Health Care Access Measures and Palliative Care Use by Race/Ethnicity among Metastatic Gynecological Cancer Patients in the United States
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Study Cohort
2.3. Palliative Care Utilization
2.4. Study Variables
2.5. Statistical Analysis
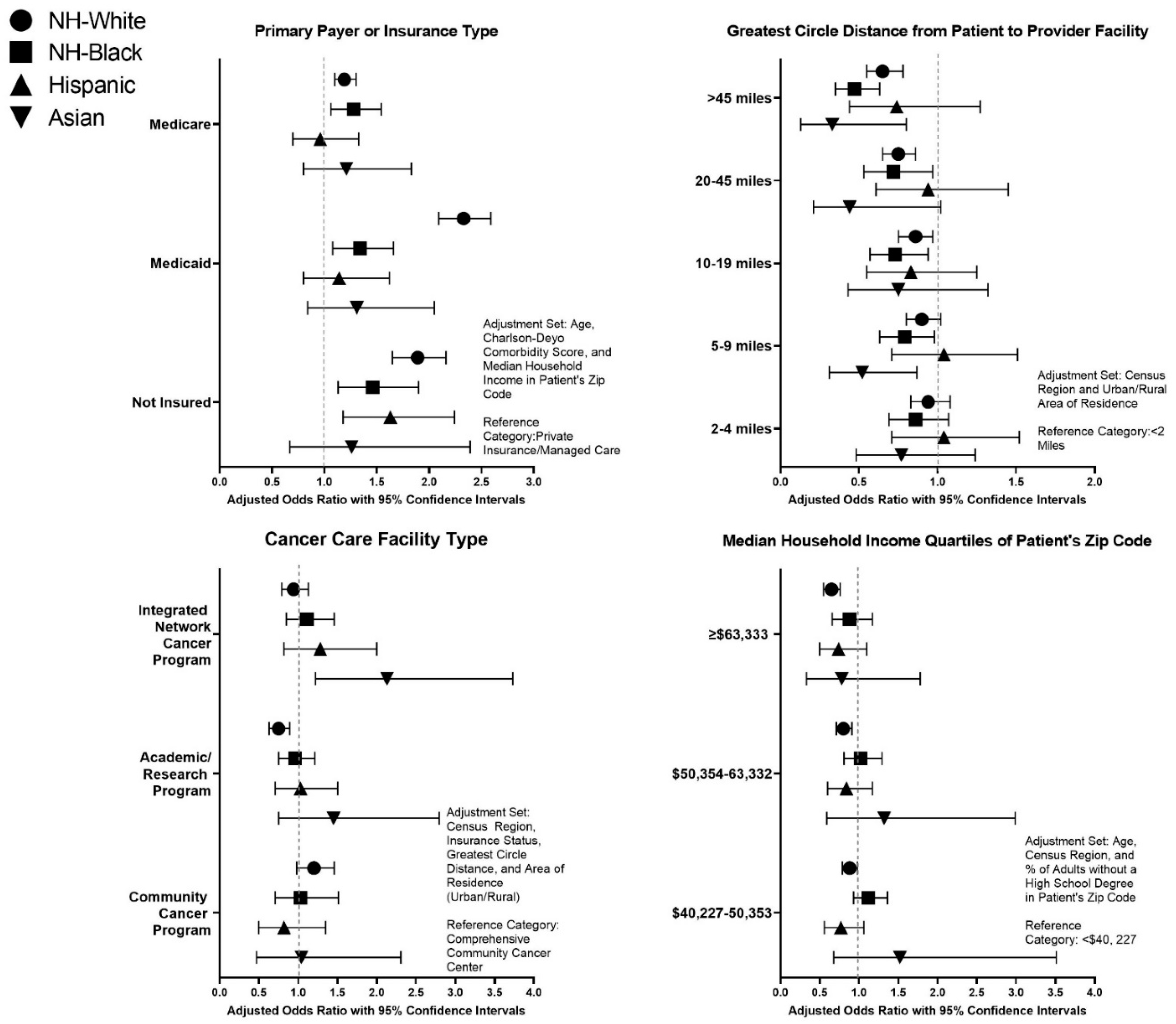
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dans, M.; Smith, T.; Back, A.; Baker, J.N.; Bauman, J.R.; Beck, A.C.; Block, S.; Campbell, T.; Case, A.A.; Dalal, S.; et al. NCCN Guidelines Insights: Palliative Care, Version 2.2017. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2017, 15, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassianos, A.P.; Ioannou, M.; Koutsantoni, M.; Charalambous, H. The impact of specialized palliative care on cancer patients’ health-related quality of life: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Support. Care Cancer 2018, 26, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakitas, M.A.; Tosteson, T.D.; Li, Z.; Lyons, K.D.; Hull, J.G.; Li, Z.; Dionne-Odom, J.N.; Frost, J.; Dragnev, K.H.; Hegel, M.T.; et al. Early Versus Delayed Initiation of Concurrent Palliative Oncology Care: Patient Outcomes in the ENABLE III Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1438–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevadunsky, N.S.; Gordon, S.; Spoozak, L.; Van Arsdale, A.; Hou, Y.; Klobocista, M.; Eti, S.; Rapkin, B.; Goldberg, G.L. The role and timing of palliative medicine consultation for women with gynecologic malignancies: Association with end of life interventions and direct hospital costs. Gynecol. Oncol. 2014, 132, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rugno, F.C.; Paiva, B.S.; Paiva, C.E. Early integration of palliative care facilitates the discontinuation of anticancer treatment in women with advanced breast or gynecologic cancers. Gynecol. Oncol. 2014, 135, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakitas, M.; Lyons, K.D.; Hegel, M.T.; Balan, S.; Brokaw, F.C.; Seville, J.; Hull, J.G.; Li, Z.; Tosteson, T.D.; Byock, I.R.; et al. Effects of a palliative care intervention on clinical outcomes in patients with advanced cancer: The Project ENABLE II randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2009, 302, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, J.A.; Pirl, W.F.; Jackson, V.A.; Muzikansky, A.; Lennes, I.T.; Heist, R.S.; Gallagher, E.R.; Temel, J.S. Effect of early palliative care on chemotherapy use and end-of-life care in patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, C.; Swami, N.; Krzyzanowska, M.; Hannon, B.; Leighl, N.; Oza, A.; Moore, M.; Rydall, A.; Rodin, G.; Tannock, I.; et al. Early palliative care for patients with advanced cancer: A cluster-randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2014, 383, 1721–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrell, B.R.; Temel, J.S.; Temin, S.; Alesi, E.R.; Balboni, T.A.; Basch, E.M.; Firn, J.I.; Paice, J.A.; Peppercorn, J.M.; Phillips, T.; et al. Integration of Palliative Care Into Standard Oncology Care: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 96–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauman, J.R.; Temel, J.S. The integration of early palliative care with oncology care: The time has come for a new tradition. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2014, 12, 1763–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Munsell, M.F.; Park, J.C.; Meyer, L.A.; Sun, C.C.; Brown, A.J.; Bodurka, D.C.; Williams, J.L.; Chase, D.M.; Bruera, E.; et al. Retrospective review of symptoms and palliative care interventions in women with advanced cervical cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2015, 139, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshields, T.L.; Potter, P.; Olsen, S.; Liu, J. The persistence of symptom burden: Symptom experience and quality of life of cancer patients across one year. Support. Care Cancer 2014, 22, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitecki, R.; Diver, E.J.; Kamdar, M.M.; Boruta, D.M., 2nd; Del Carmen, M.C.; Clark, R.M.; Goodman, A.; Schorge, J.O.; Growdon, W.B. Patterns of palliative care referral in ovarian cancer: A single institution 5 year retrospective analysis. Gynecol. Oncol. 2018, 148, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, J.Y.; Deveaux, A.; Previs, R.A.; Akinyemiju, T. Racial and ethnic disparities in palliative care utilization among gynecological cancer patients. Gynecol. Oncol. 2021, 160, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Acevedo, M.; Lowery, W.J.; Lowery, A.W.; Lee, P.S.; Havrilesky, L.J. Palliative and hospice care in gynecologic cancer: A review. Gynecol. Oncol. 2013, 131, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, J.S.; Brown, A.J.; Prescott, L.S.; Sun, C.C.; Ramondetta, L.M.; Bodurka, D.C. Dying well: How equal is end of life care among gynecologic oncology patients? Gynecol. Oncol. 2016, 140, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheu, J.; Palileo, A.; Chen, M.Y.; Hoepner, L.; Abulafia, O.; Kanis, M.J.; Lee, Y.C. Hospice utilization in advanced cervical malignancies: An analysis of the National Inpatient Sample. Gynecol. Oncol. 2019, 152, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, E.B.; Chan, J.K.; Gardner, A.B.; Curry, N.; Delic, L.; Kapp, D.S. Disparities Associated With Inpatient Palliative Care Utilization by Patients With Metastatic Gynecologic Cancers: A Study of 3337 Women. Am. J. Hosp. Palliat. Care 2018, 35, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, J.Y.; Deveaux, A.; Previs, R.A.; Akinyemiju, T. Racial disparities in palliative care utilization among metastatic gynecological cancer patients living at last follow-up: An analysis of the National Cancer Data Base. Data Brief 2021, 34, 106705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilimoria, K.Y.; Stewart, A.K.; Winchester, D.P.; Ko, C.Y. The National Cancer Data Base: A powerful initiative to improve cancer care in the United States. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2008, 15, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boffa, D.J.; Rosen, J.E.; Mallin, K.; Loomis, A.; Gay, G.; Palis, B.; Thoburn, K.; Gress, D.; McKellar, D.P.; Shulman, L.N.; et al. Using the National Cancer Database for Outcomes Research: A Review. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 1722–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, R.M. National Cancer Database: The Past, Present, and Future of the Cancer Registry and Its Efforts to Improve the Quality of Cancer Care. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 29, 323–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CTR Exam. Available online: https://www.ncra-usa.org/CTR/Certification-Exam (accessed on 9 November 2020).
- Winchester, D.P.; Stewart, A.K.; Phillips, J.L.; Ward, E.E. The national cancer data base: Past, present, and future. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 17, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, A.P.; Nguyen, D.D.; Meirkhanov, A.; Golshan, M.; Melnitchouk, N.; Lipsitz, S.R.; Kilbridge, K.L.; Kibel, A.S.; Cooper, Z.; Weissman, J.; et al. Association of Care at Minority-Serving vs Non-Minority-Serving Hospitals With Use of Palliative Care Among Racial/Ethnic Minorities With Metastatic Cancer in the United States. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e187633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, W.; Verma, V.; Butler, E.B.; Teh, B.S. Patterns of End-of-Life Oncologic Care for Stage IV Non-small Cell Lung Cancer in the United States. Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 3137–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colibaseanu, D.T.; Osagiede, O.; Spaulding, A.C.; Frank, R.D.; Merchea, A.; Mathis, K.L.; Parker, A.S.; Ailawadhi, S. The Determinants of Palliative Care Use in Patients With Colorectal Cancer: A National Study. Am. J. Hosp. Palliat. Care 2018, 35, 1295–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Cancer Data Base Participant User File (PUF) Data Dictionary. Available online: https://www.facs.org/-/media/files/quality-programs/cancer/ncdb/puf_data_dictionary.ashx (accessed on 9 November 2020).
- Medicaid.gov-Keeping America Healthy. Available online: https://www.medicaid.gov/medicaid/index.html (accessed on 25 May 2021).
- What’s Medicare? Available online: https://www.medicare.gov/what-medicare-covers/your-medicare-coverage-choices/whats-medicare (accessed on 25 May 2021).
- Medicaid Expansion. Available online: https://www.healthinsurance.org/glossary/medicaid-expansion/ (accessed on 25 May 2021).
- Takvorian, S.U.; Oganisian, A.; Mamtani, R.; Mitra, N.; Shulman, L.N.; Bekelman, J.E.; Werner, R.M. Association of Medicaid Expansion Under the Affordable Care Act With Insurance Status, Cancer Stage, and Timely Treatment Among Patients With Breast, Colon, and Lung Cancer. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e1921653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Community Survey (ACS). Available online: https://www.census.gov/programs-surveys/acs (accessed on 23 May 2021).
- About Race. Available online: https://www.census.gov/topics/population/race/about.html (accessed on 25 May 2021).
- About Hispanic Origin. Available online: https://www.census.gov/topics/population/hispanic-origin/about.html (accessed on 25 May 2021).
- Ambroggi, M.; Biasini, C.; Del Giovane, C.; Fornari, F.; Cavanna, L. Distance as a Barrier to Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment: Review of the Literature. Oncologist 2015, 20, 1378–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spees, L.P.; Brewster, W.R.; Varia, M.A.; Weinberger, M.; Baggett, C.; Zhou, X.; Petermann, V.M.; Wheeler, S.B. Examining Urban and Rural Differences in How Distance to Care Influences the Initiation and Completion of Treatment among Insured Cervical Cancer Patients. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2019, 28, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.C.; Bruinooge, S.S.; Kirkwood, M.K.; Olsen, C.; Jemal, A.; Bajorin, D.; Giordano, S.H.; Goldstein, M.; Guadagnolo, B.A.; Kosty, M.; et al. Association Between Geographic Access to Cancer Care, Insurance, and Receipt of Chemotherapy: Geographic Distribution of Oncologists and Travel Distance. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3177–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci, S.; Tergas, A.I.; Roche, K.L.; Fairbairn, M.G.; Levinson, K.L.; Dowdy, S.C.; Bristow, R.E.; Lopez, M.; Slaughter, K.; Moore, K.; et al. Geographic disparities in the distribution of the U.S. gynecologic oncology workforce: A Society of Gynecologic Oncology study. Gynecol. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 22, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff, C. Bringing Palliative Care To Underserved Rural Communities. Health Aff. 2019, 38, 1971–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osagiede, O.; Colibaseanu, D.T.; Spaulding, A.C.; Frank, R.D.; Merchea, A.; Kelley, S.R.; Uitti, R.J.; Ailawadhi, S. Palliative Care Use Among Patients With Solid Cancer Tumors: A National Cancer Data Base Study. J. Palliat. Care 2018, 33, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, R.S.; Dietrich, J.; Ladwig, S.; Quill, T.; Sacco, J.; Tangeman, J.; Meier, D.E. Palliative care consultation teams cut hospital costs for Medicaid beneficiaries. Health Aff. 2011, 30, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, R.S. Models of palliative care delivery in the United States. Curr. Opin. Support. Palliat. Care 2013, 7, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, R.S.; Penrod, J.D.; Cassel, J.B.; Caust-Ellenbogen, M.; Litke, A.; Spragens, L.; Meier, D.E. Cost savings associated with US hospital palliative care consultation programs. Arch. Intern. Med. 2008, 168, 1783–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, B.; Dietrich, J.; Du, Q.; Morrison, R.S. Variability in access to hospital palliative care in the United States. J. Palliat. Med. 2008, 11, 1094–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Washington, K.T.; Bickel-Swenson, D.; Stephens, N. Barriers to hospice use among African Americans: A systematic review. Health Soc. Work 2008, 33, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soobader, M.; LeClere, F.B.; Hadden, W.; Maury, B. Using aggregate geographic data to proxy individual socioeconomic status: Does size matter? Am. J. Public Health 2001, 91, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Total (n = 176,899) | No Palliative Care (n = 167,071) | Palliative Care Used (n = 9282) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Col % | No. | Row % | No. | Row % | |
| Age (Mean, SD) | 62.1, 14.3 | 61.8, 14.3 | 65.5, 14.7 | |||
| Cancer Type | ||||||
| Ovarian cancer | 127,237 | 71.9 | 121,767 | 95.7 | 5470 | 4.3 |
| Cervical cancer | 42,944 | 24.3 | 39,298 | 91.5 | 3646 | 8.5 |
| Uterine cancer | 6718 | 3.8 | 6006 | 89.4 | 712 | 10.6 |
| Race/Ethnicity | ||||||
| Non-Hispanic White | 128,096 | 72.4 | 120,970 | 94.4 | 7126 | 5.6 |
| Non-Hispanic Black | 19,259 | 10.9 | 17,905 | 93.0 | 1354 | 7.0 |
| Hispanic | 12,790 | 7.2 | 12,231 | 95.6 | 559 | 4.4 |
| Asian | 5066 | 2.9 | 4839 | 95.5 | 227 | 4.5 |
| American Indian/Alaskan Native | 683 | 0.4 | 650 | 95.2 | 33 | 4.8 |
| Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander | 367 | 0.2 | 332 | 90.5 | 35 | 9.5 |
| Other Race | 9561 | 5.4 | 9107 | 95.3 | 454 | 4.7 |
| Missing | 1077 | 0.6 | 1037 | 96.3 | 40 | 3.7 |
| Palliative care provided (Col %) | ||||||
| No palliative care | 167,071 | 94.4 | 167,071 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| Surgery/radiation/chemo only | 6101 | 3.4 | 0 | 0 | 6101 | 62.1 |
| Pain management only | 1198 | 0.7 | 0 | 0 | 1198 | 12.2 |
| Combination of surg/rad/chemo and pain management | 1027 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 | 1027 | 10.4 |
| Type unknown | 1502 | 0.8 | 0 | 0 | 1502 | 15.3 |
| Charlson-Deyo Score (Comorbidities) | ||||||
| 0 | 140,231 | 79.3 | 133,103 | 94.9 | 7128 | 5.1 |
| 1 | 27,557 | 15.6 | 25,715 | 93.3 | 1842 | 6.7 |
| 2 | 6393 | 3.6 | 5823 | 91.1 | 570 | 8.9 |
| ≥3 | 2718 | 1.5 | 2430 | 89.4 | 288 | 10.6 |
| Primary Payer | ||||||
| Not Insured | 9689 | 5.5 | 9055 | 93.5 | 634 | 6.5 |
| Private Insurance/Managed Care | 70,522 | 39.9 | 67,846 | 96.2 | 2676 | 3.8 |
| Medicaid | 18,784 | 10.6 | 17,463 | 93.0 | 1321 | 7.0 |
| Medicare | 73,151 | 41.4 | 68,174 | 93.2 | 4977 | 6.8 |
| Other Government | 1679 | 0.9 | 1595 | 95.0 | 84 | 5.0 |
| Insurance Status Unknown | 3074 | 1.7 | 2938 | 95.6 | 136 | 4.4 |
| Census Region | ||||||
| Northeast | 34,237 | 19.4 | 31,674 | 92.5 | 2563 | 7.5 |
| South | 62,447 | 35.3 | 59,039 | 94.5 | 3408 | 5.5 |
| Midwest | 40,047 | 22.6 | 37,689 | 94.1 | 2358 | 5.9 |
| West | 28,517 | 16.1 | 27,451 | 96.3 | 1066 | 3.7 |
| Missing | 11,651 | 6.6 | 11,218 | 96.3 | 433 | 3.7 |
| Area of Residence | ||||||
| Urban | 169,092 | 95.6 | 159,674 | 94.4 | 9418 | 5.6 |
| Rural | 3040 | 1.7 | 2854 | 93.9 | 186 | 6.1 |
| Missing | 4767 | 2.7 | 4543 | 95.3 | 224 | 4.7 |
| Percent of Adults in Patient Zip Code with No High School Degree Quartiles 2012–2016 | ||||||
| ≥17.6% | 39,998 | 22.6 | 37,767 | 94.4 | 2231 | 5.6 |
| 10.9–17.5% | 46,017 | 26.0 | 43,265 | 94.0 | 2752 | 6.0 |
| 6.3–10.8% | 47,877 | 27.1 | 45,229 | 94.5 | 2648 | 5.5 |
| <6.3% | 40,455 | 22.9 | 38,383 | 94.9 | 2072 | 5.1 |
| Missing | 2552 | 1.4 | 2427 | 95.1 | 125 | 4.9 |
| Median Household Income Quartiles of Patients in Zip Code 2012–2016 | ||||||
| <$40,227 | 35,225 | 19.9 | 32,983 | 93.6 | 2242 | 6.4 |
| $40,227–50,353 | 39,605 | 22.4 | 37,229 | 94.0 | 2376 | 6.0 |
| $50,354–63,332 | 40,619 | 23.0 | 38,378 | 94.5 | 2241 | 5.5 |
| ≥$63,333 | 58,587 | 33.1 | 55,767 | 95.2 | 2820 | 4.8 |
| Missing | 2863 | 1.6 | 2714 | 94.8 | 149 | 5.2 |
| Patient State at Diagnosis Grouped by Medicaid Expansion Status 2010–2016 * | ||||||
| Non-Expansion States | 31562 | 35.6 | 29,497 | 93.5 | 2065 | 6.5 |
| January 2014 Expansion States | 24,922 | 28.1 | 22,909 | 91.9 | 2013 | 8.1 |
| Early Expansion States (2010–2013) | 15,408 | 17.4 | 14,713 | 95.5 | 695 | 4.5 |
| Late Expansion States (after Jan. 2014) | 10,767 | 12.2 | 9,849 | 91.5 | 918 | 8.5 |
| Suppressed for Ages 0–39 | 5,978 | 6.7 | 5,714 | 95.6 | 264 | 4.4 |
| Greatest Circle Distance from Provider to Patient | ||||||
| <2 miles | 15,273 | 8.6 | 14,187 | 92.9 | 1086 | 7.1 |
| 2–4 miles | 30,521 | 17.3 | 28,551 | 93.5 | 1970 | 6.5 |
| 5–9 miles | 36,155 | 20.4 | 34,003 | 94.0 | 2152 | 6.0 |
| 10–19 miles | 34,836 | 19.7 | 32,926 | 94.5 | 1910 | 5.5 |
| 20–45 miles | 31,500 | 17.8 | 29,963 | 95.1 | 1537 | 4.9 |
| >45 miles | 28,614 | 16.2 | 27,441 | 95.9 | 1173 | 4.1 |
| Facility Type | ||||||
| Community Cancer Program | 10,475 | 5.9 | 9660 | 92.2 | 815 | 7.8 |
| Comprehensive Community Cancer Program | 63,663 | 36.0 | 59,851 | 94.0 | 3812 | 6.0 |
| Academic/Research Program | 68,317 | 38.6 | 64,939 | 95.1 | 3378 | 4.9 |
| Integrated Network Cancer Program | 22,793 | 12.9 | 21,403 | 93.9 | 1390 | 6.1 |
| Missing | 11,651 | 6.6 | 11,218 | 96.3 | 433 | 3.7 |
| NH-White | NH-Black | Hispanic | Asian | p † | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Col % | n | Col % | n | Col % | n | Col % | ||
| Primary Payer | <0.001 | ||||||||
| Not Insured | 5008 | 3.9 | 1618 | 8.4 | 2122 | 16.6 | 385 | 7.6 | |
| Private Insurance/Managed Care | 53,177 | 41.5 | 6247 | 32.4 | 3983 | 31.1 | 2372 | 46.8 | |
| Medicaid | 9997 | 7.8 | 3697 | 19.2 | 3117 | 24.4 | 833 | 16.4 | |
| Medicare | 56,933 | 44.4 | 7056 | 36.6 | 3145 | 24.6 | 1278 | 25.2 | |
| Other Government | 1141 | 0.9 | 173 | 0.9 | 91 | 0.7 | 92 | 1.8 | |
| Insurance Status Unknown | 1840 | 1.4 | 468 | 2.4 | 332 | 2.6 | 106 | 2.1 | |
| Census Region | <0.001 | ||||||||
| Northeast | 25,725 | 20.1 | 3294 | 17.1 | 1864 | 14.6 | 1033 | 20.4 | |
| South | 44,083 | 34.4 | 10,136 | 52.6 | 4221 | 33.0 | 918 | 18.1 | |
| Midwest | 31,218 | 24.4 | 3177 | 16.5 | 861 | 6.7 | 518 | 10.2 | |
| West | 20,116 | 15.7 | 1002 | 5.2 | 3945 | 30.8 | 2183 | 43.1 | |
| Missing | 6954 | 5.4 | 1650 | 8.6 | 1899 | 14.8 | 414 | 8.2 | |
| Area of Residence | <0.001 | ||||||||
| Urban | 121,835 | 95.1 | 18,695 | 97.1 | 12,499 | 97.7 | 4929 | 97.3 | |
| Rural | 2472 | 1.9 | 215 | 1.1 | 35 | 0.3 | 5 | 0.1 | |
| Missing | 3789 | 3.0 | 349 | 1.8 | 256 | 2.0 | 132 | 2.6 | |
| Percent of Adults in Patient Zip Code with No High School Degree Quartiles 2012–2016 | <0.001 | ||||||||
| ≥17.6% | 20,705 | 16.2 | 8213 | 42.6 | 7431 | 58.1 | 1402 | 27.7 | |
| 10.9–17.5% | 33,189 | 25.9 | 6193 | 32.2 | 2440 | 19.1 | 997 | 19.7 | |
| 6.3–10.8% | 38,288 | 29.9 | 3144 | 16.3 | 1688 | 13.2 | 1316 | 26.0 | |
| <6.3% | 34,060 | 26.6 | 1380 | 7.2 | 1060 | 8.3 | 1307 | 25.8 | |
| Missing | 1854 | 1.4 | 329 | 1.7 | 171 | 1.3 | 44 | 0.9 | |
| Median Household Income Quartiles of Patients in Zip Code 2012–2016 | <0.001 | ||||||||
| <$40,227 | 19,422 | 15.2 | 9026 | 46.9 | 3805 | 29.7 | 468 | 9.2 | |
| $40,227–50,353 | 29,010 | 22.6 | 3910 | 20.3 | 3075 | 24.0 | 737 | 14.5 | |
| $50,354–63,332 | 31,197 | 24.4 | 2777 | 14.4 | 2858 | 22.3 | 1114 | 22.0 | |
| ≥$63,333 | 46,363 | 36.2 | 3196 | 16.6 | 2871 | 22.4 | 2701 | 53.3 | |
| Missing | 2104 | 1.6 | 350 | 1.8 | 181 | 1.4 | 46 | 0.9 | |
| Patient State at Diagnosis Grouped by Medicaid Expansion Status 2010–2016 ‡ | <0.001 | ||||||||
| Non-Expansion States | 22,837 | 35.4 | 4677 | 44.6 | 2401 | 33.9 | 520 | 17.6 | |
| January 2014 Expansion States | 19,057 | 29.5 | 2590 | 24.7 | 1359 | 19.2 | 857 | 28.9 | |
| Early Expansion States (2010–2013) | 10,457 | 16.2 | 1164 | 11.1 | 2076 | 29.4 | 1202 | 40.6 | |
| Late Expansion States (after Jan. 2014) | 8666 | 13.4 | 1181 | 11.3 | 187 | 2.7 | 148 | 4.9 | |
| Suppressed for Ages 0–39 | 3560 | 5.5 | 879 | 8.4 | 1042 | 14.8 | 236 | 7.8 | |
| Greatest Circle Distance from Provider to Patient | <0.001 | ||||||||
| <2 miles | 10,229 | 8.0 | 2362 | 12.3 | 1258 | 9.8 | 517 | 10.2 | |
| 2–4 miles | 19,986 | 15.6 | 4683 | 24.3 | 2786 | 21.8 | 1197 | 23.6 | |
| 5–9 miles | 24,300 | 19.0 | 4843 | 25.1 | 3377 | 26.4 | 1419 | 28.0 | |
| 10–19 miles | 25,653 | 20.0 | 3041 | 15.8 | 2654 | 20.8 | 1099 | 21.7 | |
| 20–45 miles | 25,017 | 19.5 | 2330 | 12.1 | 1480 | 11.6 | 516 | 10.2 | |
| >45 miles | 22,911 | 17.9 | 2000 | 10.4 | 1235 | 9.7 | 318 | 6.3 | |
| Facility Type | <0.001 | ||||||||
| Community Cancer Program | 7843 | 6.1 | 979 | 5.1 | 669 | 5.2 | 378 | 7.5 | |
| Comprehensive Community Cancer Program | 49,259 | 38.5 | 5259 | 27.3 | 3396 | 26.6 | 1508 | 29.8 | |
| Academic/Research Program | 47,095 | 36.8 | 8936 | 46.4 | 5510 | 43.1 | 2301 | 45.4 | |
| Integrated Network Cancer Program | 16,945 | 13.2 | 2435 | 12.6 | 1316 | 10.3 | 465 | 9.2 | |
| Missing | 6954 | 5.4 | 1650 | 8.6 | 1899 | 14.8 | 414 | 8.2 | |
| Ovarian Cancer (n= 127,237) | Cervical Cancer (n = 42,944) | Uterine Cancer (n = 6718) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % Utilized Palliative Care | aOR | 95% CI | % Utilized Palliative Care | aOR | 95% CI | % Utilized Palliative Care | aOR | 95% CI | |
| Primary Payer * | |||||||||
| Not Insured | 4.2 | 1.80 | 1.53–2.12 | 8.6 | 1.45 | 1.26–1.67 | 11.6 | 1.19 | 0.81–1.73 |
| Private Insurance/Managed Care | 2.7 | Ref. | 6.5 | Ref. | 9.6 | Ref. | |||
| Medicaid | 4.9 | 1.89 | 1.64–2.19 | 8.4 | 1.41 | 1.26–1.57 | 11.3 | 1.25 | 0.93–1.69 |
| Medicare | 5.7 | 1.19 | 1.09–1.31 | 12.1 | 1.14 | 1.02–1.27 | 11.1 | 1.15 | 0.92–1.43 |
| Other Government | 4.3 | 1.57 | 1.14–2.19 | 6.4 | 0.98 | 0.67–1.46 | 8.9 | 1.08 | 0.43–2.75 |
| Percent of Adults in Patient Zip Code with No High School Degree Quartiles 2012–2016 † | |||||||||
| ≥17.6% | 3.9 | Ref. | 7.9 | Ref. | 10.8 | Ref. | |||
| 10.9–17.5% | 4.6 | 1.18 | 1.06–1.32 | 9.0 | 1.09 | 0.97–1.22 | 11.2 | 1.02 | 0.79–1.31 |
| 6.3–10.8% | 4.4 | 1.26 | 1.09–1.46 | 8.8 | 1.15 | 1.00–1.32 | 10.6 | 1.06 | 0.79–1.43 |
| <6.3% | 4.2 | 1.36 | 1.14–1.61 | 8.6 | 1.22 | 1.02–1.46 | 10.1 | 1.05 | 0.73–1.51 |
| Median Household Income Quartiles of Patients in Zip Code 2012–2016 ‡ | |||||||||
| <$40,227 | 4.6 | Ref. | 8.9 | Ref. | 11.7 | Ref. | |||
| $40,227–50,353 | 4.6 | 0.91 | 0.81–1.02 | 8.9 | 0.96 | 0.85–1.08 | 11.4 | 0.97 | 0.74–1.26 |
| $50,354–63,332 | 4.4 | 0.84 | 0.73–0.96 | 8.3 | 0.85 | 0.74–0.98 | 10.1 | 0.81 | 0.60–1.09 |
| ≥$63,333 | 3.9 | 0.65 | 0.54–0.78 | 7.8 | 0.73 | 0.61–0.87 | 9.9 | 0.76 | 0.53–1.09 |
| Patient State at Diagnosis Grouped by Medicaid Expansion Status 2010–2016 ▲ | |||||||||
| Non-Expansion States | 4.0 | Ref | 9.5 | Ref | 10.3 | Ref | |||
| January 2014 Expansion States | 5.0 | 1.26 | 1.04–1.54 | 10.8 | 1.23 | 1.04–1.45 | 12.0 | 1.21 | 0.92–1.61 |
| Early Expansion States (2010–2013) | 2.8 | 0.71 | 0.54–0.94 | 5.3 | 0.64 | 0.49–0.84 | 6.6 | 0.66 | 0.47–0.93 |
| Late Expansion States (after January. 2014) | 6.0 | 1.43 | 1.13–1.81 | 11.3 | 1.12 | 0.92–1.38 | 14.3 | 1.57 | 1.14–2.15 |
| Greatest Circle Distance from Provider to Patient§ | |||||||||
| <2 miles | 5.6 | Ref | 10.5 | Ref | 12.4 | Ref | |||
| 2–4 miles | 5.3 | 0.97 | 0.84–1.12 | 9.0 | 0.82 | 0.71–0.95 | 9.8 | 0.81 | 0.59–1.12 |
| 5–9 miles | 4.8 | 0.89 | 0.79–1.02 | 8.4 | 0.81 | 0.70–0.95 | 11.4 | 0.91 | 0.68–1.23 |
| 10–19 miles | 4.3 | 0.85 | 0.73–0.98 | 8.3 | 0.79 | 0.68–0.92 | 10.6 | 0.88 | 0.65–1.21 |
| 20–45 miles | 3.5 | 0.70 | 0.60–0.81 | 8.0 | 0.76 | 0.65–0.89 | 10.5 | 0.89 | 0.63–1.27 |
| >45 miles | 2.9 | 0.58 | 0.48–0.70 | 7.6 | 0.74 | 0.60–0.88 | 9.3 | 0.71 | 0.48–1.04 |
| Facility Type ¶ | |||||||||
| Community Cancer Program | 6.6 | 1.18 | 0.95–1.45 | 10.3 | 1.01 | 0.81–1.27 | 13.1 | 1.10 | 0.81–1.49 |
| Comprehensive Community Cancer Program | 4.9 | Ref | 9.3 | Ref | 11.4 | Ref | |||
| Academic/Research Program | 3.5 | 0.70 | 0.58–0.84 | 8.7 | 0.89 | 0.76–1.04 | 9.6 | 0.81 | 0.62–1.04 |
| Integrated Network Cancer Program | 4.5 | 0.90 | 0.73–1.10 | 11.2 | 1.18 | 1.00–1.39 | 10.3 | 0.85 | 0.63–1.15 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Islam, J.Y.; Saraiya, V.; Previs, R.A.; Akinyemiju, T. Health Care Access Measures and Palliative Care Use by Race/Ethnicity among Metastatic Gynecological Cancer Patients in the United States. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6040. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18116040
Islam JY, Saraiya V, Previs RA, Akinyemiju T. Health Care Access Measures and Palliative Care Use by Race/Ethnicity among Metastatic Gynecological Cancer Patients in the United States. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(11):6040. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18116040
Chicago/Turabian StyleIslam, Jessica Y., Veeral Saraiya, Rebecca A. Previs, and Tomi Akinyemiju. 2021. "Health Care Access Measures and Palliative Care Use by Race/Ethnicity among Metastatic Gynecological Cancer Patients in the United States" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 11: 6040. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18116040
APA StyleIslam, J. Y., Saraiya, V., Previs, R. A., & Akinyemiju, T. (2021). Health Care Access Measures and Palliative Care Use by Race/Ethnicity among Metastatic Gynecological Cancer Patients in the United States. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(11), 6040. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18116040







