Association between Dental Scaling and Reduced Risk of End-Stage Renal Disease: A Nationwide Matched Cohort Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Source of Data
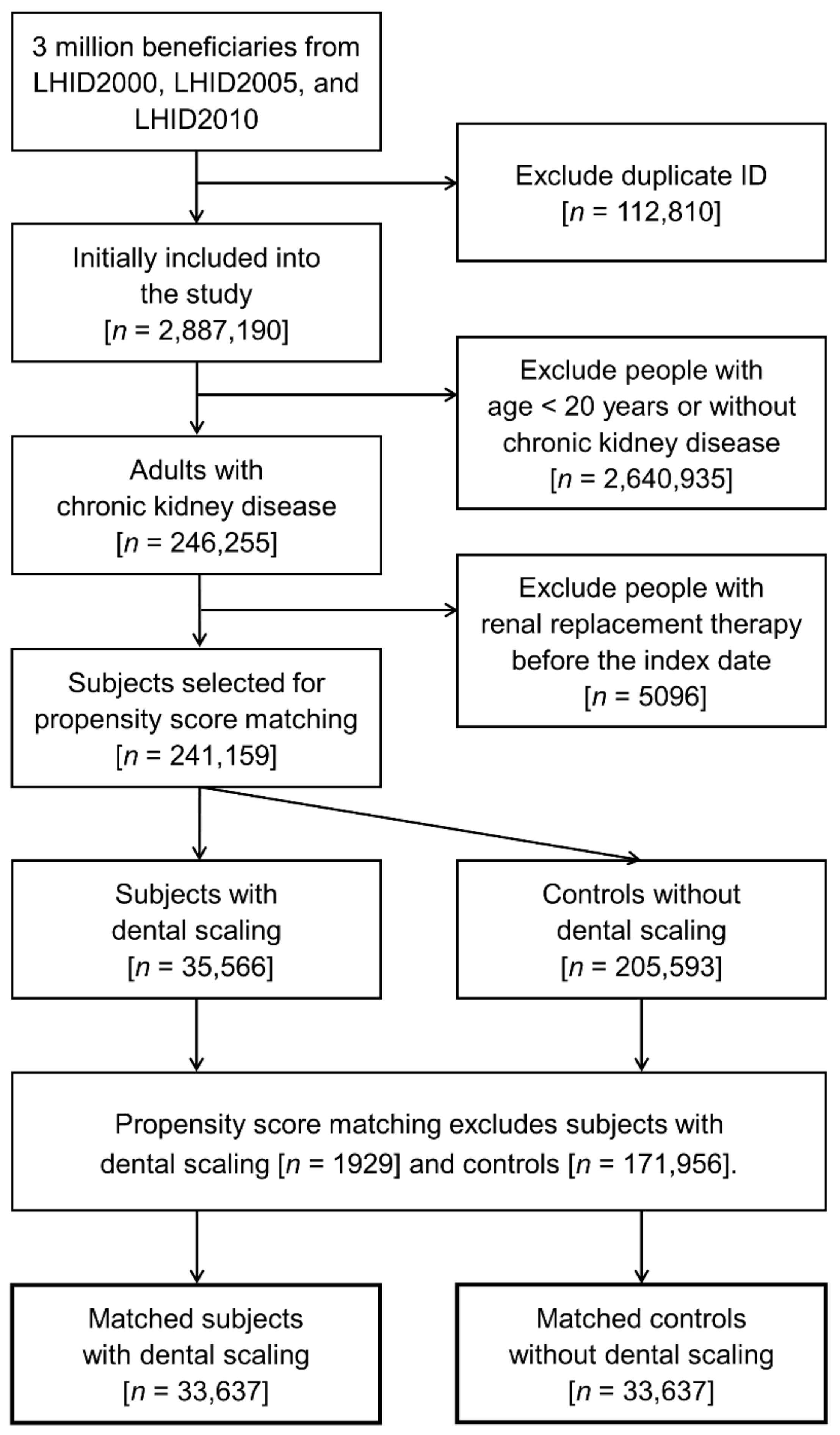
2.2. Patient Selection
2.3. Covariates for Adjustment
2.4. Primary and Secondary Outcomes
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Patient Characteristics
3.2. Dental Scaling and Progression to ESRD
3.3. Dental Scaling and MACE
3.4. Dental Scaling and All-Cause Mortality
3.5. Dental Scaling and Infections
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1789–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Ortega, M.; Rayego-Mateos, S.; Lamas, S.; Ortiz, A.; Rodrigues-Diez, R.R. Targeting the progression of chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 269–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichel, H.; Zee, J.; Tu, C.; Young, E.; Pisoni, R.L.; Stengel, B.; Duttlinger, J.; Lonnemann, G.; Robinson, B.M.; Pecoits-Filho, R.; et al. Chronic kidney disease progression and mortality risk profiles in Germany: Results from the chronic kidney disease outcomes and practice patterns study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2020, 35, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Li, P.K. Strategies to prevent kidney disease and its progression. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 129–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, S.C.; Ruospo, M.; Wong, G.; Craig, J.C.; Petruzzi, M.; De Benedittis, M.; Ford, P.; Johnson, D.W.; Tonelli, M.; Natale, P.; et al. Patterns of oral disease in adults with chronic kidney disease treated with hemodialysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2016, 31, 1647–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.T.; Shih, C.J.; Ou, S.M.; Hung, S.C.; Lin, C.H.; Tarng, D.C.; Taiwan Geriatric Kidney Disease (TGKD) Research Group. Periodontal disease and risks of kidney function decline and mortality in older people: A community-based cohort study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 66, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Khawaja, A.T.; Jin, L.; Li, K.Y.; Tonetti, M.; Pelekos, G. The directional and non-directional associations of periodontitis with chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. J. Periodontal Res. 2018, 53, 682–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scannapieco, F.A.; Bush, R.B.; Paju, S. Associations between periodontal disease and risk for atherosclerosis, cardiovascular disease, and stroke. A systematic review. Ann. Periodontol. 2003, 8, 38–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, F.; Iwamoto, Y.; Soga, Y. The periodontal host response with diabetes. Periodontol. 2000 2007, 43, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kshirsagar, A.V.; Craig, R.G.; Moss, K.L.; Beck, J.D.; Offenbacher, S.; Kotanko, P.; Klemmer, P.J.; Yoshino, M.; Levin, N.W.; Yip, J.K.; et al. Periodontal disease adversely affects the survival of patients with end-stage renal disease. Kidney Int. 2009, 75, 746–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.P.; Chiang, C.K.; Peng, Y.S.; Hsu, S.P.; Lin, C.Y.; Lai, C.F.; Hung, K.Y. Relationship between periodontal disease and mortality in patients treated with maintenance hemodialysis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2011, 57, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz, M.; Del Castillo, M.A.; Jepsen, S.; Gonzalez-Juanatey, J.R.; D’Aiuto, F.; Bouchard, P.; Chapple, I.; Dietrich, T.; Gotsman, I.; Graziani, F.; et al. Periodontitis and cardiovascular diseases: Consensus report. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2020, 47, 268–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deschamps-Lenhardt, S.; Martin-Cabezas, R.; Hannedouche, T.; Huck, O. Association between periodontitis and chronic kidney disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Oral Dis. 2019, 25, 385–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ausavarungnirun, R.; Wisetsin, S.; Rongkiettechakorn, N.; Chaichalermsak, S.; Udompol, U.; Rattanasompattikul, M. Association of dental and periodontal disease with chronic kidney disease in patients of a single, tertiary care centre in Thailand. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e011836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.P.; Chiang, C.K.; Chan, C.P.; Hung, K.Y.; Huang, C.S. Does periodontitis reflect inflammation and malnutrition status in hemodialysis patients? Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2006, 47, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amar, S.; Gokce, N.; Morgan, S.; Loukideli, M.; Van Dyke, T.E.; Vita, J.A. Periodontal disease is associated with brachial artery endothelial dysfunction and systemic inflammation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 1245–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuveling, E.M.; Hillege, H.L.; Bakker, S.J.; Gans, R.O.; De Jong, P.E.; De Zeeuw, D. C-reactive protein is associated with renal function abnormalities in a non-diabetic population. Kidney Int. 2003, 63, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidt, D.G. Inflammation in renal disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 2006, 97, 20A–27A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remuzzi, G.; Ruggenenti, P.; Perico, N. Chronic renal diseases: Renoprotective benefits of renin-angiotensin system inhibition. Ann. Intern. Med. 2002, 136, 604–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, J.M.; Coughlan, M.T.; Cooper, M.E. Oxidative stress as a major culprit in kidney disease in diabetes. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1446–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapa, S.F.; Di Iorio, B.R.; Campiglia, P.; Heidland, A.; Marzocco, S. Inflammation and oxidative stress in chronic kidney disease-potential therapeutic role of minerals, vitamins and plant-derived metabolites. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Wu, B.; Qu, Q.; Gao, J.; Yan, W.; Huang, X.; Ma, D.; Yue, J.; Chen, T.; Liu, F.; et al. The clinical response and systemic effects of non-surgical periodontal therapy in end-stage renal disease patients: A 6-month randomized controlled clinical trial. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2015, 42, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonetti, M.S.; D’Aiuto, F.; Nibali, L.; Donald, A.; Storry, C.; Parkar, M.; Suvan, J.; Hingorani, A.D.; Vallance, P.; Deanfield, J. Treatment of periodontitis and endothelial function. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehmeyer, M.M.; Kshirsagar, A.V.; Barros, S.P.; Beck, J.D.; Moss, K.L.; Preisser, J.S.; Offenbacher, S. A randomized controlled trial of intensive periodontal therapy on metabolic and inflammatory markers in patients with ESRD: Results of an exploratory study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2013, 61, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, S.C.; Ruospo, M.; Wong, G.; Craig, J.C.; Petruzzi, M.; De Benedittis, M.; Ford, P.; Johnson, D.W.; Tonelli, M.; Natale, P.; et al. Dental health and mortality in people with end-stage kidney disease treated with hemodialysis: A multinational cohort study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 66, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graziani, F.; Cei, S.; La Ferla, F.; Vano, M.; Gabriele, M.; Tonetti, M. Effects of non-surgical periodontal therapy on the glomerular filtration rate of the kidney: An exploratory trial. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2010, 37, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artese, H.P.; Sousa, C.O.; Luiz, R.R.; Sansone, C.; Torres, M.C. Effect of non-surgical periodontal treatment on chronic kidney disease patients. Braz. Oral Res. 2010, 24, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.X.; Tai, Y.H.; Chang, Y.T.; Chen, T.J.; Chen, M.H. Association between major depressive disorder and subsequent autoimmune skin diseases: A nationwide population-based cohort study. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 274, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, Y.H.; Chang, C.C.; Yeh, C.C.; Sung, L.C.; Hu, C.J.; Cherng, Y.G.; Chen, T.L.; Liao, C.C. Long-term risk of stroke and poststroke outcomes in patients with heart failure: Two nationwide studies. Clin. Epidemiol. 2020, 12, 1235–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.M.; Kuo, H.C.; Li, C.C.; Wu, H.L.; Chen, J.T.; Cherng, Y.G.; Chen, T.J.; Dai, Y.X.; Liu, H.Y.; Tai, Y.H. Preexisting dementia is associated with increased risks of mortality and morbidity following major surgery: A nationwide propensity score matching study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.; Chang, C.C.; Lin, C.S.; Yeh, C.C.; Hu, C.J.; Wu, C.Z.; Chen, T.L.; Liao, C.C. Risk of dementia in patients with periodontitis and related protective factors: A nationwide retrospective cohort study. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2020, 47, 1428–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Health Insurance Research Database. Data Subsets. Available online: https://nhird.nhri.org.tw/en/Data_Subsets.html (accessed on 3 July 2021).
- Van Oosten, M.J.M.; Logtenberg, S.J.J.; Edens, M.A.; Hemmelder, M.H.; Jager, K.J.; Bilo, H.J.G.; Stel, V.S. Health claims databases used for kidney research around the world. Clin. Kidney J. 2020, 14, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, P.C. An introduction to propensity score methods for reducing the effects of confounding in observational studies. Multivar. Behav. Res. 2011, 46, 399–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, S.C.; Chang, Y.K.; Liu, J.S.; Kuo, K.L.; Chen, Y.H.; Hsu, C.C.; Tarng, D.C. Metformin use and mortality in patients with advanced chronic kidney disease: National, retrospective, observational, cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015, 3, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockhart, P.B.; Tampi, M.P.; Abt, E.; Aminoshariae, A.; Durkin, M.J.; Fouad, A.F.; Gopal, P.; Hatten, B.W.; Kennedy, E.; Lang, M.S.; et al. Evidence-based clinical practice guideline on antibiotic use for the urgent management of pulpal- and periapical-related dental pain and intraoral swelling: A report from the American Dental Association. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2019, 150, 906–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austin, P.C. Balance diagnostics for comparing the distribution of baseline covariates between treatment groups in propensity-score matched samples. Stat. Med. 2009, 28, 3083–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.; Xu, X.; Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Xiao, Y.; Hu, B. Effects of non-surgical periodontal therapy on systemic inflammation and metabolic markers in patients undergoing haemodialysis and/or peritoneal dialysis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Oral Health 2020, 20, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Khawaja, A.T.; Jin, L.; Chan, K.W.; Tonetti, M.; Tang, S.C.W.; Pelekos, G. Effect of non-surgical periodontal therapy on renal function in chronic kidney disease patients with periodontitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of interventional studies. Clin. Oral Investig. 2020, 24, 1607–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drisko, C.H. Nonsurgical periodontal therapy. Periodontol. 2000 2001, 25, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locker, D.; Maggirias, J.; Quiñonez, C. Income, dental insurance coverage, and financial barriers to dental care among Canadian adults. J. Public Health Dent. 2011, 71, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishide, A.; Fujita, M.; Sato, Y.; Nagashima, K.; Takahashi, S.; Hata, A. Income-related inequalities in access to dental care services in Japan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhafiz, A.H.; Brown, S.H.; Bello, A.; El Nahas, M. Chronic kidney disease in older people: Physiology, pathology or both? Nephron Clin. Pract. 2010, 116, c19–c24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.S. Number of existing permanent teeth is associated with chronic kidney disease in the elderly Korean population. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2018, 33, 1150–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozumi, T.; Yashima, A.; Gomi, K.; Ujiie, Y.; Izumi, Y.; Akizuki, T.; Mizutani, K.; Takamatsu, H.; Minabe, M.; Miyauchi, S.; et al. Increased systemic levels of inflammatory mediators following one-stage full-mouth scaling and root planing. J. Periodontal Res. 2018, 53, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, K.A. Hypertensive kidney injury and the progression of chronic kidney disease. Hypertension 2017, 70, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, A.; Malhotra, R.; Grover, V.; Grover, D. Systemic antibiotic therapy in periodontics. Dent. Res. J. 2012, 9, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, P.E.; Levin, A. Kidney disease: Improving global outcomes chronic kidney disease guideline development work group members. evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease: Synopsis of the kidney disease: Improving global outcomes 2012 clinical practice guideline. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 158, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naorungroj, S.; Slade, G.D.; Divaris, K.; Heiss, G.; Offenbacher, S.; Beck, J.D. Racial differences in periodontal disease and 10-year self-reported tooth loss among late middle-aged and older adults: The dental ARIC study. J. Public Health Dent. 2017, 77, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekart, R.; Ferjuc, A.; Furman, B.; Gerjevič, Š.; Bevc, S.; Hojs, R. Chronic kidney disease progression to end stage renal disease: A single center experience of the role of the underlying kidney disease. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2013, 17, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, M.; Hofman, A.; Stricker, B.H. Confounding by indication: An example of variation in the use of epidemiologic terminology. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1999, 149, 981–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Baseline Characteristic | Dental Scaling n = 33,637 | Control n = 33,637 | SDD | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years), mean (SD) | 52.6 | 15.9 | 52.5 | 16.2 | 0.0062 |
| Age group (years), n (%) | 0.0145 | ||||
| 20–34 | 5304 | 15.8 | 5490 | 16.3 | |
| 35–49 | 9563 | 28.4 | 9539 | 28.4 | |
| 50–64 | 10,396 | 30.9 | 10,383 | 30.9 | |
| ≥65 | 8374 | 24.9 | 8225 | 24.5 | |
| Sex, n (%) | −0.0007 | ||||
| Male | 16,941 | 50.4 | 16,951 | 50.4 | |
| Female | 16,691 | 49.6 | 16,681 | 49.6 | |
| Insurance premium (USD/month), n (%) | −0.0184 | ||||
| 0–500 | 15,829 | 47.1 | 15,658 | 46.6 | |
| 501–800 | 9517 | 28.3 | 9352 | 27.8 | |
| ≥801 | 8286 | 24.6 | 8622 | 25.6 | |
| Stage 5 CKD, n (%) | 5 | 0.01 | 7 | 0.02 | −0.1855 |
| Periodontal disease, n (%) | 19,922 | 59.2 | 19,918 | 59.2 | 0.0003 |
| Lifestyle factors, n (%) | |||||
| Smoking disorders | 162 | 0.5 | 172 | 0.5 | −0.0332 |
| Alcohol abuse | 456 | 1.4 | 472 | 1.4 | −0.0193 |
| Malnutrition | 195 | 0.6 | 170 | 0.5 | 0.0761 |
| Obesity | 310 | 0.9 | 319 | 1.0 | −0.0159 |
| Comorbidity, n (%) | |||||
| Hypertension | 12,945 | 38.5 | 13,022 | 38.7 | −0.0053 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 8084 | 24.0 | 8148 | 24.2 | −0.0057 |
| Ischemic heart disease | 5241 | 15.6 | 5316 | 15.8 | −0.0093 |
| Atherosclerosis | 428 | 1.3 | 422 | 1.3 | 0.0079 |
| Cardiac dysrhythmias | 2474 | 7.4 | 2525 | 7.5 | −0.0122 |
| Heart failure | 1196 | 3.6 | 1165 | 3.5 | 0.0150 |
| Liver cirrhosis | 481 | 1.4 | 489 | 1.5 | −0.0092 |
| Chronic obstruction pulmonary disease | 3615 | 10.8 | 3528 | 10.5 | 0.0150 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 2801 | 8.3 | 2813 | 8.4 | −0.0026 |
| Dyslipidemia | 7531 | 22.4 | 7836 | 23.3 | −0.0284 |
| Malignancy | 1704 | 5.1 | 1724 | 5.1 | −0.0068 |
| Mental disorders | 8286 | 24.6 | 8463 | 25.2 | −0.0155 |
| Charlson Comorbidity Index | 0.0096 | ||||
| 0 | 4828 | 14.4 | 4959 | 14.7 | |
| 1 | 11,113 | 33.0 | 11,290 | 33.6 | |
| 2 | 6171 | 18.4 | 5955 | 17.7 | |
| 3 | 4508 | 13.4 | 4327 | 12.9 | |
| ≥4 | 7017 | 20.9 | 7106 | 21.1 | |
| Systemic antibiotics, n (%) | 13,264 | 39.4 | 12,167 | 36.2 | 0.0765 |
| Statins, n (%) | 3395 | 10.1 | 3926 | 11.7 | −0.0899 |
| Metformin, n (%) | 4856 | 14.4 | 5151 | 15.3 | −0.0382 |
| Influenza vaccination, n (%) | 262 | 0.8 | 850 | 2.5 | −0.6587 |
| Dental procedures, n (%) | |||||
| Subgingival curettage | 770 | 2.3 | 983 | 2.9 | −0.1382 |
| Periodontal flap surgery | 235 | 0.7 | 262 | 0.8 | −0.0604 |
| Other periodontal procedures | 7022 | 20.9 | 11,702 | 34.8 | −0.3882 |
| Teeth extraction | 10,770 | 32.0 | 7991 | 23.8 | 0.2278 |
| Odontectomy | 576 | 1.7 | 454 | 1.4 | 0.1333 |
| Emergent dental care | 6134 | 18.2 | 8564 | 25.5 | −0.2350 |
| Dental Scaling | Control | Outcome Risk | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Outcome | Event, n | Crude Incidence Rate/1000 PY | Event, n | Crude Incidence Rate/1000 PY | IRR | cHR (95% CI) | p | aHR (95% CI) † | p |
| Primary outcome | |||||||||
| Progression to ESRD | 1296 | 4.61 | 1203 | 5.71 | 0.81 | 0.84 (0.78–0.91) | <0.0001 | 0.83 (0.77–0.90) | <0.0001 |
| Secondary outcomes | |||||||||
| MACE ‡ | 5275 | 20.04 | 4493 | 22.68 | 0.88 | 0.92 (0.89–0.96) | <0.0001 | 0.91 (0.87–0.95) | <0.0001 |
| Septicemia or sepsis | 3592 | 13.05 | 3290 | 15.97 | 0.82 | 0.81 (0.77–0.85) | <0.0001 | 0.81 (0.77–0.85) | <0.0001 |
| Urinary tract infection | 4639 | 17.40 | 4125 | 20.67 | 0.84 | 0.88 (0.84–0.92) | <0.0001 | 0.87 (0.83–0.91) | <0.0001 |
| Pyelonephritis | 2017 | 7.33 | 1935 | 9.36 | 0.78 | 0.89 (0.83–0.95) | 0.0002 | 0.87 (0.82–0.93) | <0.0001 |
| Acute renal failure | 1982 | 7.07 | 1978 | 9.41 | 0.75 | 0.75 (0.71–0.80) | <0.0001 | 0.76 (0.71–0.81) | <0.0001 |
| All-cause mortality | 1744 | 6.07 | 1576 | 7.29 | 0.83 | 0.79 (0.74–0.85) | <0.0001 | 0.81 (0.76–0.87) | <0.0001 |
| Variable | aHR (95% CI) | p |
|---|---|---|
| Dental scaling | 0.82 (0.75–0.88) | <0.0001 |
| Insurance premium (USD/month) | <0.0001 | |
| 501–800 vs. 0–500 | 0.84 (0.76–0.92) | 0.0002 |
| ≥801 vs. ≥0–500 | 0.43 (0.37–0.49) | <0.0001 |
| Stage 5 chronic kidney disease | 106.72 (58.23–195.58) | <0.0001 |
| Hypertension | 2.00 (1.83–2.19) | <0.0001 |
| Diabetes | 2.39 (2.13–2.67) | <0.0001 |
| Chronic obstruction pulmonary disease | 0.75 (0.66–0.86) | <0.0001 |
| Ischemic heart disease | 0.83 (0.75–0.93) | 0.0008 |
| Cardiac dysrhythmias | 0.69 (0.58–0.81) | <0.0001 |
| Heart failure | 1.61 (1.36–1.91) | <0.0001 |
| Dyslipidemia | 0.79 (0.71–0.87) | <0.0001 |
| Obesity | 0.44 (0.25–0.76) | 0.0031 |
| Mental disorders | 0.70 (0.64–0.78) | <0.0001 |
| Systemic antibiotics | 0.79 (0.72–0.86) | <0.0001 |
| Statins | 1.66 (1.48–1.87) | <0.0001 |
| Metformin | 1.18 (1.05–1.32) | 0.0062 |
| Influenza vaccination | 0.51 (0.32–0.82) | 0.0058 |
| Subgingival curettage | 0.70 (0.51–0.96) | 0.0282 |
| Other periodontal procedures | 0.71 (0.64–0.78) | <0.0001 |
| Odontectomy | 0.62 (0.35–1.09) | 0.0963 |
| Subgroup | DS or Control | Event, n | Crude Incidence Rate/1000 PY | IRR | cHR (95% CI) | p | aHR (95% CI) † | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age <65 years | DS | 834 | 3.87 | 0.75 | 0.79 (0.72–0.87) | <0.0001 | 0.79 (0.72–0.88) | <0.0001 |
| Control | 829 | 5.14 | reference | reference | reference | |||
| Age ≥65 years | DS | 462 | 7.02 | 0.92 | 0.95 (0.83–1.09) | 0.4294 | 0.93 (0.81–1.07) | 0.3187 |
| Control | 374 | 7.60 | reference | reference | reference | |||
| Male | DS | 642 | 4.61 | 0.80 | 0.84 (0.75–0.94) | 0.0018 | 0.83 (0.74–0.93) | 0.0010 |
| Control | 604 | 5.76 | reference | reference | reference | |||
| Female | DS | 654 | 4.61 | 0.81 | 0.84 (0.75–0.94) | 0.0026 | 0.84 (0.75–0.95) | 0.0037 |
| Control | 599 | 5.67 | reference | reference | reference | |||
| Periodontal disease | DS | 759 | 4.68 | 1.10 | 1.17 (1.04–1.32) | 0.0099 | 1.13 (1.00–1.28) | 0.0496 |
| Control | 456 | 4.26 | reference | reference | reference | |||
| No periodontal disease | DS | 537 | 4.52 | 0.63 | 0.64 (0.57–0.71) | <0.0001 | 0.64 (0.57–0.72) | <0.0001 |
| Control | 747 | 7.22 | reference | reference | reference | |||
| Hypertension | DS | 855 | 8.39 | 0.92 | 0.97 (0.87–1.07) | 0.5206 | 0.96 (0.87–1.07) | 0.4674 |
| Control | 685 | 9.10 | reference | reference | reference | |||
| No hypertension | DS | 441 | 2.46 | 0.64 | 0.66 (0.58–0.75) | <0.0001 | 0.68 (0.60–0.78) | <0.0001 |
| Control | 518 | 3.83 | reference | reference | reference | |||
| Diabetes mellitus | DS | 681 | 10.83 | 0.85 | 0.89 (0.79–0.99) | 0.0347 | 0.89 (0.79–0.99) | 0.0369 |
| Control | 586 | 12.77 | reference | reference | reference | |||
| No diabetes mellitus | DS | 615 | 2.82 | 0.75 | 0.77 (0.69–0.87) | <0.0001 | 0.80 (0.71–0.90) | 0.0002 |
| Control | 617 | 3.75 | reference | reference | reference | |||
| Systemic antibiotics | DS | 485 | 4.34 | 0.98 | 1.02 (0.89–1.18) | 0.7876 | 0.99 (0.86 –1.15) | 0.9352 |
| Control | 330 | 4.43 | reference | reference | reference | |||
| No systemic antibiotics | DS | 811 | 4.78 | 0.75 | 0.78 (0.71–0.86) | <0.0001 | 0.78 (0.70 –0.86) | <0.0001 |
| Control | 873 | 6.41 | reference | reference | reference | |||
| Statins | DS | 280 | 11.19 | 0.83 | 0.86 (0.73–1.02) | 0.0876 | 0.85 (0.71–1.02) | 0.0725 |
| Control | 268 | 13.54 | reference | reference | reference | |||
| No statins | DS | 1016 | 3.97 | 0.81 | 0.84 (0.77–0.92) | 0.0001 | 0.83 (0.76–0.91) | <0.0001 |
| Control | 935 | 4.90 | reference | reference | reference | |||
| Metformin | DS | 440 | 11.96 | 0.84 | 0.86 (0.75–0.99) | 0.0292 | 0.86 (0.74–0.99) | 0.0308 |
| Control | 397 | 14.27 | reference | reference | reference | |||
| No metformin | DS | 856 | 3.50 | 0.79 | 0.83 (0.75–0.91) | 0.0001 | 0.83 (0.75–0.92) | 0.0003 |
| Control | 806 | 4.41 | reference | reference | reference |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chung, Y.-H.; Kuo, H.-C.; Liu, H.-Y.; Wu, M.-Y.; Chang, W.-J.; Chen, J.-T.; Cherng, Y.-G.; Chen, T.-J.; Dai, Y.-X.; Wu, H.-L.; et al. Association between Dental Scaling and Reduced Risk of End-Stage Renal Disease: A Nationwide Matched Cohort Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8910. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18178910
Chung Y-H, Kuo H-C, Liu H-Y, Wu M-Y, Chang W-J, Chen J-T, Cherng Y-G, Chen T-J, Dai Y-X, Wu H-L, et al. Association between Dental Scaling and Reduced Risk of End-Stage Renal Disease: A Nationwide Matched Cohort Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(17):8910. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18178910
Chicago/Turabian StyleChung, Yu-Hsiang, Hsien-Cheng Kuo, Hsin-Yi Liu, Mei-Yi Wu, Wei-Jen Chang, Jui-Tai Chen, Yih-Giun Cherng, Tzeng-Ji Chen, Ying-Xiu Dai, Hsiang-Ling Wu, and et al. 2021. "Association between Dental Scaling and Reduced Risk of End-Stage Renal Disease: A Nationwide Matched Cohort Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 17: 8910. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18178910
APA StyleChung, Y.-H., Kuo, H.-C., Liu, H.-Y., Wu, M.-Y., Chang, W.-J., Chen, J.-T., Cherng, Y.-G., Chen, T.-J., Dai, Y.-X., Wu, H.-L., Liu, W.-C., & Tai, Y.-H. (2021). Association between Dental Scaling and Reduced Risk of End-Stage Renal Disease: A Nationwide Matched Cohort Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(17), 8910. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18178910








