Abstract
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the relationship between hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) and diabetic retinopathy (DR) via the national health insurance research database (NHIRD) of Taiwan. All patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes (n = 47,353) in the NHIRD (2000–2012) were enrolled in the study. The case group consists of participants with diabetic ophthalmic complications; 1:1 matching by age (±1 year old), sex, and diagnosis year of diabetes was used to provide an index date for the control group that corresponded to the case group (n = 5550). Chi-square test for categorical variables and Student’s t-test for continuous variables were used. Conditional logistic regression was performed to estimate the adjusted odds ratio (aOR) of DR. The total number of HCQ user was 99 patients (1.8%) in the case group and 93 patients (1.7%) in the control group. Patients with hypertension (aOR = 1.21, 95% CI = 1.11–1.31) and hyperlipidemia (aOR = 1.65, 95% CI = 1.52–1.79) significantly increased the risk of diabetic ophthalmic complications (p < 0.001). Conversely, the use of HCQ and the presence of rheumatoid diseases did not show any significance in increased risk of DR. HCQ prescription can improve systemic glycemic profile, but it does not decrease the risk of diabetic ophthalmic complications.
1. Introduction
Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) is a unique medication commonly prescribed in rheumatology and dermatology [1]. In recent decades, several literatures have proven that HCQ is effective in minimizing the risk of new onset diabetes and improving metabolic profiles such as fasting blood sugar, insulin sensitivity, hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) and lipid profiles [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]. These benefits were reported in patients with autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus [10], ankylosing spondylitis, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis [11,12] and Sjogren’s syndrome [8].
Diabetes mellitus is a rapidly growing public health concern across the world. The pathophysiology is related to chronic hyperglycemia with impaired metabolism due to insulin secretion dysfunction and/or peripheral tissue insulin resistance [13]. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) and the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), the prevalence of DM increased from 108 million (4.7%) in 1980 to 463 million (9.3%) in 2019, and it is estimated to be 700 million (10.9%) by 2045 [14,15]. Diabetes causes substantial morbidity and mortality, increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease, blindness, kidney failure and lower limb amputation [16]. Diabetic retinopathy is a disease caused by microvascular complications resulting from chronic diabetes and remains the leading cause of blindness worldwide. Associated risk factors inducing DR include hyperglycemia, hypertension, dyslipidemia, ethnics, duration of diabetes, pregnancy, puberty and previous cataract surgery [17]. Recently, it is thought to be influenced by disruption of the blood-retinal barriers (BRBs), which is composed of retinal endothelial cells and retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) [18,19,20].
Retinal pigment epithelium constitutes a monolayer of cuboidal, polarized cells situated between the photoreceptor cells and choroid [21,22]. RPE plays an essential functional role in the maintenance of retinal homeostasis and the health of photoreceptors [23]. Impairment of the RPE causes many inherited and acquired diseases, which may result in permanent blindness [24]. Studies have shown that HCQ disrupts RPE metabolism, resulting in retinal toxicity, especially in the macula of patients under long-term use of HCQ [25]. Patients with more serious side effects may experience color vision changes or paracentral scotomas with corresponding external limiting membrane loss, disruption of the ellipsoid zone, parafoveal thinning of the outer nuclear layer, and RPE damage [26,27].
Considering the conflicting effects associated with HCQ, we aimed to evaluate the relationship between HCQ and diabetic retinopathy by analyzing the national health insurance research database (NHIRD) of Taiwan. Other systemic comorbidities were also examined in the multivariate analysis model.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
The study is a nested case-control study incorporating data from the NHIRD, which enrolled almost 99% of a population of 23 million beneficiaries in Taiwan. The database comprises all insurance claims, including outpatient visits, emergency, and hospitalization. One million subjects were sampled from the 23 million beneficiaries dating from 1999 to 2013. The sampled database contains the de-identified medical records required for medical research and the study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Chung Shan Medical University Hospital (Registration Number: CSMUH CS15134). The diagnostic codes were recorded according to the International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM).
2.2. Patient Selection
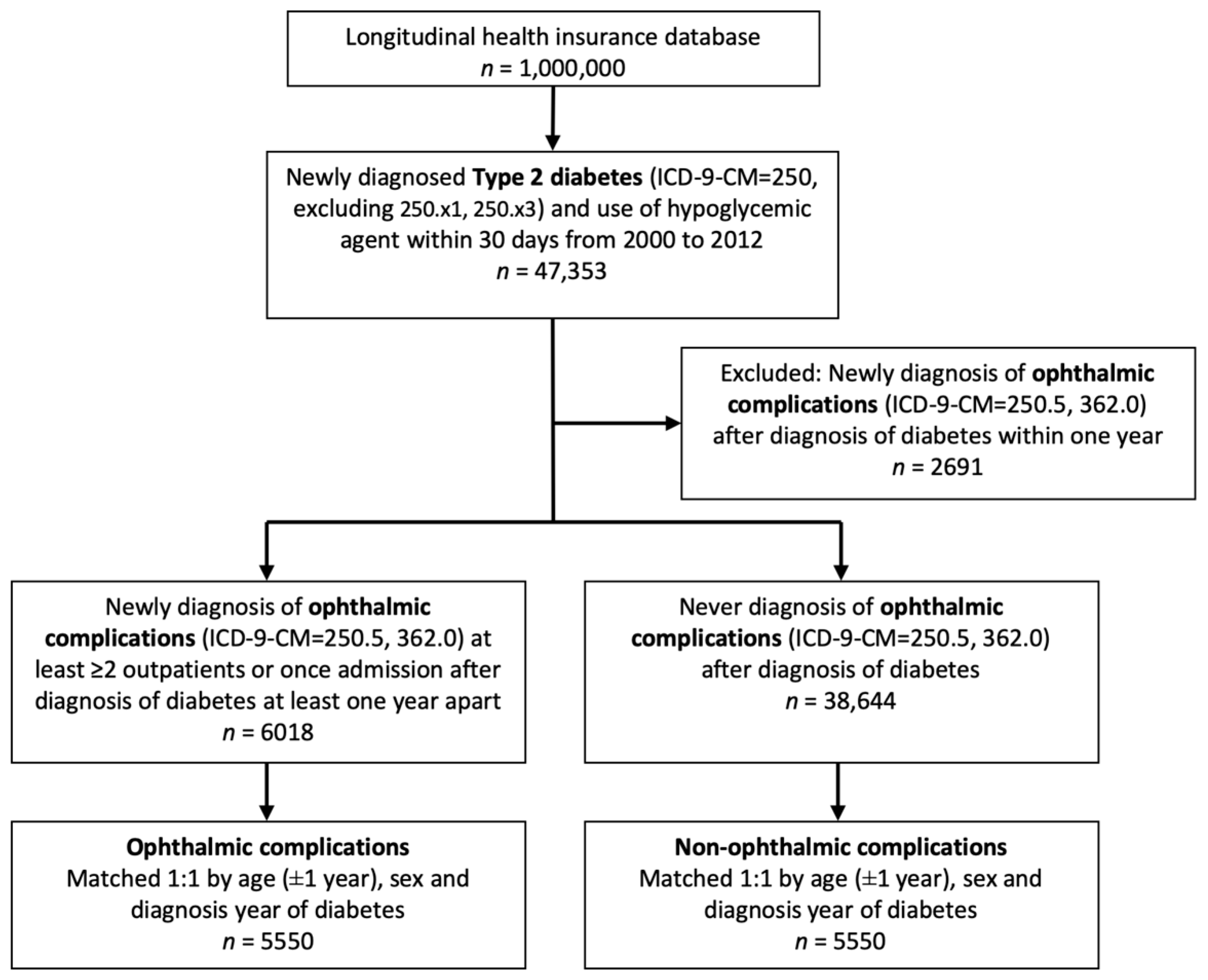
The inclusion criteria of the study population consisted of newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes (ICD-9-CM = 250) and use of hypoglycemic agents within 30 days from 2000 to 2012; the exclusion criteria consisted of type 1 diabetes (ICD-9-CM = 250.×1, 250.×3) and newly diagnosed ophthalmic complications after the diagnosis of diabetes within one year. The case group were patients diagnosed with ophthalmic complications, including diabetes with ophthalmic manifestations (ICD-9-CM = 250.5), and diabetic retinopathy (ICD-9-CM = 362.0) with at least two outpatient visits or one hospitalization after diagnosis of diabetes at least one year apart. The control group were diabetic patients without previous diagnosis of ophthalmic complications. The index date was defined as the date of the patient’s first record of ophthalmic complications. Moreover, 1:1 matching by age (±1 year old), sex, and duration of diabetes was performed to provide an index date for the control group that corresponded to the case group.
2.3. Hydroxychloroquine and Covariates
The cumulative days of hydroxychloroquine was calculated from the first date of diabetes to the index date. The baseline characteristics were age, gender, hypertension (ICD-9-CM = 401–405), hyperlipidemia (ICD-9–CM = 272.0–272.4), rheumatoid arthritis (ICD-9-CM = 714.0), ankylosing spondylitis (ICD-9-CM = 720.0), systemic lupus erythematosus (ICD-9-CM = 710.0), and Sjogren’s syndrome (ICD-9-CM = 710.2). The comorbidities included were required to be diagnosed within one year before the index date, with at least two outpatient visits or one hospitalization. Since most patients in the NHIRD were Taiwanese, race was not considered as a covariate.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
To compare the characteristics of the case and control groups, Chi-square test for categorical variables and Student’s t- test for continuous variables were used. Conditional logistic regression was used to estimate the odds ratio of effect of hydroxychloroquine. Moreover, the dose effect of hydroxychloroquine was estimated by counting the cumulative days of use. A sensitivity analysis matching hypertension and hyperlipidemia was conducted. Statistical analysis was performed with the use of SPSS version 18.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
3. Results
The flowchart of patient selection is shown in Figure 1. After inclusion and matching, 5550 patients were selected in each group. There was no difference between the age and gender in the case and the control groups after matching. The demographics of diabetic patients are listed in Table 1, separated by the presence of ophthalmic complications.
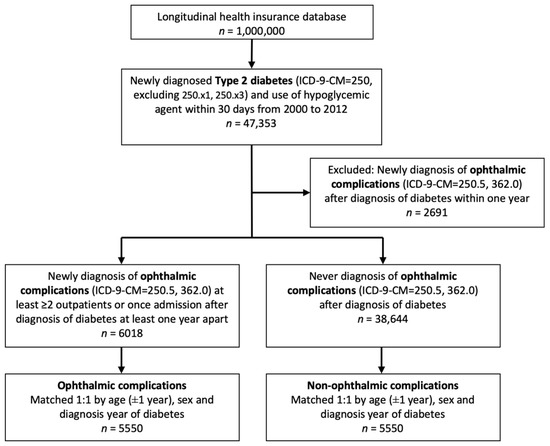
Figure 1.
Flowchart of type 2 diabetes patient enrollment with and without ophthalmic complications.

Table 1.
Demographic characteristics of diabetic patients.
The total number of HCQ user was 99 patients (1.8%) in the case group and 93 patients (1.7%) in the control group. The median age was 60.0 ± 11.3 and 60.1 ± 11.3 years and the sex ratio between female and male was 48.6% and 51.4% in two groups, respectively. The ratio of underlying medical diseases in the two groups were 65.8%/60.8% (p < 0.001) in hypertension; 57.9%/46.0% (p < 0.001) in hyperlipidemia; 1.4%/1.6% (p = 0.345) in rheumatoid arthritis; 0.4%/0.3% (p = 0.342) in ankylosing spondylitis; 0.1%/0.1% (p = 0.365) in systemic lupus erythematosus; and 0.9%/0.6% (p = 0.121) in Sjogren’s syndrome.
The conditional logistic regression of risk of developing ophthalmic complications compared with the reference group (without HCQ prescription) revealed significantly higher risk in the group with hypertension (adjust odds ratio (aOR) = 1.21, 95% confidence interval (C.I.) = 1.11–1.31, p < 0.001) and hyperlipidemia (aOR = 1.65, 95% C.I. = 1.52–1.79, p < 0.001). There was no significance in groups with HCQ prescription, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, systemic lupus erythematosus and Sjogren’s syndrome (Table 2). The sensitivity analysis was performed as supplement Figure S1, Tables S1 and S2 and there was no significance in groups with HCQ prescription and ophthalmic complications.

Table 2.
Conditional logistic regression of risk of ophthalmic complications.
Subgroup analysis of risk of ophthalmic complications revealed there was no significance among all subgroups, regardless of the use of HCQ (Table 3).

Table 3.
Subgroup analysis of risk of ophthalmic complications.
Risk of ophthalmic complications related to the cumulative days of HCQ revealed no significance in all groups regardless of the duration of HCQ prescription (Table 4).

Table 4.
Risk of ophthalmic complications with different cumulative days of HCQ.
4. Discussion
In our study, we did not find a significant correlation between HCQ and the development of diabetic ophthalmic complications. Our finding was in conflict with the evidence displayed in previous literatures, which showed a positive relationship between HCQ and systemic glycemic control [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9].
HCQ is considered toxic to the retina due to accumulation in the RPE, causing serious symptoms in long-term HCQ users. However, the mechanism of hydroxychloroquine retinal toxicity has yet to be totally understood [28]. Studies have revealed that HCQ affects the metabolism of retinal cells by binding to melanin in the RPE [29]. At the same time, the function of photoreceptor and RPE plays a key role in the progression of diabetic retinopathy [18].
However, HCQ has also shown to decrease the risk of diabetes and improve metabolic profile and hyperglycemia associated inflammation [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]. Insulin sensitivity and insulin resistance are improved because HCQ can inhibit the degradation of insulin [30], reduce hyperglycemia associated inflammation [31] and activate protein kinase β (Akt) resulting in increased glucose uptake and glycogen synthesis [32]. Furthermore, HCQ stabilizes intracellular lysosomes by decreasing the decomposition of the internalized insulin receptor complex [33]. HCQ is an acidotrophic agent, thus intracellular pH is raised with increasing intracellular concentration of HCQ. This causes inactivation of the proteolytic enzyme insulinase, which is responsible for the degradation of insulin, resulting in the recirculation of a massive proportion of insulin in the active form [34]. Moreover, HCQ can reduce the risk of cardiovascular morbidity [35,36,37], with the hypothesis of improvement in atherosclerosis [38] and anti-platelet properties through the arachidonic acid pathway [39]. The possible antidiabetic and arterial protective mechanisms of HCQ are gradually proposed, but further mechanistic, efficacy, and safety-related preclinical and clinical studies are warranted to verify the therapeutic role of this medication [9].
Due to the conflicting effects of HCQ on the retina, we designed this study to determine if HCQ has a preventive or detrimental effect on the development of diabetic retinopathy. In our study, we revealed that patients with hypertension (aOR = 1.21, 95% C.I. = 1.11–1.31) and hyperlipidemia (aOR = 1.65, 95% C.I. = 1.52–1.79) were strongly associated with the risk of diabetic ophthalmic complications (Table 1). The result was compatible with the previous studies indicating these two known comorbidities [17]. The same result was also shown in Table 2. However, HCQ prescription had no significant effect in decreasing the risk of diabetic ophthalmic complications. This result was inconsistent with the evidence proposed in previous literatures, which showed that HCQ had antidiabetic properties [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]. Rosa et al. reported that diabetes increases inflammation and oxidative stress and thus influences cellular metabolism, including autophagy, establishing a degree of cellular apoptosis and the progression of DR [40]. Chen et al. surveyed that HCQ inhibit autophagy of RPE and further aggravated the senescence of it, accompanied by an increase in oxidant species [41]. As a result, HCQ has a negative effect in cellular metabolism which may further exacerbate DR.
In the subgroup analysis of risk of ophthalmic complications (Table 3), we also revealed that HCQ had no significant effect on decreasing the risk of diabetic retinopathy in any subgroups. Interestingly, there is an increased odds ratio of diabetic complications in patients with hyperlipidemia under HCQ prescription (OR = 1.33, 95% C.I. = 0.88–2.01, p = 0.170). The result suggests that HCQ may induce progression of DR, especially in patients with an abnormal lipid profile. Chen et al. reported that HCQ aggravates RPE dysfunction due to oxidative stress mediated by lipid metabolism, contributing to high glucose-induced senescence [41]. This finding suggests an increased risk of progression of DR in diabetic patients with dyslipidemia treated with HCQ. In regard to the cumulative days of effect that HCQ has on diabetic retinopathy (Table 4), the duration of HCQ use, whether short (<90 days), long (>90 days), or as a continuous variable, has no significant effect on the development of diabetes related ophthalmic complications.
Although HCQ has proven to have systemic antidiabetic properties, our study did not show that it has the same effect in preventing diabetic retinopathies. We postulate that HCQ may influence the metabolism and pathophysiology of the retina, especially RPE, which may encourage the progression of DR. Diabetic retinopathy is a multi-factorial disease, controlled not only by blood sugar or hemoglobin A1c. Through this study, we wanted to evaluate the role of HCQ in diabetic retinopathy, which is clinically relevant for many rheumatoid patients with diabetes under prolonged use of HCQ.
There are some limitations in this study in regard to the national health insurance research database. First, we could not confirm the specificity and consistency of diabetic ophthalmic complications since it was diagnosed and coded by different ophthalmologists. Additionally, the coding rate may be underestimated due to low ophthalmologic screening rate of HCQ users in Taiwan [42]. Secondly, we could not evaluate the severity of DR with the current data. More detailed stages of DR should also be considered for evaluating the effect of HCQ on the severity of ophthalmic complication. Besides, different dose and type of antidiabetic medication combined with HCQ may have provided varying degrees of treatment on DR. Hsia et al. reported that HCQ improved glucose regulation when used as a third-line agent added to metformin and a sulfonylurea [43]. More randomized controlled trial is warranted to establish the efficacy of combining drugs with HCQ on treating diabetic retinopathy in the future. Finally, detailed information of HCQ prescription was not available in the database. The American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO) guidelines (2011 and 2016) claimed that it is a major risk factor that increases the risk of retinal toxicity after 5 years of HCQ therapy [44,45]. In our study, the number of patients under HCQ therapy longer than 5 years was too small to analyze. Besides, the 2011 AAO guidelines stated that a cumulative dose of >1000 g increases the risk of retinopathy (equating to 6.85 years of treatment at 400 mg, and 13.7 years of treatment at 200 mg) [44]. The exact cumulative dose of HCQ was not obtained in this study.
HCQ is a historical medication used broadly and commonly even in modern medicine. The research of HCQ retinopathy and systemic antidiabetic property of HCQ are gradually being established. This is a preliminary and novel study to explore the relationship between HCQ and diabetic ophthalmic complications. Our result provides some clinical insights for ophthalmologists and physicians on the management of DR in patients with concomitant diseases requiring HCQ prescription.
5. Conclusions
HCQ is commonly prescribed for rheumatic and dermatologic diseases in Taiwan, and many of these patients have diabetes. Although HCQ can improve glycemic profiles systemically with careful use, it does not seem to decrease the risk of diabetic ophthalmic complications. The protective and injurious mechanism of HCQ on diabetic retinopathy needs to be further investigated.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijerph18158154/s1. Figure S1: Flowchart of type 2 diabetes patient enrollment with and without ophthalmic complications in the sensitivity analysis, Table S1: Demographic characteristics of diabetic patients in the sensitivity analysis, Table S2: Conditional logistic regression of risk of ophthalmic complications in the sensitivity analysis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.-C.C., P.-Y.L. and J.C.-C.W.; methodology, P.-Y.L. and J.C.-C.W.; formal analysis, Y.-H.W.; resources, P.-Y.L. and J.C.-C.W.; writing—original draft preparation, H.-C.C.; writing—review and editing, H.-Y.L., M.C.-Y.C., P.-Y.L. and J.C.-C.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Chung Shan Medical University Hospital (Registration Number: CSMUH CS15134 and approval on 30 October 2015).
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent from research participants was waived because the sampled database from the national health insurance research database (NHIRD) of Taiwan was de-identified and patient’s information could not be identified.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rainsford, K.D.; Parke, A.L.; Clifford-Rashotte, M.; Kean, W.F. Therapy and pharmacological properties of hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine in treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis and related diseases. Inflammopharmacology 2015, 23, 231–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penn, S.K.; Kao, A.H.; Schott, L.L.; Elliott, J.R.; Toledo, F.G.; Kuller, L.; Manzi, S.; Wasko, M.C. Hydroxychloroquine and glycemia in women with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 2010, 37, 1136–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hage, M.P.; Al-Badri, M.R.; Azar, S.T. A favorable effect of hydroxychloroquine on glucose and lipid metabolism beyond its anti-inflammatory role. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 5, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilla, S.J.; Quan, A.Q.; Germain-Lee, E.L.; Hellmann, D.B.; Mathioudakis, N.N. Immune-Modulating Therapy for Rheumatologic Disease: Implications for Patients with Diabetes. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2016, 16, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiorino, M.I.; Bellastella, G.; Giugliano, D.; Esposito, K. Cooling down inflammation in type 2 diabetes: How strong is the evidence for cardiometabolic benefit? Endocrine 2017, 55, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozen, G.; Pedro, S.; Holmqvist, M.E.; Avery, M.; Wolfe, F.; Michaud, K. Risk of diabetes mellitus associated with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and statins in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rempenault, C.; Combe, B.; Barnetche, T.; Gaujoux-Viala, C.; Lukas, C.; Morel, J.; Hua, C. Metabolic and cardiovascular benefits of hydroxychloroquine in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.H.; Lai, T.Y.; Wang, Y.H.; Chiou, J.Y.; Hung, Y.M.; Wei, J.C. Hydroxychloroquine was associated with reduced risk of new-onset diabetes mellitus in patients with Sjögren syndrome. Qjm 2019, 112, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wondafrash, D.Z.; Desalegn, T.Z.; Yimer, E.M.; Tsige, A.G.; Adamu, B.A.; Zewdie, K.A. Potential Effect of Hydroxychloroquine in Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review on Preclinical and Clinical Trial Studies. J. Diabetes Res. 2020, 2020, 5214751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.M.; Lin, C.H.; Lan, T.H.; Chen, H.H.; Chang, S.N.; Chen, Y.H.; Wang, J.S.; Hung, W.T.; Lan, J.L.; Chen, D.Y. Hydroxychloroquine reduces risk of incident diabetes mellitus in lupus patients in a dose-dependent manner: A population-based cohort study. Rheumatol. (Oxf.) 2015, 54, 1244–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Solomon, D.H.; Massarotti, E.; Garg, R.; Liu, J.; Canning, C.; Schneeweiss, S. Association between disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and diabetes risk in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis. JAMA 2011, 305, 2525–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.H.; Chen, D.Y.; Lin, C.C.; Chen, Y.M.; Lai, K.L.; Lin, C.H. Association between use of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and diabetes in patients with ankylosing spondylitis, rheumatoid arthritis, or psoriasis/psoriatic arthritis: A nationwide, population-based cohort study of 84,989 patients. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2017, 13, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alberti, K.G.; Zimmet, P.Z. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabet. Med. 1998, 15, 539–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Lu, Y.; Hajifathalian, K.; Bentham, J.; Di Cesare, M.; Danaei, G.; Bixby, H.; Cowan, M.J.; Ali, M.K.; Taddei, C.; et al. Worldwide trends in diabetes since 1980: A pooled analysis of 751 population-based studies with 4.4 million participants. Lancet 2016, 387, 1513–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saeedi, P.; Petersohn, I.; Salpea, P.; Malanda, B.; Karuranga, S.; Unwin, N.; Colagiuri, S.; Guariguata, L.; Motala, A.A.; Ogurtsova, K.; et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9(th) edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 157, 107843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chatterjee, S.; Khunti, K.; Davies, M.J. Type 2 diabetes. Lancet 2017, 389, 2239–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, N.; Mitchell, P.; Wong, T.Y. Diabetic retinopathy. Lancet 2010, 376, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonade, D.; Kern, T.S. Photoreceptor cells and RPE contribute to the development of diabetic retinopathy. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2021, 83, 100919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, D.H.; Yun, J.H.; Cho, C.S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, C.H. Interaction between microglia and retinal pigment epithelial cells determines the integrity of outer blood-retinal barrier in diabetic retinopathy. Glia 2019, 67, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Rizzolo, L.J. Effects of diabetic retinopathy on the barrier functions of the retinal pigment epithelium. Vision Res. 2017, 139, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparrow, J.R.; Hicks, D.; Hamel, C.P. The retinal pigment epithelium in health and disease. Curr. Mol. Med. 2010, 10, 802–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caceres, P.S.; Rodriguez-Boulan, E. Retinal pigment epithelium polarity in health and blinding diseases. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2020, 62, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beranova-Giorgianni, S.; Giorgianni, F. Proteomics of Human Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) Cells. Proteomes 2018, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lakkaraju, A.; Umapathy, A.; Tan, L.X.; Daniele, L.; Philp, N.J.; Boesze-Battaglia, K.; Williams, D.S. The cell biology of the retinal pigment epithelium. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2020, 78, 100846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, R.L.; Gerber, J.P. Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine binding to melanin: Some possible consequences for pathologies. Toxicol. Rep. 2014, 1, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pasadhika, S.; Fishman, G.A. Effects of chronic exposure to hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine on inner retinal structures. Eye (Lond.) 2010, 24, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhavsar, K.V.; Mukkamala, L.K.; Freund, K.B. Multimodal imaging in a severe case of hydroxychloroquine toxicity. Ophthalmic Surg. Lasers Imaging Retin. 2015, 46, 377–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusuf, I.H.; Sharma, S.; Luqmani, R.; Downes, S.M. Hydroxychloroquine retinopathy. Eye (Lond) 2017, 31, 828–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korthagen, N.M.; Bastiaans, J.; van Meurs, J.C.; van Bilsen, K.; van Hagen, P.M.; Dik, W.A. Chloroquine and Hydroxychloroquine Increase Retinal Pigment Epithelial Layer Permeability. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2015, 29, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, D.H.; Garg, R.; Lu, B.; Todd, D.J.; Mercer, E.; Norton, T.; Massarotti, E. Effect of hydroxychloroquine on insulin sensitivity and lipid parameters in rheumatoid arthritis patients without diabetes mellitus: A randomized, blinded crossover trial. Arthritis Care Res. (Hoboken) 2014, 66, 1246–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer, E.; Rekedal, L.; Garg, R.; Lu, B.; Massarotti, E.M.; Solomon, D.H. Hydroxychloroquine improves insulin sensitivity in obese non-diabetic individuals. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2012, 14, R135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halaby, M.J.; Kastein, B.K.; Yang, D.Q. Chloroquine stimulates glucose uptake and glycogen synthase in muscle cells through activation of Akt. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 435, 708–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Singh, M.P.; Singh, A.P.; Pandey, M.S.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, S. Efficacy and safety of hydroxychloroquine when added to stable insulin therapy in combination with metformin and gimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes compare to sitagliptin. Int. J. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 7, 1959–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravorty, S.; Purkait, I.; Pareek, A.; Talware, A. Hydroxychloroquine: Looking into the Future. Rom. J. Diabetes Nutr. Metab. Dis. 2017, 24, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shapiro, M.; Levy, Y. The association between hydroxychloroquine treatment and cardiovascular morbidity among rheumatoid arthritis patients. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 6615–6622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van Halm, V.P.; Nurmohamed, M.T.; Twisk, J.W.; Dijkmans, B.A.; Voskuyl, A.E. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs are associated with a reduced risk for cardiovascular disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A case control study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, R151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharma, T.S.; Wasko, M.C.; Tang, X.; Vedamurthy, D.; Yan, X.; Cote, J.; Bili, A. Hydroxychloroquine Use Is Associated With Decreased Incident Cardiovascular Events in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e002867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tanay, A.; Leibovitz, E.; Frayman, A.; Zimlichman, R.; Shargorodsky, M.; Gavish, D. Vascular elasticity of systemic lupus erythematosus patients is associated with steroids and hydroxychloroquine treatment. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1108, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achuthan, S.; Ahluwalia, J.; Shafiq, N.; Bhalla, A.; Pareek, A.; Chandurkar, N.; Malhotra, S. Hydroxychloroquine’s Efficacy as an Antiplatelet Agent Study in Healthy Volunteers: A Proof of Concept Study. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 20, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, M.D.; Distefano, G.; Gagliano, C.; Rusciano, D.; Malaguarnera, L. Autophagy in Diabetic Retinopathy. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2016, 14, 810–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Q.; Tang, L.; Xin, G.; Li, S.; Ma, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhuang, M.; Xiong, Q.; Wei, Z.; Xing, Z.; et al. Oxidative stress mediated by lipid metabolism contributes to high glucose-induced senescence in retinal pigment epithelium. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 130, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, C.Y.; Lee, P.H.; Yen, J.C.; Chen, C.C.; Hu, H.Y.; Tseng, P.C. Current screening practice in patients under long-term hydroxychloroquine medication in Taiwan: A nationwide population-based cohort study. Med. (Baltim.) 2019, 98, e15122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsia, S.H.; Duran, P.; Lee, M.L.; Davidson, M.B. Randomized controlled trial comparing hydroxychloroquine with pioglitazone as third-line agents in type 2 diabetic patients failing metformin plus a sulfonylurea: A pilot study. J. Diabetes 2020, 12, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmor, M.F.; Kellner, U.; Lai, T.Y.; Lyons, J.S.; Mieler, W.F. Revised recommendations on screening for chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine retinopathy. Ophthalmology 2011, 118, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marmor, M.F.; Kellner, U.; Lai, T.Y.; Melles, R.B.; Mieler, W.F. Recommendations on Screening for Chloroquine and Hydroxychloroquine Retinopathy (2016 Revision). Ophthalmology 2016, 123, 1386–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).