Radiofrequency Exposure Levels from Mobile Phone Base Stations in Outdoor Environments and an Underground Shopping Mall in Japan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
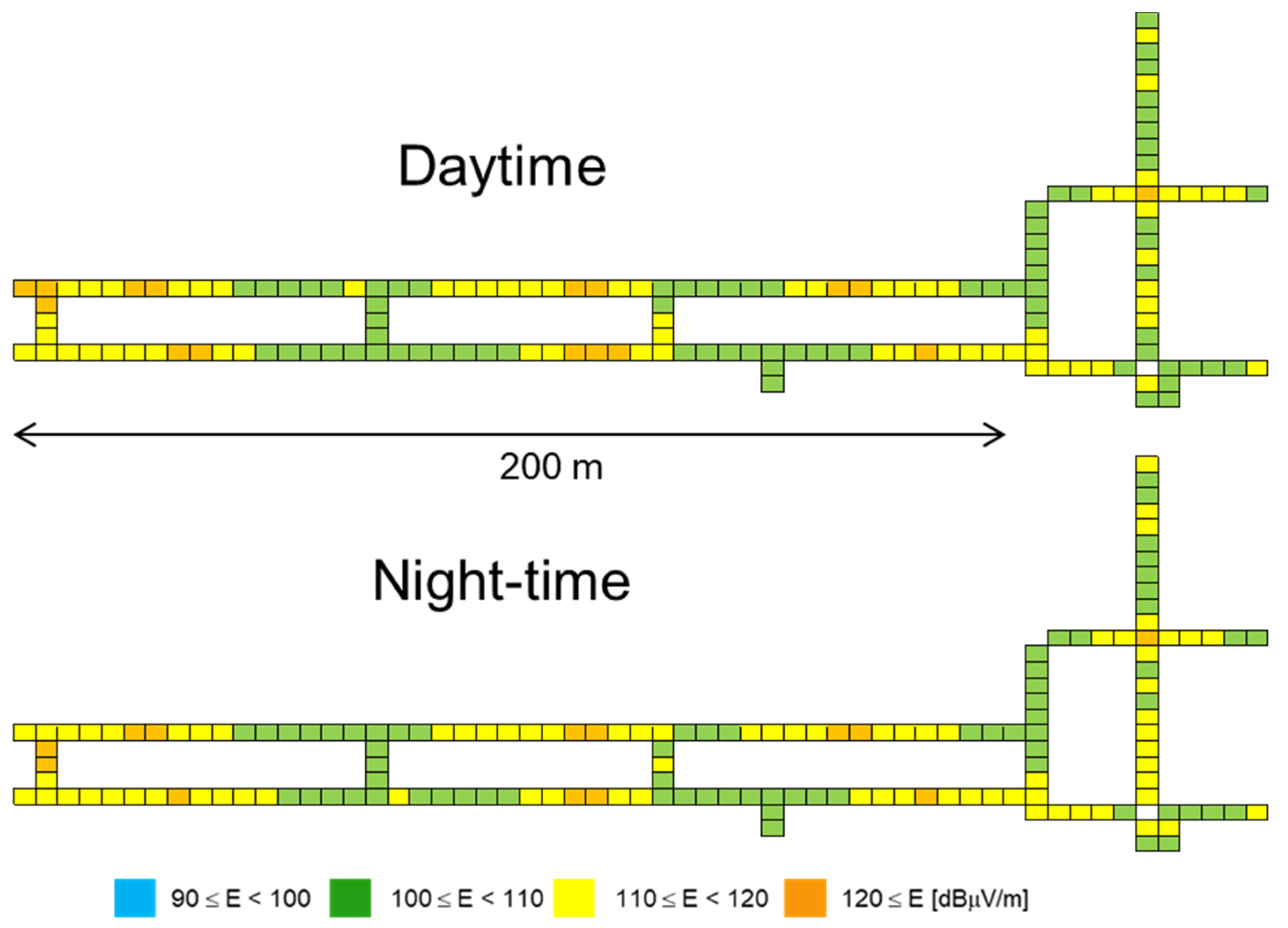
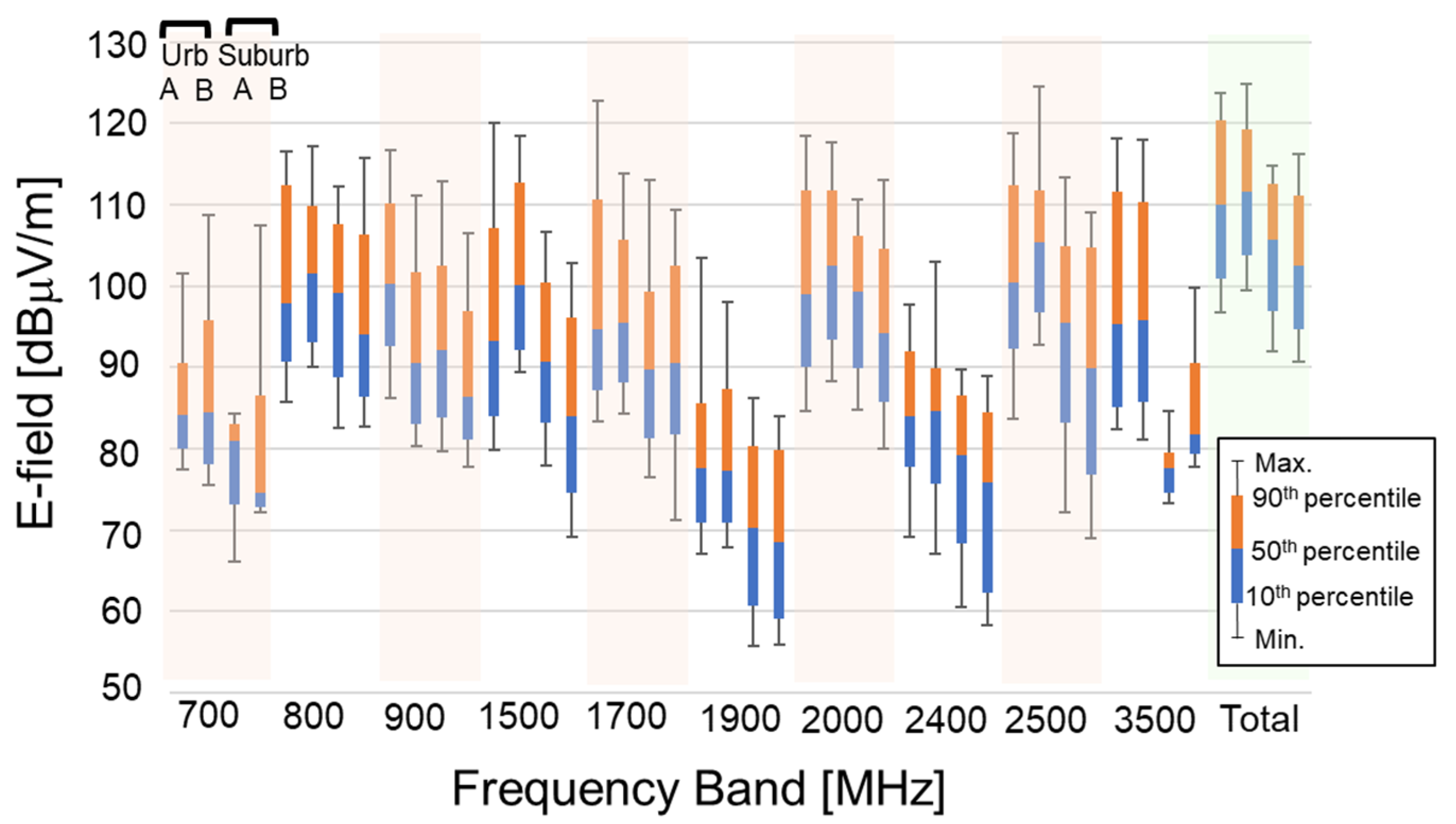
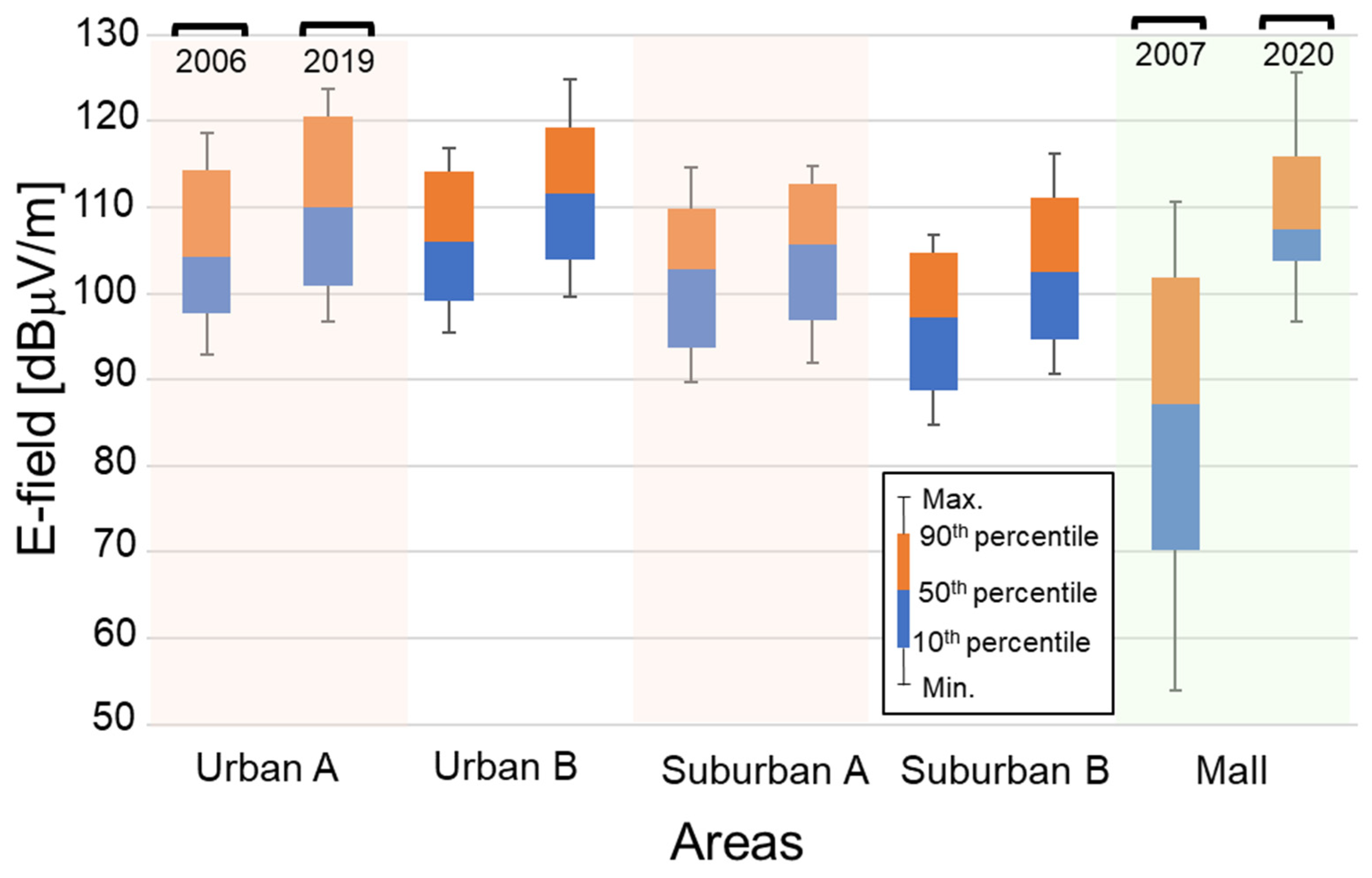
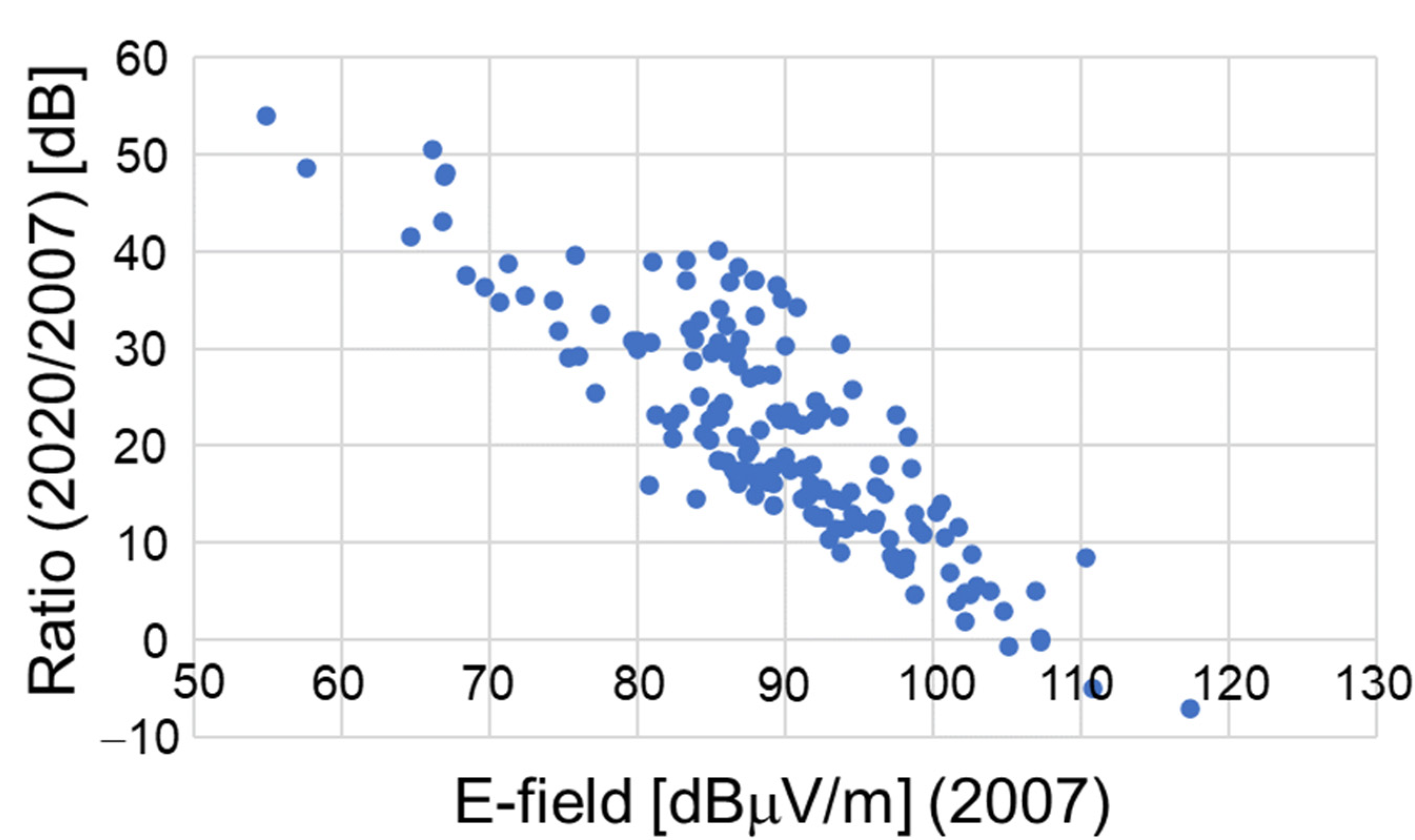
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Exposure Levels Compared with Limits
4.2. Comparison of Present Data with Previous Data
4.3. Comparison with Other Countries
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rowley, J.T.; Joyner, K.H. Comparative international analysis of radiofrequency exposure surveys of mobile communication radio base stations. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2012, 22, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, W.; Verloock, L.; Goeminne, F.; Vermeeren, G. Assessment of RF exposures from emerging wireless communication technologies in different environments. Health Phys. 2012, 102, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, B.C.; Kim, W.-K.; Lee, G.T.; Choi, H.-D.; Kim, N.; Pack, J.-K. Evaluation of Radiofrequency exposure levels from multiple wireless installations in population dense areas in Korea. Bioelectromagnetics 2014, 35, 603–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ANFR (Agence Nationale des Fréquences). Assessment of the Exposure of the General Public to 5G Electromagnetic Waves, Part 2: First Measurement Results on 5G Pilots in the 3400–3800 MHz Band, France. 2020. Available online: https://www.anfr.fr/fileadmin/mediatheque/documents/5G/20200410-ANFR-rapport-mesures-pilotes-5G-EN.pdf (accessed on 21 July 2021).
- Gledhill, M. “Exposures to Radiofrequency Fields near 5G Cellsites,” Prepared for Ministry of Health, New Zealand. 2020. Available online: https://www.health.govt.nz/publication/exposures-radiofrequency-fields-near-5g-cellsites (accessed on 21 July 2021).
- Ofcom (Office of Communications). Electromagnetic Field (EMF) Measurements near 5G Mobile Phone Base Stations, UK. 2020. Available online: https://www.ofcom.org.uk/__data/assets/pdf_file/0015/190005/emf-test-summary.pdf (accessed on 21 July 2021).
- Selmaoui, B.; Mazet, P.; Petit, P.-B.; Kim, K.; Choi, D.; de Seze, R. Exposure of South Korean population to 5G mobile phone networks (3.4–3.8 GHz). Bioelectromagnetics 2021, 42, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ITU-T K.83. Monitoring of Electromagnetic Field Levels. June 2020. Available online: https://www.itu.int/rec/T-REC-K.83-202006-I/en (accessed on 21 July 2021).
- Joseph, W.; Verloock, L.; Goeminne, F.; Vermeeren, G.; Martens, L. In situ LTE exposure of the general public: Characterization and extrapolation. Bioelectromagnetics 2012, 33, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estenberg, J.; Augustsson, T. Extensive frequency selective measurements of radiofrequency fields in outdoor environments performed with a novel mobile monitoring system. Bioelectromagnetics 2014, 35, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aerts, S.; Joseph, W.; Maslanyj, M.; Addison, D.; Mee, T.; Colussi, L.; Kamer, J.; Bolte, J. Prediction of RF-EMF exposure levels in large outdoor areas through car-mounted measurements on the enveloping roads. Environ. Int. 2016, 94, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Joseph, W.; Aerts, S.; Vandenbossche, M.; Thielens, A.; Martens, L. Drone based measurement system for radiofrequency exposure assessment. Bioelectromagnetics 2016, 37, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sagar, S.; Adem, S.M.; Struchen, B.; Loughran, S.P.; Brunjes, M.E.; Arangua, L.; Dalvie, M.A.; Croft, R.J.; Jerrett, M.; Moskowitz, J.M.; et al. Comparison of radiofrequency electromagnetic field exposure levels in different everyday microenvironments in an international context. Environ. Int. 2018, 114, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyare, R.N.; Volskiy, V.; Vandenbosch, G.A.E. Study of the electromagnetic exposure from mobile phones in a city like environment: The case study of Leuven, Belgium. Environ. Res. 2019, 175, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazloum, T.; Aerts, S.; Joseph, W.; Wiart, J. RF-EMF exposure induced by mobile phones operating in LTE small cells in two different urban cities. Ann. Telecommun. 2019, 74, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, A.-K.; Jeon, S.-B.; Choi, H.-D. EMF levels in 5G new radio environment in Seoul, Korea. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 19716–19722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, S.; Deschrijver, D.; Joseph, W.; Verloock, L.; Goeminne, F.; Martens, L.; Dhaene, T. Exposure assessment of mobile phone base station raditation in an outdoor environment using sequential surrogate modeling. Bioelectromagnetics 2013, 34, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgi, A.; Scanferla, D.; Lehmann, H. Time averaged transmitter power and exposure to electromagnetic fields from mobile phone base stations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 8025–8037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossetti, S.; de Bartolo, D.; Veronese, I.; Cantone, M.C.; Cosenza, C.; Nava, E. Extrapolation techniques evaluating 24 h of average electromagnetic field emitted by radio base station installations: Spectrum analyzer measurements of LTE and UMTS signals. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2017, 173, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aerts, S.; Wiart, J.; Martens, L.; Joseph, W. Assessment of long-term spatio-temporal radiofrequency electromagnetic field exposure. Environ. Res. 2018, 161, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Wiart, J. Sensor-aided EMF exposure assessments in an urban environment using artificial neural networks. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Minister of Internal Affairs and Communications in Japan. Report of Electric Field Measurement with Respect to Wireless Mobile Base Stations under Normal Radio Propagation Environment. January 2007. Available online: https://www.tele.soumu.go.jp/resource/j/ele/body/report/pdf/18-1.pdf (accessed on 21 July 2021).
- The Minister of Internal Affairs and Communications in Japan. Report of Electric Field Measurement in a Radio Wave Propagation Environment of a Closed Space. January 2008. Available online: https://www.tele.soumu.go.jp/resource/j/ele/body/report/pdf/19-1.pdf (accessed on 21 July 2021).
- Joseph, W.; Verloock, L.; Goeminne, F.; Vermeeren, G.; Martens, L. Assessment of general public exposure to LTE and RF sources present in an urban environment. Bioelectromagnetics 2010, 31, 576–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Minister of Internal Affairs and Communications in Japan. Radio-Radiation Protection Guidelines. 2018. Available online: https://www.tele.soumu.go.jp/resource/j/material/dwn/rrpg_e.pdf (accessed on 21 July 2021).
- Watanabe, S.; Hamada, L. Measurements of the Electromagnetic Field from a Mobile Phone Base Station. J. Natl. Inst. Inf. Commun. Technol. 2016, 63, 213–231. Available online: http://www.nict.go.jp/publication/shuppan/kihou-journal/journal-vol63no1/journal-vol63no1-03-04.pdf (accessed on 21 July 2021).
- Ministry of Posts and Telecommunications. Methods of Calculation and Measurement for the Electromagnetic Field Strength Transmitted from Radio Equipment, 1999, Japan; Notice 300. Available online: https://www.tele.soumu.go.jp/resource/j/ele/body/system/300.pdf (accessed on 29 July 2021).
- IEC 62232 ed.2. Determination of RF Field Strength, Power Density and SAR in the Vicinity of Radiocommunication Base Stations for the Purpose of Evaluating Human Exposure. 2017. Available online: https://webstore.iec.ch/publication/28673 (accessed on 21 July 2021).
- Narda Safety Test Solutions GmbH. Principles and Applications of the Selective Radiation Meter SRM-3000, June 2006; Application note. Available online: https://www.narda-sts.com/en/ (accessed on 21 July 2021).
- Information and Communication Statistics Database. Available online: https://www.soumu.go.jp/johotsusintokei/field/index.html (accessed on 21 July 2021).


| Frequency Range [MHz] | 700 | 1500 | 2100 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum deviation [dB] | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.5 |
| Item | Ratio [dB] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urban-A | Urban-B | Suburban-A | Suburban-B | Mall (Day) | Mall (Night) | |
| Maximum | −29.2 | −28.1 | −38.2 | −36.8 | −30.1 | −33.1 |
| Median | −42.9 | −41.4 | −47.3 | −50.4 | −48.0 | −48.2 |
| Frequency Band (MHz) | 2006/2007 | 2019/2020 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bandwidth (MHz) | Generation | Bandwidth (MHz) | Generation | |
| 700 | - | - | 30 | 4G |
| 800 | 44 | 2G/3G | 30 | 3G/4G |
| 900 | - | - | 15 | 4G |
| 1500 | 27 | 2G | 35 | 4G |
| 1700 | 20 | 3G | 75 | 4G |
| 1900 | 32.6 | PHS | 31 | PHS/TD-LTE |
| 2000 | 60 | 3G | 60 | 3G/4G |
| 2500 | - | - | 100 | BWA |
| 3500 | - | - | 200 | 4G |
| Total | 183.6 | - | 576 | - |
| Location | Ratio [dB] in Each Frequency Band | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 800 [MHz] | 1500 | 1700 | 2100 | |
| Outdoor environments | 7.0 | 8.0 | 8.4 | 8.1 |
| Underground mall | 7.5 | 8.2 | 9.4 | 8.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Onishi, T.; Ikuyo, M.; Tobita, K.; Liu, S.; Taki, M.; Watanabe, S. Radiofrequency Exposure Levels from Mobile Phone Base Stations in Outdoor Environments and an Underground Shopping Mall in Japan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8068. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18158068
Onishi T, Ikuyo M, Tobita K, Liu S, Taki M, Watanabe S. Radiofrequency Exposure Levels from Mobile Phone Base Stations in Outdoor Environments and an Underground Shopping Mall in Japan. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(15):8068. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18158068
Chicago/Turabian StyleOnishi, Teruo, Miwa Ikuyo, Kazuhiro Tobita, Sen Liu, Masao Taki, and Soichi Watanabe. 2021. "Radiofrequency Exposure Levels from Mobile Phone Base Stations in Outdoor Environments and an Underground Shopping Mall in Japan" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 15: 8068. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18158068
APA StyleOnishi, T., Ikuyo, M., Tobita, K., Liu, S., Taki, M., & Watanabe, S. (2021). Radiofrequency Exposure Levels from Mobile Phone Base Stations in Outdoor Environments and an Underground Shopping Mall in Japan. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(15), 8068. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18158068






