Mediating Effect of Perceived Stress on the Association between Physical Activity and Sleep Quality among Chinese College Students
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Procedures
2.2. Ethical Considerations
2.3. Physical Activity Measurement
2.4. Perceived Stress Measurement
2.5. Sleep Quality Measurement
2.6. Covariates
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
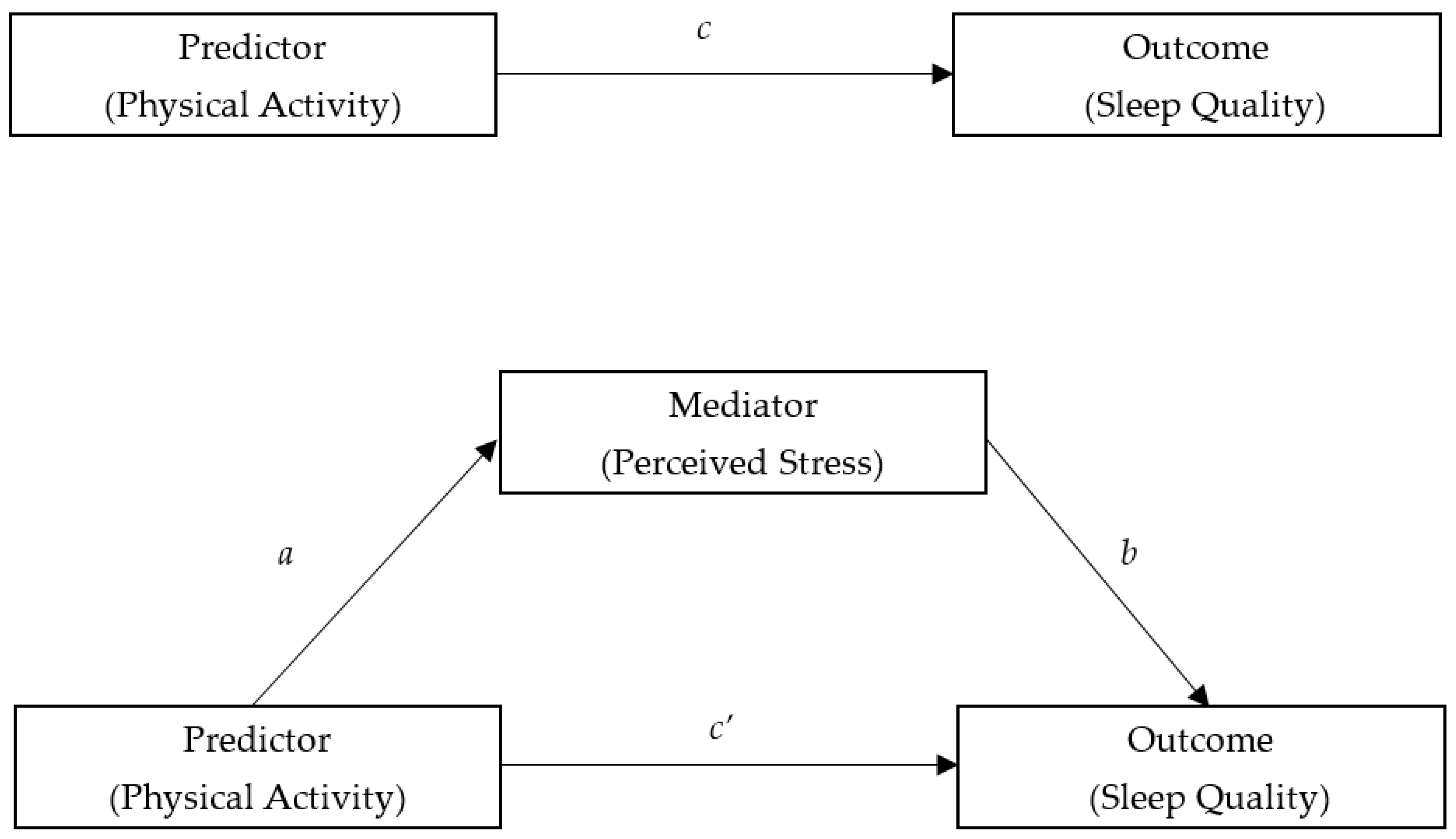
3.2. Mediation Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stranges, S.; Tigbe, W.; Gómez-Olivé, F.X.; Thorogood, M.; Kandala, N.-B. Sleep Problems: An Emerging Global Epidemic? Findings from the INDEPTH WHO-SAGE Study among More than 40,000 Older Adults from 8 Countries Across Africa and Asia. Sleep 2012, 35, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chattu, V.K.; Manzar, D.; Kumary, S.; Burman, D.; Spence, D.W.; Pandi-Perumal, S.R. The Global Problem of Insufficient Sleep and Its Serious Public Health Implications. Healthcare 2018, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daley, M.; Morin, C.M.; Leblanc, M.; Grégoire, J.-P.; Savard, J. The Economic Burden of Insomnia: Direct and Indirect Costs for Individuals with Insomnia Syndrome, Insomnia Symptoms, and Good Sleepers. Sleep 2009, 32, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohayon, M.M. Epidemiology of insomnia: What we know and what we still need to learn. Sleep Med. Rev. 2002, 6, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samaranayake, C.B.; Arroll, B.; Fernando, A.T. Sleep disorders, depression, anxiety and satisfaction with life among young adults: A survey of university students in Auckland, New Zealand. N. Z. Med. J. 2014, 127, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.-L.; Zheng, X.-Y.; Yang, J.; Ye, C.-P.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-G.; Xiao, Z.-J. A systematic review of studies on the prevalence of Insomnia in university students. Public Health 2015, 129, 1579–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Xu, D.-D.; Ng, C.H.; Ungvari, G.S.; Cui, X.; Liu, Z.-M.; et al. Prevalence of sleep disturbances in Chinese university students: A comprehensive meta-analysis. J. Sleep Res. 2018, 27, e12648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, C. Sleep quality. In Encyclopedia of Behavioral Medicine; Gellman, M.D., Turner, J.R., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 1811–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnavita, N.; Garbarino, S. Sleep, Health and Wellness at Work: A Scoping Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Ye, M.; Wang, C.; Gu, Q.; Huang, T.; Wang, K.; Chen, Z.; Fan, X. Associations among physical activity and smartphone use with perceived stress and sleep quality of Chinese college students. Ment. Health Phys. Act. 2020, 18, 100323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, E.S.; Lunt, L.; McDonagh, J. Sleep in adolescents and young adults. Clin. Med. 2017, 17, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghrouz, A.K.; Noohu, M.M.; Manzar, D.; Spence, D.W.; Bahammam, A.S.; Pandi-Perumal, S.R. Physical activity and sleep quality in relation to mental health among college students. Sleep Breath. 2019, 23, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, C.; Kalak, N.; Brand, S.; Holsboer-Trachsler, E.; Pühse, U.; Gerber, M. The relationship between physical activity and sleep from mid adolescence to early adulthood. A systematic review of methodological approaches and meta-analysis. Sleep Med. Rev. 2016, 28, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passos, G.S.; Poyares, D.L.R.; Santana, M.G.; Tufik, S.; De Mello, M.T. Is exercise an alternative treatment for chronic insomnia? Clinics 2012, 67, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCurry, S.M.; Pike, K.C.; Vitiello, M.V.; Logsdon, R.G.; Larson, E.B.; Teri, L. Increasing Walking and Bright Light Exposure to Improve Sleep in Community-Dwelling Persons with Alzheimer’s Disease: Results of a Randomized, Controlled Trial. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2011, 59, 1393–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, K.C.; Lambert, C.; Beck, C.K.; Bliwise, D.L.; Evans, W.J.; Ms, G.K.K.; Kleban, M.H.; Lorenz, R.; Rose, K.; Gooneratne, N.S.; et al. Strength Training, Walking, and Social Activity Improve Sleep in Nursing Home and Assisted Living Residents: Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2011, 59, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustian, K.M.; Sprod, L.K.; Janelsins, M.; Peppone, L.J.; Palesh, O.G.; Chandwani, K.; Reddy, P.S.; Melnik, M.K.; Heckler, C.; Morrow, G.R. Multicenter, Randomized Controlled Trial of Yoga for Sleep Quality Among Cancer Survivors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3233–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, G.; Zhang, Y.; Minichiello, V.J.; D’Ambrosio, C.M.; Wang, C. Tai Chi Improves Sleep Quality in Healthy Adults and Patients with Chronic Conditions: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Sleep Disord. Ther. 2013, 2, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, K.J.; Baron, K.G.; Lu, B.; Naylor, E.; Wolfe, L.; Zee, P.C. Aerobic exercise improves self-reported sleep and quality of life in older adults with insomnia. Sleep Med. 2010, 11, 934–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carandente, F.; Montaruli, A.; Angeli, A.; Sciolla, C.; Roveda, E.; Calogiuri, G. Effects of endurance and strength acute exercise on night sleep quality. Int. SportMed J. 2011, 12, 113–124. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, J.A.; Godbole, S.; Moran, K.; Murray, K.; James, P.; Laden, F.; Hipp, J.A.; Kerr, J.; Glanz, K. No Evidence of Reciprocal Associations between Daily Sleep and Physical Activity. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2016, 48, 1950–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngstedt, S.D.; Perlis, M.L.; O’Brien, P.M.; Palmer, C.R.; Smith, M.T.; Orff, H.J.; Kripke, D.F. No association of sleep with total daily physical activity in normal sleepers. Physiol. Behav. 2003, 78, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngstedt, S.D.; Kline, C. Epidemiology of exercise and sleep. Sleep Biol. Rhythm. 2006, 4, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Åkerstedt, T.; Orsini, N.; Petersen, H.; Axelsson, J.; Lekander, M.; Kecklund, G. Predicting sleep quality from stress and prior sleep—A study of day-to-day covariation across sixweeks. Sleep Med. 2012, 13, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Psychological Association. Stress Relief Is within Reach. Available online: https://www.apa.org/topics/stress (accessed on 29 December 2019).
- Saleh, D.; Camart, N.; Romo, L. Predictors of Stress in College Students. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borjalilu, S.; Mohammadi, A.; Mojtahedzadeh, R. Sources and Severity of Perceived Stress among Iranian Medical Students. Iran. Red Crescent Med. J. 2015, 17, e17767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doolin, J.; Vilches, J.E.; Cooper, C.; Gipson, C.; Sorensen, W. Perceived stress and worldview influence sleep quality in Bolivian and United States university students. Sleep Health 2018, 4, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwen, B.S.; Bowles, N.P.; Gray, J.D.; Hill, M.N.; Hunter, R.G.; Karatsoreos, I.N.; Nasca, C. Mechanisms of stress in the brain. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 1353–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prospéro-García, O.; Amancio-Belmont, O.; Meléndez, A.L.B.; Ruiz-Contreras, A.E.; Méndez-Díaz, M. Endocannabinoids and sleep. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 71, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirelli, C. Cellular consequences of sleep deprivation in the brain. Sleep Med. Rev. 2006, 10, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultchen, D.; Reichenberger, J.; Mittl, T.; Weh, T.R.M.; Smyth, J.M.; Blechert, J.; Pollatos, O. Bidirectional relationship of stress and affect with physical activity and healthy eating. Br. J. Health Psychol. 2019, 24, 315–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, H.W.; Melton, B.F.; Bigham, L.E.; Welle, P.D. Quantifying the impact of physical activity on stress tolerance in college students. Coll. Stud. J. 2014, 48, 559–568. [Google Scholar]
- Cairney, J.; Kwan, M.Y.W.; Veldhuizen, S.; Faulkner, G.E.J. Who Uses Exercise as a Coping Strategy for Stress? Results from a National Survey of Canadians. J. Phys. Act. Health 2014, 11, 908–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanKim, N.A.; Nelson, T.F. Vigorous Physical Activity, Mental Health, Perceived Stress, and Socializing among College Students. Am. J. Health Promot. 2013, 28, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, S.Y.; Fabián, C.; Pagán, I.; Ríos, J.L.; González, A.M.; Betancourt, J.; González, M.J.; Rivera-Soto, W.T.; Palacios, C. Physical activity and its associations with sociodemographic characteristics, dietary patterns, and perceived academic stress in students attending college in Puerto Rico. Puerto Rico Health Sci. J. 2013, 32, 44–50. [Google Scholar]
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Results from the 2019 National Survey on Drug Use and Health: Detailed Tables. Available online: https://www.samhsa.gov/data/report/2019-nsduh-detailed-tables (accessed on 29 December 2020).
- Leonard, N.R.; Gwadz, M.V.; Eritchie, A.; Linick, J.L.; Cleland, C.M.; Elliott, L.; Egrethel, M. A multi-method exploratory study of stress, coping, and substance use among high school youth in private schools. Front. Psychol. 2015, 6, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naquin, M.R.; Gilbert, G.G. College Students’ Smoking Behavior, Perceived Stress, and Coping Styles. J. Drug Educ. 1996, 26, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronda, A.C.; Irish, L.A.; Delahanty, D.L. Effect of smoke exposure on young adults’ sleep quality. Nurs. Health Sci. 2019, 22, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, K.G.; Van Arsdale, A.C. Perfectionism, perceived stress, drinking to cope, and alcohol-related problems among college students. J. Couns. Psychol. 2010, 57, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Bo, Q.-G.; Jia, C.-X.; Liu, X. Sleep Problems in Relation to Smoking and Alcohol Use in Chinese Adolescents. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 2017, 205, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Barnett, R.; Peng, S.; Yu, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, W. Individual and regional factors affecting stress and problem alcohol use: A representative nationwide study of China. Health Place 2018, 51, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.J.; Bramoweth, A.D.; Grieser, E.A.; Tatum, J.I.; Roane, B.M. Epidemiology of Insomnia in College Students: Relationship With Mental Health, Quality of Life, and Substance Use Difficulties. Behav. Ther. 2013, 44, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, A.B.; Bittel, K.M.; Russell, M.; Evans, M.B.; Mama, S.K.; Conroy, D. A systematic review of physical activity, sedentary behavior, and substance use in adolescents and emerging adults. Transl. Behav. Med. 2020, 10, 1155–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Physical Activity Questionnaire. Guidelines for Data Processing and Analysis of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ)-Short and Long Forms. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/file.PostFileLoader.html?id=5641f4c36143250eac8b45b7&assetKey=AS%3A294237418606593%401447163075131 (accessed on 29 December 2020).
- Macfarlane, D.; Lee, C.C.; Ho, E.Y.; Chan, K.; Chan, D.T. Reliability and validity of the Chinese version of IPAQ (short, last 7 days). J. Sci. Med. Sport 2007, 10, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.; Kamarck, T.; Mermelstein, R. A global measure of perceived stress. J. Health Soc. Behav. 1983, 24, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Bian, Q.; Wang, W.; Wu, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, M. Chinese version of the Perceived Stress Scale-10: A psychometric study in Chinese university students. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buysse, D.J.; Reynolds, C.F.; Monk, T.H.; Berman, S.R.; Kupfer, D.J. The Pittsburgh sleep quality index: A new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Res. 1989, 28, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tang, M.; Hu, L. Reliability and validity of the Pittsburgh sleep quality index. Chin. J. Psychiatry 1996, 29, 103–107. [Google Scholar]
- Baron, R.M.; Kenny, D.A. The moderator–mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1986, 51, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, L.M.; Graham, J.J.; Flaherty, B.P. An Alternative Framework for Defining Mediation. Multivar. Behav. Res. 1998, 33, 295–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKinnon, D.P. Contrasts in multiple mediator models. In Multivariate Applications in Substance Use Research: New Methods for New Questions; Rose, J.S., Chassin, L., Eds.; Psychology Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 141–160. [Google Scholar]
- Shrout, P.E.; Bolger, N. Mediation in experimental and nonexperimental studies: New procedures and recommendations. Psychol. Methods 2002, 7, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Lynch, J.G., Jr.; Chen, Q. Reconsidering Baron and Kenny: Myths and truths about mediation analysis. J. Consum. Res. 2010, 37, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosseel, Y. Lavaan: An R package for structural equation modeling and more. Version 0.5–12 (BETA). J. Stat. Softw. 2012, 48, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Zhang, Q.-L.; Du, Y.; Ye, Y.-L.; He, Q.-Q. Associations of Physical Activity, Screen Time with Depression, Anxiety and Sleep Quality among Chinese College Freshmen. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Zhou, L.; Xu, W.; Ma, S.; Wang, Y. Associations of physical activity and screen time with suboptimal health status and sleep quality among Chinese college freshmen: A cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semplonius, T.; Willoughby, T. Long-Term Links between Physical Activity and Sleep Quality. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2018, 50, 2418–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Reeth, O.; Weibel, L.; Spiegel, K.; Leproult, R.; Dugovic, C.; Maccari, S. PHYSIOLOGY OF SLEEP (REVIEW)–Interactions between stress and sleep: From basic research to clinical situations. Sleep Med. Rev. 2000, 4, 201–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stults-Kolehmainen, M.A.; Sinha, R. The Effects of Stress on Physical Activity and Exercise. Sports Med. 2014, 44, 81–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strygin, K.N. Sleep and stress. Ross. Fiziol. Zh. Im. I. M. Sechenova 2011, 97, 422–432. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, B.K.; Saltin, B. Evidence for prescribing exercise as therapy in chronic disease. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2006, 16, 3–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chennaoui, M.; Arnal, P.J.; Sauvet, F.; Léger, D. Sleep and exercise: A reciprocal issue? Sleep Med. Rev. 2015, 20, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnohr, P.; Kristensen, T.S.; Prescott, E.; Scharling, H. Stress and life dissatisfaction are inversely associated with jogging and other types of physical activity in leisure time—The Copenhagen City Heart Study. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2005, 15, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atlantis, E.; Chow, C.M.; Kirby, A.; Singh, M.A.F. An effective exercise-based intervention for improving mental health and quality of life measures: A randomized controlled trial. Prev. Med. 2004, 39, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zillman, D.; Bryant, J. Selective Exposure to Communication; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Cowansage, K.K.; LeDoux, J.; Monfils, M.-H. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor: A Dynamic Gatekeeper of Neural Plasticity. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2010, 3, 12–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choy, K.H.C.; De Visser, Y.; Nichols, N.R.; Buuse, M.V.D. Combined neonatal stress and young-adult glucocorticoid stimulation in rats reduce BDNF expression in hippocampus: Effects on learning and memory. Hippocampus 2008, 18, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlotz, W. Investigating associations between momentary stress and cortisol in daily life: What have we learned so far? Psychoneuroendocrinology 2019, 105, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistollato, F.; Cano, S.S.; Elio, I.; Vergara, M.M.; Giampieri, F.; Battino, M. Associations between Sleep, Cortisol Regulation, and Diet: Possible Implications for the Risk of Alzheimer Disease. Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallis, J.F.; Zakarian, J.M.; Hovell, M.F.; Hofstetter, C. Ethnic, socioeconomic, and sex differences in physical activity among adolescents. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1996, 49, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, K.; Iwamoto, K.; Kawano, N.; Noda, Y.; Ozaki, N.; Noda, A. Differential effects of physical activity and sleep duration on cognitive function in young adults. J. Sport Health Sci. 2018, 7, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, A.H.; Silberstein, R.; Armstrong, S.; Nathan, P.J. Gender differences in the cortical electrophysiological processing of visual emotional stimuli. NeuroImage 2004, 21, 632–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filkowski, M.M.; Olsen, R.M.; Duda, B.; Wanger, T.J.; Sabatinelli, D. Sex differences in emotional perception: Meta analysis of divergent activation. NeuroImage 2017, 147, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmerhorst, H.J.F.; Brage, S.; Warren, J.; Besson, H.; Ekelund, U. A systematic review of reliability and objective criterion-related validity of physical activity questionnaires. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2012, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Participant Characteristics | Male (n = 4752) | Female (n = 2221) | Total (n = 6973) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean or n | SD or % | Mean or n | SD or % | Mean or n | SD or % | p | |
| Age (years) | 19.0 | 0.7 | 19.0 | 0.7 | 19.0 | 0.7 | 0.31 |
| Nationality | |||||||
| Han Chinese | 4315 | 90.8% | 1930 | 86.9% | 6245 | 89.6% | <0.001 |
| Others | 437 | 9.2% | 291 | 13.1% | 728 | 10.4% | |
| Tobacco use | |||||||
| Never | 4624 | 97.3% | 2196 | 98.9% | 6820 | 97.8% | <0.001 |
| Rarely | 95 | 2.0% | 19 | 0.8% | 114 | 1.6% | |
| Always | 33 | 0.7% | 6 | 0.3% | 39 | 0.6% | |
| Alcohol use | |||||||
| Never | 2537 | 53.4% | 1527 | 68.8% | 4064 | 58.3% | <0.001 |
| Rarely | 2162 | 45.5% | 676 | 30.4% | 2838 | 40.7% | |
| Always | 53 | 1.1% | 18 | 0.8% | 71 | 1.0% | |
| Physical activity | |||||||
| Total MET-minutes/week | 3049.1 | 1908.8 | 2553.7 | 1667.2 | 2891.3 | 1849.6 | <0.001 |
| Perceived stress | |||||||
| PSS-10 (scores) | 17.5 | 6.8 | 19.3 | 7.1 | 18.1 | 6.9 | <0.001 |
| Sleep quality | |||||||
| PSQI (scores) | 4.7 | 2.6 | 5.2 | 2.8 | 4.8 | 2.7 | <0.001 |
| Total Effect Model (PSQI) | PSS | Direct Effect Model (PSQI) | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | β | Boot SE | t | p | Bootstrap 95%CI | β | Boot SE | t | p | Bootstrap 95%CI | β | Boot SE | t | p | Bootstrap 95%CI | ||||
| Lower | Upper | Lower | Upper | Lower | Upper | ||||||||||||||
| Male | PA | −0.074 | 0.014 | −5.421 | <0.001 | −0.101 | −0.047 | −0.082 | 0.013 | −6.140 | <0.001 | −0.109 | −0.057 | −0.043 | 0.013 | −3.363 | <0.001 | −0.068 | −0.018 |
| PSS | 0.381 | 0.013 | 28.500 | <0.001 | 0.355 | 0.407 | |||||||||||||
| Age | 0.026 | 0.014 | 1.877 | 0.06 | −0.001 | 0.053 | 0.010 | 0.014 | 0.694 | 0.49 | −0.019 | 0.038 | 0.022 | 0.013 | 1.752 | 0.08 | −0.003 | 0.048 | |
| Nationality | 0.127 | 0.052 | 2.424 | 0.02 | 0.025 | 0.229 | 0.107 | 0.045 | 2.374 | 0.02 | 0.020 | 0.194 | 0.086 | 0.049 | 1.771 | 0.08 | −0.009 | 0.182 | |
| Tobacco use | 0.361 | 0.088 | 4.082 | <0.001 | 0.194 | 0.545 | 0.182 | 0.055 | 3.318 | <0.001 | 0.076 | 0.294 | 0.291 | 0.084 | 3.476 | <0.001 | 0.131 | 0.461 | |
| Alcohol use | 0.160 | 0.028 | 5.670 | <0.001 | 0.104 | 0.216 | 0.128 | 0.028 | 4.581 | <0.001 | 0.072 | 0.183 | 0.112 | 0.026 | 4.280 | <0.001 | 0.060 | 0.162 | |
| Female | PA | −0.012 | 0.028 | −0.437 | 0.66 | −0.069 | 0.044 | −0.090 | 0.026 | −3.411 | <0.001 | −0.141 | −0.038 | 0.026 | 0.025 | 1.031 | 0.30 | −0.023 | 0.074 |
| PSS | 0.425 | 0.020 | 21.455 | <0.001 | 0.386 | 0.463 | |||||||||||||
| Age | 0.053 | 0.022 | 2.448 | 0.01 | 0.011 | 0.096 | 0.043 | 0.021 | 2.064 | 0.04 | 0.002 | 0.084 | 0.035 | 0.020 | 1.745 | 0.08 | −0.004 | 0.074 | |
| Nationality | 0.159 | 0.068 | 2.347 | 0.02 | 0.030 | 0.292 | 0.031 | 0.062 | 0.504 | 0.61 | −0.088 | 0.152 | 0.145 | 0.062 | 2.332 | 0.02 | 0.026 | 0.271 | |
| Tobacco use | 0.598 | 0.216 | 2.766 | 0.006 | 0.173 | 1.016 | 0.222 | 0.145 | 1.529 | 0.13 | −0.056 | 0.515 | 0.504 | 0.219 | 2.300 | 0.02 | 0.068 | 0.934 | |
| Alcohol use | 0.220 | 0.049 | 4.493 | <0.001 | 0.125 | 0.315 | 0.239 | 0.044 | 5.389 | <0.001 | 0.151 | 0.327 | 0.118 | 0.044 | 2.660 | 0.008 | 0.030 | 0.204 | |
| Bootstrap 95%CI | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β | Boot SE | p | Lower | Upper | PM (%) | ||
| Male | Total effect | −0.074 | 0.014 | <0.001 | −0.101 | −0.047 | − |
| Indirect effect | −0.031 | 0.005 | <0.001 | −0.042 | −0.021 | 42.4% | |
| Direct effect | −0.043 | 0.013 | <0.001 | −0.068 | −0.018 | 57.6% | |
| Female | Total effect | −0.012 | 0.028 | 0.66 | −0.069 | 0.044 | − |
| Indirect effect | −0.038 | 0.011 | <0.001 | −0.060 | −0.016 | 306.3% | |
| Direct effect | 0.026 | 0.025 | 0.30 | −0.023 | 0.074 | −206.3% | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhai, X.; Wu, N.; Koriyama, S.; Wang, C.; Shi, M.; Huang, T.; Wang, K.; Sawada, S.S.; Fan, X. Mediating Effect of Perceived Stress on the Association between Physical Activity and Sleep Quality among Chinese College Students. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18010289
Zhai X, Wu N, Koriyama S, Wang C, Shi M, Huang T, Wang K, Sawada SS, Fan X. Mediating Effect of Perceived Stress on the Association between Physical Activity and Sleep Quality among Chinese College Students. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(1):289. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18010289
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhai, Xiangyu, Na Wu, Sakura Koriyama, Can Wang, Mengyao Shi, Tao Huang, Kun Wang, Susumu S. Sawada, and Xiang Fan. 2021. "Mediating Effect of Perceived Stress on the Association between Physical Activity and Sleep Quality among Chinese College Students" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 1: 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18010289
APA StyleZhai, X., Wu, N., Koriyama, S., Wang, C., Shi, M., Huang, T., Wang, K., Sawada, S. S., & Fan, X. (2021). Mediating Effect of Perceived Stress on the Association between Physical Activity and Sleep Quality among Chinese College Students. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(1), 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18010289






