Calcium Superphosphate-Mediated Reshaping of Denitrifying Bacteria Community Contributed to N2O Mitigation in Pig Manure Windrow Composting
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Windrow Composting Experiment
2.2. Gas Sampling and Flux Measurement
2.3. Physicochemical Properties Determination
2.4. Real-Time Quantitative PCR (q-PCR) Assays of the Functional Genes
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
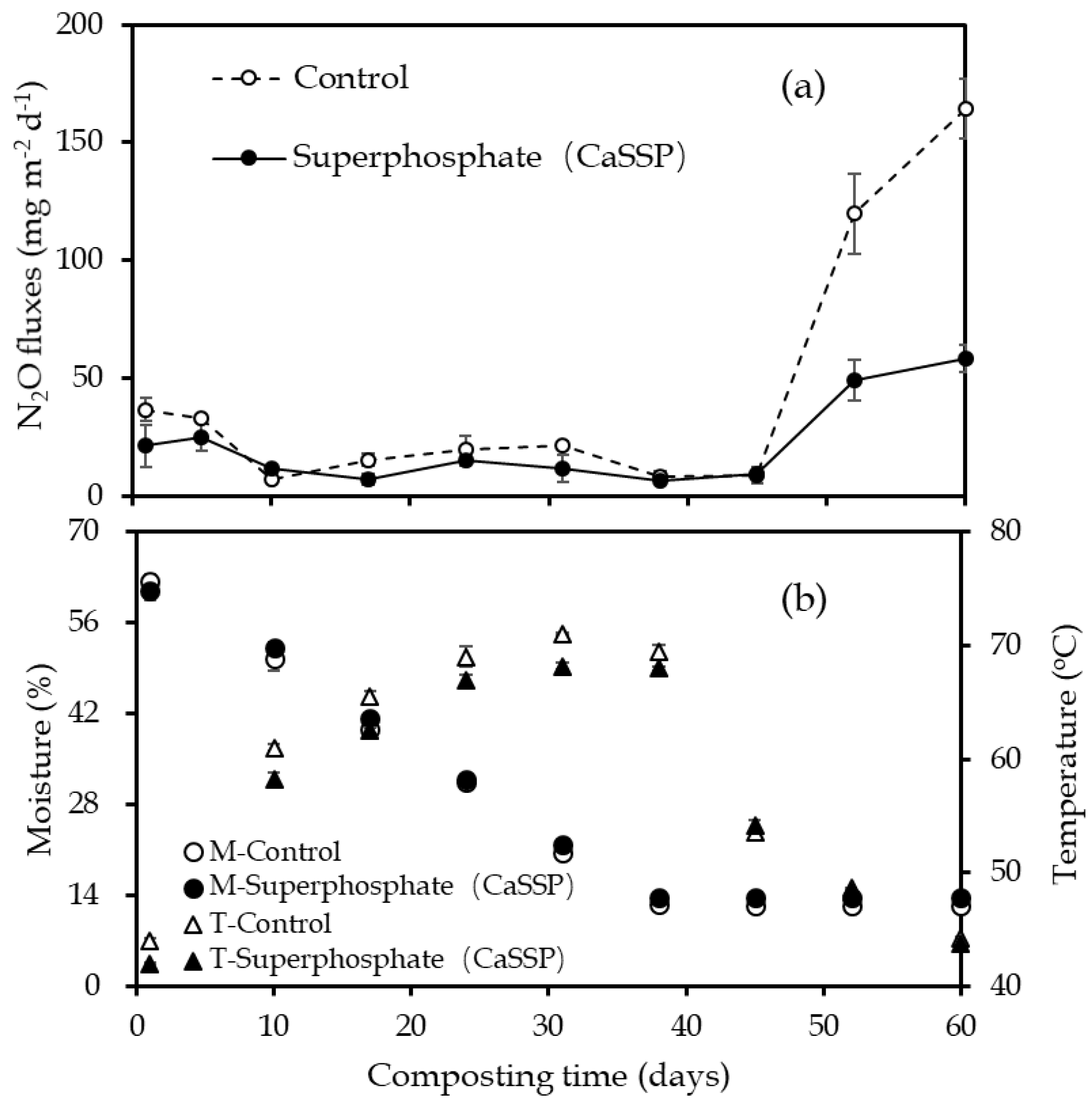
3.1. N2O Fluxes
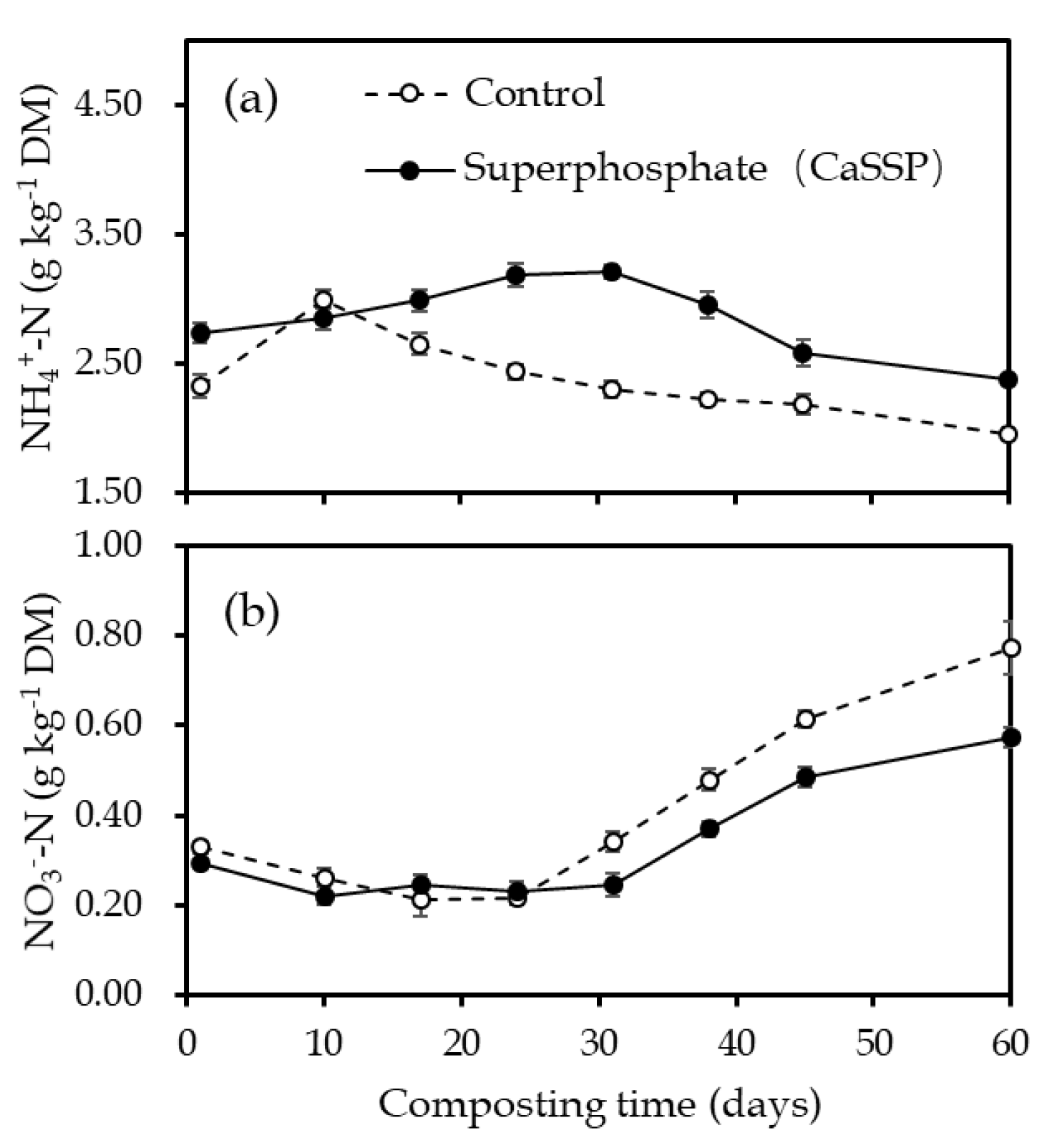
3.2. Physical and Chemical Characteristics Measurement
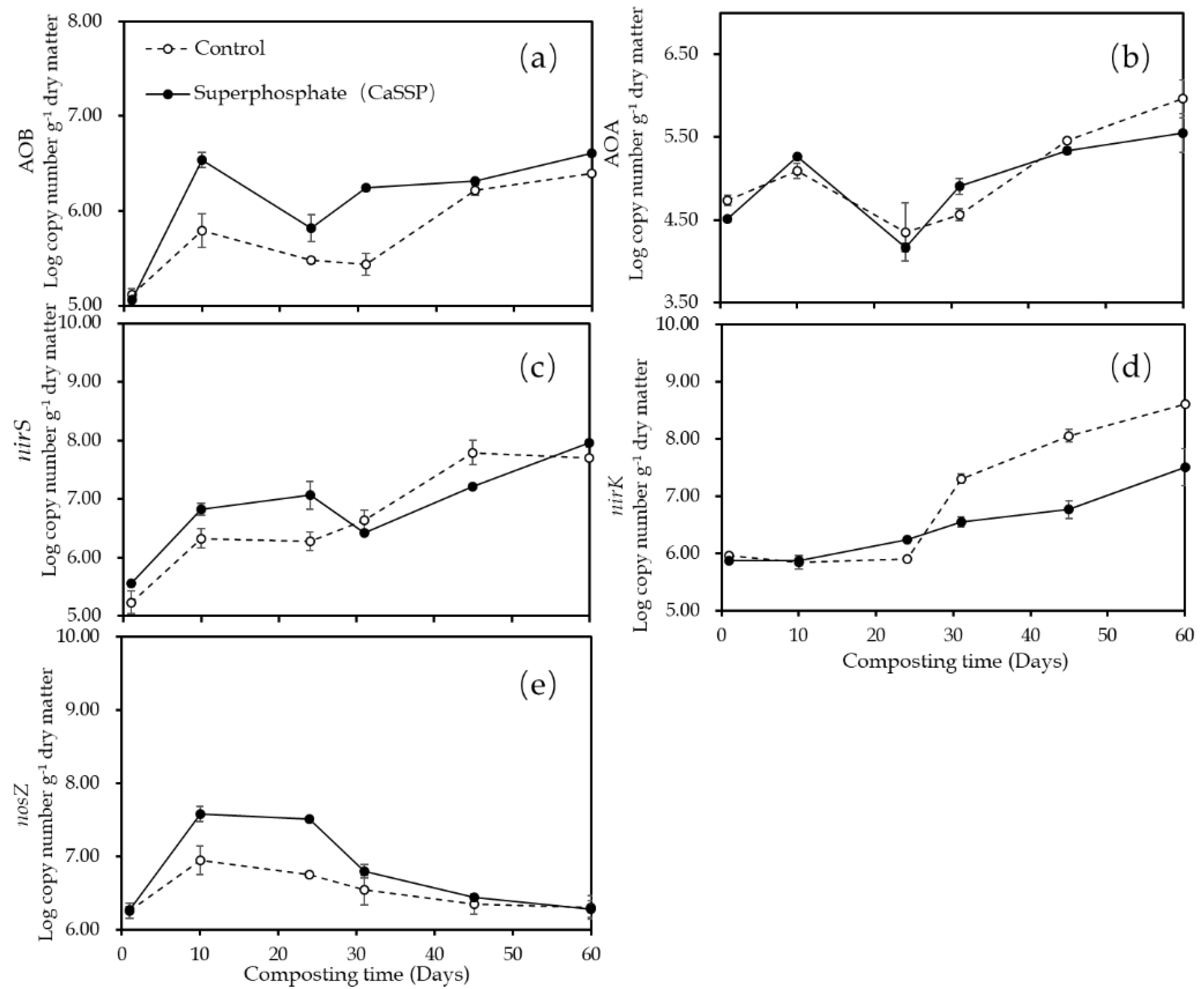
3.3. Quantification of the Functional Genes Involved in N2O Emission
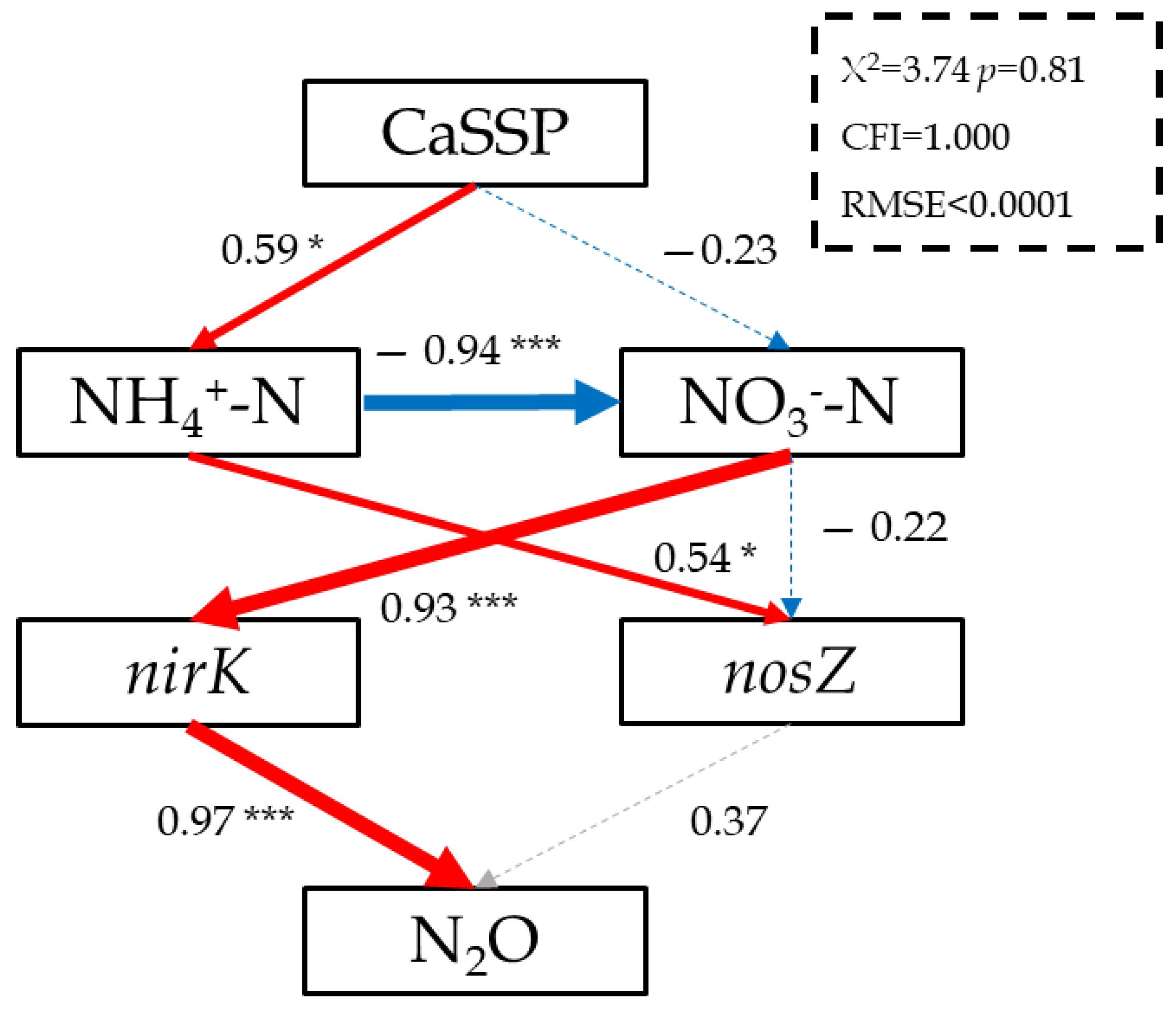
3.4. Linking N2O Emissions to the Abundance of N-Cycling Functional Microbial Genes in CaSSP-Amended Compost
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garcia-Gomez, A.; Bernal, M.P.; Roig, A. Organic Matter Fractions Involved in Degradation and Humification Processes during Composting. Compos. Sci. Util. 2005, 13, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-X.; Huang, X.-D.; Han, Z.; Huang, X.; Hu, B.; Shi, D.-Z.; Wu, W. Effects of bamboo charcoal and bamboo vinegar on nitrogen conservation and heavy metals immobility during pig manure composting. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 1177–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, M.A.; de Neergaard, A.; Jensen, L.S. Potential of aeration flow rate and biochar addition to reduce greenhouse gas and ammonia emissions during manure composting. Chemosphere 2014, 97, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kebreab, E.; Clark, K.; Wagner-Riddle, C.; France, J. Methane and nitrous oxide emissions from Canadian animal agriculture: A review. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2006, 86, 135–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippe, F.; Laitat, M.; Nicks, B.; Cabaraux, J. Ammonia and greenhouse gas emissions during the fattening of pigs kept on two types of straw floor. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 150, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, B.; Li, S.; Michel, F.C.; Li, G.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y. Control of dimethyl sulfide and dimethyl disulfide odors during pig manure composting using nitrogen amendment. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 224, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Beck-Friis, B.; Smår, S.; Jönsson, H.; Kirchmann, H. Gaseous emissions of carbon dioxide, ammonia and nitrous oxide from organic household waste in a compost reactor under different temperature regimes. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 2011, 78, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szanto, G.L.; Hamelers, H.V.M.; Rulkens, W.H.; Veeken, A.H.M. NH3, N2O and CH4 emissions during passively aerated composting of straw-rich pig manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 2659–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.; Mulbry, W.; White, J.; Kondrad, S. Pile mixing increases greenhouse gas emissions during composting of dairy manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 2904–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Ren, L.; Li, G.; Chen, T.; Guo, R. Influence of aeration on CH4, N2O and NH3 emissions during aerobic composting of a chicken manure and high C/N waste mixture. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Chadwick, D.; Zhang, D.; Li, G.; Chen, S.; Luo, W.; Du, L.; He, S.; Peng, S. Effects of aeration rate on maturity and gaseous emissions during sewage sludge composting. Waste Manag. 2016, 56, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doublet, J.; Francou, C.; Poitrenaud, M.; Houot, S. Influence of bulking agents on organic matter evolution during sewage sludge composting; consequences on compost organic matter stability and n availability. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 1298–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awasthi, M.K.; Wang, M.; Chen, H.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Ren, X.; Li, D.-S.; Awasthi, S.K.; Shen, F.; Li, R.; et al. Heterogeneity of biochar amendment to improve the carbon and nitrogen sequestration through reduce the greenhouse gases emissions during sewage sludge composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 224, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.M.; Xu, D.G.; Li, G.X. Effect of Superphosphate as Additive on Nitrogen and Carbon Losses during Pig Manure Composting. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 295, 1675–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochette, P.; Van Bochove, E.; Prévost, D.; Angers, D.A.; Côté, D.; Bertrand, N. Soil Carbon and Nitrogen Dynamics Following Application of Pig Slurry for the 19th Consecutive Year II. Nitrous Oxide Fluxes and Mineral Nitrogen. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 1396–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lu, H.; Dong, D.; Deng, H.; Strong, P.J.; Wang, H.; Wu, W. Insight into the Effects of Biochar on Manure Composting: Evidence Supporting the Relationship between N2O Emission and Denitrifying Community. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7341–7349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakase, S.; Sasaki, H.; Itoh, K.; Otawa, K.; Kitazume, O.; Nonaka, J.; Satoh, M.; Sasaki, T.; Nakai, Y. Investigation of the microbial community in a microbiological additive used in a manure composting process. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 2687–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Predotova, M.; Schlecht, E.; Gebauer, J. Nitrogen and carbon losses from dung storage in urban gardens of Niamey, Niger. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2010, 87, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.B.; Wang, Z.S.; Liao, X.D.; Liu, S.; Liang, A.M.; Wu, Q.T.; Huang, H.Z.; Zhou, L.X. Study on the odor production and control of swine manure composting. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2001, 17, 82–87. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Li, D.; Tang, H.; Chadwick, D.; Li, S.; Li, W.; Li, G. Effects of phosphogypsum, superphosphate, and dicyandiamide on gaseous emission and compost quality during sewage sludge composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 270, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Li, G.; Shi, H.; Wang, Y. Effects of phosphogypsum and superphosphate on compost maturity and gaseous emissions during kitchen waste composting. Waste Manag. 2015, 36, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angnes, G.; Nicoloso, R.D.S.; Da Silva, M.L.B.; De Oliveira, P.; Higarashi, M.M.; Mezzari, M.P.; Miller, P. Correlating denitrifying catabolic genes with N2O and N2 emissions from swine slurry composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 140, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Song, L.; Jin, Y.; Liu, S.; Shen, Q.; Zou, J. Linking N2O emission from biochar-amended composting process to the abundance of denitrify (nirK and nosZ) bacteria community. AMB Express 2016, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coyotzi, S.; Doxey, A.C.; Clark, I.D.; Lapen, D.R.; Van Cappellen, P.; Neufeld, J.D. Agricultural soil denitrifiers possess extensive nitrite reductase gene diversity. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 1189–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraft, B.; Strous, M.; Tegetmeyer, H.E. Microbial nitrate respiration-Genes, enzymes and environmental distribution. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 155, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regan, K.; Kammann, C.; Hartung, K.; Lenhart, K.; Muller, C.; Philippot, L.; Kandeler, E.; Marhan, S. Can differences in microbial abundances help explain enhanced N2O emissions in a permanent grassland under elevated atmospheric CO2? Glob. Chang. Biol. 2011, 17, 3176–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K.; Hanajima, D.; Toyoda, S.; Yoshida, N.; Morioka, R.; Osada, T. Microbiology of nitrogen cycle in animal manure compost. Microb. Biotechnol. 2011, 4, 700–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Li, S.; Geng, Y.; Miao, Y.; Ding, Y.; Liu, S.; Zou, J. Differential responses of soil N2O to biochar depend on the predominant microbial pathway. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 145, 103348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Chang, C.; Larney, F.J.; Travis, G.R. Greenhouse gas emissions during cattle feedlot manure composting. J. Environ. Qual. 2002, 31, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Larney, F.J.; Chang, C.; Travis, G.R.; Nichol, C.K.; Bremer, E. The Effect of Phosphogypsum on Greenhouse Gas Emissions during Cattle Manure Composting. J. Environ. Qual. 2005, 34, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Zheng, X.; Sass, R.L. A 3-year field measurement of methane and nitrous oxide emissions from rice paddies in China: Effects of water regime, crop residue, and fertilizer application. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2005, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Q.; Zou, J. Fe (III) fertilization mitigating net global warming potential and greenhouse gas in-tensity in paddy rice-wheat rotation systems in china. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 164, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchinson, G.L.; Mosier, A.R. Improved Soil Cover Method for Field Measurement of Nitrous Oxide Fluxes. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1981, 45, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourna, M.; Freitag, T.E.; Nicol, G.W.; Prosser, J.I. Growth, activity and temperature responses of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in soil microcosms. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephen, J.R.; Chang, Y.-J.; Macnaughton, S.J.; Kowalchuk, G.A.; Leung, K.T.; Flemming, C.A.; White, D.C. Effect of Toxic Metals on Indigenous Soil β-Subgroup Proteobacterium Ammonia Oxidizer Community Structure and Protection against Toxicity by Inoculated Metal-Resistant Bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braker, G.; Fesefeldt, A.; Witzel, K.-P. Development of PCR Primer Systems for Amplification of Nitrite Reductase Genes (nirK and nirS) To Detect Denitrifying Bacteria in Environmental Samples. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 3769–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, S.; Baudoin, E.; López-Gutiérrez, J.C.; Martin-Laurent, F.; Brauman, A.; Philippot, L. Quantification of denitrifying bacteria in soils by nirK gene targeted real-time PCR. J. Microbiol. Methods 2004, 59, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scala, D.J.; Kerkhof, L.J. Nitrous oxide reductase (nosZ) gene-specific PCR primers for detection of denitrifiers and three nosZ genes from marine sediments. FEMS. Microbiol. Lett. 1998, 162, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, J.K.; Boldrin, A.; Christensen, T.H.; Scheutz, C. Mass balances and life cycle inventory of home composting of organic waste. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 1934–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.; Hamonts, K.; Clough, T.; Condron, L. Biochar does not affect soil N-transformations or microbial community structure under ruminant urine patches but does alter relative proportions of nitrogen cycling bacteria. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 191, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.H.; Reverchon, F.; Xu, C.-Y.; Xu, Z.; Blumfield, T.J.; Zhao, H.; Van Zwieten, L.; Wallace, H.M. Wood biochar increases nitrogen retention in field settings mainly through abiotic processes. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 90, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; De, G.A.; Ziebal, C.; De, M.; Flávia, J.; Dabert, P. Impact of biodegradation of organic matters on ammonia oxidation in compost. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 136, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gödde, M.; Conrad, R. Immediate and adaptational temperature effects on nitric oxide production and nitrous oxide release from nitrification and denitrification in two soils. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1999, 30, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandeler, E.; Deiglmayr, K.; Tscherko, D.; Bru, D.; Philippot, L. Abundance of narG, nirS, nirK, and nosZ genes of denitrifying bacteria during primary successions of a glacier foreland. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5957–5962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Yujie, Y.; Lu, L.; Lihua, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, A.; et al. Response of denitrifying genes coding for nitrite (nirK or nirS) and nitrous oxide (nosZ) reductases to different physico-chemical parameters during agricultural waste composting. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 4059–4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.F.; Zheng, Y.M.; Shen, J.P.; Zhang, L.M.; He, J.Z. Response of denitrification genes nirS, nirK, and nosZ to irrigation water quality in a Chinese agricultural soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2011, 18, 1644–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Cao, X.; Zhao, L. Effects of phosphorus amendments and plant growth on the mobility of Pb, Cu, and Zn in a multi-metal-contaminated soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2011, 19, 1659–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Huang, Y.; Liu, X.; Huang, H. The effects of apple pomace, bentonite and calcium superphosphate on swine manure aerobic composting. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 1595–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Hashmi, M.Z.; Xu, J.; Brookes, P.C. Effects of inorganic and organic amendments on the uptake of lead and trace elements by Brassica chinensis grown in an acidic red soil. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Target Gene | Prime Name | Sequence (5′ to 3′) | Product Size | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AOA amoA | CrenamoA23f | ATGGTCTGGCTWAGACG | 593 bp | [35] |
| CrenamoA616r | GCCATCCATCTGTATGTCCA | |||
| AOB amoA | amoA-1F | GGGGHTTYTACTGGTGGT | 491 bp | [36] |
| amoA-2R | CCCCTCKGSAAAGCCTTCTTC | |||
| nirS | nirS-Cd3aF | GTSAACGTSAAGGARACSGG | 425 bp | [37] |
| nirS-R3cd | GASTTCGGRTGSGTCTTGA | |||
| nirK | nirK-F1aCu | ATCATGGTSCTGCCGCG | 473 bp | [38] |
| nirK-R3Cu | GCCTCGATCAGRTTGTGGTT | |||
| nosZ | nosZ-F | AGAACGACCAGCTGATCGACA | 380 bp | [39] |
| nosZ-R | TCCATGGTGACGCCGTGGTTG |
| Correlation Coefficients (r) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | NH4+-N | NO3−-N | pH | Moisture | Temperature | Total N | Total C | C/N | N2O |
| AOB | 0.00 | 0.23 | −0.49 | −0.55 | −0.11 | 0.711 ** | −0.41 | −0.63 | 0.35 |
| AOA | −0.45 | 0.70 * | −0.16 | −0.63 * | −0.45 | 0.644 * | −0.48 | −0.60 * | 0.42 |
| nirS | −0.31 | 0.57 | −0.34 | −0.83 ** | −0.15 | 0.86 *** | −0.71 * | −0.82 *** | 0.64 |
| nirK | −0.66 * | 0.81 *** | −0.21 | −0.87 *** | −0.14 | 0.83 *** | −0.83 *** | −0.89 *** | 0.79 ** |
| nosZ | 0.63 * | −0.67 * | 0.07 | 0.11 | 0.741 ** | −0.23 | 0.08 | 0.24 | −0.42 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, Y.; Miao, Y.; Geng, Y.; Huang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Song, X.; Li, S.; Zou, J. Calcium Superphosphate-Mediated Reshaping of Denitrifying Bacteria Community Contributed to N2O Mitigation in Pig Manure Windrow Composting. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18010171
Jin Y, Miao Y, Geng Y, Huang M, Zhang Y, Song X, Li S, Zou J. Calcium Superphosphate-Mediated Reshaping of Denitrifying Bacteria Community Contributed to N2O Mitigation in Pig Manure Windrow Composting. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(1):171. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18010171
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Yaguo, Yingcheng Miao, Yajun Geng, Mengyuan Huang, Yihe Zhang, Xiuchao Song, Shuqing Li, and Jianwen Zou. 2021. "Calcium Superphosphate-Mediated Reshaping of Denitrifying Bacteria Community Contributed to N2O Mitigation in Pig Manure Windrow Composting" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 1: 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18010171
APA StyleJin, Y., Miao, Y., Geng, Y., Huang, M., Zhang, Y., Song, X., Li, S., & Zou, J. (2021). Calcium Superphosphate-Mediated Reshaping of Denitrifying Bacteria Community Contributed to N2O Mitigation in Pig Manure Windrow Composting. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(1), 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18010171




