Psychometric Validation and Reference Norms for the European Spanish Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire: DCDQ-ES
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants, Procedures and Research Ethics
2.2. Measurements
European-Spanish Version of the DCDQ (DCDQ-ES)
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
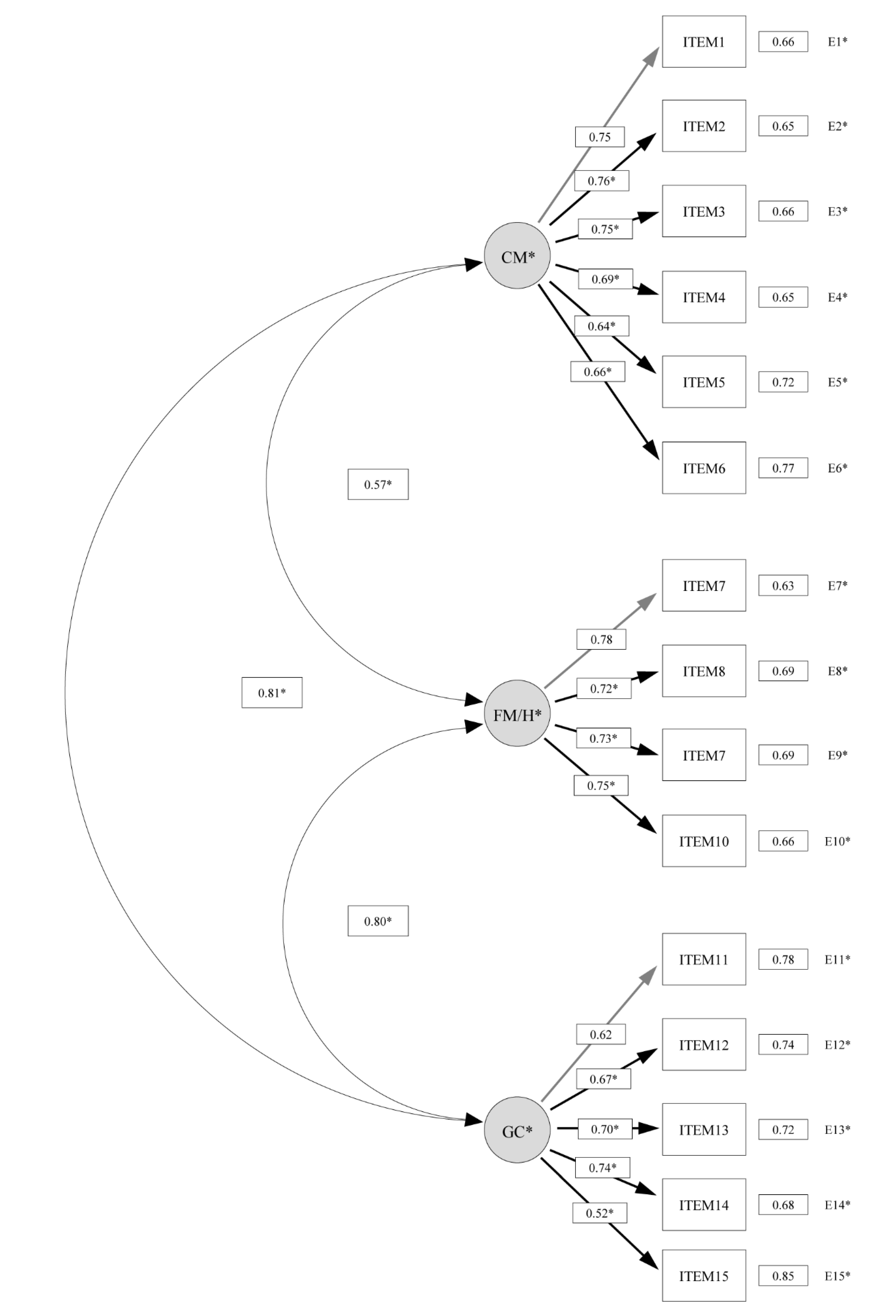
3.1. Construct Validity and Internal Consistency
3.2. Discriminant Validity
3.3. Age and Sex Differences and Age-Specific Cut-Offs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Participants | N | Boys (N (%)) |
|---|---|---|
| Normative group | 540 | 270 (50.0%) |
| 6–7 years old | 180 | 90 (50.0%) |
| 8–9 years old | 180 | 90 (50.0%) |
| 10–12 years old | 180 | 90 (50.0%) |
| pDCD group | 30 | 20 (66.7) |
| 6–7 years old | 11 | 8 (72.7) |
| 8–9 years old | 16 | 10 (62.5) |
| 10–11 years old | 3 | 1 (33.3) |
| Control group | 60 | 40 (66.7) |
| 6–7 years old | 32 | 16 (72.7) |
| 8–9 years old | 32 | 20 (62.5) |
| 10–11 years old | 6 | 2 (33.3) |
References
- Zwicker, J.G.; Missiuna, C.; Harris, S.R.; Boyd, L.A. Developmental coordination disorder: A review and update. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2012, 16, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Psychiatry Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatry Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Blank, R.; Barnett, A.L.; Cairney, J.; Green, D.; Kirby, A.; Polatajko, H.; Rosenblum, S.; Smits-Engelsman, B.; Sugden, D.; Wilson, P.; et al. International clinical practice recommendations on the definition, diagnosis, assessment, intervention, and psychosocial aspects of developmental coordination disorder. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2019, 61, 242–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairney, J.; Hay, J.; Veldhuizen, S.; Missiuna, C.; Mahlberg, N.; Faught, B.E. Trajectories of relative weight and waist circumference among children with and without developmental coordination disorder. CMAJ 2010, 182, 1167–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivilis, I.; Hay, J.; Cairney, J.; Klentrou, P.; Liu, J.; Faught, B.E. Physical activity and fitness in children with developmental coordination disorder: A systematic review. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2011, 32, 894–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.C.; Wu, S.K.; Cairney, J.; Hsieh, C.Y. Motor coordination and health-related physical fitness of children with developmental coordination disorder: A three-year follow-up study. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2011, 32, 2993–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Lobete, L.; Pértega-Díaz, S.; Santos-del-Riego, S.; Montes-Montes, R. Sensory Processing Patterns in Developmental Coordination Disorder, Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder and Typical Development. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2020, 100, 103608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrowell, I.; Hollén, L.; Lingam, R.; Emond, A. Mental health outcomes of developmental coordination disorder in late adolescence. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2017, 59, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingam, R.; Jongmans, M.J.; Ellis, M.; Hunt, L.P.; Golding, J.; Emond, A. Mental health difficulties in children with developmental coordination disorder. Pediatrics 2012, 129, e882–e891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairney, J.; Rigoli, D.; Piek, J. Developmental coordination disorder and internalizing problems in children: The environmental stress hypothesis elaborated. Dev. Rev. 2013, 33, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, L.; Sumner, E.; Hill, E.L. Emotional and behavioural problems in children with Developmental Coordination Disorder: Exploring parent and teacher reports. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2017, 70, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, L.C.; Cardoso, A.A.; Missiuna, C. Activities and participation in children with developmental coordination disorder: A systematic review. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2011, 32, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Linde, B.W.; van Netten, J.J.; Otten, E.; Postema, K.; Geuze, R.H.; Schoemaker, M.M. Activities of Daily Living in Children With Developmental Coordination Disorder: Performance, Learning, and Participation. Phys. Ther. 2015, 95, 1496–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, M.L.; Schoemaker, M.M.; Albaret, J.M.; Geuze, R.H. What is the evidence of impaired motor skills and motor control among children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)? Systematic review of the literature. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2015, 36, 338–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenblum, S.; Waissman, P.; Diamond, G.W. Identifying play characteristics of pre-school children with developmental coordination disorder via parental questionnaires. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2017, 53, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Summers, J.; Larkin, D.; Dewey, D. Activities of daily living in children with developmental coordination disorder: Dressing, personal hygiene, and eating skills. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2008, 27, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, J.; Larkin, D.; Dewey, D. What Impact does Developmental Coordination Disorder have on Daily Routines? Int. J. Disabil. Dev. Educ. 2008, 55, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrowell, I.; Hollén, L.; Lingam, R.; Emond, A. The impact of developmental coordination disorder on educational achievement in secondary school. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2018, 72, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missiuna, C.; Rivard, L.; Bartlett, D. Early identification and risk management of children with Developmental Coordination Disorder. Pediatr. Phys. Ther. 2003, 15, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoemaker, M.M.; Flapper, B.; Verheij, N.P.; Wilson, B.N.; Reinders-Messelink, H.A.; de Kloet, A. Evaluation of the Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire as a screening instrument. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2006, 48, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Lobete, L.; Santos-del-Riego, S.; Pértega-Díaz, S.; Montes-Montes, R. Prevalence of suspected developmental coordination disorder and associated factors in Spanish classrooms. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2019, 86, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carballal Mariño, M.; Gago Ageitos, A.; Ares Álvarez, J.; Del Río Garma, M.; García Cendón, C.; Goicoechea Castaño, A.; Pena Nieto, J. Prevalencia de trastornos del neurodesarrollo, comportamiento y aprendizaje en Atención Primaria. An. Pediatr. 2018, 89, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, B.N.; Crawford, S.G.; Green, D.; Roberts, G.; Aylott, A.; Kaplan, B.J. Psychometric properties of the revised Developmental Coordination Disorder. Phys. Occup. Ther. Pediatr. 2009, 29, 182–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martini, R.; St-Pierre, M.F.; Wilson, B.N. French Canadian cross-cultural adaptation of the Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire ‘07: DCDQ-FC. Can. J. Occup. Ther. 2011, 78, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy-Behr, A.; Wilson, B.N.; Rodger, S.; Mickan, S. Cross-cultural adaptation of the developmental coordination disorder questionnaire 2007 for German-speaking countries: DCDQ-G. Neuropediatrics 2013, 44, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prado, M.S.; Magalhães, L.C.; Wilson, B.N. Cross-cultural adaptation of the developmental coordination disorder questionnaire for Brazilian children. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2009, 13, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caravale, B.; Baldi, S.; Gasparini, C.; Wilson, B.N. Cross-cultural adaptation, reliability and predictive validity of the Italian version of Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire (DCDQ). Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2014, 18, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A. Cross-cultural adaptation of the Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire (DCDQ’07) for the population of Polish children. Biomed. Hum. Kinet. 2016, 8, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.; Gabbard, C. Adaptation and Preliminary Testing of the Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire (DCDQ) for Children in India. Phys. Occup. Ther. Pediatr. 2017, 37, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray-Kaeser, S.; Thommen, E.; Martini, R.; Jover, M.; Gurtner, B.; Bertrand, A.M. Psychometric assessment of the French European Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire (DCDQ-FE). PLoS ONE 2019, 24, e0217280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamanca-Duque, L.M.; Naranjo Aristizábal, M.M.C.; González Marín, A.P. Validity and reliability of developmental coordination disorder questionnaire Spanish version. Rev. Cienc. Salud 2013, 11, 263–274. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Linde, B.W.; van Netten, J.J.; Otten, B.E.; Postema, K.; Geuze, R.H.; Schoemaker, M.M. Psychometric properties of the DCDDaily-Q: A new parental questionnaire on children’s performance in activities of daily living. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2014, 35, 1711–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montes-Montes, R.; Delgado-Lobete, L.; Pereira, J.; Schoemaker, M.M.; Santos-del-Riego, S.; Pousada, T. Identifying Children with Developmental Coordination Disorder via Parental Questionnaires. Spanish Reference Norms for the DCDDaily-Q-ES and Correlation with the DCDQ-ES. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montes-Montes, R.; Delgado-Lobete, L.; Pereira, J.; Pousada, T. Cross-Cultural Adaptation and Preliminary Validation of the Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire for European Spanish Children. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Caravale, B.; Baldi, S.; Capone, L.; Presaghi, F.; Balottin, U.; Zoppello, M. Psychometric properties of the Italian versión of the Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire (DCDQ-Italian). Res. Dev. Disabil. 2015, 36, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennessy, S.; Bilker, W.B.; Berlin, J.A.; Strom, B.L. Factors influencing the optimal control-to-case ratio in matched case-control studies. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1999, 149, 195–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pértega Díaz, S.; Pita Fernández, S. Cálculo del tamaño muestral en estudios de casos y controles. Cad Aten Primaria 2002, 9, 148–150. [Google Scholar]
- Forero, C.G.; Maydeu-Olivares, A.; Gallardo-Pujol, D. Factor analysis with ordinal indicators: A monte carlo study comparing DWLS and ULS estimation. Struct. Equ. Model. 2009, 16, 625–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang-Wallentin, F.; Jöreskog, K.G.; Luo, H. Confirmatory factor analysis of ordinal variables with misspecified models. Struct. Equ. Model. 2010, 17, 392–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, S.G.; Finch, J.F.; Curran, P.J. Structural equation models with non-normal variables. In Structural Equation Modeling: Concepts, Issues and Applications; Hoyle, R.H., Ed.; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 1995; pp. 56–75. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.; Bentler, P.M. Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Struct. Equ. Model. 1999, 6, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, R.B. Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling, 2nd ed.; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Nakai, A.; Miyachi, T.; Okada, R.; Tani, I.; Nakajima, S.; Onishi, M.; Fujita, C.; Tsujii, M. Evaluation of the Japanese version of the Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire as a screening tool for clumsiness of Japanese children. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2011, 32, 1615–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivard, L.; Missiuna, C.; McCauley, D.; Cairney, J. Descriptive and factor analysis of the Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire (DCDQ‘07) in a population-based sample of children with and without Developmental Coordination Disorder. Child Care Health Dev. 2014, 40, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Lobete, L.; Montes-Montes, R.; Pértega-Díaz, S.; Santos-del-Riego, S.; Cruz-Valiño, J.M.; Schoemaker, M.M. Interrelation of Individual, Country and Activity Constraints in Motor Activities of Daily Living among Typically Developing Children: A Cross-sectional Comparison of Spanish and Dutch Populations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, B.J.; Dewey, D.M.; Crawford, S.G.; Wilson, B.N. The term comorbidity is of questionable value in reference to developmental disorders: Data and theory. J. Learn. Disabil. 2001, 34, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyahara, M.; Möbs, I.; Doll-Tepper, G. Severity of hyperactivity and the comorbidity of hyperactivity with clumsiness in three sample sources: School, support group and hospital. Child Care Health Dev. 2001, 27, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, D.; Baird, G.; Sugden, D.A. A pilot study of psychopathology in developmental coordination disorder. Child Care Health Dev. 2006, 32, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Ayuso, D.; Maciver, D.; Richmond, J.; Jorquera-Cabrera, S.; Garra-Palud, L.; Zabala-Baños, C.; Toledano-González, A.; Triviño-Juárez, J.-M. Tactile Discrimination, Praxis and Cognitive Impulsivity in ADHD Children: A Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goulardins, J.B.; Rigoli, D.; Licari, M.; Piek, J.P.; Hasue, R.H.; Oosterlaan, J.; Oliveira, J.A. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and developmental coordination disorder: Two separate disorders or do they share a common etiology. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 292, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeod, K.R.; Langevin, L.M.; Dewey, D.; Goodyear, B.G. Atypical wihin- and between-hemisphere motor network functional connections in children with developmental coordination disorder and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Neuroimage Clin. 2016, 12, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holloway, J.M.; Long, T.M.; Biasini, F. Relationships between Gross Motor Skills and Social Function in Young Boys with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Pediatr. Phys. Ther. 2018, 30, 184. [Google Scholar]
- Hilton, C.L.; Zhang, Y.; Whilte, M.R.; Klohr, C.L.; Constantino, J.N. Motor Impairment in Sibling Pairs Concordant and Discordant for Autism Spectrum Disorders. Autism 2012, 16, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, A.N.; Landa, R.J.; Galloway, J.C. (Cole) Current Perspectives on Motor Functioning in Infants, Children, and Adults with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Phys. Ther. 2011, 91, 1116–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, A.N. Is Motor Impairment in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Distinct From Developmental Coordination Disorder (DCD)? A Report from the SPARK Study. Phys. Ther. 2020, pzz190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilroy, E.; Cermak, S.A.; Aziz-Zadeh, L. A Review of Functional and Structural Neurobiology of the Action Observation Network in Autism Spectrum Disorder and Developmental Coordination Disorder. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caeyenberghs, K.; Taymans, T.; Wilson, P.H.; Vanderstraeten, G.; Hosseini, H.; van Waelvelde, H. Neural signatura of developmental coordination disorder in the structural connectome independent of comorbid autism. Dev. Sci. 2016, 19, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faebo Larsen, R.; Hvas Mortensen, L.; Martinussen, T.; Nybo Andersen, A.M. Determinants of developmental coordination disorder in 7-year-old children: A study of children in the Danish National Birth Cohort. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2013, 55, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psotta, R.; Hendl, J.; Frömel, K.; Lehnert, M. The second version of the Movement Assessment Battery for children: A comparative study in 7–10 year old children from the Czech Republic and the United Kingdom. Acta Gymn. 2012, 42, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentini, N.C.; Oliveira, M.A.; Pangelinan, M.M.; Whitall, J.; Clark, J.E. Can the MABC discriminate and predict motor impairment? A comparison of Brazilian and American children. IJTR Int. J. Ther. Rehabil. 2017, 24, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.; Gabbard, C.; Lopes Vieira, J.L.; Norraila da Silva, P.; Cheuczuk, F.; Ferreira da Rocha, F.; Matias de Souza, V.F.; Caçola, F. Reconsidering the use of cut-off scores: DCDQ-Brazil. Rev. Bras. Med. Esporte 2019, 25, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemeijer, A.S.; van Waelvelde, H.; Smits-Engelsman, B.C. Crossing the North Sea seems to make DCD disappear: Cross-validation of Movement Assessment Battery for Children-2 norms. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2015, 39, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geuze, R.H.; Jongmans, M.J.; Schoemaker, M.M.; Smits-Engelsman, B.C. Clinical and research diagnostic criteria for developmental coordination disorder: A review and discussion. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2001, 20, 7–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits-Engelsman, B.; Schoemaker, M.; Delabastita, T.; Hoskens, J.; Geuze, R. Diagnostic criteria for DCD: Past and future. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2015, 42, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| DCDQ-ES | pDCD | Control | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | ||
| Total (n = 90) | |||
| Control during movement | 20.4 (6.2) | 26.8 (3.3) | <0.001 |
| Fine motor/ handwriting | 12.0 (5.2) | 17.2 (3.0) | <0.001 |
| General coordination | 15.7 (5.5) | 21.4 (3.4) | <0.001 |
| DCDQ-ES total | 48.1 (14.0) | 65.5 (8.3) | <0.001 |
| 6–7 years (n = 33) | |||
| Control during movement | 18.2 (7.3) | 26.1 (3.1) | 0.005 |
| Fine motor/ handwriting | 10.5 (5.8) | 16.3 (2.6) | 0.008 |
| General coordination | 14.2 (5.7) | 21.1 (3.2) | 0.002 |
| DCDQ-ES total | 42.8 (15.3) | 63.5 (7.7) | <0.001 |
| 8–9 years (n = 48) | |||
| Control during movement | 21.4 (5.0) | 27.2 (3.6) | <0.001 |
| Fine motor/ handwriting | 13.2 (4.7) | 17.8 (3.2) | 0.002 |
| General coordination | 16.9 (5.3) | 21.5 (3.7) | <0.001 |
| DCDQ-ES total | 51.4 (12.9) | 66.4 (8.8) | <0.001 |
| 10–11 years (n = 9). | |||
| Control during movement | 23.0 (7.8) | 27.7 (2.3) | 0.410 |
| Fine motor/ handwriting | 11.7 (5.5) | 17.7 (2.7) | 0.056 |
| General coordination | 15.0 (6.6) | 22.0 (3.0) | 0.055 |
| DCDQ-ES total | 49.7 (12.7) | 67.3 (7.2) | 0.029 |
| DCDQ-ES | pDCD | pDCD only | pDCD/ ADHD | pDCD/ ASD | Control | p Value within Groups |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) (n = 30) | Mean (SD) (n = 16) | Mean (SD) (n = 10) | Mean (SD) (n = 4) | Mean (SD) (n =60) | ||
| Item 1 | 3.0 (1.3) | 3.4 (1.2) | 2.9 (1.2) | 1.8 (1.5) | 4.4 (0.8) | <0.001 a; 0.002 b; <0.001 c; <0.001 d |
| Item 2 | 2.8 (1.3) | 3.1 (1.1) | 2.8 (1.4) | 1.8 (1.5) | 4.5 (0.7) | <0.001 a; <0.001 b; <0.001 c; <0.001 d |
| Item 3 | 2.7 (1.4) | 2.9 (1.1) | 2.7 (1.7) | 2.0 (2.0) | 4.1 (1.0) | 0.004 a; 0.004 b; 0.004 c; <0.001 d |
| Item 4 | 4.0 (1.2) | 4.3 (0.9) | 4.1 (1.4) | 3.0 (1.6) | 4.6 (0.7) | 0.033 a; 1.000 b; 0.760 c; 0.004 d |
| Item 5 | 4.0 (1.2) | 4.1 (1.0) | 4.3 (1.3) | 2.8 (1.5) | 4.6 (0.6) | 0.016 a; 0.213 b; 1.000 c; <0.001 d |
| Item 6 | 3.8 (1.2) | 4.1 (1.0) | 3.8 (1.4) | 3.0 (1.4) | 4.8 (0.5) | <0.001 a; 0.012 b; 0.003 c; <0.001 d |
| Item 7 | 3.0 (1.5) | 3.5 (1.4) | 2.3 (1.1) | 3.0 (2.3) | 4.3 (0.8) | <0.001 a; 0.053 b; <0.001 c; 0.119 d |
| Item 8 | 3.0 (1.6) | 3.6 (1.7) | 2.5 (1.4) | 1.8 (1.0) | 4.4 (0.9) | <0.001 a; 0.082 b; <0.001 c; <0.001 d |
| Item 9 | 3.0 (1.4) | 3.6 (1.3) | 2.3 (1.1) | 2.5 (1.7) | 4.2 (1.0) | <0.001 a; 0.357 b; <0.001 c; 0.017 d |
| Item 10 | 3.0 (1.4) | 3.4 (1.3) | 2.6 (1.2) | 2.0 (1.4) | 4.3 (0.9) | <0.001 a; 0.029 b; <0.001 c; <0.001 d |
| Item 11 | 3.5 (1.5) | 3.8 (1.5) | 3.8 (1.1) | 1.8 (1.0) | 4.6 (0.7) | 0.001 a; 0.011 b; 0.087 c; <0.001 d |
| Item 12 | 3.4 (1.4) | 4.0 (1.2) | 3.2 (1.2) | 1.5 (1.0) | 4.4 (0.7) | <0.001 a; 0.666 b; 0.001 c; <0.001 d |
| Item 13 | 2.7 (1.4) | 3.3 (1.4) | 1.8 (0.9) | 2.3 (1.3) | 4.3 (1.0) | <0.001 a; 0.014 b; <0.001 c; 0.003 d |
| Item 14 | 3.3 (1.5) | 3.8 (1.4) | 3.1 (1.4) | 1.8 (1.0) | 4.3 (1.0) | 0.002 a; 0.793 b; 0.014 c; <0.001 d |
| Item 15 | 2.8 (1.5) | 3.5 (1.5) | 1.8 (0.9) | 2.8 (1.7) | 3.9 (1.1) | 0.001 a; 1.000 b; <0.001 c; 0.388 d |
| Control during movement | 20.4 (6.2) | 21.8 (4.4) | 20.6 (6.8) | 14.3 (8.8) | 26.8 (3.3) | <0.001 a; <0.001 b; <0.001 c; <0.001 d |
| Fine motor/ handwriting | 12.0 (5.2) | 14.2 (4.9) | 9.7 (4.2) | 9.3 (5.6) | 17.2 (3.0) | <0.001 a; 0.025 b; <0.001 c; <0.001 d |
| General coordination | 15.7 (5.5) | 18.4 (5.0) | 13.7 (3.8) | 10.0 (5.5) | 21.4 (3.4) | <0.001 a; 0.035 b; <0.001 c; <0.001 d |
| DCDQ-ES total | 48.1 (14.0) | 54.3 (10.7) | 44.0 (11.8) | 33.5 (18.6) | 65.5 (8.3) | <0.001 a; <0.001 b; <0.001 c; <0.001 d |
| DCDQ-ES Total and Subscales | p5 | p10 | p15 | p20 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normative group (n = 540) | ||||
| Control during movement | 19 | 21 | 22 | 24 |
| Fine motor/ handwriting | 12 | 14 | 15 | 16 |
| General coordination | 15 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| DCDQ-ES | 49 | 55 | 57 | 59 |
| 6–7 years old | ||||
| Control during movement | 18 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| Fine motor/ handwriting | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| General coordination | 14 | 16 | 17 | 18 |
| DCDQ-ES | 46 | 50 | 54 | 57 |
| 8–9 years old | ||||
| Control during movement | 19 | 21 | 22 | 24 |
| Fine motor/ handwriting | 12 | 14 | 15 | 16 |
| General coordination | 15 | 17 | 19 | 19 |
| DCDQ-ES | 50 | 55 | 58 | 60 |
| 10–12 years old | ||||
| Control during movement | 21 | 23 | 24 | 24 |
| Fine motor/ handwriting | 13 | 15 | 16 | 16 |
| General coordination | 16 | 17 | 19 | 20 |
| DCDQ-ES | 53 | 56 | 59 | 61 |
| DCDQ-ES Total Score | FP N (%) | FN N (%) | TP N (%) | TN N (%) | PPV | NPV | Youden’s Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p15 (57) | 10 (16.7) | 7 (23.3) | 23 (76.7) | 50 (83.3) | 69.7% | 87.7% | 0.833 |
| p5 (49) | 1 (1.7) | 16 (53.3) | 14 (46.7) | 59 (98.3) | 93.3% | 78.7% | 0.450 |
| Canadian Cut-Offs | ||
|---|---|---|
| Spanish Cut-Offs | Probable not DCD | Probable DCD |
| Total sample | ||
| Probably not DCD | 90.9% | 3.5% |
| Probable DCD | 0.0% | 5.6% |
| 6–7 years old | ||
| Probably not DCD | 95.0% | 0.0% |
| Probable DCD | 0.0% | 5.0% |
| 8–9 years old | ||
| Probably not DCD | 90.5% | 3.9% |
| Probable DCD | 0.0% | 5.6% |
| 10–12 years old | ||
| Probably not DCD | 87.2% | 6.7% |
| Probable DCD | 0.0% | 5.1% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Montes-Montes, R.; Delgado-Lobete, L.; Pereira, J.; Santos-del-Riego, S.; Pousada, T. Psychometric Validation and Reference Norms for the European Spanish Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire: DCDQ-ES. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2425. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17072425
Montes-Montes R, Delgado-Lobete L, Pereira J, Santos-del-Riego S, Pousada T. Psychometric Validation and Reference Norms for the European Spanish Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire: DCDQ-ES. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(7):2425. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17072425
Chicago/Turabian StyleMontes-Montes, Rebeca, Laura Delgado-Lobete, Javier Pereira, Sergio Santos-del-Riego, and Thais Pousada. 2020. "Psychometric Validation and Reference Norms for the European Spanish Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire: DCDQ-ES" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 7: 2425. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17072425
APA StyleMontes-Montes, R., Delgado-Lobete, L., Pereira, J., Santos-del-Riego, S., & Pousada, T. (2020). Psychometric Validation and Reference Norms for the European Spanish Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire: DCDQ-ES. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(7), 2425. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17072425









