Mapping the Scientific Landscape of Diabetes Research in Malaysia (2000–2018): A Systematic Scientometrics Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources and Search Strategy
2.2. Data Extraction
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of Malaysia’s Diabetes Research Productivity
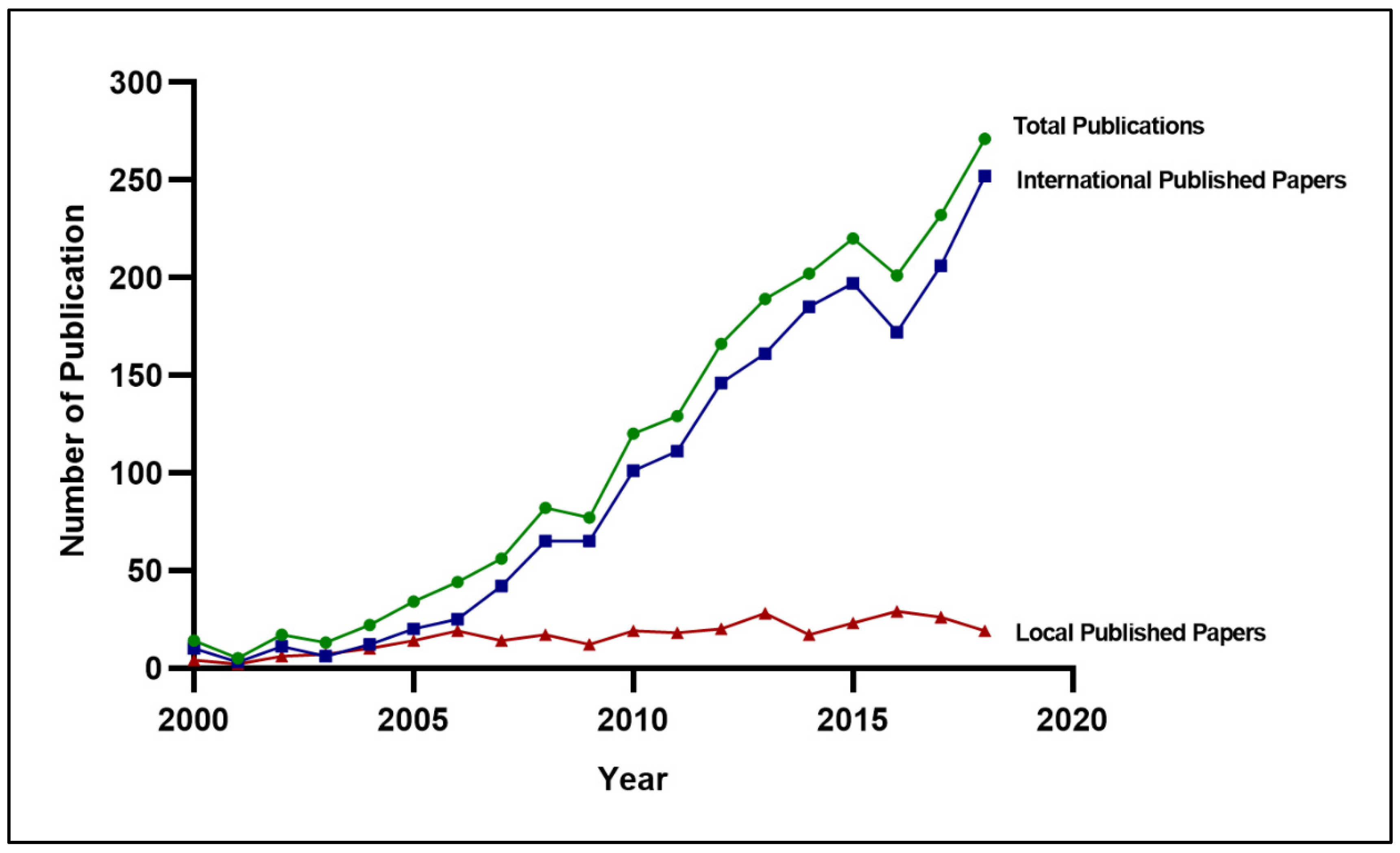
3.1.1. Trend Analysis
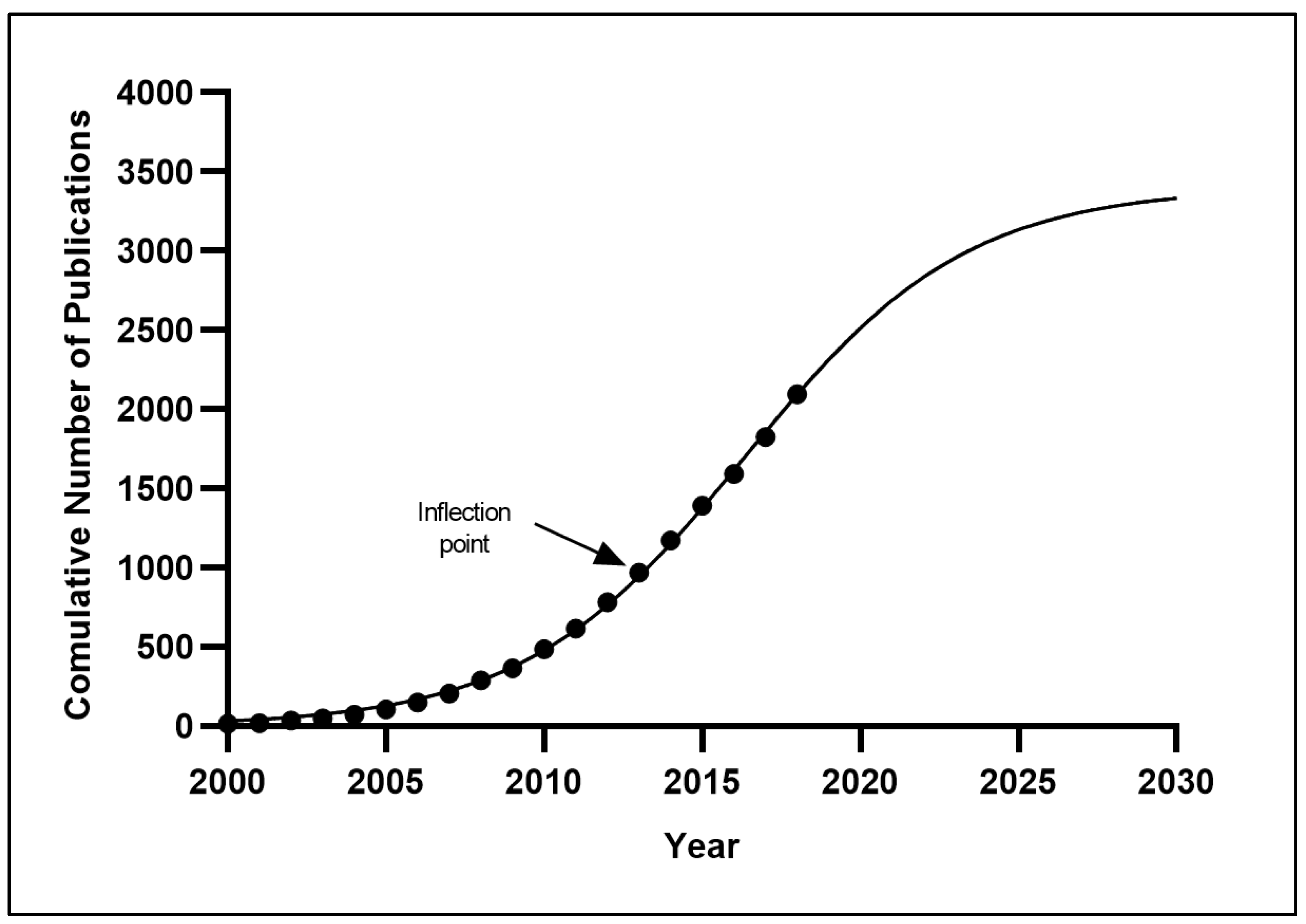
3.1.2. Diabetes Research Productivity over Time
3.1.3. Frequency Analysis
3.1.4. Distributional Hotspot Analysis
3.2. Citation Analyses of Malaysia’s Diabetes Research Productivity
3.2.1. Citation Trend
3.2.2. Citation Frequency of the Identified Papers
3.3. Source Evaluation of Malaysia’s Diabetes Research Productivity
3.3.1. Highly Contributing Journals
3.3.2. Highly Contributing Institutions
3.3.3. Highly Contributing Author-Researchers
3.3.4. Comparison of the Author-Researcher Contributions and the Needs-Demand Analysis
3.4. Content Evaluation of Malaysia’s Diabetes Research Productivity
3.4.1. Document Analyses of the Study Types and Designs
3.4.2. Keyword Links Visualization and Thematic Cluster Analyses
4. Discussion
4.1. Diabetes Research Productivity
4.2. Citation Impact of Research Publications
4.3. Source Evaluation of Research Productivity
4.4. Content Evaluation of Research Outputs
4.5. Study Limitations and Strengths
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Diabetes Federation. Diabetes Facts & Figures. 2020. Available online: https://www.idf.org/aboutdiabetes/what-is-diabetes/facts-figures.html#:~:text=In%202019%2C,low%2D%20and%20middle%2Dincome%20countries (accessed on 21 September 2020).
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, C. Prevalence of Gestational Diabetes and Risk of Progression to Type 2 Diabetes: A Global Perspective. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2016, 16, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobasseri, M.; Shirmohammadi, M.; Amiri, T.; Vahed, N.; Hosseini Fard, H.; Ghojazadeh, M. Prevalence and Incidence of Type 1 Diabetes in the World: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Health Promot. Perspect. 2020, 10, 98–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Diabetes Federation. Diabetes in South-East Asia. 2020. Available online: https://www.idf.org/our-network/regions-members/south-east-asia/diabetes-in-sea.html (accessed on 21 September 2020).
- International Diabetes Federation. Western Pacific Members. 2020. Available online: https://idf.org/our-network/regions-members/western-pacific/members/108-malaysia.html (accessed on 21 September 2020).
- Ganasegeran, K.; Hor, C.P.; Jamil, M.F.A.; Loh, H.C.; Noor, J.M.; Hamid, N.A.; Suppiah, P.D.; Manaf, M.R.A.; Ch’ng, A.S.H.; Looi, I. A Systematic Review of the Economic Burden of Type 2 Diabetes in Malaysia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Thomas, V.J. Inter-Country R&D Efficiency Analysis: An Application of Data Envelopment Analysis. Scientometrics 2008, 76, 483. [Google Scholar]
- Ivancheva, L. Scientometrics Today: A Methodological Overview. COLLNET J. Scientometr. Inf. Manag. 2008, 2, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragos, C.M.; Dinu, V.; Pop, C.M.; Dabija, D.C. Scientometric Approach of Productivity in Scholarly Economics and Business. Econ. Res. Ekon. Istraž. 2014, 27, 496–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Correia, A.; Paredes, H.; Fonseca, B. Scientometric Analysis of Scientific Publications in CSCW. Scientometrics 2018, 114, 31–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, S.D.J.; Silveira, M.S.; Gasparini, I. What Publications Metadata Tell Us about the Evolution of a Scientific Community: The Case of the Brazilian Human-Computer Interaction Conference Series. Scientometrics 2017, 110, 275–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasolabadi, M.; Khaledi, S.; Ardalan, M.; Kalhor, M.M.; Penjvini, S.; Gharib, A. Diabetes Research in Iran: A Scientometric Analysis of Publications Output. Acta Inform. Med. 2015, 23, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emami, Z.; Hariri, N.; Khamseh, M.E.; Nooshinfard, F. Mapping Diabetes Research in Middle Eastern Countries During 2007–2013: A Scientometric Analysis. Med. J. Islam. Repub. Iran 2018, 32, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, B.X.; Nguyen, L.H.; Pham, N.M.; Vu, H.T.T.; Nguyen, H.T.; Phan, D.H.; Ha, G.H.; Pham, H.Q.; Nguyen, T.P.; Latkin, C.A.; et al. Global Mapping of Interventions to Improve Quality of Life of People with Diabetes in 1990–2018. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kucharavy, D.; Guio, R.D. Application of Logistic Growth Curve. Procedia Eng. 2015, 131, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagley, S.C.; White, H.; Golomb, B.A. Logistic Regression in the Medical Literature: Standards for Use and Reporting, with Particular Attention to One Medical Domain. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2001, 54, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waltman, L.; van Eck, N.J.; Noyons, E.C.M. A Unified Approach to Mapping and Clustering of Bibliometric Networks. J. Inform. 2010, 4, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corbin, J.; Strauss, A. Basics of Qualitative Research: Techniques and Procedures for Developing Grounded Theory; Sage Publications: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamoorthy, G.; Ramakrishnan, J.S.D. Bibliometric Analysis of Literature on Diabetes (1995–2004). Ann. Lib. Inf. Stud. 2009, 56, 150–155. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, B.M.; Kaur, H.; Bala, A. Mapping of Indian Diabetes Research during 1999–2008: A Scientometric Analysis of Publications Output. DESIDOC J. Lib. Inf. Technol. 2011, 31, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Guo, L.; Yuan, M.; He, X.; Lin, Y.; Gu, C.; Li, Q.; Zhao, L.; Tong, X. Growing Trend of China’s Contribution to Global Diabetes Research: A Systematic Literature Review. Medicine 2016, 95, e3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweileh, W.M.; Sa’ed, H.Z.; Al-Jabi, S.W.; Sawalha, A.F. Bibliometric Analysis of Diabetes Mellitus Research Output from Middle Eastern Arab Countries During the Period (1996–2012). Scientometrics 2014, 101, 819–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harande, Y.I. Exploring the Literature of Diabetes in Nigeria: A Bibliometrics Study. Afr. J. Diabetes Med. 2011, 19, 8–11. [Google Scholar]
- Harande, Y.I.; Alhaji, I.U. Basic Literature of Diabetes: A Bibliometrics Analysis of Three Countries in Different World Regions. J. Lib. Inf. Sci. 2014, 2, 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Geaney, F.; Scutaru, C.; Kelly, C.; Glynn, R.W.; Perry, I.J. Type 2 Diabetes Research Yield, 1951–2012: Bibliometrics Analysis and Density-Equalizing Mapping. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Institute for Public Health (IPH), National Institutes of Health, Ministry of Health Malaysia. The Third National Health and Morbidity Survey 2006 (NHMS III) 2006, Diabetes Mellitus. 2008. Available online: http://iku.moh.gov.my/images/IKU/Document/REPORT/2006/DiabetesMellitus.pdf (accessed on 21 September 2020).
- Institute for Public Health (IPH), National Institutes of Health, Ministry of Health Malaysia. National Health and Morbidity Survey (NHMS) 2019: Vol. I: NCDs—Non-Communicable Diseases: Risk Factors and Other Health Problems. 2020. Available online: http://iku.moh.gov.my/images/IKU/Document/REPORT/NHMS2019/Report_NHMS2019-NCD_v2.pdf (accessed on 21 September 2020).
- Department of Public Health, Ministry of Health Malaysia. National Strategic Plan for Non-Communicable Disease Medium Term Strategic Plan to Further Strengthen the NCD Prevention and Control Program in Malaysia (2016–2025). 2016. Available online: https://www2.moh.gov.my/moh/resources/Penerbitan/Rujukan/NCD/National%20Strategic%20Plan/FINAL_NSPNCD.pdf (accessed on 21 September 2020).
- DOSM. Time Series Population Projection in Malaysia by 2025. 2020. Available online: https://www.data.gov.my/data/en_US/dataset/time-series-population-projection-by-ethnic-group-and-sex-malaysia-2020-2025-2030-2035-and-2040/resource/e47083dc-78a8-4ec2-872e-eb85e422c1f2 (accessed on 21 September 2020).
- Corrales-Reyes, I.E.; Fornaris-Cedeño, Y.; Dorta-Contreras, A.J.; Mejia, C.R.; Pacheco-Mendoza, J.; Arencibia-Jorge, R. Cuban Scientific Production on Diabetes, 2000–2017: Peer-reviewed Publications, Collaboration and Impact. MEDICC Rev. 2019, 21, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hussein, Z.; Taher, S.W.; Gilcharan Singh, H.K.; Chee Siew Swee, W. Diabetes Care in Malaysia: Problems, New Models, and Solutions. Ann. Glob. Health 2015, 81, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganasegeran, K.; Ch’ng, A.S.H.; Jamil, M.F.A.; Looi, I. Clinicians’ Publication Output: Self-Report Survey and Bibliometric Analysis. Publications 2020, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ministry of Higher Education. Malaysia Research Assessment (MyRA). 2020. Available online: https://www.mohe.gov.my/en/ (accessed on 20 December 2020).
- Aksnes, D.W. Characteristics of Highly Cited Papers. Res. Eval. 2003, 12, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narin, F.; Stevens, K.; Whitlow, E. Scientific Co-Operation in Europe and the Citation of Multinationally Authored Papers. Scientometrics 2005, 21, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, A.; Gupta, B.M. Diabetes Research in India, China and Brazil: A Comparative Quantitative Study, 2000–2009. J. Health Med. Inform. 2012, 3, 1000110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hughes, D.; Hughes, A.; Powell, A.; Al-Sarireh, B. Hepatocellular Carcinoma’s 100 Most Influential Manuscripts: A Bibliometric Analysis. Int. J. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. 2019, 9, 100083Z04DH2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, A.G.; Hughes, D.L.; Wheat, J.R.; Lewis, W.G. The 100 Most Influential Manuscripts in Gastric Cancer: A Bibliometric Analysis. Int. J. Surg. 2016, 28, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pho, P.; Mantzaris, A.V. Regularized Simple Graph Convolution (SGC) for Improved Interpretability of Large Datasets. J. Big Data 2020, 7, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perozzi, B.; Al-Rfou, R.; Skiena, S. DeepWalk—Online Learning of Social Representations. In Proceedings of the 20th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, New York, NY, USA, 24–27 August 2014; pp. 701–710. [Google Scholar]








| Year | International Collaboration | National Collaboration | No Collaboration | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Publication | Citation | Publication | Citation | Publication | Citation | |
| 2000 | 3 | 103 | 0 | 0 | 11 | 261 |
| 2001 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 54 | 4 | 58 |
| 2002 | 3 | 210 | 5 | 81 | 9 | 453 |
| 2003 | 2 | 110 | 1 | 19 | 10 | 249 |
| 2004 | 6 | 260 | 4 | 47 | 12 | 296 |
| 2005 | 5 | 354 | 9 | 145 | 20 | 532 |
| 2006 | 7 | 631 | 12 | 315 | 25 | 608 |
| 2007 | 14 | 676 | 14 | 298 | 28 | 846 |
| 2008 | 20 | 640 | 19 | 548 | 43 | 1008 |
| 2009 | 15 | 1269 | 20 | 345 | 42 | 1472 |
| 2010 | 32 | 1027 | 29 | 755 | 59 | 1673 |
| 2011 | 41 | 1324 | 30 | 955 | 58 | 996 |
| 2012 | 42 | 1827 | 42 | 830 | 82 | 1902 |
| 2013 | 61 | 1692 | 45 | 1134 | 83 | 1279 |
| 2014 | 61 | 840 | 68 | 1291 | 73 | 947 |
| 2015 | 67 | 885 | 104 | 1121 | 49 | 238 |
| 2016 | 69 | 732 | 80 | 524 | 52 | 321 |
| 2017 | 99 | 628 | 62 | 189 | 71 | 216 |
| 2018 | 108 | 167 | 61 | 46 | 102 | 70 |
| Total | 655 | 13,375 | 606 | 8697 | 833 | 13,425 |
| No. | Title | Author | Year of Publication | Journal Name | Citations | MOH/University | Collaboration Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Liraglutide, a once-daily human GLP-1 analogue, added to a sulphonylurea over 26 weeks produces greater improvements in glycaemic and weight control compared with adding rosiglitazone or placebo in subjects with Type 2 diabetes (LEAD-1 SU) | Marre, M.; Shaw, J.; Brandle, M.; Bebakar, W.M.W.; Kamaruddin, N.A.; Strand, J.; Zdravkovic, M.; Le Thi, T.D.; Colagiuri, S. | 2009 | Diabetic Medicine | 947 | USM | International Collaboration |
| 2 | How common is non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in the Asia-Pacific region and are there local differences? | Amarapurkar, D.N.; Hashimoto, E.; Lesmana, L.A.; Sollano, J.D.; Chen, P.J.; Goh, K.L. | 2007 | Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology (Australia) | 387 | UM | International Collaboration |
| 3 | The role of oxidative stress and antioxidants in diabetic complications | Matough, F.A.; Budin, S.B.; Hamid, Z.A.; Alwahaibi, N.; Mohamed, J. | 2012 | Sultan Qaboos University Medical Journal | 324 | UKM | International Collaboration |
| 4 | In vitro alpha-glucosidase and alpha-amylase enzyme inhibitory effects of Andrographis paniculata extract and andrographolide | Subramanian, R.; Asmawi, M.Z.; Sadikun, A. | 2008 | Acta Biochim Pol | 274 | USM | No Collaboration |
| 5 | Antidiabetic and antioxidant activity of Annona squamosa extract in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats | Kaleem, M.; Asif, M.; Ahmed, Q.U.; Bano, B. | 2006 | Singapore Medical Journal | 257 | UIAM | International Collaboration |
| 6 | An alarmingly high prevalence of diabetic nephropathy in Asian type 2 diabetic patients: The MicroAlbuminuria Prevalence (MAP) Study | Wu, A.Y.T.; Kong, N.C.T.; De Leon, F.A.; Pan, C.Y.; Tai, T.Y.; Yeung, V.T.F.; Yoo, S.J.; Rouillon, A.; Weir, M.R. | 2005 | Diabetologia | 243 | UKM | International Collaboration |
| 7 | Omega-3 fatty acids: a comprehensive review of their role in health and disease | Yashodhara, B.M.; Umakanth, S.; Pappachan, J.M.; Bhat, S.K.; Kamath, R.; Choo, B.H. | 2009 | Postgraduate Medical Journal | 241 | Manipal Medical College | No Collaboration |
| 8 | Diabetes-associated macrovasculopathy: pathophysiology and pathogenesis | Rahman, S.; Rahman, T.; Ismail, A.A.; Rashid, A.R. | 2007 | Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism | 216 | USM | No Collaboration |
| 9 | The improvement of hypertension by probiotics: effects on cholesterol, diabetes, renin, and phytoestrogens | Lye, H.S.; Kuan, C.Y.; Ewe, J.A.; Fung, W.Y.; Liong, M.T. | 2009 | International Journal of Molecular Sciences | 210 | USM | No Collaboration |
| 10 | Prevalence of diabetes in the Malaysian National Health Morbidity Survey III 2006 | Letchuman, G.R.; Wan Nazaimoon, W.M.; Wan Mohamad, W.B.; Chandran, L.R.; Tee, G.H.; Jamaiyah, H.; Isa, M.R.; Zanariah, H.; Fatanah, I.; Ahmad Faudzi, Y. | 2010 | Medical Journal of Malaysia | 204 | MOH | National Collaboration |
| No. | Journal | Total | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Medical Journal of Malaysia | 95 | 4.5 |
| 2 | Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) | 68 | 3.2 |
| 3 | Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice | 45 | 2.1 |
| 4 | Singapore Medical Journal | 31 | 1.5 |
| 5 | International Medical Journal | 29 | 1.4 |
| 6 | Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences | 27 | 1.3 |
| 7 | Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine | 25 | 1.2 |
| 8 | PLoS One | 23 | 1.1 |
| 9 | International Medical Journal Malaysia | 22 | 1.1 |
| 10 | Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research | 22 | 1.1 |
| Cluster Size | Cluster Concept | Keywords | Thematic Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (75 items) | Clinical studies | Human (1141), male (947), female (813), adult (748), type 2 diabetes mellitus (745), diabetes mellitus (662), middle aged (501), major clinical study (457), age (430), hemoglobin a1c (319), risk factor (252), cross-sectional study (209), hypertension (199), glycemic control (174), body mass index (159), prevalence (158), type 1 diabetes mellitus (135), complication (153), treatment outcome (130), questionnaire (128), disease association (127), clinical article (105), retrospective study (102), disease duration (98), follow-up studies (94), nephropathy (90), prospective studies (86), quality of life (86), adolescent (83), risk assessment (80), case report (79), blood pressure (78), oral antidiabetic agent (78), outcome assessment (78), young adult (75), hemoglobin blood level (74), Asian (68), case-control study (68), cohort studies (63), comorbidity (63), aged 80 and over (62), creatinine (62), disease severity (62), primary healthcare (59), neuropathy (57), demography (56), genetics (56), diabetic foot (53), sex difference (53), clinical feature (52), mortality (51), incidence (50), diabetes control (46), disease course (46), exercise (46), waist circumference (46), wound healing (46), ethnology (45), time factor (45), age distribution (44), diet (43), genotype (42), antihypertensive agent (41), ethnicity (41), medical record (41), insulin treatment (40), physical activity (40), Chinese (39), Malaysian (39), creatinine blood level (38), ischemic heart disease (38), genetic association (37), lifestyle (37), smoking (37) | Clinical studies involving human subjects across different age groups. Some studies evaluated risks attributable to diabetes. These risks were evaluated across established demographic, anthropometric, and lifestyle factors, in addition to novel postulations, such as genetic associations. The cluster also explored diabetes complications, treatment efficacy, severity of the disease progression, and potential health and treatment outcomes using a variety of study designs and types, ranging from observational to interventional studies. |
| 2 (45 items) | Animal studies | Controlled study (711), glucose blood level (464), animal model (449), glucose (421), nonhuman (421), insulin (397), Sprague Dawley rats (364), antidiabetic agent (332), diabetes (312), unclassified drug (244), streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus (229), metabolism (226), hypoglycemic agents (221), plant extract (199), drug effect (193), antioxidant (178), animal tissue (162), diabetes mellitus, experimental (149), hyperglycemia (125), body weight (114), glibenclamide (114), chemistry (109), animal cell (103), Wistar rats (92), insulin blood level (89), enzyme activity (77), histopathology (77), biological marker (72), medicinal plant (66), treatment duration (65), drug mechanism (63), plant leaf (63), dose response (58), enzyme inhibition (55), alpha glucosidase inhibitor (51), antidiabetic (48), mice (46), phytochemistry (45), flavonoid (43), drug dose–response relationship (42), anti-inflammatory agent (41), enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (38), phytotherapy (36), fruit (35), protein blood level (35) | This cluster emphasized laboratory-based experimental study design through animal models and cellular studies to explore potential novel drug therapies, ranging from chemical components to phytochemicals for the treatment of diabetes. |
| 3 (9 items) | Co-morbidities | Low-density lipoprotein (129), triacylglycerol (125), high-density lipoprotein (125), cholesterol blood level (97), cholesterol (103), lipid (71), systolic blood pressure (56), diastolic blood pressure (41), blood sampling (35) | This cluster included studies that explored co-morbid conditions regarding diabetes, blood pressure, and lipid metabolism. |
| 4 (9 items) | Drug studies | Randomized controlled trial (159), metformin (154), hypoglycemia (110), drug efficacy (104), drug safety (67), multicenter study (47), sulfonylurea (44), acarbose (40), monotherapy (36) | This cluster’s sole emphasis was on drug trials that evaluated the efficacy and safety of anti-diabetic therapies. |
| 5 (8 items) | Biomarker studies | Oxidative stress (125), inflammation (56), superoxide dismutase (53), lipid peroxidation (43), malonaldehyde (41), catalase (39), interleukin 6 (36), C-reactive protein (35) | The cluster included studies that evaluated conventional and novel biomarkers. |
| 6 (8 items) | Complications | Review (198), obesity (112), hyperlipidemia (106), cardiovascular disease (94), cardiovascular risk (57), metabolic syndrome (40), Asia (38), practice guideline (38) | This cluster included studies related to cardiovascular risk factors and macrovascular complications. |
| 7 (8 items) | Treatment | Insulin resistance (100), pathophysiology (70), insulin release (65), gene expression (57), protein expression (55), pancreas islet beta-cell (50), insulin sensitivity (47), physiology (46) | This cluster explored studies related to physiological processes and genetic influences on glucose metabolism. |
| 8 (8 items) | Control measures | Blood glucose (238), blood (187), comparative study (71), diet restriction (68), blood glucose monitoring (56), diagnosis (44), diet therapy (37), fasting (35) | This cluster examined studies related to the control and prevention of diabetes. |
| 9 (6 items) | Eye complications | Retinopathy (162), pathology (89), procedures (79), eye protection (58), sensitivity and specificity (44), image processing (36) | This cluster focused solely on microvascular complications of diabetes, emphasizing ophthalmic complications and treatment procedures. |
| 10 (6 items) | Health-related quality of life, knowledge, attitude, and practices | Psychology (51), patient compliance (49), attitude to health (48), self-care (45), health knowledge, attitudes, practice (40), patient education (35) | This cluster solely evaluated health outcomes from a psycho-socio-behavioral perspective, together with conventional knowledge, attitudes, and practice studies. |
| 11 (5 items) | Gestational diabetes | Pregnancy (67), pregnancy diabetes mellitus (59), gestational diabetes mellitus (54), glucose tolerance test (52), oral glucose tolerance test (51) | This cluster uniquely evaluated studies related to gestational diabetes and its diagnosis. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ganasegeran, K.; Hor, C.P.; Jamil, M.F.A.; Suppiah, P.D.; Noor, J.M.; Hamid, N.A.; Chuan, D.R.; Manaf, M.R.A.; Ch’ng, A.S.H.; Looi, I. Mapping the Scientific Landscape of Diabetes Research in Malaysia (2000–2018): A Systematic Scientometrics Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18010318
Ganasegeran K, Hor CP, Jamil MFA, Suppiah PD, Noor JM, Hamid NA, Chuan DR, Manaf MRA, Ch’ng ASH, Looi I. Mapping the Scientific Landscape of Diabetes Research in Malaysia (2000–2018): A Systematic Scientometrics Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(1):318. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18010318
Chicago/Turabian StyleGanasegeran, Kurubaran, Chee Peng Hor, Mohd Fadzly Amar Jamil, Purnima Devi Suppiah, Juliana Mohd Noor, Norshahida Abdul Hamid, Deik Roy Chuan, Mohd Rizal Abdul Manaf, Alan Swee Hock Ch’ng, and Irene Looi. 2021. "Mapping the Scientific Landscape of Diabetes Research in Malaysia (2000–2018): A Systematic Scientometrics Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 1: 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18010318
APA StyleGanasegeran, K., Hor, C. P., Jamil, M. F. A., Suppiah, P. D., Noor, J. M., Hamid, N. A., Chuan, D. R., Manaf, M. R. A., Ch’ng, A. S. H., & Looi, I. (2021). Mapping the Scientific Landscape of Diabetes Research in Malaysia (2000–2018): A Systematic Scientometrics Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(1), 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18010318






