Ultrasound-Guided Popliteal Nerve Block with Short-Acting Lidocaine in the Surgical Treatment of Ingrown Toenails
Abstract
:1. Background
2. Methods
2.1. Subjects
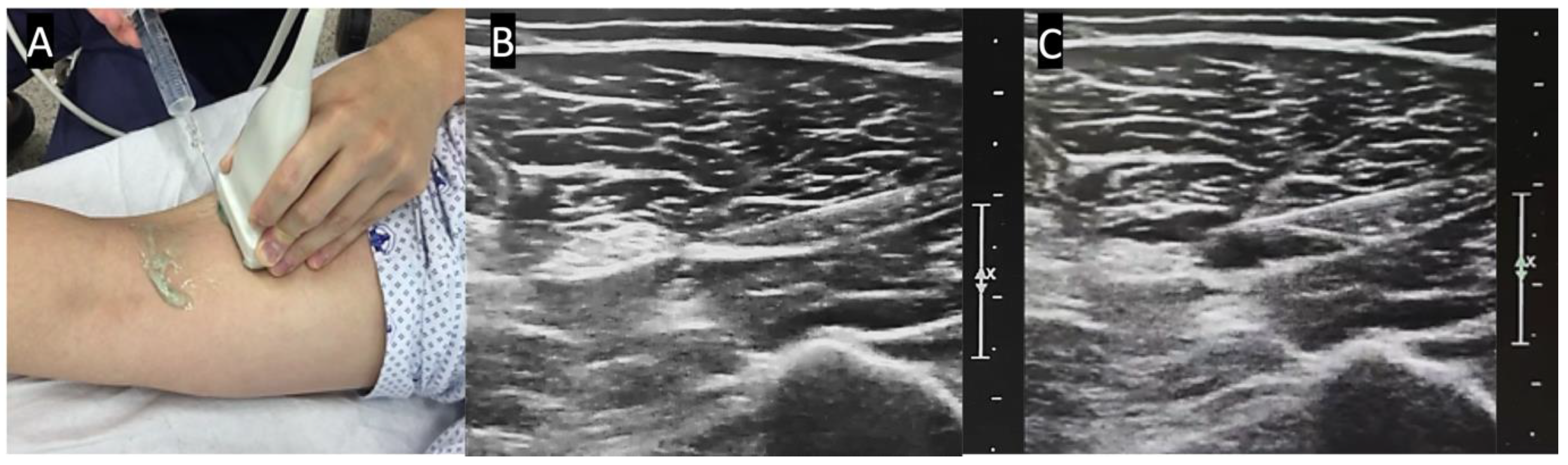
2.2. Anesthetic Method and Technique
2.3. Surgical Technique
2.4. Outcome Measures
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DB | Digital Nerve Block |
| PB | Popliteal Sciatic Nerve Block |
| US | Ultrasound |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| VAS | Visual Analogue Scale |
| MEV | Minimal Effective Volume |
References
- Kayalar, M.; Bal, E.; Toros, T.; Ozaksar, K.; Gurbuz, Y.; Ademoglu, Y. Results of partial matrixectomy for chronic ingrown toenail. Foot Ankle Int. 2011, 32, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieg, J.D.; Anderson, J.H.; Ireland, A.J.; Anderson, J.R. The surgical treatment of ingrowing toenails. J. Bone JoInt. Surg. Br. 1991, 73, 131–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eekhof, J.A.; Van Wijk, B.; Knuistingh Neven, A.; van der Wouden, J.C. Interventions for ingrowing toenails. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, CD001541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Kim, Y.S.; Yi, Y. Short-term surgical outcome of the partial nail extraction in ingrown nail of military trainee: Is matrixectomy necessary? J. Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2019, 23, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haneke, E. Nail surgery. Clin. Dermatol. 2013, 31, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.G.; Lalonde, D.H. Randomized comparison of the single-injection volar subcutaneous block and the two-injection dorsal block for digital anesthesia. Plast Reconstr. Surg. 2006, 118, 1195–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, C.J.; Lalonde, D.H. Randomized double-blind comparison of duration of anesthesia among three commonly used agents in digital nerve block. Plast Reconstr. Surg. 2006, 118, 429–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keramidas, E.G.; Rodopoulou, S.G. Ropivacaine versus lidocaine in digital nerve blocks: A prospective study. Plast Reconstr. Surg. 2007, 119, 2148–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Cho, Y.S.; Kang, B.; Kim, G.W.; Han, S. The difference of subcutaneous digital nerve block method efficacy according to injection location. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2020, 38, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, B.; Chan, L.; Rowlinson, J.S.; Baker, M.; Clancy, M. Digital anaesthesia: One injection or two? Emerg. Med. J. 2010, 27, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgeat, A.; Blumenthal, S.; Lambert, M.; Theodorou, P.; Vienne, P. The feasibility and complications of the continuous popliteal nerve block: A 1001-case survey. Anesth. Analg. 2006, 103, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosser, D.M.; Herr, M.J.; Claridge, R.J.; Barker, L.G. Preoperative lateral popliteal nerve block for intraoperative and postoperative pain control in elective foot and ankle surgery: A prospective analysis. Foot Ankle Int. 2007, 28, 1271–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaramonte, R.; Bonfiglio, M.; Castorina, E.G.; Antoci, S.A.M. The primacy of ultrasound in the assessment of muscle architecture: Precision, accuracy, reliability of ultrasonography. Physiatrist, radiologist, general internist, and family practitioner’s experiences. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2019, 65, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.Q.H.; Dugani, S.; Pham, K.; Finlayson, R.J. A randomized comparison between subepineural and conventional ultrasound-guided popliteal sciatic nerve block. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2011, 36, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelleri, G.; Cedrati, V.L.; Fedele, L.L.; Gemma, M.; Camici, L.; Loiero, M.; Gallazzi, M.B.; Cornaggia, G. Effects of the intraneural and subparaneural ultrasound-guided popliteal sciatic nerve block: A prospective, randomized, double-blind clinical and electrophysiological comparison. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2016, 41, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heifetz, C.J. Operative management of ingrown toenail. Mo. Med. 1945, 42, 213. [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, C.J.; Hamilton, P.D. Current concepts review: Regional anesthesia for foot and ankle surgery. Foot Ankle Int. 2010, 31, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.H.; Chou, T.A.; Tsai, S.W.; Chen, C.F.; Wu, P.K.; Chen, W.M. The efficacy and safety of continuous versus single-injection popliteal sciatic nerve block in outpatient foot and ankle surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2019, 20, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.F.; Issioui, T.; Skrivanek, G.D.; Early, J.S.; Wakefield, C. The use of a continuous popliteal sciatic nerve block after surgery involving the foot and ankle: Does it improve the quality of recovery? Anesth. Analg. 2003, 97, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serour, F.; Ben-Yehuda, Y.; Boaz, M. EMLA (R) cream prior to digital nerve block for ingrown nail surgery does not reduce pain at injection of anesthetic solution. Acta Anaesth. Scand. 2002, 46, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kose, O.; Saylan, S.; Ediz, N.; Yigit, S. Effects of topical alkane vapocoolant spray on pain intensity prior to digital nerve block for ingrown nail surgery. Foot Ankle Spec. 2010, 3, 73–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christoph, R.A.; Buchanan, L.; Begalla, K.; Schwartz, S. Pain reduction in local anesthetic administration through pH buffering. Ann. Emerg. Med. 1988, 17, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haneke, E. Surgical anatomy of the nail apparatus. Dermatol. Clin. 2006, 24, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rorie, D.K.; Byer, D.E.; Nelson, D.O.; Sittipong, R.; Johnson, K.A. Assessment of block of the sciatic nerve in the popliteal fossa. Anesth. Analg. 1980, 59, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlas, A.; Brull, R.; Chan, V.W.; McCartney, C.J.; Nuica, A.; Abbas, S. Ultrasound guidance improves the success of sciatic nerve block at the popliteal fossa. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2008, 33, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, E.; Eshelman, M.R.; Cracchiolo III, A. Popliteal fossa neural blockade as the sole anesthetic technique for outpatient foot and ankle surgery. Foot Ankle Int. 2000, 21, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myerson, M.S.; Ruland, C.M.; Allon, S.M. Regional anesthesia for foot and ankle surgery. Foot Ankle 1992, 13, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| PB Group (n = 44) | DB Group (n = 66) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male, n (%) | 44 (100) | 66 (100) | N/A |
| Age, years | 20.7 ± 2.8 | 20.9 ± 2.0 | 0.663 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 23.6 ± 2.8 | 24.6 ± 3.0 | 0.082 |
| Laterality, n (Right/Left) | 18/26 | 34/32 | 0.331 |
| Side of nail fold, n (Medial/Lateral/Both) | 13/15/16 | 16/33/17 | 0.246 |
| Variables | PB Group (n = 44) | DB Group (n = 66) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time to sensory block, mean ± SD, min | 20.8 ± 4.6 | 6.5 ± 1.6 | < 0.01 |
| Duration of sensory block, mean ± SD, min | 187.9 ± 22.0 | 106.5 ± 19.1 | < 0.01 |
| Needs for additional injections, n (%) | 0 (0) | 16 (24.2) | < 0.01 |
| Adverse events, n (%) | 2 (4.5) | 4 (6.1) | 0.732 |
| Palpitation, n (%) | 1 (2.3) | 0 (0) | |
| Dizziness, n (%) | 1 (2.3) | 2 (3.0) | |
| Syncope, n (%) | 0 (0) | 2 (3.0) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, B.S.; Kim, K.; Day, J.; Seilern Und Aspang, J.; Kim, J. Ultrasound-Guided Popliteal Nerve Block with Short-Acting Lidocaine in the Surgical Treatment of Ingrown Toenails. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5059. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18105059
Kim BS, Kim K, Day J, Seilern Und Aspang J, Kim J. Ultrasound-Guided Popliteal Nerve Block with Short-Acting Lidocaine in the Surgical Treatment of Ingrown Toenails. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(10):5059. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18105059
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Beom Suk, Kyungho Kim, Jonathan Day, Jesse Seilern Und Aspang, and Jaeyoung Kim. 2021. "Ultrasound-Guided Popliteal Nerve Block with Short-Acting Lidocaine in the Surgical Treatment of Ingrown Toenails" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 10: 5059. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18105059
APA StyleKim, B. S., Kim, K., Day, J., Seilern Und Aspang, J., & Kim, J. (2021). Ultrasound-Guided Popliteal Nerve Block with Short-Acting Lidocaine in the Surgical Treatment of Ingrown Toenails. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(10), 5059. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18105059






