Motor Function of Children with SMA1 and SMA2 Depends on the Neck and Trunk Muscle Strength, Deformation of the Spine, and the Range of Motion in the Limb Joints
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Examinations of Participants
2.3. Statistical Methods
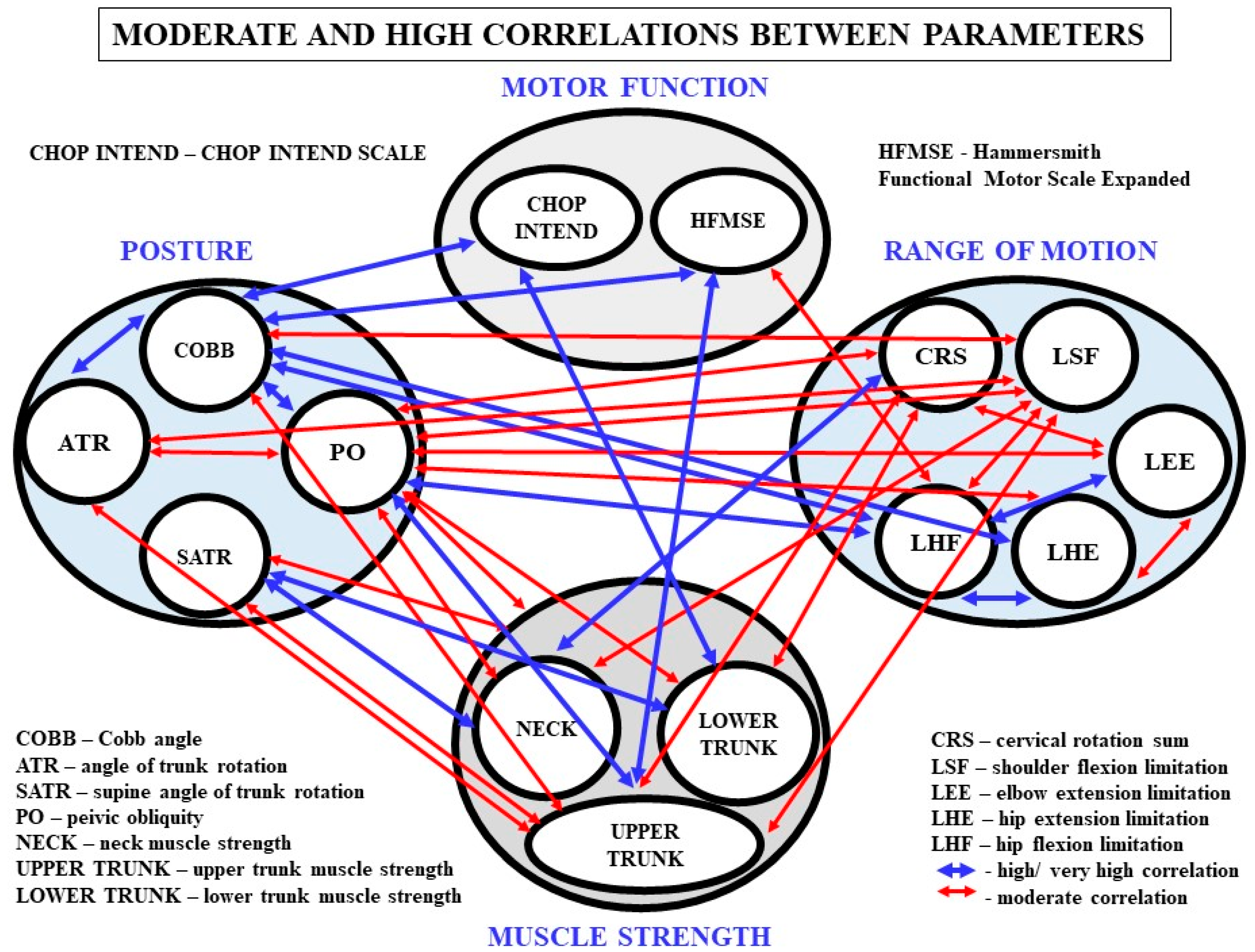
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of Ranges of Motion, Muscle Strength and Postural Parameters in Groups
3.2. Relationships between MF and Other Parameters in Groups
3.3. Relationships between Spinal Deformity, ROM and Muscle Strength
3.4. Relationships between Ranges of Motion
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lefebvre, S.; Buirglen, L.; Reboullet, S.; Clermont, O.; Burlet, P.; Viollet, L.; Benichou, B.; Cruaud, C.; Millasseau, F.; Zeviani, M.; et al. Identification and characterization of a spinal muscular atrophy-determining gene. Cell 1995, 80, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kroksmark, A.K.; Beckung, E.; Tulinius, M. Muscle strength and motor function in children and adolescents with spinal muscular atrophy II and III. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2001, 5, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Yang, Y.H.; Jong, Y.J. Evaluation of muscle strength in patients with spinal muscular atrophy. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2002, 18, 241–247. [Google Scholar]
- Merlini, L.; Bertini, E.; Minetti, C.; Mongini, T.; Morandi, L.; Angelini, C.; Vita, G. Motor function-muscle strength relationship in spinal muscular atrophy. Muscle Nerve 2004, 29, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Febrer, A.; Rodriguez, N.; Alias, L.; Tizzano, E. Measurement of muscle strength with a handheld dynamometer in patients with chronic spinal muscular atrophy. J. Rehabil. Med. 2010, 42, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaufmann, P.; McDermott, M.P.; Darras, B.T.; Finkel, R.S.; Sproule, D.M.; Kang, P.B.; Oskoui, M.; Constantinescu, A.; Gooch, C.L.; Foley, A.R.; et al. Prospective cohort study of spinal muscular atrophy types 2 and 3. Neurology 2012, 79, 1889–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujak, A.; Raab, W.; Schuh, A.; Richter, S.; Forst, R.; Forst, J. Natural course of scoliosis in proximal spinal muscular atrophy type II and IIIa: Descriptive clinical study with retrospective data collection of 126 patients. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2013, 14, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stępień, A.; Mazurkiewicz, Ł.; Maślanko, K.; Rekowski, W.; Jędrzejowska, M. Cervical rotation, chest deformity and pelvic obliquity in patients with spinal muscular atrophy. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2020, 21, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujak, A.; Kopschina, C.; Gras, F.; Forst, R.; Forst, J. Contractures of the upper extremities in spinal muscular atrophy type II. Descriptive clinical study with retrospective data collection. Ortop. Traumatol. Rehabil. 2010, 12, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stępień, A.; Sikora-Chojak, J.; Maślanko, K.; Kiebzak, W. Hip abduction and supported standing affect the ranges of hips extension in spinal muscular atrophy patients. Pol. Ann. Med. 2020, 28, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, G.T.; Abresch, R.T.; Fowler, W.M.; Johnson, E.R.; Kilmer, D.D.; McDonald, C.M. Profiles of neuromuscular diseases. Spinal muscular atrophy. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1995, 74, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mercuri, E.; Finkel, R.; Montes, J.; Mazzone, E.S.; Sormani, M.P.; Main, M.; Ramsey, D.; Mayhew, A.; Glanzman, A.M.; Dunaway, S.; et al. Patterns of disease progression in type 2 and 3 SMA: Implications for clinical trials. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2016, 26, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadman, R.I.; Wijngaarde, C.A.; Stam, M.; Bartels, B.; Otto, L.A.M.; Lemmink, H.H.; Schoenmakers, M.A.G.C.; Cuppen, I.; van den Berg, L.H.; van der Pol, W.L. Muscle strength and motor function throughout life in a cross-sectional cohort of 180 patients with spinal muscular atrophy types 1c-4. Eur. J. Neurol. 2018, 25, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercuri, E.; Darras, B.T.; Chiriboga, C.A.; Day, J.W.; Campbell, C.; Connolly, A.M.; Iannaccone, S.T.; Kirschner, J.; Kuntz, N.L.; Saito, K.; et al. Nusinersen versus Sham Control in Later-Onset Spinal Muscular Atrophy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 15, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claborn, M.K.; Stevens, D.L.; Walker, C.K.; Gildon, B.L. Nusinersen: A Treatment for Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Ann. Pharmacother. 2019, 53, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darras, B.T.; Chiriboga, C.A.; Iannaccone, S.T.; Swoboda, K.J.; Montes, J.; Mignon, L.; Xia, S.; Bennett, C.F.; Bishop, K.M.; Shefner, J.M.; et al. Nusinersen in later-onset spinal muscular atrophy: Long-term results from the phase 1/2 studies. Neurology 2019, 92, e2492–e2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wadman, R.I.; van der Pol, W.L.; Bosboom, W.M.; Asselman, F.L.; van den Berg, L.H.; Iannaccone, S.T.; Vrancken, A.F. Drug treatment for spinal muscular atrophy types II and III. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 6, CD006282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modrzejewska, S.; Kotulska, K.; Kopyta, I.; Grędowska, E.; Emich-Widera, E.; Tomaszek, K.; Paprocka, J.; Chmielewski, D.; Pilch, J.; Pietruszewski, J.; et al. Nusinersen treatment of Spinal Muscular Atrophy Type 1—Results of expanded access programme in Poland. Neurol. Neurochir. Pol. 2021, 55, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, S. Risdiplam: First Approval. Drugs 2020, 80, 1853–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.N.; Ottesen, E.W.; Singh, N.N. The First Orally Deliverable Small Molecule for the Treatment of Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Neurosci. Insights 2020, 15, 2633105520973985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glanzman, A.M.; Mazzone, E.; Main, M.; Pelliccioni, M.; Wood, J.; Swoboda, K.J.; Scott, C.; Pane, M.; Messina, S.; Bertini, E.; et al. The Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia Infant Test of Neuromuscular Disorders (CHOP INTEND): Test development and reliability. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2010, 20, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glanzman, A.M.; McDermott, M.P.; Montes, J.; Martens, W.B.; Flickinger, J.; Riley, S.; Quigley, J.; Dunaway, S.; O’Hagen, J.; Deng, L.; et al. Validation of the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia Infant Test of Neuromuscular Disorders (CHOP INTEND). Pediatr. Phys. Ther. 2011, 23, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krosschell, K.J.; Maczulski, J.A.; Crawford, T.O.; Scott, C.; Swoboda, K.J. A modified Hammersmith functional motor scale for use in multi-center research on spinal muscular atrophy. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2006, 16, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Glanzman, A.M.; O’Hagen, J.M.; McDermott, M.P.; Martens, W.B.; Flickinger, J.; Riley, S.; Quigley, J.; Montes, J.; Dunaway, S.; Deng, L.; et al. Validation of the Expanded Hammersmith Functional Motor Scale in spinal muscular atrophy type II and III. J. Child Neurol. 2011, 26, 1499–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krosschell, K.J.; Scott, C.B.; Maczulski, J.A.; Lewelt, A.J.; Reyna, S.P.; Swoboda, K.J. Reliability of the Modified Hammersmith Functional Motor Scale in young children with spinal muscular atrophy. Muscle Nerve 2011, 44, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Negrini, S.; Donzelli, S.; Aulisa, A.G.; Czaprowski, D.; Schreiber, S.; de Mauroy, J.C.; Diers, H.; Grivas, T.B.; Knott, P.; Kotwicki, T.; et al. 2016 SOSORT guidelines: Orthopaedic and rehabilitation treatment of idiopathic scoliosis during growth. Scoliosis Spinal Disord. 2018, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stępień, A.; Jędrzejowska, M.; Guzek, K.; Rekowski, W.; Stępowska, J. Reliability of four tests to assess body posture and the range of selected movements in individuals with spinal muscular atrophy. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2019, 20, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stępień, A.; Osiak, T.; Rekowski, W.; Wit, A. Neck and trunk muscle strength in children with spinal muscular atrophy is lower than in healthy controls and depends on disease type. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukaka, M.M. Statistics corner: A guide to appropriate use of correlation coefficient in medical research. Malawi Med. J. 2012, 24, 69–71. [Google Scholar]
- Salazar, R.; Montes, J.; Dunaway Young, S.; McDermott, M.P.; Martens, W.; Pasternak, A.; Quigley, J.; Mirek, E.; Glanzman, A.M.; Civitello, M.; et al. Quantitative Evaluation of Lower Extremity Joint Contractures in Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Implications for Motor Function. Pediatr. Phys. Ther. 2018, 30, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canavese, F.; Sussman, M.D. Strategies of hip management in neuromuscular disorders: Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy, Spi-nal Muscular Atrophy, Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease and Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita. Hip Int. 2009, 19 (Suppl. 6), 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullender, M.G.; Blom, N.A.; De Kleuver, M.; Fock, J.M.; Hitters, W.M.; Horemans, A.M.; Kalkman, C.J.; Pruijs, J.; Timmer, R.; Titarsolej, P.J.; et al. A Dutch guideline for the treatment of scoliosis in neuromuscular disorders. Scoliosis 2008, 3, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roberts, S.B.; Tsirikos, A.I. Factors influencing the evaluation and management of neuromuscular scoliosis: A review of the literature. J. Back Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 2016, 21, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercuri, E.; Bertini, E.; Iannaccone, S.T. Childhood spinal muscular atrophy: Controversies and challenges. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lager, C.; Kroksmark, A.K. Pain in adolescents with spinal muscular atrophy and Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2015, 19, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Engel-Hoek, L.; de Swart, B.J.; Erasmus, C.E.; de Groot, I.J. Is head balance a major determinant for swallowing problems in patients with spinal muscular atrophy type 2? J. Child Neurol. 2008, 23, 919–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canseco, J.A.; Schroeder, G.D.; Patel, P.D.; Grasso, G.; Chang, M.; Kandziora, F.; Vialle, E.N.; Oner, F.C.; Schnake, K.J.; Dvorak, M.F.; et al. Regional and experiential differences in surgeon preference for the treatment of cervical facet injuries: A case study survey with the AO Spine Cervical Classification Validation Group. Eur. Spine J. 2021, 30, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, A.; Amano, M.; Okamura, Y.; Numazawa, T.; Ueyama, K.; Nishikawa, S.; Toh, S. Muscle atrophy after treatment with Halovest. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2005, 1, E8–E12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Mean Values (±SD) Min-Max | All Participants (n = 27) | CHOP Group (n = 15) | HFMSE Group (n = 12) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age [years] | 5.23 ± 3.49 | 4.66 ± 3.39 | 5.95 ± 3.62 * |
| Min–Max | 0.80–14.40 | 0.80–13.50 | 2.50–14.40 |
| Body mass [kg] | 15.64 ± 8.73 | 12.71 ± 5.72 | 19.42 ± 10.47 ** |
| Min-Max | 6.00–37.00 | 6.00–27.00 | 10.00–37.00 |
| Body height [m] | 1.04 ± 0.22 | 0.99 ± 0.23 | 1.10 ± 0.20 * |
| Min-Max | 0.65–1.50 | 0.65–1.50 | 0.80–1.40 |
| Gender | |||
| Girls | 11 [40.7%] | 7 [46.7%] | 4 [33.3%] |
| Boys | 16 [59.3%] | 8 [53.3%] | 8 [66.7%] |
| Type of SMA [n] | |||
| SMA1 | 19 [70.4%] | 15 [100.0%] | 4 [33.3%] |
| SMA2 | 8 [29.6%] | - | 8 [66.7%] |
| Motor abilities [n] | |||
| Non-sitters | 13 [ 48.1%] | 13 [86.7%] | - |
| Sitters | 13 [48.1%] | 2 [13.3%] | 11 [91.7%] |
| Walkers | 1 [3.6%] | - | 1 [8.3%] |
| SMN2 copy number [n] | |||
| 2 copies | 13 [48.1%] | 12 [80.0%] | 1 [8.3%] |
| 3 copies | 12 [44.4%] | 3 [20.0%] | 9 [75.0%] |
| 4 copies | 2 [7.5%] | - | 2 [16.7%] |
| Hip subluxation | 19 [70.4%] | 12 [80.0%] | 7 [58.3%] |
| Scoliosis [n] | 16 [59.3%] | 10 [66.7%] | 6 [50.0%] |
| - single scoliosis | 10 [37.0%] | 6 [40.0%] | 4 [33.3%] |
| - double scoliosis | 6 [22.3%] | 4 [26.7%] | 2 [16.7%] |
| Mean Values (±SD) Min-Max | All Participants n = 27 | CHOP Group n = 15 | HFMSE Group n = 12 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Postural parameters | |||
| Cobb angle [°] | 38.20 ± 25.40 (n = 16) | 39.10 ± 28.20 (n = 10) | 36.83 ± 22.35 (n = 6) |
| Min-Max | 14.00–90.00 | 17.00–90.00 | 14.00–78.00 |
| ATRT [°] | 7.96 ± 9.37 | 10.29 ± 11.61 | 5.25 ± 5.05 |
| Min-Max | 0.00–40.00 | 0.00–40.00 | 0.00–13.00 |
| ATRL [°] | 3.19 ± 3.55 | 2.43 ± 2.34 | 4.08 ± 4.54 |
| Min-Max | 0.00–15.00 | 0.00–5.00 | 0.00–15.00 |
| SATRU [°] | 3.48 ± 3.25 | 3.67 ± 3.37 | 3.25 ± 3.22 |
| Min-Max | 0.00–11.00 | 0.00–10.00 | 0.00–11.00 |
| SATRL [°] | 2.81 ± 3.01 | 3.33 ± 3.64 | 2.17 ± 1.95 |
| Min-Max | 0.00–11.00 | 0.00–11.00 | 0.00–5.00 |
| PO [°] | 4.71 ± 3.58 (n = 14) | 1.00 ± 1.41 (n = 2) | 5.33 ± 3.47 (n = 12) |
| Min-Max | 0.00–12.00 | 0.00–2.00 | 1.00–12.00 |
| Ranges of motion | |||
| CRS [°] Min-Max | 60.89 ± 15.72 14.00–80.00 | 58.07 ± 18.22 14.00–80.00 | 64.42 ± 11.72 36.00–80.00 |
| LSF [°] Min-Max | 34.15 ± 57.48 0.00–170.00 | 57.20 ± 69.14 0.00–170.00 | 5.33 ± 9.70* 0.00–24.00 |
| LEE [°] Min-Max | 14.78 ± 25.08 0.00–80.00 | 19.80 ± 30.06 0.00–80.00 | 8.50 ± 6.12 0.00–54.00 |
| LHE [°] | 44.89 ± 44.98 | 44.60 ± 48.45 | 45.25 ± 42.36 |
| Min-Max | 0.00–129.00 | 0.00–129.00 | 0.00–92.00 |
| LHF [°] | 66.89 ± 45.45 | 72.13 ± 45.57 | 60.33 ± 46.43 |
| Min-Max | 0.00–146.00 | 0.00–146.00 | 0.00–134.00 |
| Motor function | |||
| MF score | - | 28.27 ± 14.04 | 21.67 ± 15.45 |
| Min-Max | - | 2.00–49.00 | 4.00–54.00 |
| Muscle strength [Nm/kg] | |||
| Neck | |||
| n = 13 | n = 7 | n = 6 | |
| NFL R & NFR R | 0.18 ± 0.06 & 0.18 ± 0.07 | 0.16 ± 0.05 & 0.15 ± 0.06 | 0.21 ± 0.08 * & 0.22 ± 0.08 |
| Min | 0.09 & 0.10 | 0.09 & 0.10 | 0.13 & 0.13 |
| Max | 0.34 & 0.33 | 0.22 & 0.27 | 0.34 & 0.33 |
| NEL R & NER R | 0.31 ± 0.12 & 0.32 ± 0.15 | 0.24 ± 0.09 & 0.23 ± 0.13 | 0.39 ± 0.11& 0.41 ± 0.12 |
| Min | 0.12 & 0.10 | 0.12 & 0.10 | 0.24 & 0.26 |
| Max | 0.58 & 0.58 | 0.39 & 0.45 | 0.58 & 0.58 |
| Scapula–upper trunk | |||
| SFL R & SFR R | 0.20 ± 0.09 & 0.25 ± 0.12 | 0.15 ± 0.07 & 0.18 ± 0.10 | 0.27 ± 0.07 * & 0.32 ± 0.09 * |
| Min | 0.07 & 0.07 | 0.07 & 0.07 | 0.19 & 0.19 |
| Max | 0.38 & 0.43 | 0.29 & 0.35 | 0.38 & 0.43 |
| SBL R & SBR R | 0.34 ± 0.20 & 0.28 ± 0.15 | 0.22 ± 0.07 & 0.20 ± 0.05 | 0.49 ± 0.21 ** & 0.37 ± 0.18 ** |
| Min | 0.12 & 0.11 | 0.12 & 0.11 | 0.30 & 0.24 |
| Max | 0.89 & 0.71 | 0.32 & 0.27 | 0.89 & 0.71 |
| Pelvis–lower trunk | |||
| PFL R & PFR R | 0.26 ± 0.12 & 0.28 ± 0.11 | 0.19 ± 0.07 & 0.23 ± 0.10 | 0.34 ± 0.13 * & 0.35 ± 0.08 |
| Min | 0.08 & 0.13 | 0.08 & 0.13 | 0.21 & 0.27 |
| Max | 0.55 & 0.48 | 0.29 & 0.37 | 0.55 & 0.48 |
| PBL R & PBR R | 0.54 ± 0.22 & 0.52 ± 0.16 | 0.41 ± 0.21 & 0.44 ± 0.14 | 0.70 ± 0.09 * & 0.62 ± 0.14 * |
| Min | 0.12 & 0.25 | 0.12 & 0.25 | 0.55 & 0.42 |
| Max | 0.78 & 0.75 | 0.67 & 0.62 | 0.78 & 0.75 |
| Muscle strength sum | |||
| RS | 3.68 ± 1.29 | 2.80 ± 0.66 | 4.70 ± 1.06 ** |
| Min-Max | 1.64–6.17 | 1.64–3.57 | 3.50–6.17 |
| Chop Intend (n = 7) | ||||||
| Muscle Strength | MF | CRS | LSF | LEE | LHE | LHF |
| NFL (Nm/kg) | −0.071 p = 0.879 | 0.071 p = 0.879 | −0.214 p = 0.645 | −0.036 p = 0.939 | 0.108 p = 0.818 | 0.643 p = 0.119 |
| NEL (Nm/kg) | 0.571 p = 0.180 | −0.036 p = 0.939 | −0.214 p = 0.645 | 0.643 p = 0.119 | 0.180 p = 0.699 | 0.786 * p = 0.036 |
| SFL (Nm/kg) | 0.360 p = 0.427 | −0.505 p = 0.248 | 0.108 p = 0.818 | 0.649 p = 0.115 | 0.555 p = 0.196 | 0.829 * p = 0.021 |
| SBL (Nm/kg) | 0.750 p = 0.052 | 0.000 p = 1.000 | −0.250 p = 0.589 | 0.286 p = 0.535 | −0.018 p = 0.969 | −0.286 p = 0.535 |
| PFL (Nm/kg | 0.090 p = 0.848 | −0.324 p = 0.478 | −0.054 p = 0.908 | 0.180 p = 0.699 | 0.900 ** p = 0.006 | 0.234 p = 0.613 |
| PBL (Nm/kg) | 0.750 p = 0.052 | −0.357 p = 0.432 | −0.036 p = 0.939 | 0.500 p = 0.253 | 0.216 p = 0.641 | −0.143 p = 0.760 |
| NFR (Nm/kg) | 0.721 p = 0.068 | −0.144 p = 0.758 | −0.072 p = 0.878 | 0.829 * p = 0.021 | −0.109 p = 0.816 | 0.559 p = 0.192 |
| NER (Nm/kg) | −0.071 p = 0.879 | 0.464 p = 0.294 | −0.107 p = 0.819 | 0.393 p = 0.383 | 0.180 p = 0.690 | 0.536 p = 0.215 |
| SFR (Nm/kg) | 0.357 p = 0.432 | −0.571 p = 0.180 | 0.393 p = 0.383 | 0.393 p = 0.383 | 0.306 p = 0.504 | −0.214 p = 0.645 |
| SBR (Nm/kg) | −0.107 p = 0.819 | 0.071 p = 0.879 | 0.071 p = 0.879 | 0.500 p = 0.253 | 0.378 p = 0.403 | 0.714 p = 0.071 |
| PFR (Nm/kg) | 0.144 p = 0.758 | −0.180 p = 0.699 | 0.360 p = 0.427 | 0.721 p = 0.068 | 0.700 p = 0.008 | 0.541 p = 0.210 |
| PBR (Nm/kg) | 0.821 * p = 0.023 | 0.000 p = 1.000 | −0.143 p = 0.760 | 0.714 p = 0.071 | −0.018 p = 0.969 | 0.250 p = 0.589 |
| Hammersmith Functional Motor Scale Expanded (n = 6) | ||||||
| Muscle strength | MF | CRS | LSF | LEE | LHE | LHF |
| NFL (Nm/kg) | 0.580 p = 0.228 | 0.870 * p = 0.024 | 0.000 p = 1.000 | −0.515 p = 0.296 | 0.261 p = 0.618 | 0.116 p = 0.827 |
| NEL (Nm/kg) | 0.600 p = 0.208 | 0.943 ** p = 0.005 | 0.135 p = 0.798 | −0.754 p = 0.084 | −0.143 p = 0.787 | −0.029 p = 0.957 |
| SFL (Nm/kg) | 0.714 p = 0.111 | −0.139 p = 0.666 | 0.270 p = 0.604 | −0.232 p = 0.658 | 0.086 p = 0.872 | 0.086 p = 0.872 |
| SBL (Nm/kg) | 0.829 * p = 0.042 | 0.943 ** p = 0.005 | −0.270 p = 0.604 | −0.725 p = 0.103 | −0.314 p = 0.544 | −0.429 p = 0.397 |
| PFL (Nm/kg) | 0.486 p = 0.329 | 0.600 p = 0.208 | 0.507 p = 0.305 | 0.116 p = 0.827 | 0.600 p = 0.208 | 0.371 p = 0.468 |
| PBL (Nm/kg) | 0.314 p = 0.544 | 0.771 p = 0.072 | −0.101 p = 0.848 | −0.928 ** p = 0.008 | −0.257 p = 0.623 | 0.029 p = 0.957 |
| NFR (Nm/kg) | 0.522 p = 0.288 | 0.696 p = 0.125 | 0.274 p = 0.599 | −0.088 p = 0.868 | 0.580 p = 0.228 | 0.290 p = 0.577 |
| NER (Nm/kg) | 0.486 p = 0.329 | 0.829 * p = 0.042 | 0.372 p = 0.468 | −0.580 p = 0.228 | −0.086 p = 0.872 | 0.143 p = 0.787 |
| SFR (Nm/kg) | 0.200 p = 0.704 | 0.771 p = 0.072 | 0.304 p = 0.558 | −0.812 * p = 0.050 | 0.086 p = 0.872 | 0.314 p = 0.544 |
| SBR (Nm/kg) | 0.714 p = 0.111 | 0.829 * p = 0.042 | −0.507 p = 0.305 | −0.841 * p = 0.036 | −0.486 p = 0.329 | −0.543 p = 0.266 |
| PFR (Nm/kg) | −0.257 p = 0.623 | 0.086 p = 0.872 | 0.372 p = 0.468 | −0.029 p = 0.957 | 0.829 * p = 0.042 | 0.543 p = 0.266 |
| PBR (Nm/kg) | 0.429 p = 0.397 | 0.886 * p = 0.019 | 0.135 p = 0.798 | −0.812 * p = 0.050 | −0.086 p = 0.872 | 0.143 p = 0.787 |
| Cobb(o) n = 16 | ATRT(o) n = 27 | ATRL(o) n = 27 | SATRU(o) n = 27 | SATRL(o) n = 27 | PO(o) n = 14 | CRS(o) n = 27 | LSF(o) n== 27 | LEE(o) n = 27 | LHE(o) n = 27 | LHF(o) n = 27 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATRT (o) n = 27 | 0.618 * p = 0.011 | NA | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| ATRL (o) n = 27 | 0.708 ** p = 0.002 | 0.501 ** p = 0.009 | NA | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| SATRU (o) n = 27 | 0.021 p = 0.940 | 0.257 p = 0.205 | 0.254 p = 0.210 | NA | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| SATRL (o) n = 27 | 0.353 p = 0.180 | 0.469 * p = 0.016 | 0.165 p = 0.420 | 0.078 p = 0.700 | NA | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| PO (o) n = 14 | 0.740 ** p = 0.001 | 0.537 ** p = 0.005 | 0.457 * p = 0.019 | 0.308 p = 0.126 | 0.155 p = 0.499 | NA | - | - | - | - | - |
| CRS (o) n = 27 | −0.410 p = 0.115 | −0.373 p = 0.061 | −0.224 p = 0.272 | −0.301 p = 0.128 | −0.358 p = 0.067 | −0.649 ** p = 0.000 | NA | - | - | - | - |
| LSF (o) n = 27 | 0.607 * p = 0.013 | 0.649 ** p = 0.000 | 0.337 p = 0.092 | 0.337 p = 0.092 | 0.418 * p = 0.030 | 0.646 ** p = 0.000 | −0.404 * p = 0.037 | NA | - | - | - |
| LEE (o) n = 27 | 0.483 p = 0.058 | 0.287 p = 0.155 | 0.217 p = 0.286 | 0.082 p = 0.683 | 0.417 * p = 0.030 | 0.612 ** p = 0.001 | −0.554 ** p = 0.003 | 0.479 * p = 0.011 | NA | - | - |
| LHE (o) n = 27 | 0.816 ** p = 0.001 | 0.241 p = 0.235 | 0.318 p = 0.113 | −0.081 p = 0.686 | 0.322 p = 0.101 | 0.665 ** p = 0.001 | −0.353 p = 0.070 | 0.428 * p = 0.026 | 0.675 ** p = 0.001 | NA | - |
| LHF (o) n = 27 | 0.718 ** p = 0.002 | 0.498 ** p = 0.010 | 0.497 ** p = 0.010 | −0.034 p = 0.868 | 0.253 p = 0.202 | 0.717 ** p = 0.001 | −0.401 * p = 0.038 | 0.509 ** p = 0.007 | 0.709 ** p = 0.001 | 0.742 ** p = 0.001 | NA |
| NFL (Nm/kg) n = 13 | −0.352 p = 0.261 | −0.295 p = 0.328 | 0.182 p = 0.551 | −0.370 p = 0.213 | −0.292 p = 0.333 | −0.266 p = 0.380 | 0.543 p = 0.055 | −0.396 p = 0.181 | −0.292 p = 0.333 | 0.076 p = 0.804 | 0.202 p = 0.507 |
| NEL (Nm/kg) n = 13 | −0.520 p = 0.083 | −0.412 p = 0.162 | −0.072 p = 0.816 | −0.603 * p = 0.029 | −0.166 p = 0.587 | −0.664 * p = 0.013 | 0.658 * p = 0.014 | −0.617 * p = 0.025 | −0.172 p = 0.575 | −0.127 p = 0.680 | 0.019 p = 0.950 |
| SFL (Nm/kg) n = 13 | −0.069 p = 0.831 | −0.282 p = 0.350 | 0.208 p = 0.495 | −0.446 p = 0.126 | 0.150 p = 0.626 | −0.321 p = 0.285 | 0.306 p = 0.310 | −0.430 p = 0.142 | −0.058 p = 0.850 | 0.164 p = 0.592 | 0.114 p = 0.710 |
| SBL (Nm/kg) n = 13 | −0.589 * p = 0.044 | −0.564 * p = 0.045 | −0.136 p = 0.657 | −0.502 p = 0.081 | 0.013 p = 0.967 | −0.842 ** p = 0.001 | 0.588 * p = 0.034 | −0.659 * p = 0.014 | −0.349 p = 0.243 | −0.239 p = 0.432 | −0.516 p = 0.071 |
| PFL (Nm/kg) n = 13 | 0.172 p = 0.594 | −0.232 p = 0.445 | 0.478 p = 0.099 | −0.330 p = 0.271 | 0.346 p = 0.247 | −0.355 p = 0.233 | 0.430 p = 0.143 | −0.342 p = 0.252 | −0.111 p = 0.719 | 0.415 p = 0.158 | 0.012 p = 0.968 |
| PBL (Nm/kg) n = 13 | −0.442 p = 0.151 | −0.221 p = 0.468 | −0.247 p = 0.416 | −0.505 p = 0.078 | 0.296 p = 0.326 | −0.638 * p = 0.019 | 0.380 p = 0.201 | −0.492 p = 0.088 | −0.276 p = 0.361 | −0.182 p = 0.552 | −0.350 p = 0.241 |
| NFR (Nm/kg) n = 13 | −0.349 p = 0.261 | −0.398 p = 0.178 | 0.054 p = 0.862 | −0.723 ** p = 0.005 | 0.091 p = 0.768 | −0.524 p = 0.066 | 0.492 p = 0.088 | −0.467 p = 0.108 | 0.192 p = 0.530 | −0.062 p = 0.839 | 0.207 p = 0.498 |
| NER (Nm/kg) n = 13 | −0.257 p = 0.421 | −0.188 p = 0.538 | 0.055 p = 0.859 | −0.250 p = 0.410 | 0.003 p = 0.993 | −0.598 * p = 0.031 | 0.769 ** p = 0.002 | −0.549 p = 0.052 | −0.158 p = 0.607 | −0.086 p = 0.781 | 0.074 p = 0.809 |
| SFR (Nm/kg) n = 13 | −0.226 p = 0.480 | −0.055 p = 0.858 | −0.006 p = 0.985 | −0.599 * p = 0.031 | 0.442 p = 0.130 | −0.445 p = 0.128 | 0.327 p = 0.275 | −0.164 p = 0.593 | −0.199 p = 0.515 | −0.008 p = 0.979 | −0.179 p = 0.558 |
| SBR (Nm/kg) n = 13 | −0.274 p = 0.388 | −0.279 p = 0.355 | 0.086 p = 0.781 | −0.148 p = 0.630 | −0.020 p = 0.949 | −0.613 * p = 0.026 | 0.534 p = 0.060 | −0.662 * p = 0.014 | −0.321 p = 0.285 | −0.080 p = 0.795 | −0.228 p = 0.455 |
| PFR (Nm/kg) n = 13 | 0.294 p = 0.353 | 0.044 p = 0.886 | 0.339 p = 0.257 | −0.498 p = 0.083 | 0.527 p = 0.064 | −0.325 p = 0.278 | 0.276 p = 0.362 | −0.159 p = 0.605 | 0.080 p = 0.794 | 0.464 p = 0.110 | 0.115 p = 0.709 |
| PBR (Nm/kg) n = 13 | −0.505 p = 0.094 | −0.331 p = 0.269 | −0.168 p = 0.582 | −0.701 ** p = 0.008 | 0.169 p = 0.581 | −0.685 ** p = 0.010 | 0.605 * p = 0.028 | −0.537 p = 0.058 | −0.122 p = 0.692 | −0.198 p = 0.516 | −0.063 p = 0.837 |
| RS (Nm/kg) n = 13 | −0.329 p = 0.296 | −0.335 p = 0.264 | 0.022 p = 0.942 | −0.588 * p = 0.034 | 0.206 p = 0.500 | −0.643 * p = 0.018 | 0.537 p = 0.058 | −0.549 p = 0.052 | −0.113 p = 0.712 | −0.055 p = 0.858 | −0.084 p = 0.785 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stępień, A.; Gajewska, E.; Rekowski, W. Motor Function of Children with SMA1 and SMA2 Depends on the Neck and Trunk Muscle Strength, Deformation of the Spine, and the Range of Motion in the Limb Joints. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9134. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18179134
Stępień A, Gajewska E, Rekowski W. Motor Function of Children with SMA1 and SMA2 Depends on the Neck and Trunk Muscle Strength, Deformation of the Spine, and the Range of Motion in the Limb Joints. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(17):9134. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18179134
Chicago/Turabian StyleStępień, Agnieszka, Ewa Gajewska, and Witold Rekowski. 2021. "Motor Function of Children with SMA1 and SMA2 Depends on the Neck and Trunk Muscle Strength, Deformation of the Spine, and the Range of Motion in the Limb Joints" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 17: 9134. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18179134
APA StyleStępień, A., Gajewska, E., & Rekowski, W. (2021). Motor Function of Children with SMA1 and SMA2 Depends on the Neck and Trunk Muscle Strength, Deformation of the Spine, and the Range of Motion in the Limb Joints. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(17), 9134. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18179134







