Does the Summer Season Affect the Amniotic Fluid Volume during Pregnancy?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
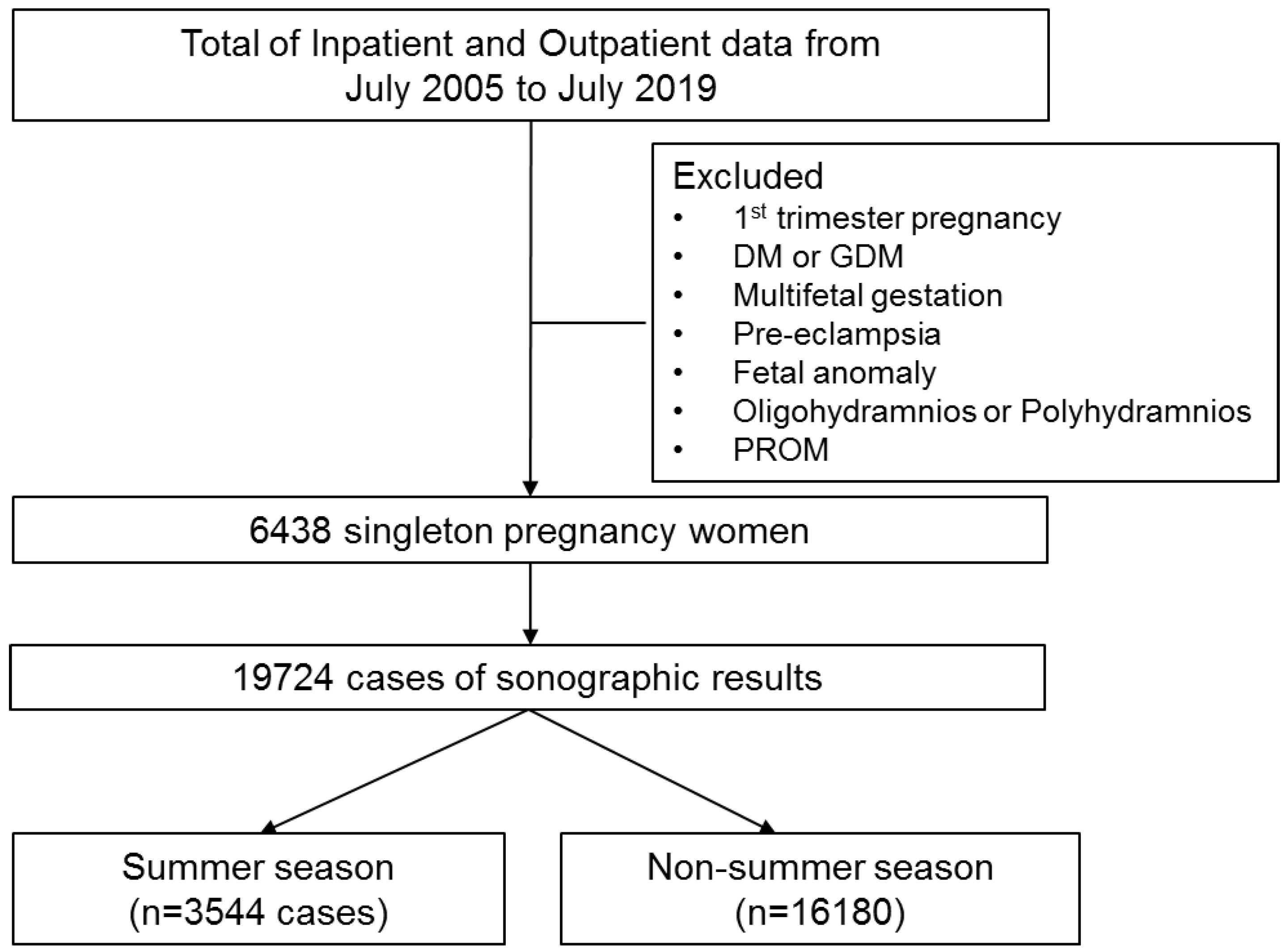
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Measuring AFI According to the Seasons
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moore, T.R.; Cayle, J.E. The Amniotic Fluid Index in Normal Human Pregnancy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1990, 162, 1168–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brace, R.; Wolf, E. Normal Amniotic Fluid Volume Changes Throughout Pregnancy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1989, 161, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, T.R. Amniotic Fluid Dynamics Reflect Fetal and Maternal Health and Disease. Obstet. Gynecol. 2010, 116, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phelan, J.P.; Smith, C.V.; Broussard, P.; Small, M. Amniotic Fluid Volume Assessment with the Four-Quadrant Technique at 36-42 Weeks’ Gestation. J. Reprod. Med. 1987, 32, 540–542. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moore, T.R. Clinical Assessment of Amniotic Fluid. Clin. Obstet. Gynecol. 1997, 40, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American College of Obstetrics and Gynecologists. Practice Bulletin 175: Ultrasound in Pregnancy. Obstet. Gyneocol. 2016, 128, e241–e256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutherford, S.E.; Phelan, J.P.; Smith, C.V.; Jacobs, N. The Four-Quadrant Assessment of Amniotic Fluid Volume: An Adjunct to Antepartum Fetal Heart Rate Testing. Obstet. Gynecol. 1987, 70, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Magann, E.F.; Chauhan, S.P.; Hitt, W.C.; Dubil, E.A.; Morrison, J.C. Borderline or Marginal Amniotic Fluid Index and Peripartum Outcomes: A Review of the Literature. J. Ultrasound Med. 2011, 30, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelan, J.P.; Ahn, M.O.; Smith, C.V.; Rutherford, S.E.; Anderson, E. Amniotic Fluid Index Measurements during Pregnancy. J. Reprod. Med. 1987, 32, 601–604. [Google Scholar]
- Petrozella, L.N.; Dashe, J.S.; McIntire, D.D.; Leveno, K.J. Clinical Significance of Borderline Amniotic Fluid Index and Oligohydramnios in Preterm Pregnancy. Obstet. Gynecol. 2011, 117, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumus, I.I.; Koktener, A.; Turhan, N.O. Perinatal Outcomes of Pregnancies with Borderline Amniotic Fluid Index. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2007, 276, 17–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Frias, M.L.; Bermejo, E.; Rodriguez-Pinilla, E.; Frias, J.L. Maternal and Fetal Factors Related to Abnormal Amniotic Fluid. J. Perinatol. 1999, 19, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hofmeyr, G.J.; Gulmezoglu, A.M. Maternal Hydration for Increasing Amniotic Fluid Volume in Oligohydramnios and Normal Amniotic Fluid Volume. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullo, M.; Tschumi, S.; Bucher, B.S.; Bianchetti, M.G.; Simonetti, G.D. Pregnancy Outcome Following Exposure to Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors or Angiotensin Receptor Antagonists: A Systematic Review. Hypertension 2012, 60, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Locatelli, A.; Vergani, P.; Toso, L.; Verderio, M.; Pezzullo, J.C.; Ghidini, A. Perinatal Outcome Associated with Oligohydramnios in Uncomplicated Term Pregnancies. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2004, 269, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahin, E.; Madendag, Y.; Tayyar, A.T.; Sahin, M.E.; Col Madendag, I.; Acmaz, G.; Unsal, D.; Senol, V. Perinatal Outcomes in Uncomplicated Late Preterm Pregnancies with Borderline Oligohydramnios. J. Matern. Fetal. Neonatal Med. 2018, 31, 3085–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisell, H.; Ek, S. Perinatal Risks Associated with Borderline Amniotic Fluid Index. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2000, 182, 750–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, B.M.; McIntire, D.D.; Bloom, S.L.; Lucas, M.J.; Santos, R.; Twickler, D.M.; Ramus, R.M.; Leveno, K.J. Pregnancy Outcomes After Antepartum Diagnosis of Oligohydramnios at or Beyond 34 Weeks’ Gestation. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2000, 182, 909–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreyer, P.; Sherman, D.J.; Ervin, M.G.; Day, L.; Ross, M.G. Maternal Dehydration: Impact on Ovine Amniotic Fluid Volume and Composition. J. Dev. Physiol. 1990, 13, 283–287. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.W.; Jin, Y.; Jang, E.B.; Kim, H.S.; Sohn, I.S.; Kwon, H.S.; Hwang, H.S. Management of Isolated Oligohydramnios in Korea: A Questionnaire-Based Study of Clinical Practice Patterns among the Members of the Korean Society of Maternal Fetal Medicine. Obstet. Gynecol. Sci. 2020, 63, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luton, D.; Alran, S.; Fourchotte, V.; Sibony, O.; Oury, J.F. Paris Heat Wave and Oligohydramnios. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2004, 191, 2103–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamyabi, Z.; Naderi, T. The Effect of Ramadan Fasting on Amniotic Fluid Volume. Saudi Med. J. 2004, 25, 45–46. [Google Scholar]
- Korea Meteological Administration. 2021. Available online: https://data.kma.go.kr/climate/RankState/selectRankStatisticsDivisionList.do?pgmNo=179 (accessed on 8 September 2021).
- Gizzo, S.; Noventa, M.; Vitagliano, A.; Dall’Asta, A.; D’Antona, D.; Aldrich, C.J.; Quaranta, M.; Frusca, T.; Patrelli, T.S. An Update on Maternal Hydration Strategies for Amniotic Fluid Improvement in Isolated Oligohydramnios and Normohydramnios: Evidence from a Systematic Review of Literature and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Battaglia, F.; Lubchenco, L. A Practical Classification of Newborn Infants by Weight and Gestational Age. J. Pediatr. 1967, 71, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, S.; Moser, C.; Baack, M. Respiratory Distress in the Newborn. Pediatr. Rev. 2014, 35, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dargaville, P.A.; Copnell, B. The Epidemiology of Meconium Aspiration Syndrome: Incidence, Risk Factors, Therapies, and Outcome. Pediatrics 2006, 117, 1712–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magann, E.F.; Sanderson, M.; Martin, J.N.; Chauhan, S. The Amniotic Fluid Index, Single Deepest Pocket, and Two-Diameter Pocket in Normal Human Pregnancy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2000, 182, 1581–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallak, M.; Kirshon, B.; Smith, E.O.; Cotton, D.B. Amniotic Fluid Index. Gestational Age-Specific Values for Normal Human Pregnancy. J. Reprod. Med. 1993, 38, 853–856. [Google Scholar]
- Feldman, I.; Friger, M.; Wiznitzer, A.; Mazor, M.; Holcberg, G.; Sheiner, E. Is Oligohydramnios More Common during the Summer Season? Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2009, 280, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebbar, S.; Rai, L.; Adiga, P.; Guruvare, S. Reference Ranges of Amniotic Fluid Index in Late Third Trimester of Pregnancy: What should the Optimal Interval between Two Ultrasound Examinations be? J. Pregnancy 2015, 2015, 319204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwon, J.Y.; Kwon, H.S.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, Y.W. Abnormal Doppler Velocimetry is Related to Adverse Perinatal Outcome for Borderline Amniotic Fluid Index during Third Trimester. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2006, 32, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, S.L.; Newton, J.M.; Wang, L.; Lesser, K. Borderline Amniotic Fluid Index and its Relation to Fetal Intolerance of Labor: A 2-Center Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Ultrasound Med. 2014, 33, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristics | Value |
|---|---|
| Maternal age | 32.0 (21.0–42.0) |
| Gestational age at birth | 39.0 (32.0–41.3) |
| BMI at birth | 26.4(20.4–36.5) |
| Parity | |
| Nulliparity | 3374 (52.4%) |
| Multiparity | 3064 (47.6%) |
| Labor induction | |
| No labor induction | 4009 (62.3%) |
| Labor induction | 2429 (37.7%) |
| Delivery | |
| Vaginal delivery | 4141 (64.3%) |
| Cesarean delivery | 3576 (55.5%) |
| Summer | Non-Summer | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| AFI in 2nd trimester | 14.6 ± 2.3 | 14.6 ± 2.4 | 0.727 |
| AFI in 3rd trimester | 13.5 ± 2.9 | 13.7 ± 2.9 | 0.005 |
| Temperature (°C) | 25.9 ± 9.1 | 10.2 ± 1.1 | <0.001 |
| Humidity (%) | 72.9 ± 4.1 | 57.1 ± 2.0 | <0.001 |
| 2nd Trimester | 3rd Trimester | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Humidity (%) | Temperature (°C) | Humidity (%) | Temperature (°C) | |||||
| r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | |
| AFI (cm) | −0.001 | 0.952 | −0.001 | 0.980 | −0.16 | 0.056 | −0.09 | 0.265 |
| Temperature (°C) | 0.815 | <0.001 | 0.819 | <0.001 | ||||
| Summer | Non-Summer | p | OR (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Borderline oligohydramnios in 2nd Trimester | 21 (2.3) | 62(1.4) | 0.530 | 1.63 (0.99–2.69) |
| Borderline oligohydramnios in 3rd Trimester | 268 (10.1) | 966 (8.1) | <0.001 | 1.27 (1.11–1.47) |
| Normal AFI (n = 2326) | Borderline Oligohydramnios, (n = 226) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gestational age at birth | 39.0 (32.0–41.3) | 39.1 (32.4–41.3) | 0.846 |
| Birth weight | 3365.0 (1576–4580) | 3080.0 (1465–3890) | <0.001 |
| 1 min APGAR score | 8 (7–9) | 8 (6–8) | 0.867 |
| 5 min APGAR score | 9 (8–10) | 9 (8–9) | 0.584 |
| SGA | 153 (6.6%) | 51 (22.6%) | <0.001 |
| NICU admission | 121 (5.2%) | 18 (7.9%) | 0.016 |
| RDS | 37 (1.6%) | 9 (4.1%) | 0.481 |
| MAS | 74 (3.2%) | 9 (4.1%) | 0.831 |
| Neonatal jaundice | 563 (24.2%) | 38 (16.8%) | 0.450 |
| Neonatal death | None | None |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, A.-Y.; Lee, J.-Y.; Sohn, I.-S.; Kwon, H.-S.; Seo, Y.-S.; Kim, M.-H.; Yang, S.-W.; Hwang, H.-S. Does the Summer Season Affect the Amniotic Fluid Volume during Pregnancy? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9483. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18189483
Choi A-Y, Lee J-Y, Sohn I-S, Kwon H-S, Seo Y-S, Kim M-H, Yang S-W, Hwang H-S. Does the Summer Season Affect the Amniotic Fluid Volume during Pregnancy? International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(18):9483. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18189483
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Ah-Young, Jun-Yi Lee, In-Sook Sohn, Han-Sung Kwon, Yong-Soo Seo, Myoung-Hwan Kim, Seung-Woo Yang, and Han-Sung Hwang. 2021. "Does the Summer Season Affect the Amniotic Fluid Volume during Pregnancy?" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 18: 9483. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18189483
APA StyleChoi, A.-Y., Lee, J.-Y., Sohn, I.-S., Kwon, H.-S., Seo, Y.-S., Kim, M.-H., Yang, S.-W., & Hwang, H.-S. (2021). Does the Summer Season Affect the Amniotic Fluid Volume during Pregnancy? International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(18), 9483. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18189483






