Effect of Digestate and Straw Combined Application on Maintaining Rice Production and Paddy Environment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment Treatments
2.2. Sampling and Analytical Procedures
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Rice Yield and Plant N Distribution under Different Treatments
3.1.1. Rice Yield and Yield Components
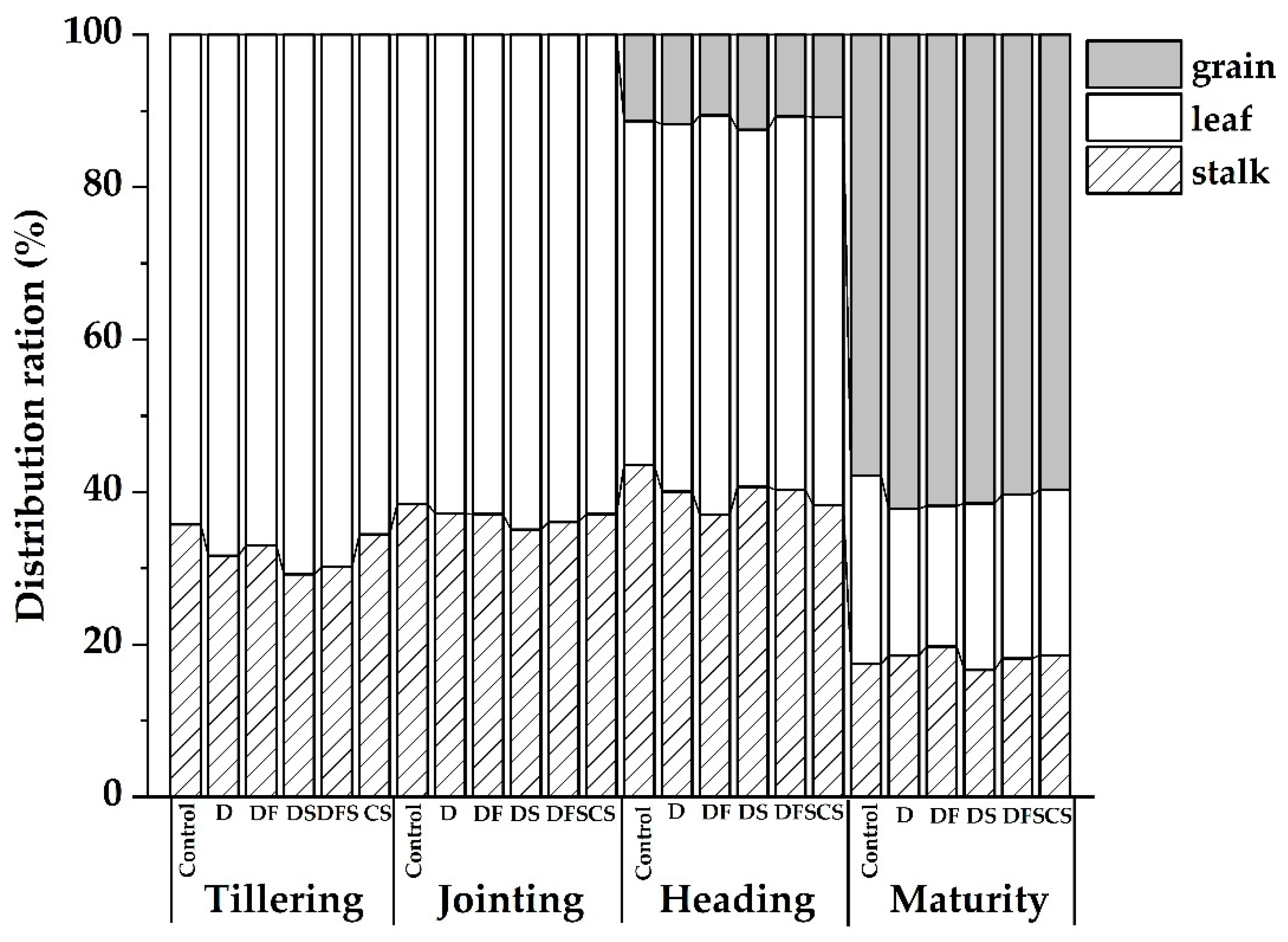
3.1.2. Plant N Distribution
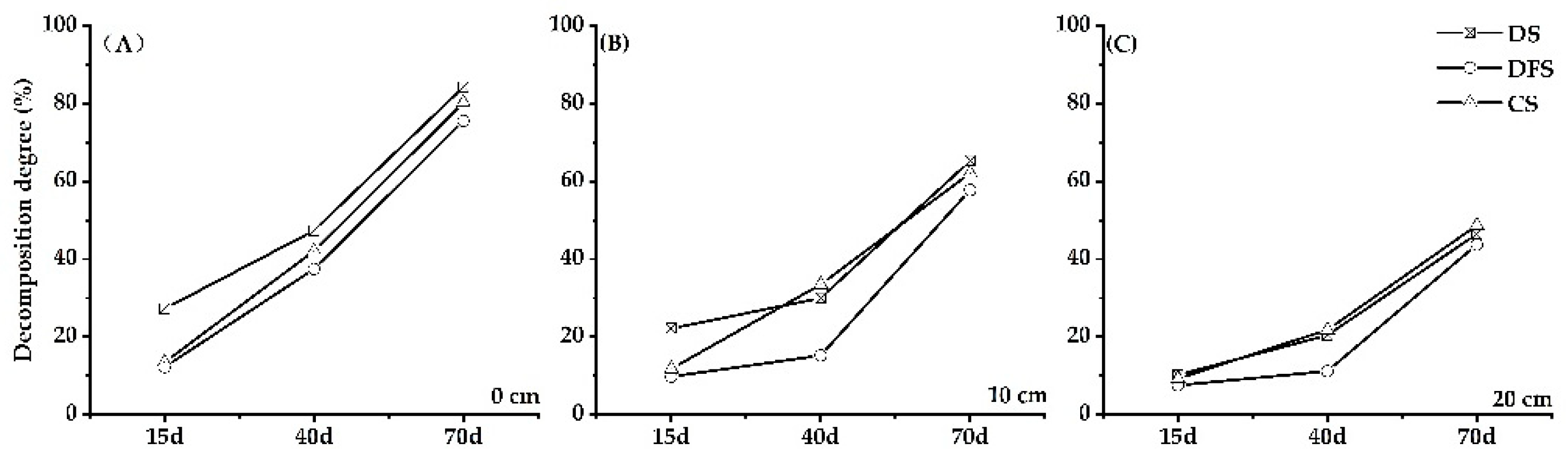
3.2. The Degree of Straw Decomposition
3.3. Soil Enzymatic Activities
3.4. Nutrients in Soil and Surface Water
3.4.1. Soil Organic Matter and Nutrient Contents
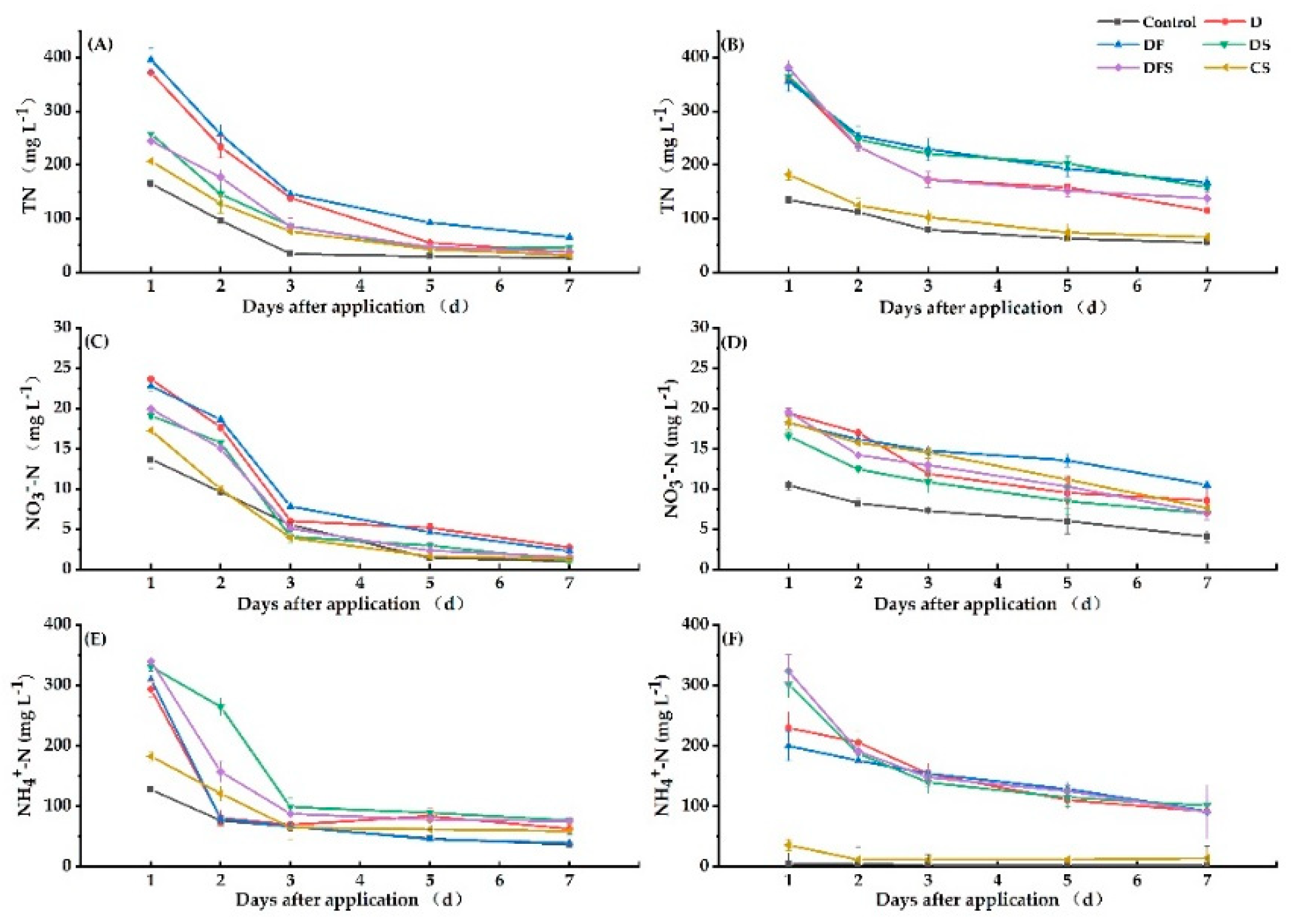
3.4.2. TN, NO3−-N and NH4+-N Contents in Soil Surface Water
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.G.; Diamond, J. China’s environment in a globalizing world. Nature 2005, 435, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, K.; Shang, J. Research on the Fertilizer Application Behavior and Agricultural Non-point Source Pollution Control in Green Agricultural Planting. B. Malariol. Salud Amb. 2018, 58, 12–19. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Chen, X.; Wei, T.; Yang, Z.; Jia, Z.; Yang, B.; Han, Q.; Ren, X. Effects of straw incorporation on the soil nutrient contents, enzyme activities, and crop yield in a semiarid region of China. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 160, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Lan, M.; Liu, J.; Gao, M. Soil aggregate and organic carbon distribution at dry land soil and paddy soil: The role of different straws returning. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 27942–27952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.Y.; Tan, X.; Show, P.L.; Rambabu, K.; Banat, F.; Veeramuthu, A.; Lau, B.F.; Ng, E.P.; Ling, T.C. Incorporating biowaste into circular bioeconomy: A critical review of current trend and scaling up feasibility. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 19, 101034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilayn, F.; Benbrahim, M.; Rouez, M.; Crest, M.; Patureau, D.; Jimenez, J. Humic-like substances extracted from different digestates: First trials of lettuce biostimulation in hydroponic culture. Waste Manag. 2020, 104, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nag, R.; Auer, A.; Markey, B.K.; Whyte, P.; Nolan, S.; O’Flaherty, V.; Russell, L.; Bolton, D.; Fenton, O.; Richards, K.; et al. Anaerobic digestion of agricultural manure and biomass—Critical indicators of risk and knowledge gaps. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 690, 460–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorelli, R.; Valboa, G.; Lagomarsino, A.; Fabiani, A.; Simoncini, S.; Zaghi, M.; Vignozzi, N. Recycling Biogas Digestate from Energy Crops: Effects on Soil Properties and Crop Productivity. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, O.P.; Hultberg, M.; Bergstrand, K.-J.; Larsson-Jönsson, H.; Caspersen, S.; Asp, H. Biogas Digestate in Vegetable Hydroponic Production: pH Dynamics and pH Management by Controlled Nitrification. Waste Biomass Valorization 2021, 12, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, J.; Huang, H.; Zhu, C. Temporal effects of repeated application of biogas slurry on soil antibiotic resistance genes and their potential bacterial hosts. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchowska-Kisielewicz, M.; Jędrczak, A. The Evaluation of Indicators Used to Assess the Suitability of Agricultural Waste for Fermentation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2019, 16, 1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Sui, P.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Long, P.; Cui, J.; Yan, L.; Chen, Y. Comparison of net GHG emissions between separated system and crop-swine integrated system in the North China Plain. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 149, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, Q.; Ma, J.; Chapman, S.; Zou, P.; Ye, J.; Yu, Q.; Sun, W.; Lin, H.; Jiang, L. Soil microbial activity and community composition as influenced by application of pig biogas slurry in paddy field in southeast China. Paddy Water Environ. 2020, 18, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Wen, G.; Li, P.; Dai, C.; Han, J. Effects of Biogas Slurry Application on Crop Production and Soil Properties in a Rice–Wheat Rotation on Coastal Reclaimed Farmland. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Chen, X.; Qi, X.; Li, Z.; Nan, J.; Deng, J. The effects of biochar and hoggery biogas slurry on fluvo-aquic soil physical and hydraulic properties: A field study of four consecutive wheat–maize rotations. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 2050–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somayaji, D.; Khanna, S. Biomethanation of rice and wheat straw. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1994, 10, 521–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lal, R. World crop residues production and implications of its use as a biofuel. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turmel, M.-S.; Speratti, A.; Baudron, F.; Verhulst, N.; Govaerts, B. Crop residue management and soil health: A systems analysis. Agric. Syst. 2015, 134, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtinen, T.; Schlatter, N.; Baumgarten, A.; Bechini, L.; Krüger, J.; Grignani, C.; Zavattaro, L.; Costamagna, C.; Spiegel, H. Effect of crop residue incorporation on soil organic carbon and greenhouse gas emissions in European agricultural soils. Soil Use Manag. 2014, 30, 524–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wei, T.; Jia, Z.; Han, Q.; Ren, X. Soil aggregate and crop yield changes with different rates of straw incorporation in semiarid areas of northwest China. Geoderma 2014, 230–231, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, C.; He, R.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X. Does extending recycling chain of using rice straw contribute to improving yield and reducing GHGs emissions in paddy field? An integrated analysis based on field research and system assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 264, 121508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Xu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C. Effect of returning corn straw into soil on soil fertility. Ying yong sheng tai xue bao = J. Appl. Ecol. 2002, 13, 539–542. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.; Chen, F.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Feng, C.; Wu, J.; Zheng, B. Effect of straw and polyacrylamide on the stability of land/water ecotone soil and the field implementation. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 94, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, B.; Hu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Mu, X.; Liu, K.; Li, C. Effects of Deep Tillage and Straw Returning on Soil Microorganism and Enzyme Activities. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Bo, G.; Zhang, Z.-F.; Wang, Y.; Shen, G.-M. Effects of Straw Incorporation on Soil Nutrients, Enzymes, and Aggregate Stability in Tobacco Fields of China. Sustainability 2016, 8, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandratos, N.; Bruinsma, J. World Agriculture Towards 2030/2050: The 2012 Revision. 2012. Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/ap106e/ap106e.pdf (accessed on 9 December 2020).
- FAOSTAT. Available online: http://faostat.fao.org/default.aspx?lang=en (accessed on 6 December 2020).
- Chen, Y.; Fan, P.; Li, L.; Tian, H.; Ashraf, U.; Mo, Z.; Duan, M.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, X.; et al. Straw Incorporation Coupled with Deep Placement of Nitrogen Fertilizer Improved Grain Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Direct-Seeded Rice. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2020, 20, 2338–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, H. Effects of agricultural practices on nitrogen distribution in unsaturated soils. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Xu, C.; Ye, C.; Chen, S.; Chu, G.; Zhang, X. Low recovery efficiency of basal fertilizer-N in plants does not indicate high basal fertilizer-N loss from split-applied N in transplanted rice. Field Crop. Res. 2018, 229, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kpomblekou, A.K. Relative proportion of inorganic and total nitrogen in broiler litter as determined by various methods. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2006, 86, 2354–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, T.; Herath, I.; Kumarathilaka, P.; Seneviratne, M.; Seneviratne, G.; Rajakaruna, N.; Vithanage, M.; Ok, Y.S. Role of woody biochar and fungal-bacterial co-inoculation on enzyme activity and metal immobilization in serpentine soil. J. Soils Sediments 2017, 17, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, A.H.; Vicente, A.A.; Rocha, J.C.; Trevisan, H.C. A new application of humic substances: Activation of supports for invertase immobilization. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2000, 368, 730–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bair, K.E.; Davenport, J.R. Plant Available Phosphorus Analysis for Recently Acidified Soils of the Columbia Basin Washington State. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2013, 77, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidêncio, P.H.; Poppi, R.J.; De Andrade, J.C.; Cantarella, H. Determination of organic matter in soil using near-infrared spectroscopy and partial least squares regression. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2002, 33, 1607–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, L.C.; King, C.A. Total Nitrogen Determination in Plant Material by Persulfate Digestion. Agron. J. 1907, 88, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kioussis, D.R.; Wheaton, F.W.; Kofinas, P. Reactive nitrogen and phosphorus removal from aquaculture wastewater effluents using polymer hydrogels. Aquac. Eng. 2000, 23, 315–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, Z.; Yin, X.; Sun, W. Identification of Nitrate Sources, and the Fate of Nitrade in Downstream Areas: A case Study in the Taizi River Basin. Huanjing Kexue 2018, 39, 1076–1084. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Szögi, A.; Hunt, P. Distribution of ammonium-N in the water-soil interface of a surface-flow constructed wetland for swine wastewater treatment. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 44, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yu, D.; Zhou, J.; Zhai, S.; Bian, X.; Weih, M. Rice-duck co-culture for reducing negative impacts of biogas slurry application in rice production systems. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 213, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Kou, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, J.; Xu, R.; Han, G.; Wu, L.; Zhu, L. Zizania aquatica–duck ecosystem with recycled biogas slurry maintained crop yield. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 2019, 115, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zhao, X.; Guo, Y.; Yang, G.; Xi, J.; Ren, G. Changes in the Material Characteristics of Maize Straw during the Pretreatment Process of Methanation. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Lin, X.; Shi, W.; Min, J.; Gao, N.; Zhang, H.; Yin, R.; He, X. Higher rates of nitrogen fertilization decrease soil enzyme activities, microbial functional diversity and nitrification capacity in a Chinese polytunnel greenhouse vegetable land. Plant Soil 2010, 337, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, F.; Zhu, Q.; Guo, X.; He, L. Effects of digestate on biomass of a selected energy crop and soil properties. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, L.; Kai, S.; Bin, Z.; Qingling, D.; Geng, L.; HuiFang, H.; Zengjia, L.; Tangyuan, N. Impacts of straw, biogas slurry, manure and mineral fertilizer applications on several biochemical properties and crop yield in a wheat-maize cropping system. Plant Soil Environ. 2019, 65, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Qi, X.; Liu, Y.; Fan, X.; Li, Z. Peanut-Shell Biochar and Biogas Slurry Improve Soil Properties in the North China Plain: A Four-Year Field Study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, X.; Hong, J.; Qiao, Z. Effect of Biogas Slurry on Biological Properties of Cabbage Continuous Cropping Soil. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2011, 17, 384–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Tian, L.; Lu, Y.; Xu, L.; Huang, Y.; Meng, K.; Liu, Z. Effects of Combined Application of Biogas Slurry, Biogas Residue and Chemical Fertilizer on Soil Fertility. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2016, 32, 78–81. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Yu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, S. Soil properties and enzyme activities as affected by biogas slurry irrigation in the Three Gorges Reservoir areas of China. J. Environ. Biol. 2015, 36, 513–520. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, H.; Shen, Y.; Fei, H.; Cheng, W. Biogas slurry use as N fertilizer for two-season Zizania aquatica Turcz. in China. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 2017, 107, 303–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyungeko, C.; Liang, X.; Liu, C.; Liu, Z.-W.; Sheteiwy, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, J.; Tian, G. Effect of biogas slurry application rate on colloidal phosphorus leaching in paddy soil: A column study. Geoderma 2018, 325, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, G.; Otto, R.; Almeida, R.F.; Cardoso, E.J.B.N.; Cantarella, H.; Vitti, G.C. Conversion of ammonium to nitrate and abundance of ammonium-oxidizing-microorganism in Tropical soils with nitrification inhibitor. Scientia Agricola 2020, 77, e20180370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Treatments | Basal Fertilizer | Tillering Fertilizer | Jointing Fertilizer | Panicle Fertilizer | Straw Incorporation Rate (t hm−2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Digestate (t hm−2) | Compound Fertilizer (kg hm−2) | Urea (kg hm−2) | Urea (kg hm−2) | Digestate (t hm−2) | Urea (kg hm−2) | ||
| Control | \ | \ | \ | \ | \ | \ | \ |
| D | 120 | \ | \ | \ | 90 | \ | \ |
| DF | 120 | \ | 211.5 | \ | 90 | \ | \ |
| DS | 120 | \ | \ | \ | 90 | \ | 7.5 |
| DFS | 120 | \ | 211.5 | \ | 90 | \ | 7.5 |
| CS | \ | 525 | 211.5 | 130.5 | \ | 64.5 | 7.5 |
| Treatments | Ear Number (104 hm−2) | Grains per Spike | Seed Setting Rate (%) | 1000-Grain Weight (g) | Theoretical Yield (t hm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 273.38 ± 13.32 c | 115.49 ± 12.12 b | 79.64 ± 0.10 a | 28.06 ± 1.08 a | 7.06 ± 0.06 d |
| D | 293.06 ± 19.98 c | 147.82 ± 12.37 a | 75.48 ± 0.05 b | 26.86 ± 0.34 c | 8.78 ± 0.67 c |
| DF | 346.32 ± 23.64 b | 126.79 ± 3.65 b | 82.20 ± 0.07 a | 27.30 ± 0.55 b | 9.86 ± 0.60 a |
| DS | 339.66 ± 19.98 b | 131.71 ± 1.24 ab | 71.19 ± 0.02 c | 27.39 ± 0.28 b | 8.72 ± 0.97 c |
| DFS | 373.35 ± 6.66 a | 122.62 ± 7.95 b | 76.68 ± 0.02 b | 27.83 ± 0.03 a | 9.77 ± 1.18 a |
| CS | 368.32 ± 26.63 a | 120.72 ± 17.14 c | 77.17 ± 0.07 b | 27.79 ± 0.01 b | 9.53 ± 1.60 ab |
| Enzymes | Treatments | Tillering | Jointing | Heading | Maturity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Catalase (Ug−1) | Control | 28.08 ± 1.06 b | 45.06 ± 1.33 c | 34.34 ±1.35 c | 33.09 ± 1.88 c |
| D | 28.37 ± 1.12 b | 47.36 ± 0.84 b | 35.59 ± 0.35 b | 34.74 ± 1.55 b | |
| DF | 29.12 ± 2.01 b | 52.99 ± 2.19 a | 36.80 ± 1.65 ab | 36.87 ± 0.60 a | |
| DS | 30.77 ± 1.16 a | 51.49 ± 1.40 a | 38.33 ± 1.80 a | 37.62 ± 0.93 a | |
| DFS | 32.19 ± 0.38 a | 51.21 ± 1.85 a | 37.49 ± 1.29 a | 36.60 ± 1.14 a | |
| CS | 27.58 ± 1.64 c | 40.49 ± 1.73 d | 31.48 ± 0.52 c | 32.92 ± 0.90 c | |
| Alkaline phosphatase (Ug−1) | Control | 9.67 ± 0.81 c | 14.70 ± 0.84 b | 12.10 ± 0.03 bc | 7.81 ± 0.31 b |
| D | 12.99 ± 0.36 a | 16.92 ± 0.61 a | 12.28 ± 0.41 b | 8.53 ± 0.36 b | |
| DF | 14.05 ± 0.21 a | 18.24 ± 0.71 a | 15.91 ± 0.63 a | 8.03 ± 0.21 b | |
| DS | 11.77 ± 0.11 ab | 14.80 ± 0.51 ab | 13.59 ± 0.11 ab | 10.44 ± 0.35 a | |
| DFS | 12.08 ± 0.24 ab | 15.91 ± 0.61 a | 14.50 ± 0.21 a | 10.72 ± 0.23 a | |
| CS | 10.47 ± 0.83 b | 15.51 ± 0.20 ab | 15.20 ± 0.71 a | 9.66 ± 0.56 a | |
| Urease (Ug−1) | Control | 1.63 ± 0.14 b | 1.02 ± 0.04 c | 1.18 ± 0.02 ab | 2.15 ± 0.38 cd |
| D | 1.73 ± 0.06 b | 1.05 ± 0.03 b | 1.25 ± 0.05 a | 2.69 ± 0.22 b | |
| DF | 1.70 ± 0.08 b | 1.06 ± 0.02 b | 1.22 ± 0.06 a | 2.56 ± 0.12 b | |
| DS | 1.92 ± 0.01 a | 1.16 ± 0.08 a | 1.19 ± 0.04 ab | 3.38 ± 0.10 a | |
| DFS | 1.80 ± 0.07 a | 1.16 ± 0.01 a | 1.21 ± 0.01 a | 2.52 ± 0.16 b | |
| CS | 1.73 ± 0.11 ab | 1.17 ± 0.03 a | 1.19 ± 0.06 ab | 2.27 ± 0.17 c | |
| Sucrase (Ug−1) | Control | 3.43 ± 0.05 b | 3.11 ± 0.39 c | 2.50 ± 0.08 b | 3.21 ± 0.28 bc |
| D | 3.67 ± 0.20 a | 3.76 ± 0.33 a | 2.64 ± 0.07 a | 3.86 ± 0.29 a | |
| DF | 3.73 ± 0.29 a | 3.62 ± 0.14 ab | 2.79 ± 0.06 a | 3.61 ± 0.01 ab | |
| DS | 3.64 ± 0.01 a | 3.82 ± 0.04 a | 2.85 ± 0.01 a | 3.88 ± 0.18 a | |
| DFS | 3.65 ± 0.05 a | 3.71 ± 0.10 a | 2.76 ± 0.07 a | 3.67 ± 0.26 ab | |
| CS | 3.81 ± 0.10 a | 3.45 ± 0.01 b | 2.31 ± 0.13 b | 3.35 ± 0.18 b |
| Treatments | SOM (g mg−1) | TN (g mg−1) | AN (mg kg−1) | AP (mg kg−1) | AK (mg kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 19.54 ± 0.65 c | 1.68 ± 0.03 c | 123.90 ± 5.40 c | 19.38 ± 0.22 d | 187.50 ± 9.85 c |
| D | 21.71 ± 0.73 b | 1.72 ± 0.23 c | 135.82 ± 5.61 b | 26.04 ± 1.02 b | 231.37 ± 5.98 b |
| DF | 22.07 ± 1.26 b | 1.83 ± 0.06 b | 128.48 ± 2.42 c | 26.22 ± 0.51 b | 245.33 ± 7.88 a |
| DS | 24.30 ± 1.39 a | 1.86 ± 0.11 b | 159.89 ± 2.39 a | 31.48 ± 0.32 a | 247.32 ± 9.97 a |
| DFS | 25.49 ± 1.13 a | 2.05 ± 0.03 a | 140.09 ± 6.20 b | 26.78 ± 0.55 b | 227.38 ± 5.98 b |
| CS | 20.71 ± 1.65 b | 1.88 ± 0.08 b | 138.94 ± 5.24 b | 22.53 ± 0.25 c | 223.39 ± 8.96 b |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, X.; Liu, H.; Xu, C.; Huang, X.; Jiang, M.; Zhuang, H.; Huang, L. Effect of Digestate and Straw Combined Application on Maintaining Rice Production and Paddy Environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5714. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18115714
Hu X, Liu H, Xu C, Huang X, Jiang M, Zhuang H, Huang L. Effect of Digestate and Straw Combined Application on Maintaining Rice Production and Paddy Environment. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(11):5714. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18115714
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Xue, Hongyi Liu, Chengyu Xu, Xiaomin Huang, Min Jiang, Hengyang Zhuang, and Lifen Huang. 2021. "Effect of Digestate and Straw Combined Application on Maintaining Rice Production and Paddy Environment" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 11: 5714. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18115714
APA StyleHu, X., Liu, H., Xu, C., Huang, X., Jiang, M., Zhuang, H., & Huang, L. (2021). Effect of Digestate and Straw Combined Application on Maintaining Rice Production and Paddy Environment. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(11), 5714. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18115714






