The Awareness and Attitude of Parents towards the Legislation of Child Restraint in Two Cities of China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mandatory Child Restraint Regulations in Shanghai and Shenzhen:
2.2. Investigation Method:
- Should have at least one child aged 0–6 years in the family.
- Should have at least one private car in the family.
- Has driven the child aged 0–6 years out most often or accompanied the child in the private car most often.
2.3. Investigation Content:
2.4. Sample Size:
2.5. Sampling Methods and Procedures
2.6. Respondents Recruitment
2.7. Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristic
3.2. Awareness of Local Legislation in the Two Cities
3.3. Support of National Legislation in the Two Cities
4. Discussion
4.1. Awareness of Legislation:
4.2. Support Status of National Mandatory Child Restraint Law
4.3. Limitation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. World report on child injury prevention. Available online: https://www.who.int/violence_injury_prevention/child/injury/world_report/en/ (accessed on 30 January 2020).
- Ye, P.P.; Jin, Y.; Duan, L.L. Mortality of road traffic injury among children aged 0-14 years in China from 1990 to 2015. Chin. J. Dis. Control Prev. 2018, 22, 656–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Road traffic Safety Research Center of the Ministry of Public Security. The National Center for Chronic and Noncommunicable Disease Control and Prevention, the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. In A Study on Road Traffic Injuries of Children in China; People’s Medical Electronic Audio Video Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Global Status Report on Road Safety 2018. Available online: https://www.who.int/violence_injury_prevention/road_safety_status/2018/en/ (accessed on 30 January 2020).
- Jakobsson, L.; Isaksson-Hellman, I.; Lundell, B. Safety for the Growing Child—Experiences from Swedish Accident Data. 2005. Available online: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.541.3024&rep=rep1&type=pdf (accessed on 1 April 2020).
- Deng, X.; Jin, Y.; Duan, L.L. Survey on the awareness and use of child safety seat among 9 484 cases in three Chinese cities. Chin. J. Woman Child Health Res. 2016, 5, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Y.; Zhou, H.B.; Ma, J.P.; Wang, C.Y.; Chen, Z.W.; Chen, S.H. Knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors related to child safety restraint in citizens of shenzhen municipality, china, and the associations between these factors. Traffic Inj. Prev. 2018, 19, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- China Automotive Technology Research Center. Road traffic safety research center of the Ministry of public security. In Blue Book of China Child Road Traffic Safety in 2015; China Quality Inspection Press: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- FIA Foundation, WHO. GRSP and the World Bank. Seat-Belts and Child Restraints: A Road Safety Manual for Decision-Makers and Practitioners. 2009. Available online: https://www.who.int/roadsafety/projects/manuals/seatbelt/en/ (accessed on 30 January 2020).
- Shanghai Municipal People’s Congress. Regulations of Shanghai Municipality on Road Traffic Administration, 2016 update. Available online: http://search.chinalaw.gov.cn/law/searchTitleDetail?LawID=355548&Query=%E4%B8%8A%E6%B5%B7%E5%B8%82%E9%81%93%E8%B7%AF%E4%BA%A4%E9%80%9A%E7%AE%A1%E7%90%86%E6%9D%A1%E4%BE%8B&IsExact= (accessed on 30 January 2020).
- Shenzhen Municipal People’s Congress. Regulations of Shenzhen Special Economic Zone on Punishment of Illegal Acts of Road Traffic Safety, 2015 Update. Available online: http://search.chinalaw.gov.cn/law/searchTitleDetail?LawID=341778&Query=%E6%B7%B1%E5%9C%B3%E7%BB%8F%E6%B5%8E%E7%89%B9%E5%8C%BA%E9%81%93%E8%B7%AF%E4%BA%A4%E9%80%9A%E5%AE%89%E5%85%A8%E8%BF%9D%E6%B3%95%E8%A1%8C%E4%B8%BA%E5%A4%84%E7%BD%9A%E6%9D%A1%E4%BE%8B&IsExact= (accessed on 30 January 2020).
- Shandong Municipal People’s Congress. Regulations of Shandong Province on Highway Traffic Safety, 2014 Update. Available online: http://search.chinalaw.gov.cn/law/searchTitleDetail?LawID=347211&Query=%E5%B1%B1%E4%B8%9C%E7%9C%81%E9%AB%98%E9%80%9F%E5%85%AC%E8%B7%AF%E4%BA%A4%E9%80%9A%E5%AE%89%E5%85%A8%E6%9D%A1%E4%BE%8B&IsExact= (accessed on 30 January 2020).
- Piontkowski, S.R.; Peabody, J.S.; Reede, C.; Velascosoltero, J.; Tsatoke, G.; Shelhamer, T. Reducing motor vehicle-related injuries at an arizona indian reservation: Ten years of application of evidence-based strategies. Glob. Health Sci. Pract. 2015, 3, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y. Shenzhen Traffic Police Issued the First Ticket on not Using Child Restraint which is Also the First Ticket in China. [EB / OL]. Available online: https://www.sohu.com/a/78563918_372711 (accessed on 1 April 2020).
- Klinich, K.D.; Benedetti, M.; Manary, M.A.; Flannagan, C.A. Rating child passenger safety laws relative to best practice recommendations for occupant protection. Traffic Inj. Prev. 2016, 18, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Yang, J.; Peek-Asa, C.; Li, L.P. Parents’ experience with child safety restraint in China. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Deng, X.; Ye, P.P.; Duan, L.L. Analysis on influence of the self-confidence, motivation and authoritative advice factors on the use of child restraint. Chin. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 40, 1376–1380. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, J.Y.; Anderson, E.; Silver, D.; Macinko, J. Child passenger safety laws in the united states, 1978–2010: Policy diffusion in the absence of strong federal intervention. Soc. Sci. Med. 2014, 100, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, A.F. Restraint use legislation: Its prospects for increasing the protection of children in cars. Accid. Anal. Prev. 1979, 11, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, M.; Weinberg, K. Coverage gaps in child-restraint and seat-belt laws affecting children. Accid. Anal. Prev. 1994, 26, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segui-Gomez, M.; Wittenberg, E.; Glass, R.; Levenson, S.; Graham, J.D. Where children sit in cars: The impact of rhode island’s new legislation. Am. J. Public Health 2001, 91, 311–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brubacher, J.R.; Desapriya, E.; Erdelyi, S.; Chan, H. The impact of child safety restraint legislation on child injuries in police-reported motor vehicle collisions in british columbia: An interrupted time series analysis. Paediatr. Child Health 2016, 21, e27–e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United Nations. UN Regulation No. 129. Increasing the Safety of Children in Vehicles for Policy Makers and Concerned Citizens; Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE): Geneva, Switzerland, 2016; Available online: https://www.unece.org/fileadmin/DAM/trans/publications/WP29/CHILD_RESTRAINT_SYSTEMS_brochure.pdf (accessed on 30 January 2020).
- Clay, C.; van As, A.B.S.; Hunter, K.; Peden, M. Latest results show urgent need to address child restraint use. S. Afr. Med. J. 2019, 109, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristic | Shanghai | Shenzhen | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Percentage (95%CI) | Number | Percentage (95%CI) | ||
| Education of parents | Primary school | 3 | 0.082 (0.021, 0.33) | 32 | 0.79 (0.49, 1.26) |
| Junior middle school | 157 | 4.46 (2.78, 7.08) | 406 | 9.45 (7, 12.66) | |
| High school / Secondary vocational / Technical School | 437 | 11.69 (8.92, 15.19) | 1067 | 23.97 (19.96, 28.5) | |
| University (Specialized subject) | 996 | 23.34 (21.23, 25.6) | 1311 | 27.67 (25.09, 30.42) | |
| University | 2201 | 51.32 (46.44, 56.18) | 1766 | 33.63 (28.57, 39.08) | |
| Postgraduate | 402 | 9 (7.07, 11.38) | 295 | 4.03 (2.94, 5.5) | |
| Others | 5 | 0.1 (0.032, 0.31) | 34 | 0.46 (0.28, 0.74) | |
| Total | 4198 | 100 | 4879 | 100 | |
| Income of the family | ≦721 U.S. dollars /month | 186 | 4.49 (3.26, 6.14) | 346 | 7.92 (6.28, 9.94) |
| > 721 & ≦1442 U.S. dollars /month | 740 | 20.46 (17.31, 24.03) | 1086 | 25.89 (22.95, 29.07) | |
| >1442 and ≦2883 U.S. dollars/month | 1489 | 35.59 (32.55, 38.74) | 1510 | 33.95 (31.72, 36.26) | |
| >2883 and ≦14,417 U.S. dollars /month | 1567 | 34.18 (29.99, 38.64) | 1262 | 21.17 (17.83, 24.93) | |
| >14,417 U.S. dollars/month and upper | 64 | 1.68 (1.19, 2.35) | 359 | 5.63 (4.75, 6.67) | |
| Unknown | 148 | 3.61 (2.67, 4.85) | 348 | 5.44 (4.38, 6.74) | |
| Total | 4194 | 100 | 4911 | 100 | |
| Car price | ≦14,417 U.S. dollars/month | 337 | 8.53 (6.53, 11.07) | 514 | 12.42 (10.21, 15.02) |
| >14,417 and≦24,508 U.S. dollars /month | 1662 | 39.83 (36.23, 43.55) | 1561 | 36.1 (32.27, 40.12) | |
| >24,508 and≦36,042 U.S. dollars /month | 1080 | 25.37 (23.16, 27.71) | 1060 | 21.73 (19.35, 24.32) | |
| >36,042 and ≦50,458 U.S. dollars /month | 597 | 14.84 (12.94, 16.96) | 664 | 11.89 (10.23, 13.77) | |
| >50,458 | 417 | 9.26 (7.81, 10.95) | 639 | 10.01 (8.17, 12.21) | |
| Unknown | 108 | 2.17 (1.64, 2.87) | 473 | 7.85 (6.21, 9.87) | |
| Total | 4201 | 100 | 4911 | 100 | |
| Age of children | 0–3 y | 1346 | 57.53 (52.23, 62.66) | 1777 | 63.28 (54.82, 70.99) |
| 4–6 y | 2855 | 42.47 (37.34, 47.77) | 3134 | 36.72 (29.01, 45.18) | |
| Total | 4201 | 100 | 4911 | 100 | |
| Gender of children | Male | 2187 | 51.51 (49.89, 53.12) | 2598 | 53.18 (51.32, 55.04) |
| Female | 2014 | 48.49 (46.88, 50.11) | 2313 | 46.82 (44.96, 48.68) | |
| Total | 4201 | 100 | 4911 | 100 | |
| Weight of children | – | 18.10 ± 5.38 kg | 17.02 ± 5.18 kg | ||
| Height of children | – | 105.59 ± 16.74 cm | 102.74 ± 17.09 cm | ||
| Trip frequency of children | Every day / Almost every day | 1150 | 23.33 (19.82, 27.26) | 980 | 16.88 (13.23, 21.29) |
| 2–3 times a week | 1836 | 43.05 (39.6, 46.57) | 1623 | 33.84 (31.22, 36.55) | |
| 2–4 times a month | 949 | 25.73 (23.66, 27.91) | 1459 | 31.29 (27.64, 35.19) | |
| Once a month or less | 266 | 7.89 (6.25, 9.91) | 849 | 18 (14.82, 21.69) | |
| Total | 4201 | 100 | 4911 | 100 | |
| Travel distance of children | Less than 3 km | 1114 | 26.28 (21.75, 31.38) | 1395 | 26.86 (22.99, 31.12) |
| 3–5 km | 1423 | 34.86 (31.84, 38) | 1404 | 28.98 (25.26, 33.01) | |
| 6–10 km | 986 | 23.27 (20.27, 26.57) | 1184 | 25.27 (22.71, 28.01) | |
| 10km and upper | 677 | 15.59 (13.2, 18.31) | 928 | 18.89 (16.04, 22.11) | |
| Total | 4200 | 100 | 4911 | 100 | |
| Driver wearing safety belt | Always | 3708 | 87.77 (84.45, 90.47) | 4267 | 86.93 (83.91, 89.45) |
| Often | 229 | 6.17 (4.59, 8.25) | 317 | 6.19 (4.93, 7.74) | |
| Sometimes | 140 | 3.08 (1.95, 4.84) | 172 | 3.68 (2.49, 5.4) | |
| Seldom | 81 | 1.85 (1.32, 2.6) | 121 | 2.33 (1.83, 2.96) | |
| Never | 43 | 1.12 (0.69, 1.8) | 34 | 0.87 (0.56, 1.37) | |
| Total | 4201 | 100 | 4911 | 100 | |
| Utilization rate of child restraint | Always | 1609 | 40.79 (35.94, 45.83) | 1536 | 28.75 (24.73, 33.13) |
| Often | 497 | 12.53 (10.4, 15.03) | 528 | 10.64 (9.25, 12.2) | |
| Sometimes | 406 | 8.94 (7.42, 10.74) | 508 | 9.78 (8.32, 11.47) | |
| Seldom | 483 | 10.89 (9.43, 12.55) | 546 | 11.08 (9.7, 12.63) | |
| Never | 288 | 6.21 (4.97, 7.73) | 238 | 5.15 (4.2, 6.3) | |
| Not own child restraint | 918 | 20.64 (16.38, 25.66) | 1555 | 34.61 (28.81, 40.91) | |
| Total | 4201 | 100 | 4911 | 100 | |
| Variables | Shanghai | Shenzhen | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Percentage (95%CI) | Number | Percentage (95%CI) | |
| Awareness of legislation | ||||
| Unknown | 2015 | 53.76 (49.17, 58.29) | 2535 | 55.85 (49.99, 61.55) |
| Known | 2186 | 46.24 (41.71, 50.83) | 2373 | 44.15 (38.45, 50.01) |
| Total | 4201 | 100 | 4908 | 100 |
| Awareness of enforcement and punishment | ||||
| Unknown | 328 | 14.78 (12.41, 17.52) | 123 | 6.78 (4.67, 9.74) |
| Known | 1858 | 85.22 (82.48, 87.59) | 2235 | 93.22 (90.26, 95.33) |
| Total | 2186 | 100 | 2358 | 100 |
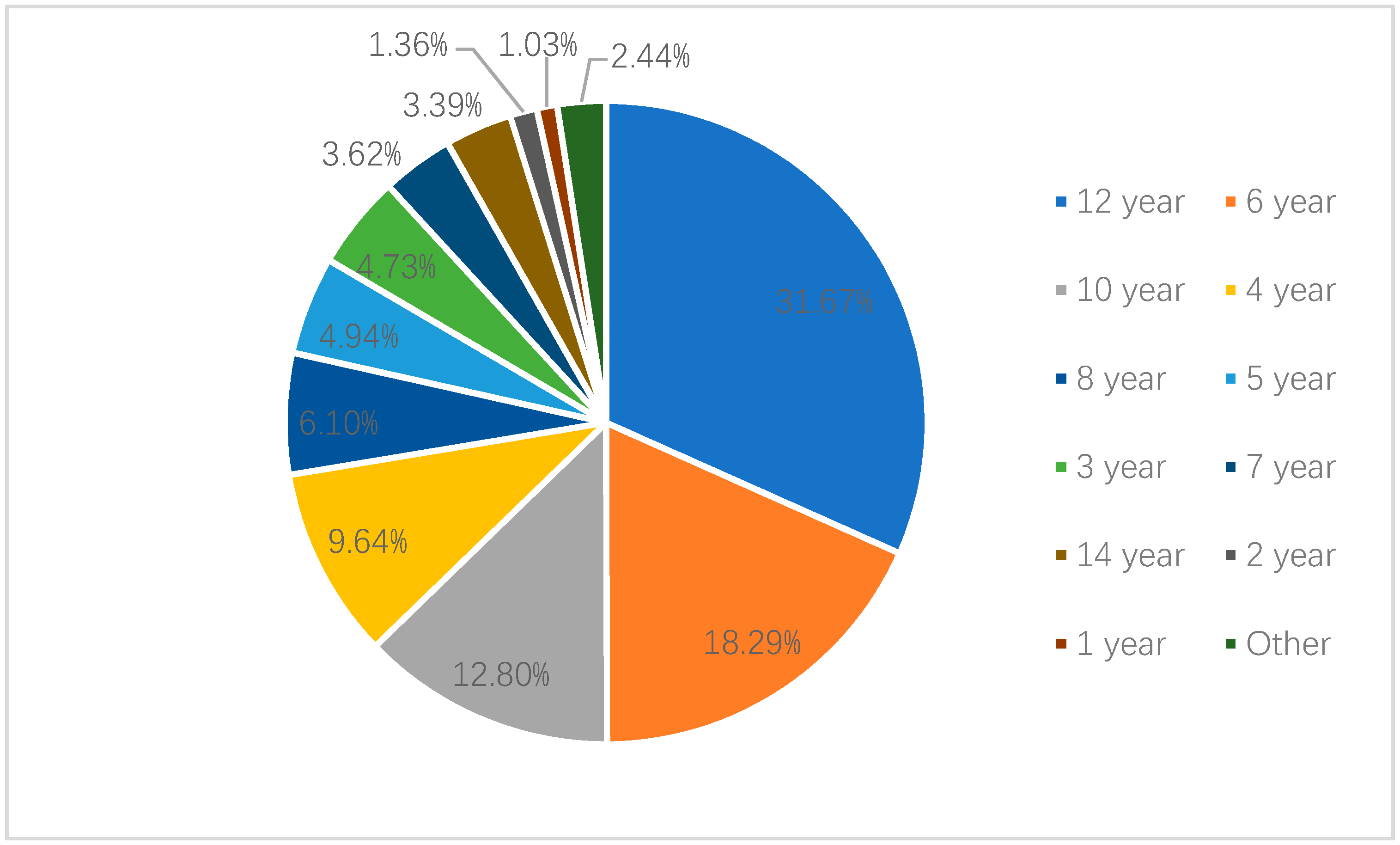
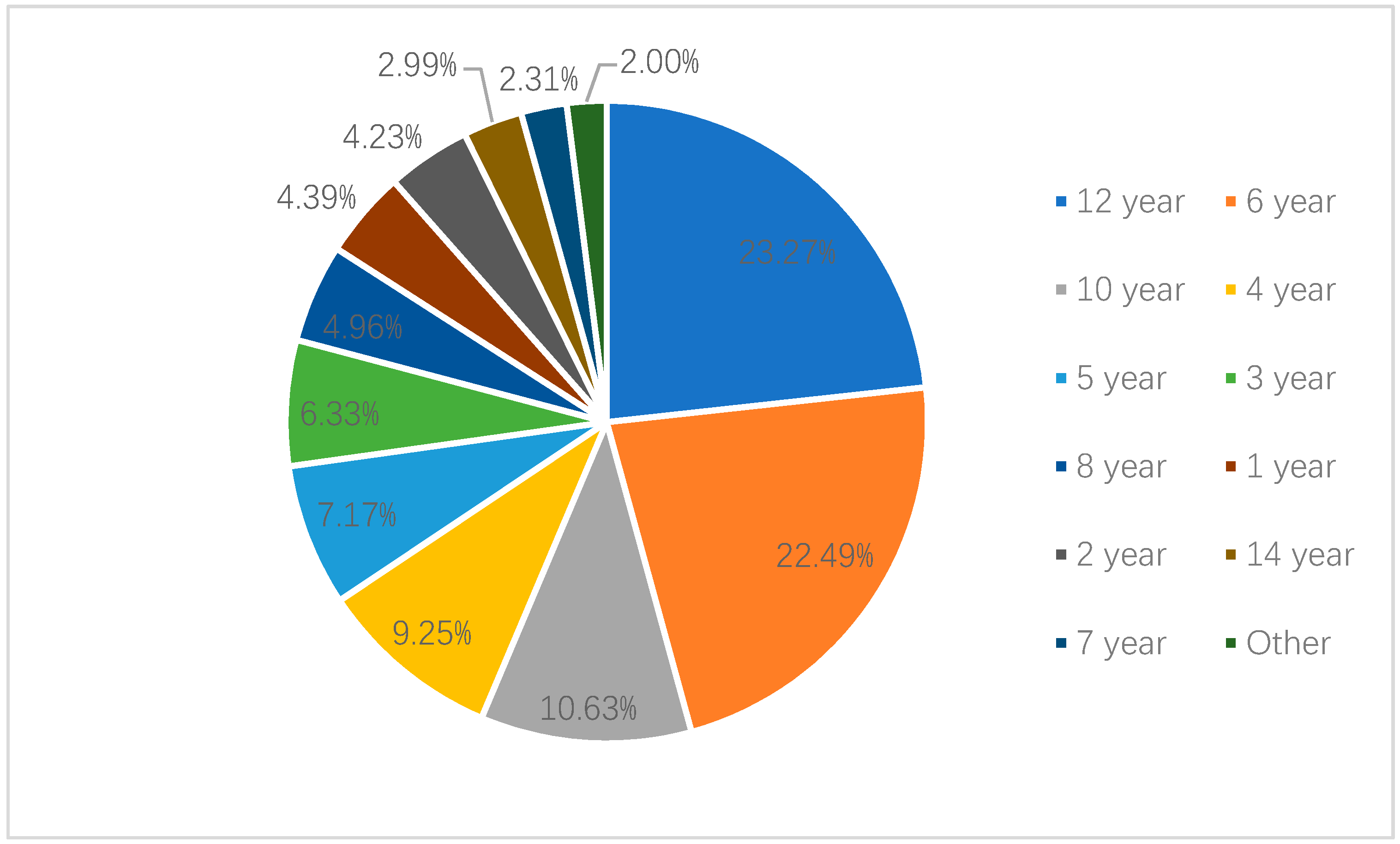
| Awareness of age criteria of legislation | ||||
| Under 2 years | 53 | 2.29 (1.54, 3.41) | 58 | 3.53 (2.42, 5.12) |
| Under 4 years | 516 | 21.88 (19.1, 24.93) | 600 | 21.72 (19.16, 24.51) |
| Under 6 years | 230 | 10.13 (8.59, 11.92) | 371 | 15.61 (12.11, 19.89) |
| Under 8 years | 53 | 2.6 (1.83, 3.67) | 54 | 2.4 (1.76, 3.27) |
| Under 10 years | 47 | 2.12 (1.42, 3.13) | 44 | 2.37 (1.65, 3.39) |
| Under 12 years | 1131 | 53.35 (49.43, 57.24) | 947 | 41.02 (38.19, 43.92) |
| Other | 6 | 0.19 (0.064, 0.55) | 13 | 0.48 (0.23, 0.99) |
| Unknown | 150 | 7.44 (5.64, 9.76) | 276 | 12.87 (10.74, 15.34) |
| Total | 2186 | 100 | 2363 | 100 |
| Variables | Shanghai | Shenzhen | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Percentage (95%CI) | Number | Percentage (95%CI) | |
| Support for national legislation | ||||
| Yes | 3113 | 73.8 (70.73, 76.66) | 3549 | 73.66 (71.08, 76.1) |
| No | 417 | 9.29 (7.88, 10.92) | 625 | 11.79 (10.43, 13.29) |
| Indifferent | 671 | 16.91 (14.69, 19.4) | 737 | 14.55 (12.75, 16.55) |
| Total | 4201 | 100 | 4911 | 100 |
| Criteria for legislation | ||||
| Age | 2065 | 58.42 (52, 64.57) | 2864 | 61.76 (59.2, 64.26) |
| Height | 1349 | 24.87 (20.28, 30.11) | 1473 | 28.16 (25.49, 30.99) |
| Other | 75 | 1.33 (0.88, 2) | 51 | 1.11 (0.68, 1.81) |
| Indifferent | 544 | 15.38 (12.01, 19.48) | 466 | 8.97 (7.64, 10.5) |
| Total | 4033 | 100 | 4854 | 100 |
| Support for enforcement and punishment | ||||
| Yes | 2813 | 73.62 (71.11, 75.98) | 3,360 | 78.64 (75.89, 81.15) |
| No | 330 | 8.56 (7.13, 10.24) | 365 | 8.23 (7.01, 9.64) |
| Indifferent | 641 | 17.82 (15.47, 20.45) | 555 | 13.13 (11.33, 15.18) |
| Total | 4201 | 100 | 4905 | 100 |
| Types of enforcement and punishment | ||||
| Fine | 2215/2813 | 78.06 (73.34, 82.16) | 2674/3360 | 78.42 (74.22, 82.1) |
| 44 U.S. dollars and upper | 563/2813 | 21.53 (18.62, 24.76) | 824/3360 | 23.83 (20.78, 27.19) |
| 29-43 U.S. dollars | 462/2813 | 17.52 (15.6, 19.62) | 676/3360 | 20.76 (17.08, 24.99) |
| 15-28 U.S. dollars | 666/2813 | 21.45 (18.6, 24.61) | 704/3360 | 20.62 (16.96, 24.84) |
| Under 14 U.S. dollars | 524/2813 | 17.56 (15.2, 20.19) | 470/3360 | 13.2 (11.77, 14.78) |
| Deduction | 823/2813 | 28.06 (24.95, 31.4) | 790/3360 | 22.53 (17.64, 28.31) |
| Education | 1171/2813 | 40.84 (36.18, 45.67) | 1532/3360 | 46.71 (43.03, 50.44) |
| Other | 15/2813 | 0.48 (0.26, 0.89) | 34/3360 | 0.68 (0.41, 1.11) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, Y.; Deng, X.; Ye, P.; Peng, J.; Peng, J.; Lei, L.; Yu, Y.; Duan, L. The Awareness and Attitude of Parents towards the Legislation of Child Restraint in Two Cities of China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2405. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17072405
Jin Y, Deng X, Ye P, Peng J, Peng J, Lei L, Yu Y, Duan L. The Awareness and Attitude of Parents towards the Legislation of Child Restraint in Two Cities of China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(7):2405. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17072405
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Ye, Xiao Deng, Pengpeng Ye, Ji Peng, Juanjuan Peng, Lin Lei, Yan Yu, and Leilei Duan. 2020. "The Awareness and Attitude of Parents towards the Legislation of Child Restraint in Two Cities of China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 7: 2405. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17072405
APA StyleJin, Y., Deng, X., Ye, P., Peng, J., Peng, J., Lei, L., Yu, Y., & Duan, L. (2020). The Awareness and Attitude of Parents towards the Legislation of Child Restraint in Two Cities of China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(7), 2405. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17072405




