Incidence of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Diagnoses in Navarre (Spain) from 2003 to 2019
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Participants and Follow-Up
2.3. ADHD Diagnostic Codes and Study Variables
2.4. Data Analyses
2.4.1. ADHD Incidence
2.4.2. ADHD Prevalence
2.5. Study Approval
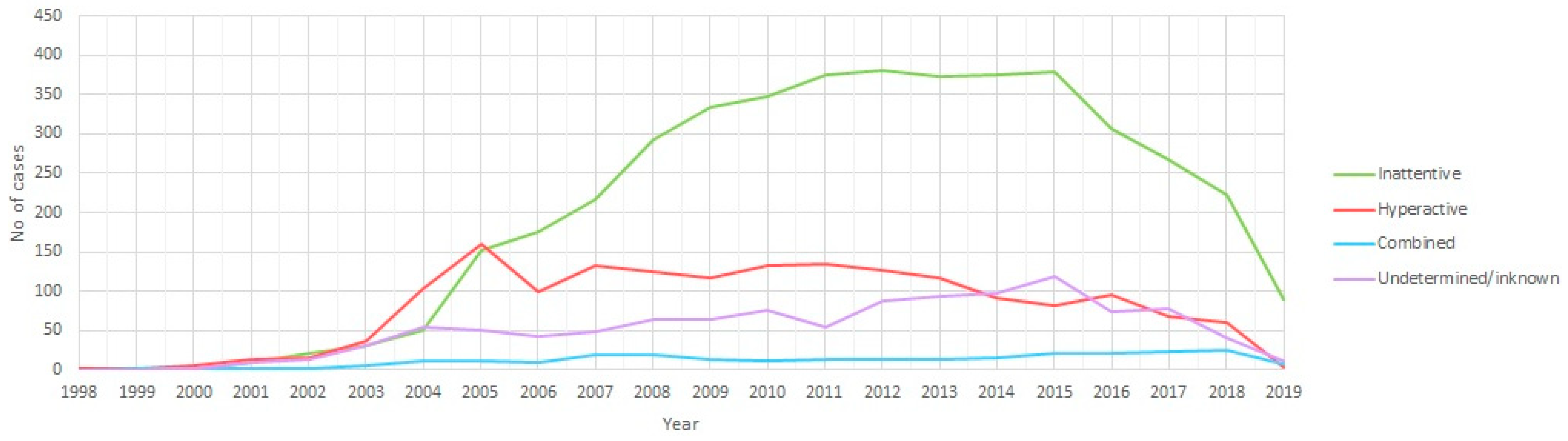
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Arlington, VA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Thapar, A.; Cooper, M. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Lancet 2016, 387, 1240–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiz, L.C. Psicoestimulantes para el TDAH: Análisis integral para una medicina basada en la prudencia. Rev. Asoc. Esp. Neuropsiq 2018, 38, 301–330. [Google Scholar]
- Döpfner, M.; Breuer, D.; Wille, N.; Erhart, M.; Ravens-Sieberer, U. How often do children meet ICD-10/DSM-IV criteria of attention deficit-/hyperactivity disorder and hyperkinetic disorder? Parent-based prevalence rates in a national sample—Results of the BELLA study. Eur. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2008, 17, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayal, K.; Chudal, R.; Hinkka-Yli-Salomäki, S.; Joelsson, P.; Sourander, A. Relative age within the school year and diagnosis of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: A nationwide population-based study. Lancet Psychiatry 2017, 4, 868–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, R.L.; Garland, E.J.; Wright, J.M.; Maclure, M.; Taylor, S.; Dormuth, C.R. Influence of relative age on diagnosis and treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2012, 184, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russell, A.E.; Ford, T.; Russell, G. Socioeconomic associations with ADHD: Findings from a mediation analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, A.S.; Skipper, B.J.; Rabiner, D.L.; Qeadan, F.; Campbell, R.A.; Naftel, A.J.; Umbach, D.M. Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): Interaction between socioeconomic status and parental history of ADHD determines prevalence. J. Child. Psychol. Psychiatry Allied Discip. 2018, 59, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Shin, J.; Cho, K.H.; Park, E.C. Change in household income and risk for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder during childhood: A nationwide population-based cohort study. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 27, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cénat, J.M.; Blais-Rochette, C.; Morse, C.; Vandette, M.P.; Noorishad, P.G.; Kogan, C.; Ndengeyingoma, A.; Labelle, P.R. Prevalence and Risk Factors Associated with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder among US Black Individuals: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry 2021, 78, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kooij, J.J.S.; Bijlenga, D.; Salerno, L.; Jaeschke, R.; Bitter, I.; Balázs, J.; Thome, J.; Dom, G.; Kasper, S.; Nunes Filipe, C.; et al. Updated European Consensus Statement on diagnosis and treatment of adult ADHD. Eur. Psychiatry 2019, 56, 14–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinshaw, S.P.; Nguyen, P.T.; O’Grady, S.M.; Rosenthal, E.A. Annual Research Review: Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in girls and women: Underrepresentation, longitudinal processes, and key directions. J. Child. Psychol. Psychiatry Allied Discip. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Huang, K.; Hsu, J.; Tsai, S.; Su, T.; Chen, T.; Bai, Y. Effect of Relative Age on Childhood Mental Health: A Cohort of 9,548,393 Children and Adolescents. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2021, 144, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posner, J.; Polanczyk, G.V.; Sonuga-Barke, E. Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Lancet 2020, 395, 450–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.; Sanders, S.; Doust, J.; Beller, E.; Glasziou, P. Prevalence of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatrics 2015, 135, e994–e1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Polanczyk, G.; De Lima, M.S.; Horta, B.L.; Biederman, J.; Rohde, L.A. The worldwide prevalence of ADHD: A systematic review and metaregression analysis. Am. J. Psychiatry 2007, 164, 942–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanczyk, G.V.; Salum, G.A.; Sugaya, L.S.; Caye, A.; Rohde, L.A. Annual research review: A meta-analysis of the worldwide prevalence of mental disorders in children and adolescents. J. Child. Psychol. Psychiatry Allied Discip. 2015, 56, 345–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barican, J.L.; Yung, D.; Schwartz, C.; Zheng, Y.; Georgiades, K.; Waddell, C. Prevalence of childhood mental disorders in high-income countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis to inform policymaking. Evid. Based. Ment. Health 2021, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akmatov, M.K.; Steffen, A.; Holstiege, J.; Hering, R.; Schulz, M.; Bätzing, J. Trends and regional variations in the administrative prevalence of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder among children and adolescents in Germany. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalá-López, F.; Peiró, S.; Ridao, M.; Sanfélix-Gimeno, G.; Gènova-Maleras, R.; Catalá, M.A. Prevalence of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder among children and adolescents in Spain: A systematic review and meta-analysis of epidemiological studies. BMC Psychiatry 2012, 12, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vasiliadis, H.M.; Diallo, F.B.; Rochette, L.; Smith, M.; Langille, D.; Lin, E.; Kisely, S.; Fombonne, E.; Thompson, A.H.; Renaud, J.; et al. Temporal Trends in the Prevalence and Incidence of Diagnosed ADHD in Children and Young Adults between 1999 and 2012 in Canada: A Data Linkage Study. Can. J. Psychiatry 2017, 62, 818–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cybulski, L.; Ashcroft, D.M.; Carr, M.J.; Garg, S.; Chew-Graham, C.A.; Kapur, N.; Webb, R.T. Temporal trends in annual incidence rates for psychiatric disorders and self-harm among children and adolescents in the UK, 2003–2018. BMC Psychiatry 2021, 21, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hire, A.J.; Ashcroft, D.M.; Springate, D.A.; Steinke, D.T. ADHD in the United Kingdom: Regional and Socioeconomic Variations in Incidence Rates Amongst Children and Adolescents (2004-2013). J. Atten. Disord. 2018, 22, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, C.M.; Steinhausen, H.C. Time trends in incidence rates of diagnosed attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder across 16 years in a nationwide Danish registry study. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2015, 76, e334–e341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, I.C.; Lin, C.H.; Chou, Y.J.; Chou, P. Prevalence, incidence, and stimulant use of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in Taiwan, 1996-2005: A national population-based study. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2012, 47, 1885–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Crespo, L.; Canals-Sans, J.; Suades-González, E.; Guxens, M. Temporal trends and geographical variability of the prevalence and incidence of attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder diagnoses among children in Catalonia, Spain. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raman, S.R.; Man, K.K.C.; Bahmanyar, S.; Berard, A.; Bilder, S.; Boukhris, T.; Bushnell, G.; Crystal, S.; Furu, K.; KaoYang, Y.H.; et al. Trends in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder medication use: A retrospective observational study using population-based databases. Lancet Psychiatry 2018, 5, 824–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, H.A.; Savitsky, B.; Ashkenasi, A.; Hoshen, M. Seasonality of Methylphenidate Administration among Children in Israel. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. 2016, 18, 655–660. [Google Scholar]
- Shyu, Y.C.; Lee, S.Y.; Yuan, S.S.; Yang, C.J.; Yang, K.C.; Lee, T.L.; Wang, L.J. Seasonal Patterns of Medications for Treating Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: Comparison of Methylphenidate and Atomoxetine. Clin. Ther. 2016, 38, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carstensen, B. Age-period-cohort models for the Lexis diagram. Stat. Med. 2007, 26, 3018–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2012; Available online: http://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 31 March 2021).
- Carstensen, B.; Plummer, M.; Laara, E.; Hills, M. Epi: A Package for Statistical Analysis in Epidemiology. R Package Version 2.44. 2021. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=Epi (accessed on 31 March 2021).
- Davidovitch, M.; Koren, G.; Fund, N.; Shrem, M.; Porath, A. Challenges in defining the rates of ADHD diagnosis and treatment: Trends over the last decade. BMC Pediatr. 2017, 17, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dalsgaard, S.; Thorsteinsson, E.; Trabjerg, B.B.; Schullehner, J.; Plana-Ripoll, O.; Brikell, I.; Wimberley, T.; Thygesen, M.; Madsen, K.B.; Timmerman, A.; et al. Incidence Rates and Cumulative Incidences of the Full Spectrum of Diagnosed Mental Disorders in Childhood and Adolescence. JAMA Psychiatry 2020, 77, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
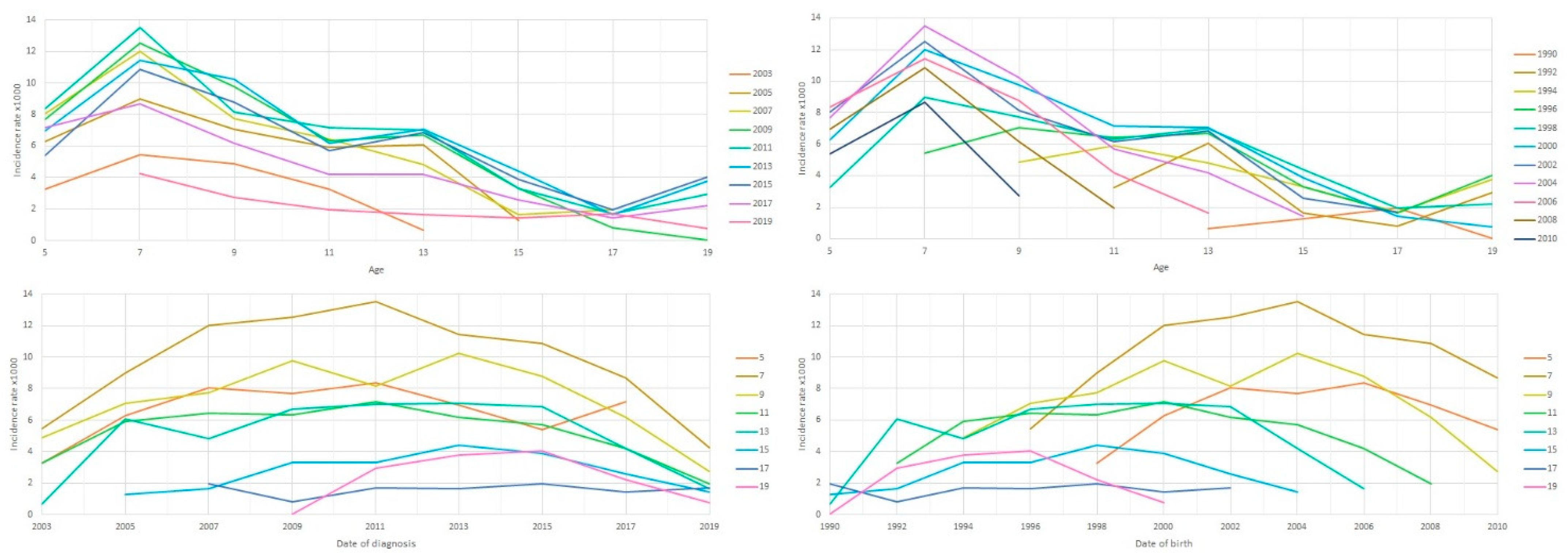


| Calendar Year | Age at the Time of ADHD Diagnosis (Years) | Incidence Rate (Per 1000 Persons) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | Males | Females | |||
| 2003 | 5 | 3.26 | 4.76 | 1.69 | <0.01 |
| 7 | 5.42 | 8.53 | 2.26 | <0.01 | |
| 9 | 4.85 | 8.26 | 1.22 | <0.01 | |
| 11 | 3.27 | 5.25 | 1.06 | <0.01 | |
| 13 | 0.63 | 1.18 | 0.00 | -- | |
| 15 | -- | -- | -- | -- | |
| 17 | -- | -- | -- | -- | |
| 19 | -- | -- | -- | -- | |
| 2005 | 5 | 6.29 | 9.90 | 2.52 | <0.01 |
| 7 | 8.99 | 13.08 | 4.77 | <0.01 | |
| 9 | 7.05 | 11.07 | 3.02 | <0.01 | |
| 11 | 5.91 | 9.30 | 2.35 | <0.01 | |
| 13 | 6.07 | 10.64 | 1.07 | <0.01 | |
| 15 | 1.27 | 2.41 | 0.00 | -- | |
| 17 | -- | -- | -- | -- | |
| 19 | -- | -- | -- | -- | |
| 2007 | 5 | 8.07 | 11.71 | 4.35 | <0.01 |
| 7 | 12.02 | 17.15 | 6.77 | <0.01 | |
| 9 | 7.73 | 11.69 | 3.73 | <0.01 | |
| 11 | 6.41 | 9.61 | 3.26 | <0.01 | |
| 13 | 4.81 | 8.01 | 1.51 | <0.01 | |
| 15 | 1.65 | 2.35 | 0.91 | 0.07 | |
| 17 | 1.96 | 2.50 | 1.36 | 1 | |
| 19 | -- | -- | -- | -- | |
| 2009 | 5 | 7.69 | 11.37 | 3.82 | <0.01 |
| 7 | 12.50 | 17.47 | 7.54 | <0.01 | |
| 9 | 9.77 | 13.15 | 6.35 | <0.01 | |
| 11 | 6.34 | 9.96 | 2.74 | <0.01 | |
| 13 | 6.67 | 9.54 | 3.89 | <0.01 | |
| 15 | 3.29 | 3.76 | 2.82 | 0.33 | |
| 17 | 0.81 | 1.04 | 0.56 | 0.51 | |
| 19 | -- | -- | -- | -- | |
| 2011 | 5 | 8.34 | 12.48 | 4.11 | <0.01 |
| 7 | 13.49 | 19.00 | 7.83 | <0.01 | |
| 9 | 8.16 | 10.14 | 6.22 | <0.01 | |
| 11 | 7.16 | 10.16 | 4.17 | <0.01 | |
| 13 | 6.99 | 10.51 | 3.53 | <0.01 | |
| 15 | 3.31 | 4.62 | 2.04 | <0.01 | |
| 17 | 1.69 | 2.45 | 0.92 | 0.03 | |
| 19 | 2.95 | 3.61 | 2.24 | 0.36 | |
| 2013 | 5 | 6.96 | 9.52 | 4.26 | <0.01 |
| 7 | 11.43 | 15.15 | 7.68 | <0.01 | |
| 9 | 10.21 | 14.41 | 5.99 | <0.01 | |
| 11 | 6.19 | 9.52 | 2.94 | <0.01 | |
| 13 | 7.08 | 10.74 | 3.48 | <0.01 | |
| 15 | 4.42 | 6.47 | 2.44 | <0.01 | |
| 17 | 1.65 | 2.01 | 1.31 | 0.29 | |
| 19 | 3.75 | 6.00 | 1.50 | <0.01 | |
| 2015 | 5 | 5.38 | 8.22 | 2.42 | <0.01 |
| 7 | 10.84 | 15.41 | 6.09 | <0.01 | |
| 9 | 8.78 | 11.90 | 5.67 | <0.01 | |
| 11 | 5.69 | 8.47 | 2.92 | <0.01 | |
| 13 | 6.85 | 10.49 | 3.37 | <0.01 | |
| 15 | 3.87 | 4.61 | 3.16 | 0.1 | |
| 17 | 1.96 | 2.27 | 1.67 | 0.42 | |
| 19 | 4.01 | 5.96 | 2.19 | <0.01 | |
| 2017 | 5 | 7.16 | 11.06 | 3.04 | <0.01 |
| 7 | 8.66 | 13.05 | 4.15 | <0.01 | |
| 9 | 6.16 | 7.94 | 4.33 | <0.01 | |
| 11 | 4.19 | 5.82 | 2.58 | <0.01 | |
| 13 | 4.18 | 6.17 | 2.22 | <0.01 | |
| 15 | 2.59 | 3.12 | 2.10 | 0.18 | |
| 17 | 1.45 | 1.34 | 1.55 | 0.85 | |
| 19 | 2.19 | 3.19 | 1.26 | 0.07 | |
| 2019 | 5 | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| 7 | 4.23 | 5.91 | 2.49 | 0.03 | |
| 9 | 2.71 | 4.27 | 1.14 | <0.01 | |
| 11 | 1.96 | 2.76 | 1.16 | 0.14 | |
| 13 | 1.64 | 2.21 | 1.08 | 0.2 | |
| 15 | 1.43 | 2.45 | 0.50 | 0.03 | |
| 17 | 1.71 | 1.87 | 1.57 | 1 | |
| 19 | 0.76 | 0.86 | 0.69 | 1 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leache, L.; Arrizibita, O.; Gutiérrez-Valencia, M.; Saiz, L.C.; Erviti, J.; Librero, J. Incidence of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Diagnoses in Navarre (Spain) from 2003 to 2019. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9208. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18179208
Leache L, Arrizibita O, Gutiérrez-Valencia M, Saiz LC, Erviti J, Librero J. Incidence of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Diagnoses in Navarre (Spain) from 2003 to 2019. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(17):9208. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18179208
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeache, Leire, Olast Arrizibita, Marta Gutiérrez-Valencia, Luis Carlos Saiz, Juan Erviti, and Julián Librero. 2021. "Incidence of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Diagnoses in Navarre (Spain) from 2003 to 2019" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 17: 9208. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18179208
APA StyleLeache, L., Arrizibita, O., Gutiérrez-Valencia, M., Saiz, L. C., Erviti, J., & Librero, J. (2021). Incidence of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Diagnoses in Navarre (Spain) from 2003 to 2019. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(17), 9208. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18179208






