Does Regular Dancing Improve Static Balance?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
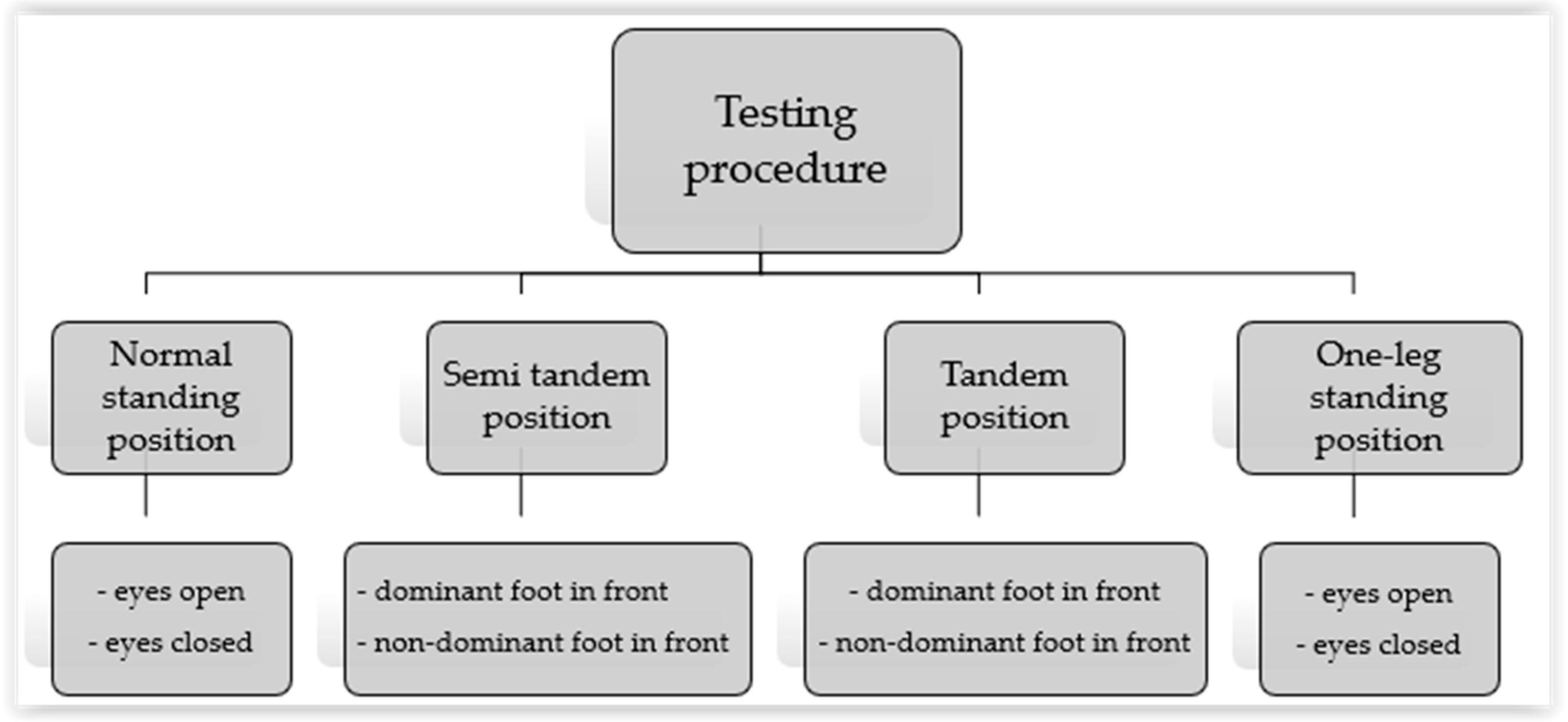
2.2. Experimental Procedures and Instruments
- MV Y (mm/s): the mean velocity of the sway of the center of feet pressure (COP) in the sagittal plane,
- MV X (mm/s): the mean velocity of the sway of the COP in the frontal plane,
- Spectrum Y (Hz, mm): the value of the middle of the spectrum in the saggital plane, the spectrum was characterized by two codependent variables, such as frequency (Hz) and excursion (mm),
- Spectrum X (Hz, mm): the value of the middle of the spectrum in the frontal plane (frequency and excursion).
- Normal standing with eyes open (NS EO) and eyes closed (NS EC) positions
- Semi-tandem position (ST)
- Tandem position (TP)
- One-leg standing position (1L)
2.2.1. Normal Standing Position (NS)
2.2.2. Semi-Tandem Position (ST)
2.2.3. Tandem Position (TP)
2.2.4. One-Leg Standing Position (1L)
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Normal Standing Position (NS)
3.2. Semi-Tandem Position (ST)
3.3. Tandem Position (TP)
3.4. One-Leg Standing Position (1L)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, H.S.; Law, C.L.; Pan, H.F.; Hsiao, Y.P.; Hu, J.H.; Chuang, F.-K.; Huang, M.-H. Preliminary results of dancing exercise on postural stability in adolescent females. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2011, 27, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dunsky, A.; Zeev, A.; Netz, Y. Balance Performance Is Task Specific in Older Adults. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 6987017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cherng, R.J.; Chen, J.J.; Su, F.C. Vestibular system in performance of standing balance of children and young adults under altered sensory conditions. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2001, 92 Pt 2, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montemurro, N.; Herbet, G.; Duffau, H. Right Cortical and Axonal Structures Eliciting Ocular Deviation During Electrical Stimulation Mapping in Awake Patients. Brain Topogr. 2016, 29, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuisinier, R.; Olivier, I.; Vaugoyeau, M.; Nougier, V.; Assaiante, C. Reweighting of Sensory Inputs to Control Quiet Standing in Children from 7 to 11 and in Adults. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goślińska, J.; Wareńczak, A.; Miedzyblocki, M.; Hejdysz, K.; Adamczyk, E.; Sip, P.; Chlebuś, E.; Gośliński, J.; Owczarek, P.; Woźniak, A.; et al. Wireless Motion Sensors—Useful in Assessing the Effectiveness of Physiotherapeutic Methods Used in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis—Preliminary Report. Sensors 2020, 20, 2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paillard, T.; Noé, F. Techniques and Methods for Testing the Postural Function in Healthy and Pathological Subjects. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 891390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monteiro-Junior, R.S.; Ferreira, A.S.; Puell, V.N.; Lattari, E.; Machado, S.; César, A.O.V.; da Silva, B.E. Wii Balance Board: Reliability and clinical use in assessment of balance in healthy elderly women. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2015, 14, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewan, B.M.; Roger James, C.; Kumar, N.A.; Sawyer, S.F. Kinematic Validation of Postural Sway Measured by Biodex Biosway (Force Plate) and SWAY Balance (Accelerometer) Technology. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mancini, M.; Horak, F.B. The relevance of clinical balance assessment tools to differentiate balance deficits. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2010, 46, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kilroy, E.A.; Crabtree, O.M.; Crosby, B.; Parker, A.; Barfield, W.R. The Effect of Single-Leg Stance on Dancer and Control Group Static Balance. Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2016, 9, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lesinski, M.; Hortobágyi, T.; Muehlbauer, T.; Gollhofer, A.; Granacher, U. Effects of Balance Training on Balance Performance in Healthy Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2015, 45, 1721–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Douka, S.; Zilidou, V.I.; Lilou, O.; Manou, V. Traditional Dance Improves the Physical Fitness and Well-Being of the Elderly. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keogh, J.W.; Kilding, A.; Pidgeon, P.; Ashley, L.; Gillis, D. Physical benefits of dancing for healthy older adults: A review. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2009, 17, 479–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steinberg, N.; Waddington, G.; Adams, R.; Karin, J.; Tirosh, O. Should Ballet Dancers Vary Postures and Underfoot Surfaces When Practicing Postural Balance? Motor Control 2018, 22, 45–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janura, M.; Procházková, M.; Svoboda, Z.; Bizovská, L.; Jandová, S.; Konečný, P. Standing balance of professional ballet dancers and non-dancers under different conditions. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugel, F.; Cadopi, M.; Kohler, F.; Perrin, P. Postural control of ballet dancers: A specific use of visual input for artistic purposes. Int. J. Sports Med. 1999, 20, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruyneel, A.V.; Mesure, S.; Paré, J.C.; Bertrand, M. Organization of postural equilibrium in several planes in ballet dancers. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 485, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutt, K.; Redding, E. The effect of an eyes-closed dance-specific training program on dynamic balance in elite pre-professional ballet dancers: A randomized controlled pilot study. J. Dance Med. Sci. 2014, 18, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahal, M.A.; Alonso, A.C.; Andrusaitis, F.R.; Rodrigues, T.S.; Speciali, D.S.; D’Andréa Greve, G.M.; Leme, L.E.G. Analysis of static and dynamic balance in healthy elderly practitioners of Tai Chi Chuan versus ballroom dancing. Clinics 2015, 70, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, N.; Adams, R.; Waddington, G.; Karin, J.; Tirosh, O. Is There a Correlation Between Static and Dynamic Postural Balance Among Young Male and Female Dancers? J. Mot. Behav. 2017, 49, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, B.V.; Reed, A.N.; Rogers, R.R.; Marshall, M.R.; Pederson, J.A.; Williams, T.D.; Ballmann, C.J. Differences in Balance Ability and Motor Control between Dancers and Non-Dancers with Varying Foot Positions. J. Funct Morphol. Kinesiol. 2020, 5, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajala, S.; Era, P.; Koskenvuo, M.; Kaprio, J.; Törmäkangas, T.; Rantanen, T. Force platform balance measures as predictors of indoor and outdoor falls in community-dwelling women aged 63–76 years. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2008, 63, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, H.; Cho, K.; Lee, W. Reliability of the good balance system(®) for postural sway measurement in poststroke patients. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2014, 26, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wareńczak, A.; Lisiński, P.; Huber, J. Importance of the functional examination in lower extremities in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Bioeng Biomech. 2014, 16, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bremer, Z. Dance as a form of exercise. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2007, 57, 166. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Federici, A.; Bellagamba, S.; Rocchi, M.B. Does dance-based training improve balance in adult and young old subjects? A pilot randomized controlled trial. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2005, 17, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Mello, M.C.; De sá Ferreira, A.; Ramiro Felicio, L. Postural Control During Different Unipedal Positions in Professional Ballet Dancers. J. Dance Med. Sci. 2017, 21, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalska, J.; Kamieniarz, A.; Fredyk, A.; Bacik, B.; Juras, G.; Słomka, K.J. Effect of expertise in ballet dance on static and functional balance. Gait Posture 2018, 64, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, P.; Deviterne, D.; Hugel, F.; Perrot, C. Judo, better than dance, develops sensorimotor adaptabilities involved in balance control. Gait Posture 2002, 15, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assländer, L.; Hettich, G.; Mergner, T. Visual contribution to human standing balance during support surface tilts. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2015, 41, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muelas Pérez, R.; Sabido Solana, R.; Barbado Murillo, D.; Moreno Hernández, F.J. Visual availability, balance performance and movement complexity in dancers. Gait Posture 2014, 40, 556–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuczyński, M.; Szymańska, M.; Bieć, E. Dual-task effect on postural control in high-level competitive dancers. J. Sports Sci. 2011, 29, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casabona, A.; Leonardi, G.; Aimola, E.; La Grua, G.; Polizzi, C.M.; Cioni, M.; Valle, M.S. Specificity of foot configuration during bipedal stance in ballet dancers. Gait Posture 2016, 46, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharnuke, J.K.; Mullerpatan, R.P.; Hiller, C. Evaluation of Standing Balance Performance in Indian Classical Dancers. J. Dance Med. Sci. 2020, 24, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crotts, D.; Thompson, B.; Nahom, M.; Ryan, S.; Newton, R. Balance abilities of professional dancers on select balance tests. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 1996, 23, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Dancers | Control Group | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Mean ± SD | Median | Min-Max | Mean ± SD | Median | Min-Max | p |
| weight (kg) | 56.52 ± 7.59 | 54.00 | 45.00–80.00 | 58.48 ± 6.80 | 57.00 | 47.00–73.00 | 0.19 * |
| height (cm) | 165.70 ± 5.86 | 167.00 | 151.00–176.00 | 167.00 ± 6.33 | 167.50 | 155.00–180.00 | 0.47 |
| BMI | 20.59 ± 2.52 | 20.06 | 15.39–28.69 | 20.94 ± 1.93 | 20.89 | 17.47–25.39 | 0.40 * |
| Dancers Group | Control Group | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Mean ± SD | Median | Min-Max | Mean ± SD | Median | Min-Max | p-Value | |
| NS EO | MV Y (mm/s) | 4.15 ± 1.12 | 3.80 | 2.70–6.50 | 4.54 ± 0.75 | 4.70 | 3.20–5.8 | 0.07 * |
| MV X (mm/s) | 2.43 ± 0.96 | 2.20 | 1.20–4.60 | 2.86 ± 0.90 | 3.05 | 1.10–4.50 | 0.08 * | |
| Spectrum Y (Hz) | 0.436 ± 0.173 | 0.398 | 0.142–0.805 | 0.347 ± 0.121 | 0.352 | 0.120–0.540 | 0.04 | |
| Spectrum Y (mm) | 0.322 ± 0.030 | 0.321 | 0.247–0.382 | 0.327 ± 0.033 | 0.322 | 0.282–0.402 | 0.61 | |
| Spectrum X (Hz) | 0.282 ± 0.156 | 0.156 | 0.124–0.758 | 0.299 ± 0.146 | 0.244 | 0.135–0.691 | 0.54 * | |
| Spectrum X (mm) | 0.080 ± 0.054 | 0.069 | 0.041–0.307 | 0.078 ± 0.024 | 0.080 | 0.038–0.127 | 0.35 * | |
| NS EC | MV Y (mm/s) | 6.69 ± 2.09 | 6.30 | 4.10–12.30 | 6.80 ± 1.91 | 6.40 | 4.20–11.00 | 0.77 * |
| MV X (mm/s) | 3.02 ± 0.90 | 3.00 | 1.80–6.00 | 3.30 ± 1.08 | 3.20 | 1.70–5.90 | 0.31 * | |
| Spectrum Y (Hz) | 0.460 ± 0.127 | 0.440 | 0.263–0.712 | 0.375 ± 0.123 | 0.372 | 0.201–0.672 | 0.02 | |
| Spectrum Y (mm) | 0.354 ± 0.041 | 0.346 | 0.298–0.447 | 0.350 ± 0.070 | 0.349 | 0.108–0.473 | 0.90 * | |
| Spectrum X (Hz) | 0.386 ± 0.176 | 0.365 | 0.183–0.867 | 0.335 ± 0.147 | 0.292 | 0.183–0.636 | 0.23 * | |
| Spectrum X (mm) | 0.078 ± 0.020 | 0.079 | 0.039–0.115 | 0.091 ± 0.036 | 0.083 | 0.040–0.177 | 0.11 | |
| Dancers Group | Control Group | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Mean ± SD | Median | Min-Max | Mean ± SD | Median | Min-Max | p-Value | |
| SDF | MV Y (mm/s) | 6.87 ± 1.37 | 6.80 | 3.50–9.20 | 7.26 ± 1.64 | 6.65 | 4.70–11.10 | 0.38 |
| MV X (mm/s) | 6.62 ± 1.32 | 6.50 | 4.40–9.30 | 7.47 ± 1.70 | 7.20 | 4.20–11.90 | 0.06 | |
| Spectrum Y (Hz) | 0.536 ± 0.199 | 0.527 | 0.242–0.949 | 0.440 ± 0.181 | 0.422 | 0.209–1.066 | 0.07 * | |
| Spectrum Y (mm) | 0.403 ± 0.044 | 0.398 | 0.335–0.502 | 0.409 ± 0.053 | 0.403 | 0.308–0.544 | 0.70 | |
| Spectrum X (Hz) | 0.312 ± 0.117 | 0.305 | 0.133–0.554 | 0.292 ± 0.096 | 0.298 | 0.135–0.533 | 0.51 | |
| Spectrum X (mm) | 0.219 ± 0.044 | 0.214 | 0.145–0.347 | 0.261 ± 0.060 | 0.261 | 0.142–0.403 | 0.01 | |
| SNF | MV Y (mm/s) | 6.51 ± 1.52 | 6.20 | 3.20–9.50 | 7.19 ± 2.08 | 6.50 | 4.90–13.50 | 0.32 * |
| MV X (mm/s) | 6.67 ± 1.09 | 6.50 | 4.70–8.60 | 7.49 ± 1.66 | 7.20 | 4.90–10.70 | 0.05 | |
| Spectrum Y (Hz) | 0.454 ± 0.222 | 0.379 | 0.200–1.120 | 0.459 ± 0.202 | 0.410 | 0.192–1.044 | 0.66 * | |
| Spectrum Y (mm) | 0.407 ± 0.055 | 0.409 | 0.307–0.515 | 0.415 ± 0.081 | 0.394 | 0.288–0.632 | 0.76 * | |
| Spectrum X (Hz) | 0.299 ± 0.100 | 0.283 | 0.184–0.471 | 0.323 ± 0.115 | 0.294 | 0.181–0.593 | 0.63 * | |
| Spectrum X (mm) | 0.224 ± 0.042 | 0.218 | 0.158–0.321 | 0.259 ± 0.065 | 0.256 | 0.152–0.374 | 0.03 | |
| Dancers Group | Control Group | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Mean ± SD | Median | Min-Max | Mean ± SD | Median | Min-Max | p-Value | |
| TDF | MV Y (mm/s) | 8.97 ± 1.82 | 8.90 | 6.10–12.90 | 10.34 ± 2.41 | 9.70 | 7.70–16.80 | 0.07 * |
| MV X (mm/s) | 8.76 ± 1.60 | 8.40 | 6.10–13.40 | 10.00 ± 2.46 | 9.45 | 7.50–18.90 | 0.04 * | |
| Spectrum Y (Hz) | 0.475 ± 0.173 | 0.474 | 0.216–0.972 | 0.503 ± 0.239 | 0.474 | 0.177–1.150 | 0.77 * | |
| Spectrum Y (mm) | 0.329 ± 0.076 | 0.327 | 0.232–0.498 | 0.332 ± 0.061 | 0.321 | 0.248–0.482 | 0.86 | |
| Spectrum X (Hz) | 0.366 ± 0.124 | 0.347 | 0.180–0.655 | 0.276 ± 0.088 | 0.266 | 0.150–0.450 | 0.01 | |
| Spectrum X (mm) | 0.269 ± 0.037 | 0.271 | 0.206–0.350 | 0.329 ± 0.060 | 0.322 | 0.227–0.540 | <0.01 * | |
| TNF | MV Y (mm/s) | 8.57 ± 2.00 | 7.80 | 6.20–13.40 | 10.35 ± 2.31 | 10.25 | 7.20–17.10 | <0.01 * |
| MV X (mm/s) | 8.44 ± 2.21 | 8.10 | 4.60–15.00 | 10.27 ± 3.32 | 9.60 | 6.80–23.80 | 0.01 * | |
| Spectrum Y (Hz) | 0.417 ± 0.188 | 0.343 | 0.166–0.837 | 0.471 ± 0.156 | 0.459 | 0.267–0.837 | 0.28 | |
| Spectrum Y (mm) | 0.300 ± 0.093 | 0.290 | 0.025–0.489 | 0.330 ± 0.057 | 0.330 | 0.254–0.478 | 0.18 | |
| Spectrum X (Hz) | 0.340 ± 0.113 | 0.326 | 0.161–0.561 | 0.362 ± 0.134 | 0.352 | 0.161–0.599 | 0.55 | |
| Spectrum X (mm) | 0.270 ± 0.051 | 0.265 | 0.177–0.373 | 0.323 ± 0.086 | 0.312 | 0.191–0.623 | 0.02 * | |
| Dancers Group | Control Group | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Mean ± SD | Median | Min-Max | Mean ± SD | Median | Min-Max | p | |
| 1L EO | MV Y mm/s | 14.50 ± 4.11 | 13.60 | 8.90–24.30 | 16.03 ± 3.26 | 15.40 | 11.60–24.30 | 0.18 |
| MV X mm/s | 16.00 ± 3.10 | 15.70 | 10.70–25.20 | 17.27 ± 3.64 | 17.05 | 10.80–24.70 | 0.22 | |
| Spectrum Y (Hz) | 0.400 ± 0.159 | 0.401 | 0.217–0.756 | 0.470 ± 0.164 | 0.443 | 0.285–0.898 | 0.41 * | |
| Spectrum Y (mm) | 0.597 ± 0.108 | 0.595 | 0.445–0.815 | 0.608 ± 0.057 | 0.608 | 0.475–0.720 | 0.67 | |
| Spectrum X (Hz) | 0.693 ± 0.216 | 0.667 | 0.388–1.117 | 0.638 ± 0.195 | 0.610 | 0.328–1.058 | 0.37 | |
| Spectrum X (mm) | 0.424 ± 0.054 | 0.421 | 0.322–0.540 | 0.465 ± 0.071 | 0.442 | 0.366–0.616 | 0.08 * | |
| 1L EC | MV Y mm/s | 33.60 ± 11.43 | 32.00 | 14.10–70.80 | 37.67 ± 7.39 | 36.70 | 23.90–53.80 | 0.04 * |
| MV X mm/s | 36.88 ± 10.15 | 37.60 | 19.20–55.30 | 38.47 ± 7.90 | 38.65 | 25.30–60.10 | 0.59 | |
| Spectrum Y (Hz) | 0.435 ± 0.087 | 0.424 | 0.272–0.575 | 0.455 ± 0.150 | 0.447 | 0.250–0.723 | 0.62 | |
| Spectrum Y (mm) | 1.060 ± 0.340 | 1.019 | 0.612–2.082 | 1.180 ± 0.340 | 1.190 | 0.712–2.276 | 0.15 * | |
| Spectrum X (Hz) | 0.564 ± 0.083 | 0.556 | 0.407–0.746 | 0.564 ± 0.082 | 0.554 | 0.436–0.750 | 0.99 | |
| Spectrum X (mm) | 0.962 ± 0.277 | 0.895 | 0.479–1.565 | 0.943 ± 0.148 | 0.952 | 0.664–1.238 | 0.78 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stawicki, P.; Wareńczak, A.; Lisiński, P. Does Regular Dancing Improve Static Balance? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5056. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18105056
Stawicki P, Wareńczak A, Lisiński P. Does Regular Dancing Improve Static Balance? International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(10):5056. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18105056
Chicago/Turabian StyleStawicki, Przemysław, Agnieszka Wareńczak, and Przemysław Lisiński. 2021. "Does Regular Dancing Improve Static Balance?" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 10: 5056. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18105056
APA StyleStawicki, P., Wareńczak, A., & Lisiński, P. (2021). Does Regular Dancing Improve Static Balance? International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(10), 5056. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18105056






