez, A. Test SIG/AER, aeróbico específico sobre el terreno para jugadores de baloncesto. In Libro de Actas del Congreso Científico Olímpico 1995. Bioquímica, Fisiología del Ejercicio y Medicina del Deporte, 1st ed.; Unisport, Ed.; Instituto Andaluz del Deporte: Málaga, Spain, 1995; Volume 4, pp. 217–225. [Google Scholar]
- Ibáñez, S.J.; Sáenz-López, P.; Gutiérrez, A. Test SIG/ANA, anaeróbico específico sobre el terreno para jugadores de baloncesto. In Libro de Actas del Congreso Científico Olímpico 1995. Bioquímica, Fisiología del Ejercicio y Medicina del Deporte, 1st ed.; Unisport, Ed.; Instituto Andaluz del Deporte: Málaga, Spain, 1995; Volume 4, pp. 209–216. [Google Scholar]
- Ibáñez, S.J.; Antúnez, A.; Pino-Ortega, J.; García-Rubio, J. Control del entrenamiento mediante el empleo de tecnologías en tiempo real en balonmano. In Avances Científicos Para el Aprendizaje y Desarrollo del Balonmano, 1st ed.; Feu, S., García-Rubio, J., Ibáñez, S.J., Eds.; Universidad de Extremadura: Cáceres, Spain, 2018; pp. 167–192. [Google Scholar]
- Barreira, P.; Robinson, M.A.; Drust, B.; Nedergaard, N.; Raja Azidin, R.M.F.; Vanrenterghem, J. Mechanical Player Load™ using trunk-mounted accelerometry in football: Is it a reliable, task-and player-specific observation? J. Sports Sci. 2017, 35, 1674–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schelling, X.; Torres-Ronda, L. An integrative approach to strength and neuromuscular power training for basketball. Strength Cond. J. 2016, 38, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, A. Discovering Statistics Using SPSS, 3rd ed.; SAGE: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins, W.; Marshall, S.; Batterham, A.; Hanin, J. Progressive statistics for studies in sports medicine and exercise science. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pardo, A.; Ruiz, M.Á. SPSS 11: Guía Para el Análisis de Datos; Mc Graw Hill: Madrid, Spain, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- O’Donoghue, P. Statistics for Sport and Exercise Studies: An. Introduction; Routledge: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Padulo, J.; Attene, G.; Migliaccio, G.M.; Cuzzolin, F.; Vando, S.; Ardigò, L.P. Metabolic optimisation of the basketball free throw. J. Sports Sci. 2015, 33, 1454–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziv, G.; Lindor, R. Physical attributes, physiological characteristics, on-court performances and nutritional strategies of female and male basketball players. Sports Med. 2009, 39, 547–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scalan, A.T.; Dascombe, B.J.; Kidcaff, A.P.; Peucker, J.L.; Dalbo, V.J. Gender-specific activity demands experienced during semiprofessional basketball game play. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2015, 10, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Tabar, I.; Llodio, I.; Sánchez-Medina, L.; Ruesta, M.; Ibáñez, J.; Gorostiaga, E.M. Heart Rate-Based prediction of fixed blood lactate thresholds in professional team-sport players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2015, 29, 2794–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, S.; Volossovitch, A.; Ferreira, A.P.; Fragoso, I.; Massuça, L. Differences in maturity, morphological and physical attributes between players selected to the primary and secondary teams of a Portuguese Basketball elite academy. J. Sports Sci. 2019, 37, 1681–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, S.E.; Carlson, J.S.; Jones, C.J.; McKenna, M.J. The physiological load imposed on basketball players during competition. J. Sports Sci. 1995, 13, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struzik, A.; Pietraszewski, B.; Zawadzki, J. Biomechanical analysis of the jump shot in basketball. J. Hum. Kinet. 2014, 42, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramos, S.; Volossovitch, A.; Ferreira, A.P.; Barrigas, C.; Fragoso, I.; Massuça, L. Differences in maturity, morphological and fitness attributes between the better- and lower-ranked male and female U-14 Portuguese elite regional basketball teams. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Calleja-González, J.; Leibar, X.; Terrados, N. Análisis de la concentración de lactato en competición en jugadores internacionales junior de baloncesto. Arch. Med. Deporte. 2008, 25, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Clearly, T.J.; Zimmerman, B.J. Self-regulation differences during athletic practice by experts, non-experts, and novices. J. Appl. Sport Psychol. 2001, 13, 185–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, J.R.; Tenenbaum, G.; Maresh, C.M.; Kraemer, W.J. Relationship between athletic performance test and playing time in elite college basketball players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 1996, 10, 67–71. [Google Scholar]
- Narazaki, K.; Berg, K.; Stergiou, N.; Chen, B. Physiological demands of competitive basketball. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2009, 19, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
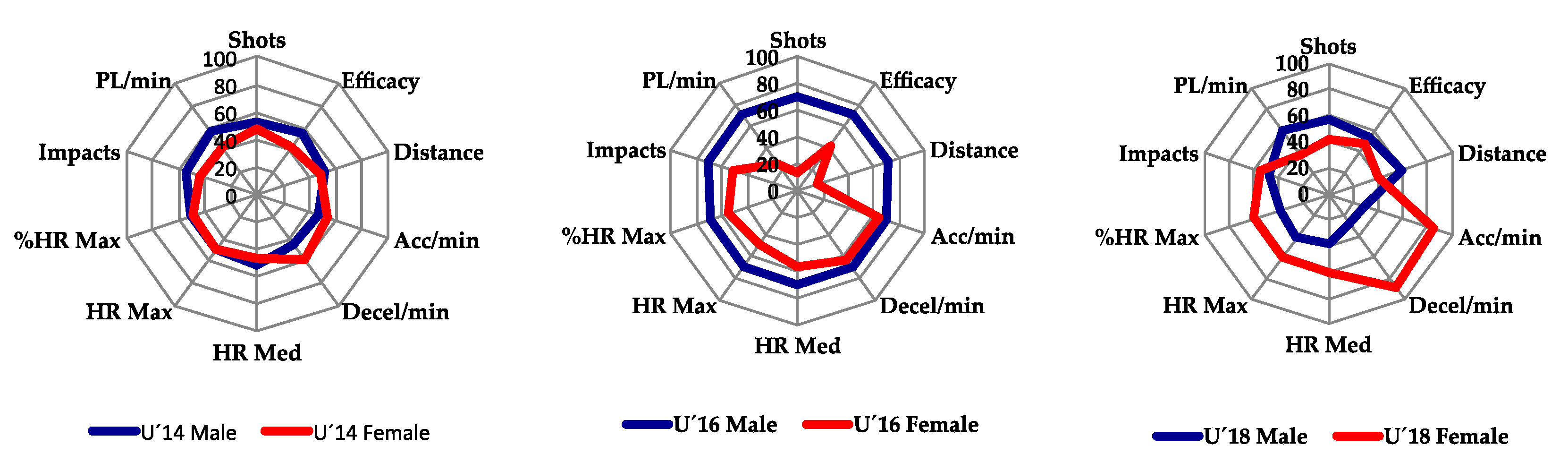
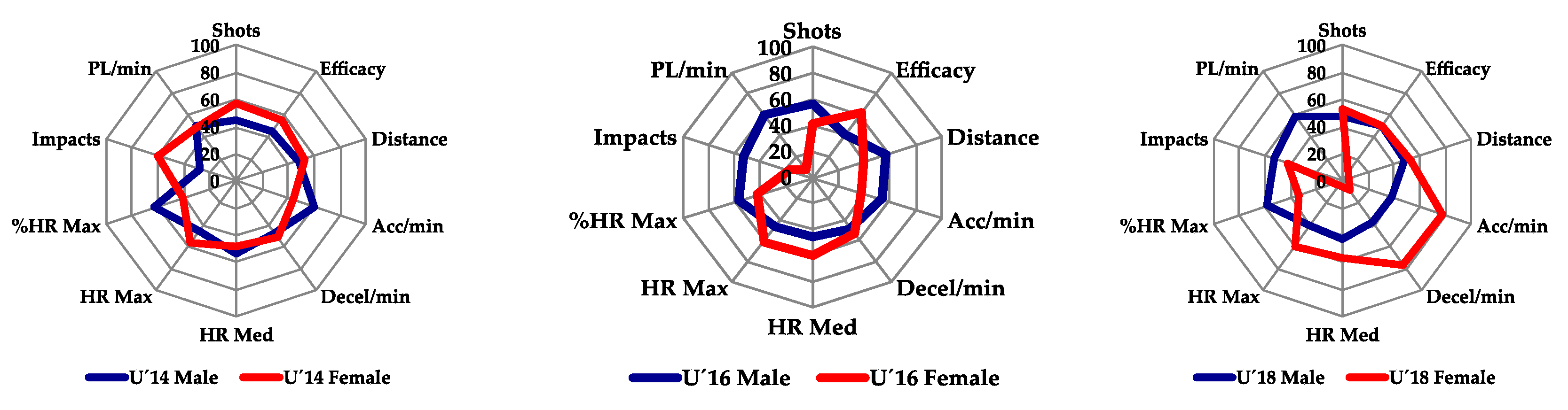
| Aerobic Capacity | Anaerobic Capacity | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MALE | FEMALE | MALE | FEMALE | |||||||
| sig. | ES | sig. | ES | Sig. | ES | sig. | ES | |||
| Technical-tactical Variables | Shots | U´14–U´16 | 0.000 * | −1.524 | 0.099 | 0.682 | 0.000 * | −0.662 | 0.099 | 0.585 |
| U´14–U´18 | 0.000 * | −1.384 | 0.000 * | −1.243 | 0.000 * | −0.658 | 0.000 * | −0.618 | ||
| U´16–U´18 | 0.287 | 0.312 | 0.000 * | −2.386 | 0.287 | 0.049 | 0.000 * | −1.38 | ||
| Scores | U´14–U´16 | 0.000 * | −1.226 | 0.843 | −0.816 | 0.000 * | −1.617 | 0.843 | −0.561 | |
| U´14–U´18 | 0.000 * | −0.967 | 0.008 * | −0.839 | 0.000 * | −1.341 | 0.008 * | −0.998 | ||
| U´16–U´18 | 0.698 | 0.197 | 0.292 | −0.47 | 0.698 | 0.12 | 0.292 | −0.504 | ||
| Efficacy | U´14–U´16 | 0.000 * | −0.89 | 0.306 | −0.991 | 0.000 * | 0.049 | 0.306 | −0.345 | |
| U´14–U´18 | 0.000 * | −0.711 | 0.04 * | −0.7 | 0.000 * | −0.054 | 0.04 * | 0.563 | ||
| U´16–U´18 | 1.000 | 0.136 | 1.000 | −0.128 | 1.000 | −0.111 | 1.000 | 0.93 | ||
| Objective External Load Kinematics V. related to Distance | Parts of Circ. | U´14–U´16 | 0.000 * | −1.176 | 0.017 * | 0.876 | 0.000 * | −0.515 | 0.017 * | 0.355 |
| U´14–U´18 | 0.000 * | −1.035 | 0.181 | −0.535 | 0.000 * | −0.483 | 0.181 | −0.889 | ||
| U´16–U´18 | 0.287 | 0.321 | 0.000 * | −1.915 | 0.287 | 0.066 | 0.000 * | −1.329 | ||
| Distance (m) | U´14–U´16 | 0.000 * | −1.176 | 0.017 * | 0.875 | 0.000 * | −0.515 | 0.017 * | 0.355 | |
| U´14–U´18 | 0.000 * | −1.034 | 0.181 | −0.536 | 0.000 * | −0.483 | 0.181 | −0.888 | ||
| U´16–U´18 | 0.287 | 0.321 | 0.000 * | −1.915 | 0.287 | 0.065 | 0.000 * | −1.329 | ||
| Objective External Load Kinematics V. related to Accelerometry | Acc. | U´14–U´16 | 0.978 | −0.172 | 0.000 * | −1.257 | 0.978 | −0.126 | 0.000 * | −0.499 |
| U´14–U´18 | 1.000 | −0.011 | 0.000 * | −2.453 | 1.000 | 1.447 | 0.000 * | −1.208 | ||
| U´16–U´18 | 1.000 | 0.178 | 0.18 | −0.633 | 1.000 | 1.387 | 0.18 | −0.918 | ||
| Decel | U´14–U´16 | 0.229 | −0.307 | 0.000 * | −1.257 | 0.229 | −0.806 | 0.000 * | −1.247 | |
| U´14–U´18 | 1.000 | −0.142 | 0.000 * | −3,069 | 1.000 | 0.781 | 0.000 * | −1.497 | ||
| U´16–U´18 | 1.000 | 0.186 | 0.002 * | −1.093 | 1.000 | 1.15 | 0.002 * | −0.735 | ||
| Acc/min | U´14–U´16 | 0.751 | −0.2 | 0.000 * | −1.264 | 0.751 | −0.114 | 0.000 * | −0.412 | |
| U´14–U´18 | 1.000 | −0.045 | 0.000 * | −2.438 | 1.000 | 1.342 | 0.000 * | −1.216 | ||
| U´16–U´18 | 1.000 | 0.174 | 0.188 | −0.626 | 1.000 | 1.303 | 0.188 | −1.01 | ||
| Decel/min | U´14–U´16 | 0.163 | −0.332 | 0.000 * | −1.264 | 0.163 | −0.832 | 0.000 * | −1.105 | |
| U´14–U´18 | 0.881 | −0.174 | 0.000 * | −3.049 | 0.881 | 0.704 | 0.000 * | −1.503 | ||
| U´16–U´18 | 1.000 | 0.18 | 0.002 * | −1.087 | 1.000 | 1.068 | 0.002 * | −0.821 | ||
| Objective Internal Load V. | HR Med | U´14–U´16 | 0.021 * | 0.486 | 1.000 | −0.266 | 0.021 * | 0.648 | 1.000 | −0.111 |
| U´14–U´18 | 0.000 * | 1.122 | 1.000 | −0.247 | 0.000 * | 1.758 | 1.000 | 0.488 | ||
| U´16–U´18 | 0.001 * | 0.636 | 1.000 | −0.07 | 0.001 * | 0.58 | 1.000 | 0.829 | ||
| HR Max | U´14–U´16 | 0.241 | 0.337 | 0.496 | 0.514 | 0.241 | 0.837 | 0.496 | 1.708 | |
| U´14–U´18 | 0.000 * | 0.775 | 1.000 | −0.161 | 0.000 * | 1.868 | 1.000 | 1.434 | ||
| U´16–U´18 | 0.023 * | 0.455 | 0.103 | −0.621 | 0.023 * | 0.591 | 0.103 | 0.405 | ||
| HR Rest | U´14–U´16 | 0.013 * | −0.575 | 0.056 | 1.148 | 0.013 * | 1.424 | 0.056 | −0.953 | |
| U´14–U´18 | 0.000 * | 0.774 | 0.003 * | 0.925 | 0.000 * | 2.477 | 0.003 * | 0.764 | ||
| U´16–U´18 | 0.000 * | 1.337 | 1.000 | 0.116 | 0.000 * | 0.906 | 1.000 | 1.792 | ||
| % HR Max | U´14–U´16 | 0.059 | 0.453 | 1.000 | 0.171 | 0.059 | −0.203 | 1.000 | −0.57 | |
| U´14–U´18 | 0.000 * | 1.053 | 1.000 | −0.035 | 0.000 * | 0.403 | 1.000 | 0.042 | ||
| U´16–U´18 | 0.002 * | 0.636 | 1.000 | −0.143 | 0.002 * | 0.569 | 1.000 | 0.179 | ||
| Objective External Load Neuromuscular V. | Impacts | U´14–U´16 | 0.179 | 0.359 | 1.000 | 0.768 | 0.179 | −0.599 | 1.000 | 1.037 |
| U´14–U´18 | 1.000 | −0.081 | 0.002 * | −0.952 | 1.000 | −1.152 | 0.002 * | 0.572 | ||
| U´16–U´18 | 0.057 | −0.397 | 0.000 * | −1.275 | 0.057 | −0.407 | 0.000 * | −0.971 | ||
| PlayerLoad | U´14–U´16 | 0.000 * | −0.761 | 0.005 * | 0.974 | 0.000 * | −0.213 | 0.005 * | 1.561 | |
| U´14–U´18 | 0.000 * | −0.941 | 0.185 | −0.616 | 0.000 * | 0.439 | 0.185 | 2.165 | ||
| U´16–U´18 | 1.000 | 0.034 | 0.000 * | −1.785 | 1.000 | 0.578 | 0.000 * | 0.086 | ||
| PlayerLoad/min | U´14–U´16 | 0.000 * | −0.767 | 0.006 * | 0.976 | 0.000 * | −0.213 | 0.006 * | 1.56 | |
| U´14–U´18 | 0.007 * | −0.656 | 0.168 | −0.625 | 0.007 * | 0.439 | 0.168 | 2.164 | ||
| U´16–U´18 | 0.323 | 0.034 | 0.000 * | −1.792 | 0.323 | 0.578 | 0.000 * | 0.083 | ||
| Aerobic Capacity | Anaerobic Capacity | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sig. | ES | Sig. | ES | |||
| Technical-tactical V. | Shots | U´14 | 0.606 | 0.242 | 0.002 * | −0.499 |
| U´16 | 0.167 | 2.571 | 0.22 | 0.645 | ||
| U´18 | 0.819 | 0.679 | 0.001 * | −0.25 | ||
| Scores | U´14 | 0.103 | 0.597 | 0.001 * | −0.654 | |
| U´16 | 0.002 * | 1.255 | 0.798 | 0.78 | ||
| U´18 | 0.075 | 0.402 | 0.086 | 0.041 | ||
| Efficacy | U´14 | 0.279 | 0.536 | 0.126 | −0.475 | |
| U´16 | 0.201 | 0.679 | 0.091 | −0.994 | ||
| U´18 | 0.013 * | 0.307 | 0.264 | 0.034 | ||
| Objective External Load Kinematics V. related to Distance | Parts of Circuits | U´14 | 0.78 | 0.168 | 0.003 * | −0.143 |
| U´16 | 0.064 | 2.420 | 0.07 * | 0.743 | ||
| U´18 | 0.436 | 0.914 | 0.000 * | −0.132 | ||
| Distance (m.) | U´14 | 0.78 | 0.169 | 0.003 * | −0.144 | |
| U´16 | 0.064 | 2.420 | 0.07 * | 0.743 | ||
| U´18 | 0.436 | 0.914 | 0.000 * | −0.132 | ||
| Objective External Load Kinematics V. related to Accelerometry | Acc. | U´14 | 0.03 * | −0.294 | 0.004 * | 0.865 |
| U´16 | 0.403 | −1.480 | 0.000 * | 0.364 | ||
| U´18 | 0.000 * | −2.167 | 0.000 * | −1.626 | ||
| Decel | U´14 | 0.001 * | −0.440 | 0.596 | −0.172 | |
| U´16 | 0.515 | −1.318 | 0.01 * | −0.337 | ||
| U´18 | 0.000 * | −2.35 | 0.000 * | −1.555 | ||
| Acc/Min | U´14 | 0.024 * | −0.333 | 0.021 * | 0.868 | |
| U´16 | 0.436 | −1.503 | 0.000 * | 0.476 | ||
| U´18 | 0.000 * | −2.163 | 0.000 * | −1.518 | ||
| Decel/Min | U´14 | 0.001 * | −0.476 | 0.735 | −0.161 | |
| U´16 | 0.502 | −1.339 | 0.016 | −0.186 | ||
| U´18 | 0.000 * | −2.351 | 0.000 * | −1.45 | ||
| Objective Internal Load V. | HR Med | U´14 | 0.008 * | 0.202 | 0.000 * | 0.352 |
| U´16 | 0.307 | −0.494 | 0.015 * | 0.458 | ||
| U´18 | 0.815 | −1.155 | 0.472 | 0.987 | ||
| HR Max | U´14 | 0.677 | −0.009 | 0.044 * | 0.217 | |
| U´16 | 0.037 * | 0.220 | 0.005 * | 0.56 | ||
| U´18 | 0.794 | −0.859 | 0.878 | 0.79 | ||
| HR Rest | U´14 | 0.289 | −0.611 | 0.003 * | 0.487 | |
| U´16 | 0.106 | 1.041 | 0.154 | 0.98 | ||
| U´18 | 0.804 | −0.389 | 0.543 | 0.57 | ||
| % HR Max | U´14 | 0.006 * | 0.034 | 0.04 * | 0.231 | |
| U´16 | 0.309 | −0.346 | 0.615 | 0.345 | ||
| U´18 | 0.734 | −1.084 | 0.002 * | 0.974 | ||
| Objective External Load Neuromuscular V. | Impacts | U´14 | 0.162 | −0.049 | 0.000 * | −1.511 |
| U´16 | 0.011 * | −0.021 | 0.001 * | 0.361 | ||
| U´18 | 0.003 * | −0.951 | 0.000 * | 0.413 | ||
| PlayerLoad | U´14 | 0.447 | 0.668 | 0.21 | 0.062 | |
| U´16 | 0.062 | 1.802 | 0.000 * | 1.175 | ||
| U´18 | 0.003 * | 1.228 | 0.000 * | 1.136 | ||
| PlayerLoad/Min | U´14 | 0.525 | 0.680 | 0.209 | 0.063 | |
| U´16 | 0.041 * | 1.776 | 0.000 * | 1.175 | ||
| U´18 | 0.01 * | 0.896 | 0.000 * | 1.135 | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mancha-Triguero, D.; García-Rubio, J.; Antúnez, A.; Ibáñez, S.J. Physical and Physiological Profiles of Aerobic and Anaerobic Capacities in Young Basketball Players. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17041409
Mancha-Triguero D, García-Rubio J, Antúnez A, Ibáñez SJ. Physical and Physiological Profiles of Aerobic and Anaerobic Capacities in Young Basketball Players. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(4):1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17041409
Chicago/Turabian StyleMancha-Triguero, David, Javier García-Rubio, Antonio Antúnez, and Sergio J. Ibáñez. 2020. "Physical and Physiological Profiles of Aerobic and Anaerobic Capacities in Young Basketball Players" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 4: 1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17041409
APA StyleMancha-Triguero, D., García-Rubio, J., Antúnez, A., & Ibáñez, S. J. (2020). Physical and Physiological Profiles of Aerobic and Anaerobic Capacities in Young Basketball Players. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(4), 1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17041409







