Positivity to Cocaine and/or Benzoylecgonine in Confirmation Analyses for On-Road Tests in Spain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
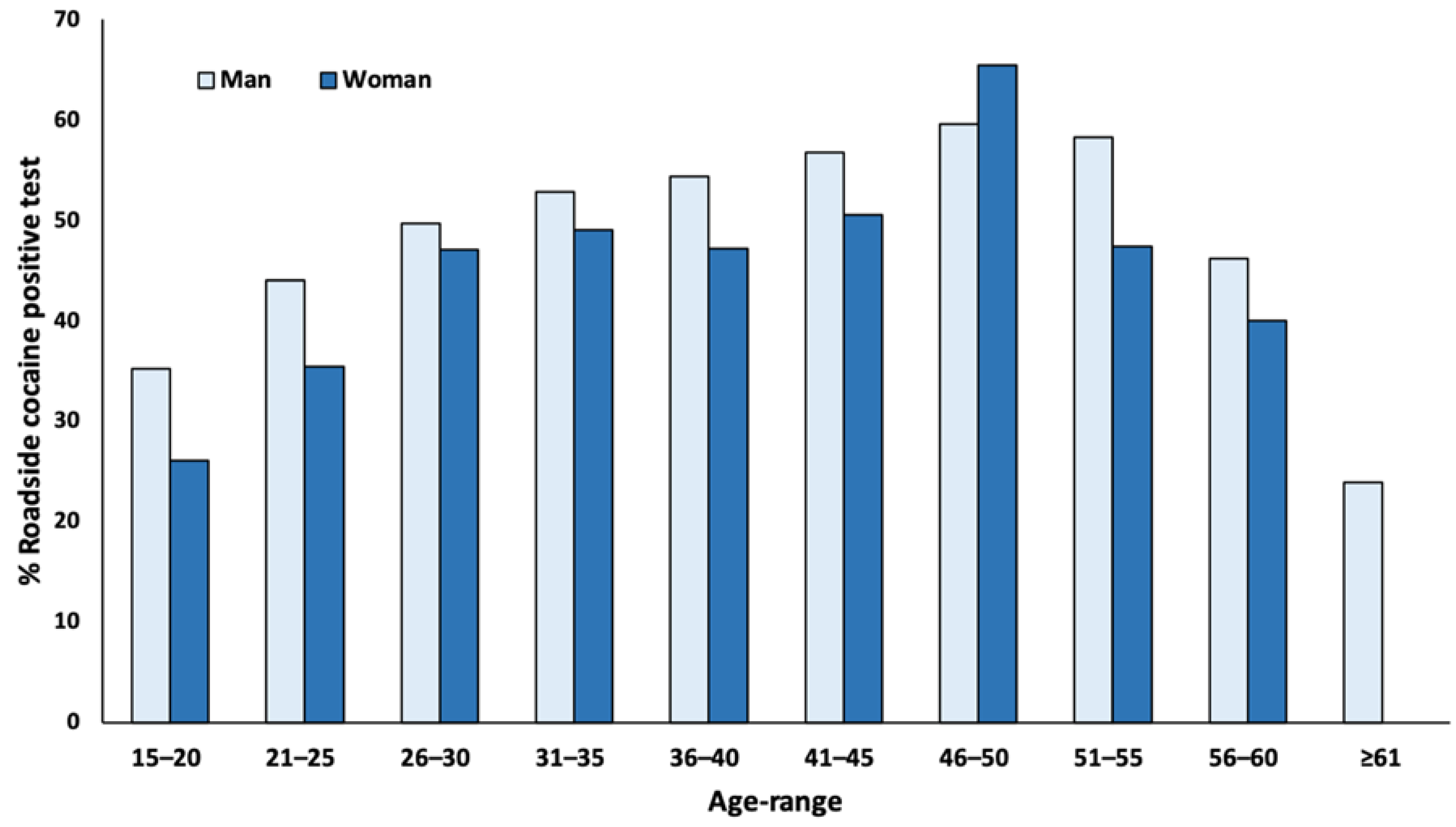
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Drug Use and Road Safety: A Policy Brief; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016; Available online: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/249533/1/WHO-MSD-NVI-2016.01-eng.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2021).
- Schulze, H.; Shumacher, M.; Urmeew, R.; Auerbach, K.; Alvarez, F.J.; Bernhoft, I.M.; De Gier, H.; Hagenzieker, M.; Houwing, S.; Knoche, A.; et al. Driving Under the Influence of Drugs, Alcohol and Medicines in Europe Findings from the DRUID Project; European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA): Lisbon, Portugal, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Elvik, R. Risk of Road Accident Associated with the Use of Drugs: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Evidence from Epidemiological Studies. Accid Anal. Prev. 2013, 60, 254–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummer, O.H.; Gerostamoulos, D.; Di Rago, M.; Woodford, N.W.; Morris, C.; Frederiksen, T.; Jachno, K.; Wolfe, R. Odds of Culpability Associated with Use of Impairing Drugs in Injured Drivers in Victoria, Australia. Accid Anal. Prev. 2020, 135, 105389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera-Gómez, F.; García-Mingo, M.; Colás, M.; González-Luque, J.C.; Álvarez, F.J. Opioids in Oral Fluid of Spanish Drivers. Drug Alcohol. Depend 2018, 187, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desrosiers, N.A.; Huestis, M.A. Oral Fluid Drug Testing: Analytical Approaches, Issues and Interpretation of Results. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2019, 43, 415–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Musshoff, F.; Hokamp, E.G.; Bott, U.; Madea, B. Performance Evaluation of On-Site Oral Fluid Drug Screening Devices in Normal Police Procedure in Germany. Forensic. Sci. Int. 2014, 238, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busardo, F.P.; Pichini, S.; Pellegrini, M.; Montana, A.; Lo Faro, A.F.; Zaami, S.; Graziano, S. Correlation between Blood and Oral Fluid Psychoactive Drug Concentrations and Cognitive Impairment in Driving under the Influence of Drugs. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2018, 16, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strano-Rossi, S.; Castrignanò, E.; Anzillotti, L.; Serpelloni, G.; Mollica, R.; Tagliaro, F.; Pascali, J.P.; di Stefano, D.; Sgalla, R.; Chiarotti, M. Evaluation of Four Oral Fluid Devices (DDS®, Drugtest 5000®, Drugwipe 5+® and RapidSTAT®) for on-Site Monitoring Drugged Driving in Comparison with UHPLC-MS/MS Analysis. Forensic. Sci. Int. 2012, 221, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lema-Atán, J.Á.; de Castro, A.; Lendoiro, E.; López-Rivadulla, M.; Cruz, A. Toxicological Oral Fluid Results among Spanish Drivers Testing Positive on On-Site Drug Controls from 2013 to 2015. Drug Alcohol. Depend. 2019, 195, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coe, M.A.; Jufer Phipps, R.A.; Cone, E.J.; Walsh, S.L. Bioavailability and Pharmacokinetics of Oral Cocaine in Humans. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2018, 42, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellefsen, K.N.; Concheiro, M.; Pirard, S.; Gorelick, D.A.; Huestis, M.A. Oral Fluid Cocaine and Benzoylecgonine Concentrations Following Controlled Intravenous Cocaine Administration. Forensic. Sci. Int. 2016, 260, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrera-Gómez, F.; García-Mingo, M.; Colás, M.; González-Luque, J.C.; Alvarez, F.J. Drivers Who Tested Positive for Cannabis in Oral Fluid: A Longitudinal Analysis of Administrative Data for Spain between 2011 and 2016. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e026648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Gómez, F.; García-Mingo, M.; Álvarez, F.J. Benzodiazepines in the Oral Fluid of Spanish Drivers. Subst. Abuse Treat. Prev. Policy 2020, 15, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benchimol, E.I.; Smeeth, L.; Guttmann, A.; Harron, K.; Moher, D.; Petersen, I.; Sørensen, H.T.; von Elm, E.; Langan, S.M. RECORD Working Committee The REporting of Studies Conducted Using Observational Routinely-Collected Health Data (RECORD) Statement. PLoS Med. 2015, 12, e1001885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christophersen, A.S.; Mørland, J.; Stewart, K.; Gjerde, H. International Trends in Alcohol and Drug Use among Vehicle Drivers. Forensic. Sci. Rev. 2016, 28, 37–66. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gjerde, H.; Strand, M.C.; Mørland, J. Driving Under the Influence of Non-Alcohol Drugs--An Update Part I: Epidemiological Studies. Forensic. Sci. Rev. 2015, 27, 89–113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ji Kwon, N.; Han, E. A Review of Drug Abuse in Recently Reported Cases of Driving under the Influence of Drugs (DUID) in Asia, USA, and Europe. Forensic. Sci. Int. 2019, 302, 109854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fierro, I.; González-Luque, J.C.; Seguí-Gómez, M.; Álvarez, F.J. Alcohol and Drug Use by Spanish Drivers: Comparison of Two Cross-Sectional Road-Side Surveys (2008-9/2013). Int. J. Drug Policy 2015, 26, 794–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gómez-Talegón, T.; Fierro, I.; González-Luque, J.C.; Colás, M.; López-Rivadulla, M.; Javier Álvarez, F. Prevalence of Psychoactive Substances, Alcohol, Illicit Drugs, and Medicines, in Spanish Drivers: A Roadside Study. Forensic Sci. Int. 2012, 223, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo-Salvany, A.; Herrero, M.J.; Fernandez, B.; Perez, J.; Del Real, P.; González-Luque, J.C.; de la Torre, R. Prevalence of Psychoactive Substances, Alcohol and Illicit Drugs, in Spanish Drivers: A Roadside Study in 2015. Forensic. Sci. Int. 2017, 278, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellefsen, K.N.; Concheiro, M.; Pirard, S.; Gorelick, D.A.; Huestis, M.A. Cocaine and Benzoylecgonine Oral Fluid On-Site Screening and Confirmation. Drug Test. Anal. 2016, 8, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjerde, H.; Clausen, G.B.; Andreassen, E.; Furuhaugen, H. Evaluation of Dräger DrugTest 5000 in a Naturalistic Setting. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2018, 42, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, A.J.; Oyler, J.M.; Cone, E.J. Comparison of Heroin and Cocaine Concentrations in Saliva with Concentrations in Blood and Plasma. J. Anal. Toxicol. 1995, 19, 359–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cone, E.J.; Oyler, J.; Darwin, W.D. Cocaine Disposition in Saliva Following Intravenous, Intranasal, and Smoked Administration. J. Anal. Toxicol. 1997, 21, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jufer, R.; Walsh, S.L.; Cone, E.J.; Sampson-Cone, A. Effect of Repeated Cocaine Administration on Detection Times in Oral Fluid and Urine. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2006, 30, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dams, R.; Choo, R.E.; Lambert, W.E.; Jones, H.; Huestis, M.A. Oral Fluid as an Alternative Matrix to Monitor Opiate and Cocaine Use in Substance-Abuse Treatment Patients. Drug Alcohol. Depend 2007, 87, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scheidweiler, K.B.; Spargo, E.A.K.; Kelly, T.L.; Cone, E.J.; Barnes, A.J.; Huestis, M.A. Pharmacokinetics of Cocaine and Metabolites in Human Oral Fluid and Correlation with Plasma Concentrations after Controlled Administration. Ther. Drug Monit. 2010, 32, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ellefsen, K.N.; Concheiro, M.; Pirard, S.; Gorelick, D.A.; Huestis, M.A. Pharmacodynamic Effects and Relationships to Plasma and Oral Fluid Pharmacokinetics after Intravenous Cocaine Administration. Drug Alcohol. Depend 2016, 163, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorentin, T.R.; Scherer, J.N.; Marcelo, M.C.A.; Sousa, T.R.V.; Pechansky, F.; Ferrão, M.F.; Limberger, R.P. Comparison of Cocaine/Crack Biomarkers Concentrations in Oral Fluid, Urine and Plasma Simultaneously Collected From Drug Users. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2018, 42, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Fazio, V.; Wille, S.M.R.; Toennes, S.W.; van Wel, J.H.P.; Ramaekers, J.G.; Samyn, N. Driving under the Influence of Cocaine: Quantitative Determination of Basic Drugs in Oral Fluid Obtained during Roadside Controls and a Controlled Study with Cocaine Users. Drug Test. Anal. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langel, K.; Gjerde, H.; Favretto, D.; Lillsunde, P.; Øiestad, E.L.; Ferrara, S.D.; Verstraete, A.G. Comparison of Drug Concentrations between Whole Blood and Oral Fluid. Drug Test. Anal. 2014, 6, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wille, S.M.R.; Raes, E.; Lillsunde, P.; Gunnar, T.; Laloup, M.; Samyn, N.; Christophersen, A.S.; Moeller, M.R.; Hammer, K.P.; Verstraete, A.G. Relationship between Oral Fluid and Blood Concentrations of Drugs of Abuse in Drivers Suspected of Driving under the Influence of Drugs. Ther. Drug Monit. 2009, 31, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gjerde, H.; Langel, K.; Favretto, D.; Verstraete, A.G. Detection of Illicit Drugs in Oral Fluid from Drivers as Biomarker for Drugs in Blood. Forensic. Sci. Int. 2015, 256, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramaekers, J.G. Driving Under the Influence of Cannabis: An Increasing Public Health Concern. JAMA 2018, 319, 1433–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Cocaine and Benzoylecgonine | Cocaine without Benzoylecgonine | Benzoylecgonine without Cocaine | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of positive roadside drug tests to any drug carried out 2011 to 2016 | 65,244 | 65,244 | 65,244 |
| Drivers with a positive test for…. n (%) | 25,773 (39.50) | 5436 (8.33) | 498 (0.76) |
| Cocaine and/or Benzoylecgonine Alone n (%) | 4707 (18.26) | 422 (7.76) | 55 (11.05) |
| In combination with other drugs | 21,066 (81.74) | 5014 (92.24) | 443 (88.95) |
| Tetrahydrocannabinol | 17,572 (68.19) | 4715 (86.74) | 392 (78.71) |
| Opioids | 5355 (20.78) | 1220 (22.44) | 78 (15.66) |
| Amphetamine-like substances | 4320 (16.76) | 233 (4.29) | 59 (11.85) |
| Benzodiazepines | 1843 (7.15) | 166 (3.05) | 27 (5.42) |
| Zoplicone, zolpidem | 51 (0.20) | 5 (0.09) | 0 (0) |
| Cocaine and Benzoylecgonine | Cocaine without Benzoylecgonine | Benzoylecgonine without Cocaine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cocaine | Benzoylecgonine | |||
| Mean (SD) | 780.60 (4364.83) | 338.72 (2540.41) | 16.57 (20.55) | 38.55 (94.21) |
| Median (Q1–Q3) | 249.30 (55.30–405.00) | 137.90 (27.80–405.00) | 11.00 (7.23–19.29) * | 9.90 (6.80–24.25) ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Herrera-Gómez, F.; Gutiérrez-Abejón, E.; García-Mingo, M.; Álvarez, F.J. Positivity to Cocaine and/or Benzoylecgonine in Confirmation Analyses for On-Road Tests in Spain. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5371. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18105371
Herrera-Gómez F, Gutiérrez-Abejón E, García-Mingo M, Álvarez FJ. Positivity to Cocaine and/or Benzoylecgonine in Confirmation Analyses for On-Road Tests in Spain. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(10):5371. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18105371
Chicago/Turabian StyleHerrera-Gómez, Francisco, Eduardo Gutiérrez-Abejón, Mercedes García-Mingo, and F. Javier Álvarez. 2021. "Positivity to Cocaine and/or Benzoylecgonine in Confirmation Analyses for On-Road Tests in Spain" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 10: 5371. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18105371
APA StyleHerrera-Gómez, F., Gutiérrez-Abejón, E., García-Mingo, M., & Álvarez, F. J. (2021). Positivity to Cocaine and/or Benzoylecgonine in Confirmation Analyses for On-Road Tests in Spain. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(10), 5371. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18105371









