Dust Events and Indoor Air Quality in Residential Homes in Kuwait
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Home Selection
2.2. Sampling Techniques
2.3. Dust Event Identification
2.4. Home Tightness Analysis
2.5. Coarse-to-Fine Particle Ratio Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
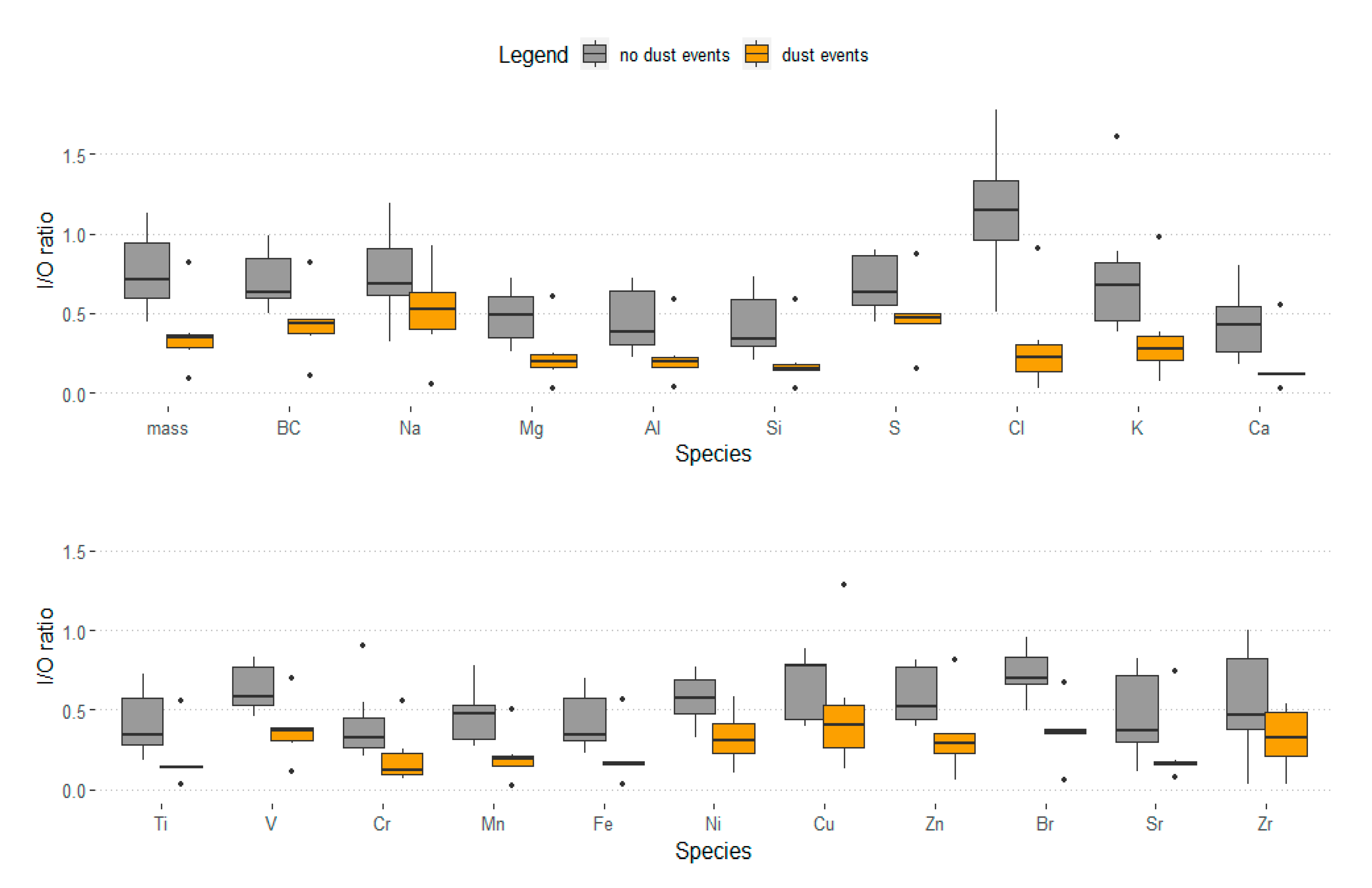
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgment
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, K.H.; Kabir, E.; Kabir, S. A Review on the Human Health Impact of Airborne Particulate Matter. Environ. Int. 2015, 74, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristovski, Z.D.; Miljevic, B.; Surawski, N.C.; Morawska, L.; Fong, K.M.; Goh, F.; Yang, I.A. Respiratory Health Effects of Diesel Particulate Matter. Respirology 2012, 17, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacks, J.D.; Stanek, L.W.; Luben, T.J.; Johns, D.O.; Buckley, J.B.; Brown, J.S.; Ross, M. Particulate Matter-Induced Health Effects: Who Is Susceptible? Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebi, K.L.; McGregor, G. Climate Change, Tropospheric Ozone and Particulate Matter, and Health Impacts. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 1449–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valavanidis, A.; Fiotakis, K.; Vlachogianni, T. Airborne Particulate Matter and Human Health: Toxicological Assessment and Importance of Size and Composition of Particles for Oxidative Damage and Carcinogenic Mechanisms. J. Environ. Sci. Health 2008, C26, 339–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belli, A.J.; Bose, S.; Aggarwal, N.; Dasilva, C.; Thapa, S.; Grammer, L.; Paulin, L.M.; Hansel, N.N. Indoor Particulate Matter Exposure Is Associated with Increased Black Carbon Content in Airway Macrophages of Former Smokers with COPD. Environ. Res. 2016, 150, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Karottki, D.; Spilak, M.; Frederiksen, M.; Anderson, Z.J.; Madsen, A.; Ketzel, M.; Massling, A.; Gunnarsen, L.; Møller, P.; Loft, S. Indoor and Outdoor Exposure to Ultrafine, Fine and Microbiologically Derived Particulate Matter Related to Cardiovascular and Respiratory Effects in a Panel of Elderly Urban Citizens. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 1667–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, J.A.; Alexis, N.; Bacchus, H.; Bernstein, I.L.; Fritz, P.; Horner, E.; Li, N.; Mason, S.; Nel, A.; Oullette, J.; et al. The Health Effects of Nonindustrial Indoor Air Pollution. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 121, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, P.J. Indoor Air Quality and Respiratory Health of Children. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2007, 8, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameri, I.S.; Briant, R.M.; Engels, S. Drought Severity and Increased Dust Storm Frequency in the Middle East: A Case Study from the Tigris–Euphrates Alluvial Plain, Central Iraq. Weather 2019, 74, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córdoba-Jabonero, C.; Sabbah, I.; Sorribas, M.; Adame, J.A.; Cuevas, E.; Sharifi, F.A.; Gil-Ojeda, M. Saharan and Arabian Dust Aerosols: A Comparative Case Study of Lidar Ratio. EPJ Web Conf. 2016, 119, 08002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Garshick, B.; Al-Hemoud, A.; Huang, S.; Koutrakis, P. Impacts of meteorology and vegetationon surface dust concentrations in Middle Eastern countries. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 136597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yassin, M.F.; Almutairi, S.K.; Al-Hemoud, A. Dust storms backward trajectories’ and source identification over Kuwait. Atmos. Res. 2018, 212, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achilleos, S.; Al-Ozairi, E.; Alahmad, B.; Garshick, E.; Neophytou, A.M.; Bouhamra, W.; Yassin, M.F.; Koutrakis, P. Acute effects of air pollution on mortality: A 17-year analysis in Kuwait. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, L.; Nugent, K. The Health Effects of Dust Storms in the Southwest United States. Southwest Respir. Crit. Care Chron. 2018, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaniabadi, Y.O.; Daryanoosh, S.M.; Amrane, A.; Polosa, R.; Hopke, P.K.; Goudarzi, G.; Mohammadi, M.J.; Sicard, P.; Armin, H. Impact of Middle Eastern Dust Storms on Human Health. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2017, 8, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandstrom, T.; Forsberg, B. Desert Dust. Epidemiology 2008, 19, 808–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alolayan, M.A.; Brown, K.W.; Evans, J.S.; Bouhamra, W.S.; Koutrakis, P. Source apportionment of fine particles in Kuwait City. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 448, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Baroud, A.; Al-Baroud, F.; Al-Sahali, M.; Ettouney, H. Annual Variations of Air Pollution in Jahra, Kuwait. J. Eng. Technol. 2012, 1, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hemoud, A.; Al-Awadi, L.; Al-Rashidi, M.; Rahman, K.A.; Al-Khayat, A.; Behbehani, W. Comparison of indoor air quality in schools: Urban vs. Industrial ‘oil & gas’ zones in Kuwait. Build. Environ. 2017, 122, 50–60. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Hubail, J.; Al-Temeemi, A. Assessment of school building air quality in a desert climate. Build. Environ. 2015, 94, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkilani, A.; Bouhamra, W. Estimation of optimum requirements for indoor air quality and energy consumption in some residences in Kuwait. Environ. Int. 2001, 27, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhamra, W.S.; BoHamra, S.S.; Thomson, M.S. Determination of volatile organic compounds in indoor and ambient air of residences in Kuwait. Environ. Int. 1997, 23, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhamra, W.S. Estimation of volatile organic compounds in Kuwaiti houses after the Gulf war. Environ. Pollut. 1995, 90, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnov, H.; Katra, I.; Friger, M.D. Insights into indoor/outdoor PM concentration ratios due to dust storms in an arid region. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 879–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraga, D.; Maggos, T.; Sadoun, E.; Fthenou, E.; Hassan, H.; Tsiouri, V.; Karavoltsos, S.; Sakellari, A.; Vasilakos, C.; Kakosimos, K. Chemical characterization of indoor and outdoor particulate matter (PM2.5, PM10) in Doha, Qatar. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 1156–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahle, D.; Wickham, H. Ggmap: Spatial Visualization with ggplot2. R J. 2013, 5, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.W.; Bouhamra, W.; Lamoureux, D.P.; Evans, J.S.; Koutrakis, P. Characterization of Particulate Matter for Three Sites in Kuwait. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2008, 58, 994–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavouras, I.G.; Ferguson, S.T. Development and Validation of A High-Volume, Low-Cutoff Inertial Impactor. Inhal. Toxicol. 2000, 12, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.M.; Jeong, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Moon, J.H.; Chung, Y.S.; Kim, K.H. The Analysis of PM2.5 and Associated Elements and Their Indoor/outdoor Pollution Status in an Urban Area. Indoor Air 2010, 21, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koponen, I.K.; Asmi, A.; Keronen, P.; Puhto, K.; Kulmala, M. Indoor Air Measurement Campaign in Helsinki, Finland 1999—The Effect of Outdoor Air Pollution on Indoor Air. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 1465–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koistinen, K.J.; Edwards, R.D.; Mathys, P.; Ruuskanen, J.; Künzli, N.; Jantunen, M.J. Sources of Fine Particulate Matter in Personal Exposures and Residential Indoor, Residential Outdoor and Workplace Microenvironments in the Helsinki Phase of the EXPOLIS Study. Scand. J. Work Environ. Health 2004, 30, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Habre, R.; Coull, B.; Moshier, E.; Godbold, J.; Grunin, A.; Nath, A.; Castro, W. Sources of Indoor Air Pollution in New York City Residences of Asthmatic Children. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2013, 24, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, W.; Li, H.; Zhao, B.; Deng, F. Tracer Element for Indoor PM2.5 in China Migrated from Outdoor. Atmospheric Environment. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 176, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darus, F.M.; Nasir, R.A.; Sumari, S.M.; Ismail, Z.S.; Omar, N.A. Heavy Metals Composition of Indoor Dust in Nursery Schools Building. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 38, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedrizzi, L.; Deflorian, F.; Bonora, P. Evaluation of the Protective Properties of Organic Coatings on Copper Pipes for Refrigerator Cooling Circuit. Electrochim. Acta 1999, 44, 4251–4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutrakis, P.; Brauer, M.; Briggs, S.L.K.; Leaderer, B.P. Indoor Exposures to Fine Aerosols and Acid Gases. Environ. Health Perspect. 1991, 95, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nazaroff, W.W. Indoor Particle Dynamics. Indoor Air 2004, 14, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geller, M.D.; Chang, M.; Sioutas, C.; Ostro, B.D.; Lipsett, M.J. Indoor/outdoor Relationship and Chemical Composition of Fine and Coarse Particles in the Southern California Deserts. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abt, E.; Suh, H.H.; Allen, G.; Koutrakis, P. Characterization of Indoor Particle Sources: A Study Conducted in the Metropolitan Boston Area. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, W.E.; Suh, H.H. Fine Particles and Coarse Particles: Concentration Relationships Relevant to Epidemiologic Studies. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 1997, 47, 1238–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Species | Indoor Concentration N = 13 | Outdoor Concentration N = 13 | I/O Ratio | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
| Mass | 28.52 | 17.94 | 44.34 | 8.789 | 0.70 |
| BC | 2.134 | 0.930 | 3.672 | 0.865 | 0.59 |
| Na | 0.234 | 0.096 | 0.388 | 0.112 | 0.64 |
| Mg | 0.113 | 0.069 | 0.328 | 0.085 | 0.37 |
| Al | 0.320 | 0.231 | 0.950 | 0.339 | 0.36 |
| Si | 0.644 | 0.531 | 2.072 | 0.787 | 0.33 |
| S | 2.556 | 1.212 | 4.450 | 1.866 | 0.59 |
| Cl | 0.035 | 0.032 | 0.050 | 0.046 | 1.10 |
| K | 0.239 | 0.182 | 0.436 | 0.109 | 0.57 |
| Ca | 0.421 | 0.358 | 1.452 | 0.484 | 0.31 |
| Ti | 0.018 | 0.014 | 0.059 | 0.020 | 0.32 |
| V | 0.008 | 0.003 | 0.016 | 0.004 | 0.52 |
| Cr | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.003 | 0.001 | 0.32 |
| Mn | 0.006 | 0.004 | 0.020 | 0.005 | 0.35 |
| Fe | 0.252 | 0.176 | 0.816 | 0.249 | 0.33 |
| Ni | 0.003 | 0.001 | 0.006 | 0.002 | 0.46 |
| Cu | 0.011 | 0.008 | 0.019 | 0.008 | 0.58 |
| Zn | 0.039 | 0.020 | 0.091 | 0.060 | 0.48 |
| Br | 0.013 | 0.006 | 0.023 | 0.006 | 0.56 |
| Sr | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.009 | 0.002 | 0.37 |
| Zr | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.005 | 0.001 | 0.45 |
| Species | Indoor Concentration N = 7 | Outdoor Concentration N = 7 | I/O Ratio | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
| Mass | 40.55 | 22.99 | 116.8 | 18.38 | 0.34 |
| BC | 2.668 | 0.974 | 4.668 | 1.173 | 0.58 |
| Na | 0.293 | 0.076 | 0.345 | 0.095 | 0.89 |
| Mg | 0.295 | 0.213 | 0.988 | 0.153 | 0.30 |
| Al | 0.917 | 0.768 | 2.710 | 0.646 | 0.32 |
| Si | 2.082 | 1.870 | 6.936 | 1.673 | 0.29 |
| S | 2.781 | 0.734 | 3.813 | 1.461 | 0.78 |
| Cl | 0.061 | 0.033 | 0.197 | 0.194 | 0.44 |
| K | 0.444 | 0.313 | 1.030 | 0.209 | 0.43 |
| Ca | 1.888 | 1.790 | 8.302 | 1.509 | 0.22 |
| Ti | 0.059 | 0.054 | 0.228 | 0.048 | 0.25 |
| V | 0.011 | 0.004 | 0.023 | 0.003 | 0.48 |
| Cr | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.014 | 0.002 | 0.22 |
| Mn | 0.017 | 0.013 | 0.066 | 0.014 | 0.27 |
| Fe | 0.783 | 0.681 | 3.264 | 0.641 | 0.23 |
| Ni | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.015 | 0.002 | 0.31 |
| Cu | 0.019 | 0.013 | 0.042 | 0.020 | 0.48 |
| Zn | 0.061 | 0.017 | 0.173 | 0.107 | 0.45 |
| Br | 0.018 | 0.005 | 0.031 | 0.006 | 0.60 |
| Sr | 0.011 | 0.009 | 0.047 | 0.009 | 0.24 |
| Zr | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.015 | 0.006 | 0.27 |
| Species | Coarse Indoor (μg/m3) | Coarse Outdoor (μg/m3) | Fine Indoor (μg/m3) | Fine Outdoor (μg/m3) | Indoor Ratio a | Outdoor Ratio b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mass | 13.43 | 71.74 | 27.12 | 45.04 | 0.4 | 1.6 |
| Fe | 0.474 | 2.471 | 0.309 | 0.792 | 1.3 | 3.2 |
| Ca | 1.346 | 6.829 | 0.542 | 1.473 | 2.1 | 4.8 |
| Si | 1.218 | 4.794 | 0.865 | 2.142 | 1.2 | 2.3 |
| Al | 0.499 | 1.759 | 0.418 | 0.951 | 1.0 | 1.9 |
| Ti | 0.036 | 0.171 | 0.023 | 0.058 | 1.3 | 3.1 |
| K | 0.124 | 0.551 | 0.320 | 0.479 | 0.4 | 1.2 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, Y.; Alahmad, B.; Kang, C.-M.; Al-Marri, F.; Kommula, V.; Bouhamra, W.; Koutrakis, P. Dust Events and Indoor Air Quality in Residential Homes in Kuwait. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2433. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17072433
Yuan Y, Alahmad B, Kang C-M, Al-Marri F, Kommula V, Bouhamra W, Koutrakis P. Dust Events and Indoor Air Quality in Residential Homes in Kuwait. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(7):2433. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17072433
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Yufei, Barrak Alahmad, Choong-Min Kang, Fhaid Al-Marri, Venkateswarlu Kommula, Walid Bouhamra, and Petros Koutrakis. 2020. "Dust Events and Indoor Air Quality in Residential Homes in Kuwait" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 7: 2433. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17072433
APA StyleYuan, Y., Alahmad, B., Kang, C.-M., Al-Marri, F., Kommula, V., Bouhamra, W., & Koutrakis, P. (2020). Dust Events and Indoor Air Quality in Residential Homes in Kuwait. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(7), 2433. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17072433






