Relationship of Overweight and Obesity with Body Self-Image Dissatisfaction in Urban Mediterranean Adolescents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Anthropometric Measures and Weight Status
2.3. Body Self-Image Evaluation
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Weight Status
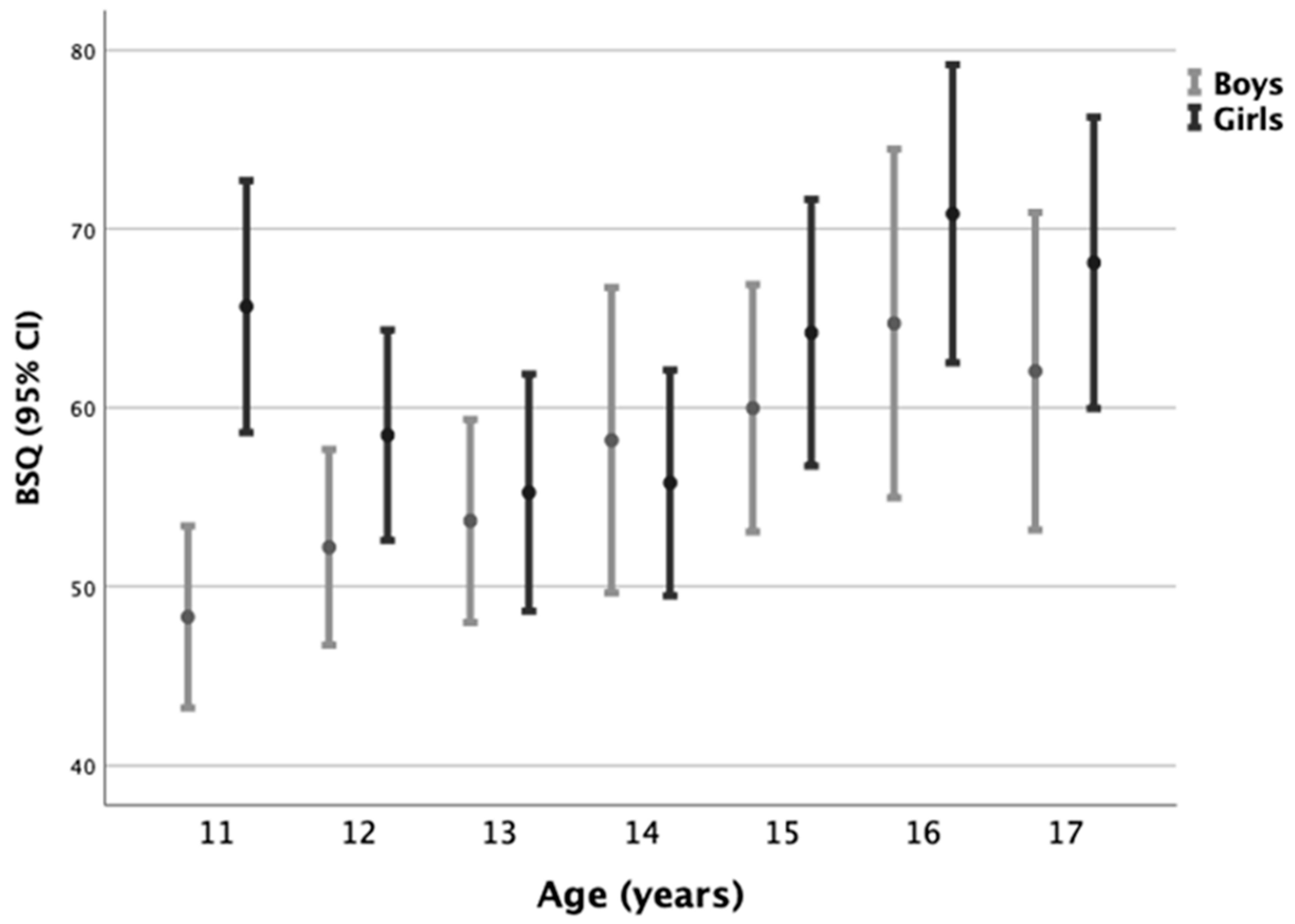
3.2. Body Shape Questionnaire (BSQ) Scores
3.3. Correlations between BSQ and Anthropometry
3.4. BSQ and Weight Status
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
5.1. What Do We Already Know about This Topic?
5.2. How Does Your Research Contribute to the Field?
5.3. What Are the Implications of Your Research in Terms of Theory, Practice, or Policy?
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lobstein, T.; Jackson-Leach, R.; Moodie, M.L.; Hall, K.D.; Gortmaker, S.L.; Swinburn, B.A.; James, P.T.; Wang, Y.; McPherson, K. Child and adolescent obesity: Part of a bigger picture. Lancet 2015, 385, 2510–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Cesare, M.; Sorić, M.; Bovet, P.; Miranda, J.J.; Bhutta, Z.; Stevens, G.A.; Laxmaiah, A.; Kengne, A.-P.; Bentham, J. The epidemiological burden of obesity in childhood: A worldwide epidemic requiring urgent action. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. Obesity and Overweight. 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016, a pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128·9 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet 2017, 390, 2627–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López-Sánchez, G.F.; Sgroi, M.; D’Ottavio, S.; Díaz-Suárez, A.; González-Víllora, S.; Veronese, N.; Smith, L. Body composition in children and adolescents residing in Southern Europe: Prevalence of overweight and obesity according to different international references. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Cruz, J.; Jiménez-Moleón, J.; Fernández-Quesada, F.; Sánchez, M. Prevalence of child and youth obesity in Spain in 2012. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2013, 66, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.H.; Falconer, C.; Viner, R.M.; Kinra, S. The impact of childhood obesity on morbidity and mortality in adulthood: A systematic review. Obes. Rev. 2012, 13, 985–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedemann, C.; Heneghan, C.; Mahtani, K.; Thompson, M.; Perera, R.; Ward, A.M. Cardiovascular disease risk in healthy children and its association with body mass index: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2012, 345, e4759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pulgaron, E.R.; Delamater, A.M. Obesity and type 2 diabetes in children: Epidemiology and treatment. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2014, 14, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rankin, J.; Matthews, L.; Cobley, S.; Han, A.; Sanders, R.; Wiltshire, H.D.; Baker, J.S. Psychological consequences of childhood obesity: Psychiatric comorbidity and prevention. Adolesc. Health Med. Ther. 2016, 7, 125–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quek, Y.H.; Tam, W.W.S.; Zhang, M.W.B.; Ho, R.C.M. Exploring the association between childhood and adolescent obesity and depression: A meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2017, 18, 742–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeifer, J.; Allen, N. Puberty initiates cascading relationships between neurodevelopmental, social, and internalizing processes across adolescence. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 89, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siervogel, R.M.; Demerath, E.W.; Schubert, C.; Remsberg, K.E.; Chumlea, W.C.; Sun, S.; Czerwinski, S.A.; ·Towne, B. Puberty and body composition. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2003, 60 (Suppl. S1), 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, M.P.; Ricciardelli, L.A. A longitudinal study of pubertal timing and extreme body change behaviors among adolescent boys and girls. Adolescence 2004, 39, 145–166. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, M.B.; Brownell, K.D. Obesity and body image. Body Image 2004, 1, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwimmer, J.B.; Burwinkle, T.M.; Varni, J.W. Health-related quality of life of severely obese children and adolescents. JAMA 2003, 289, 1813–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wardle, J.; Cooke, L. The impact of obesity on psychological well-being. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 19, 421–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’avila, H.F.; Poll, F.A.; Reuter, C.P.; Burgos, M.S.; Mello, E.D. Health-related quality of life in adolescents with excess weight. J. Pediatr. 2019, 95, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolak, L.; Thompson, J.K. (Eds.) Body Image, Eating Disorders, and Obesity in Youth: Assessment, Prevention, and Treatment; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Harriger, J.A.; Thompson, J.K. Psychological consequences of obesity: Weight bias and body image in overweight and obese youth. Int. Rev. Psychiatry 2012, 24, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberger, N.A.; Kersting, A.; Riedel-Heller, S.G.; Luck-Sikorski, C. Body dissatisfaction in individuals with obesity compared to normal-weight individuals: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Facts 2016, 9, 424–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricciardelli, L.A.; McCabe, M.P. Children’s body image concerns and eating disturbance: A review of the literature. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2001, 21, 325–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolak, L. Body image in children and adolescents: Where do we go from here? Body Image 2004, 1, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.K. The (mis) measurement of body image: Ten strategies to improve assessment for applied and research purposes. Body Image 2004, 1, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinquart, M. Do the parent-child relationship and parenting behaviors differ between families with a child with and without chronic illness? A meta-analysis. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2013, 38, 708–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cooper, P.J.; Taylor, M.J.; Cooper, Z.; Fairbum, C.G. The development and validation of the body shape questionnaire. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 1987, 6, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raich, R.M.; Mora, M.; Soler, A.; Ávila, C.; Clos, I.; Zapater, L. Adaptación de un instrumento de evaluación de la insatisfacción corporal. Clínica Salud 1996, 7, 51–66. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, C.C.; Chumlea, W.C.; Roche, A.F. Stature, recumbent length, and weight. In Anthropometric Standardization Reference Manual; Lohman, T.G., Roche, A.F., Martorel, R., Eds.; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 1988; pp. 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, T.J.; Bellizzi, M.C.; Flegal, K.M.; Dietz, W.H. Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: International survey. BMJ 2000, 320, 1240–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cole, T.J.; Flegal, K.M.; Nicholls, D.; Jackson, A.A. Body mass index cut offs to define thinness in children and adolescents: International survey. BMJ 2007, 335, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delisle, H. Nutrition in Adolescence: Issues and Challenges for the Health Sector: Issues in Adolescent Health and Development; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005; ISBN 92-4-159366-0. [Google Scholar]
- Cordás, T.A.; Castilho, S. Body image on the eating disorders—Evaluation instruments: “Body Shape Questionnaire”. Psiquiatr. Biol. 1994, 2, 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1988; ISBN 0-8058-0283-5. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno, L.A.; Mesana, M.I.; Fleta, J.; Ruiz, J.R.; González-Gross, M.; Sarría, A.; Marcos, A.; Bueno, M. Overweight, obesity and body fat composition in Spanish adolescents. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2005, 49, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranceta-Bartrina, J.; Gianzo-Citores, M.; Pérez-Rodrigo, C. Prevalence of overweight, obesity and abdominal obesity in the Spanish population aged 3 to 24 years. The ENPE study. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2020, 73, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baile, J.I.; Guevara, R.M.; González-Calderón, M.J.; Urchaga, J.D. The relationship between weight profile, health-related quality of life, and life satisfaction in a sample of Spanish adolescents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, M.A.; Cordás, T.A.; Latorre, M.R. A study of the validity and reliability of the Brazilian version of the body shape questionnaire (BSQ) among adolescents. Rev. Bras. Saúde Mater. Infant. 2009, 9, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miranda, V.P.; Conti, M.A.; de Carvalho, P.H.; Bastos, R.R.; Ferreira, M.E. Body image in different periods of adolescence. Rev. Paul. Pediatr. 2014, 32, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Helfert, S.; Warschburger, P. A prospective study on the impact of peer and parental pressure on body dissatisfaction in adolescent girls and boys. Body Image 2011, 8, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondoli, D.M.; Corning, A.F.; Salafia, E.H.; Bucchianeri, M.M.; Fitzsimmons, E.E. Heterosocial involvement, peer pressure for thinness, and body dissatisfaction among young adolescent girls. Body Image 2011, 8, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laus, M.F.; Miranda, V.P.; Almeida, S.S.; Braga Costa, T.M.; Ferreira, M.E. Geographic location, sex and weight status play an important role in body image concerns among Brazilian adolescents. J. Health Psychol. 2013, 18, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloney, M.J.; McGuire, J.; Daniels, S.R.; Specker, B. Dieting behavior and eating attitudes in children. Pediatrics 1989, 84, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Araújo, C.L.; Dumith, S.C.; Menezes, A.M.; Hallal, P.C. Peso medido, peso percebido e fatores associados em adolescentes [Measured weight, self-perceived weight, and associated factors in adolescents]. Rev. Panam. Salud Publica. 2010, 27, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holmqvist, K.; Frisén, A. Body dissatisfaction across cultures: Findings and research problems. Eur. Eat Disord. Rev. 2010, 18, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matias, T.S.; Rolim, M.K.; Kretzer, F.L.; Schmoelz, C.P.; Andrade, A. Corporal satisfaction associated with physical activity practice during adolescence. Motriz. Rev. Educ. Fis. 2010, 16, 370–378. [Google Scholar]
- Presnell, K.; Bearman, S.K.; Stice, E. Risk factors for body dissatisfaction in adolescent boys and girls: A prospective study. Int. J. Eat Disord. 2004, 36, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.C.; Vigfusdottir, T.H.; Lee, Y. Body image and the appearance culture among adolescent girls and boys: An examination of friend conversations, peer criticism, appearance magazines, and the internalization of appearance ideals. J. Adolesc. Res. 2004, 19, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, I.R.; Levy, R.B.; Cardoso Lde, O.; dos Passos, M.D.; Vasconcelos Sardinha, L.M.; Tavares, L.F.; Dutra, S.P.; Martins, A. Body image, weight status and practices for weight control among Brazilian adolescents. Cien. Saude Colet. 2010, 15 (Suppl. S2), 3099–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos Silva, D.A.; Nahas, M.V.; de Sousa, T.F.; Del Duca, G.F.; Peres, K.G. Prevalence and associated factors with body image dissatisfaction among adults in southern Brazil: A population-based study. Body Image 2011, 8, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bruin, A.P.K.; Woertman, L.; Bakker, F.C.; Oudejans, R.R.D. Weight-related sport motives and girls’ body image, weight control behaviors, and self-esteem. Sex Roles 2009, 60, 628–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Boys | Girls | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EAP n = 211 Mean ± SD | MAP n = 99 Mean ± SD | LAP n = 103 Mean ± SD | p * | EAP n = 193 Mean ± SD | MAP n = 119 Mean ± SD | LAP n = 84 Mean ± SD | p * | |
| BSQ Scores | 51.5 ± 23.0 | 59.3 ± 26.4 | 63.3 ± 33.0 | 0.001 | 59.3 ± 26.2 | 60.1 ± 26.6 | 69.7 ± 26.4 | 0.001 |
| BSQ Classification, n (%) | ||||||||
| Satisfied | 179 (85.6) | 80 (81.6) | 80 (77.7) | 158 (81.9) § | 88 (75.9) | 58 (69.0) | ||
| Mild Dissatisfaction | 25 (12.0) | 13 (13.3) | 16 (15.5) | 24 (12.4) | 24 (20.7) | 21 (25.0) §§ | ||
| Moderate Dissatisfaction | 4 (1.9) | 4 (4.1) | 2 (1.9) | 7 (3.6) | 3 (2.6) | 4 (4.8) | ||
| Severe Dissatisfaction | 1 (0.5) ** | 1 (1.0) | 5 (4.9) | 4 (2.1) | 1 (0.9) | 1 (1.2) | ||
| Boys (n = 410) | Girls (n = 393) | Total Sample (n = 813) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pearson’s Correlation | Sig. (Bilateral) | Pearson’s Correlation | Sig. (Bilateral) | Pearson’s Correlation | Sig. (Bilateral) | |
| Age | 0.192 | <0.001 | 0.102 | 0.043 | 0.148 | <0.001 |
| BMI | 0.213 | <0.001 | 0.065 | 0.199 | 0.139 | <0.001 |
| Body mass | 0.260 | <0.001 | 0.077 | 0.129 | 0.170 | <0.001 |
| Calf skinfold | 0.115 | 0.020 | 0.034 | 0.501 | 0.093 | 0.009 |
| Thigh skinfold | 0.119 | 0.016 | 0.032 | 0.530 | 0.099 | 0.005 |
| Abdominal skinfold | 0.147 | 0.003 | 0.019 | 0.710 | 0.098 | 0.005 |
| Suprailiac skinfold | 0.163 | 0.001 | −0.007 | 0.894 | 0.095 | 0.007 |
| Triceps skinfold | 0.130 | 0.008 | −0.015 | 0.773 | 0.079 | 0.025 |
| Biceps skinfold | 0.125 | 0.011 | −0.011 | 0.824 | 0.065 | 0.066 |
| Σ 6 skinfolds | 0.154 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.954 | 0.100 | 0.005 |
| Fat mass | 0.246 | <0.001 | 0.024 | 0.634 | 0.151 | <0.001 |
| Fat percentage | 0.161 | 0.001 | −0.016 | 0.752 | 0.093 | 0.009 |
| FMI | 0.198 | <0.001 | 0.013 | 0.805 | 0.119 | 0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Escrivá, D.; Moreno-Latorre, E.; Caplliure-Llopis, J.; Benet, I.; Barrios, C. Relationship of Overweight and Obesity with Body Self-Image Dissatisfaction in Urban Mediterranean Adolescents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7770. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18157770
Escrivá D, Moreno-Latorre E, Caplliure-Llopis J, Benet I, Barrios C. Relationship of Overweight and Obesity with Body Self-Image Dissatisfaction in Urban Mediterranean Adolescents. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(15):7770. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18157770
Chicago/Turabian StyleEscrivá, Dolores, Esther Moreno-Latorre, Jordi Caplliure-Llopis, Inmaculada Benet, and Carlos Barrios. 2021. "Relationship of Overweight and Obesity with Body Self-Image Dissatisfaction in Urban Mediterranean Adolescents" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 15: 7770. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18157770
APA StyleEscrivá, D., Moreno-Latorre, E., Caplliure-Llopis, J., Benet, I., & Barrios, C. (2021). Relationship of Overweight and Obesity with Body Self-Image Dissatisfaction in Urban Mediterranean Adolescents. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(15), 7770. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18157770






