Natural Contaminants in Wines: Determination of Biogenic Amines by Chromatographic Techniques
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Instruments
2.3. Standard Solution
2.4. Samples
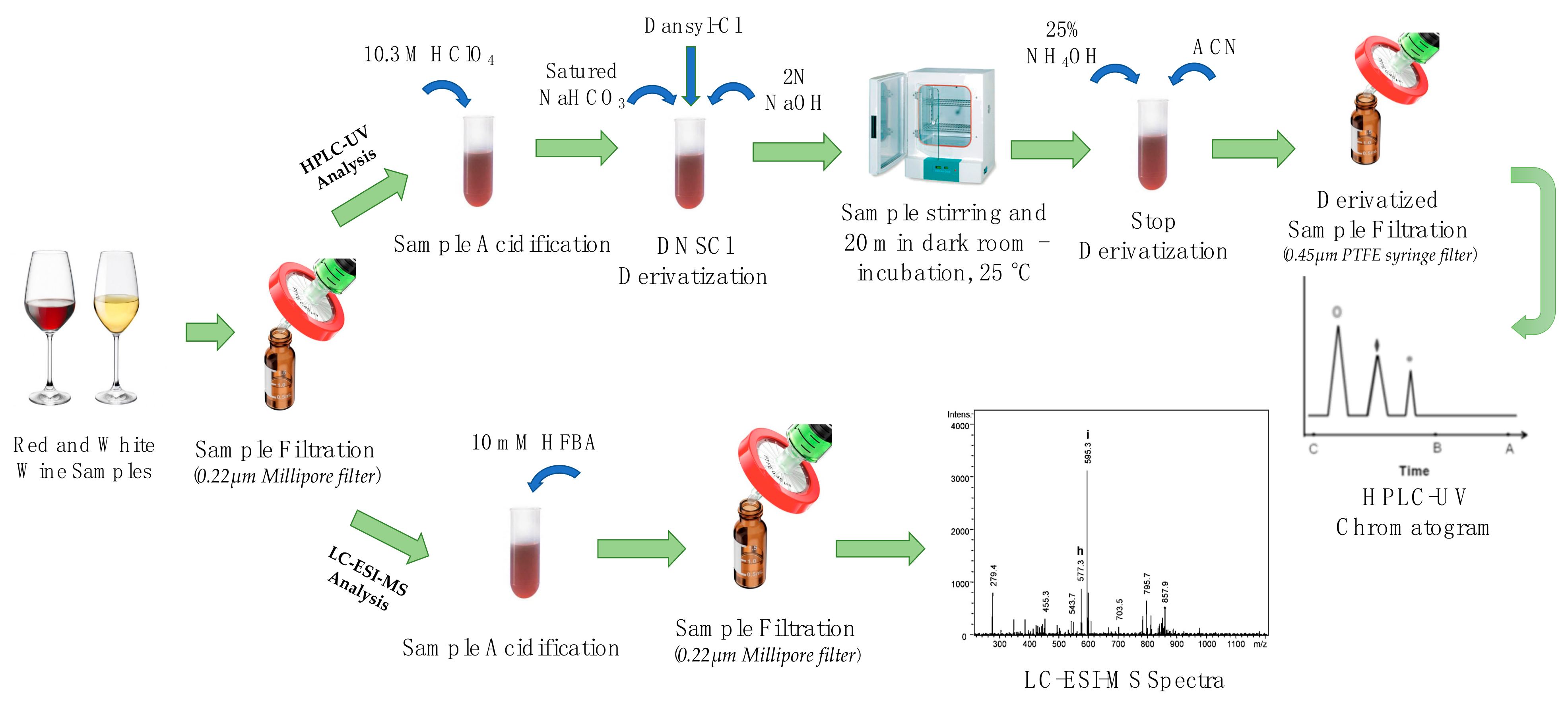
2.5. Biogenic Amines Extraction
2.6. HPLC-UV/Vis Method
2.7. LC-ESI-MS Method
2.8. Descriptive Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Wine Samples Analysis by HPLC-UV/Vis and LC-ESI-MS
3.1.1. Optimization and Performance Characteristics of the HPLC-UV/Vis Method
3.1.2. Optimization and Performances of the LC-ESI-MS Method
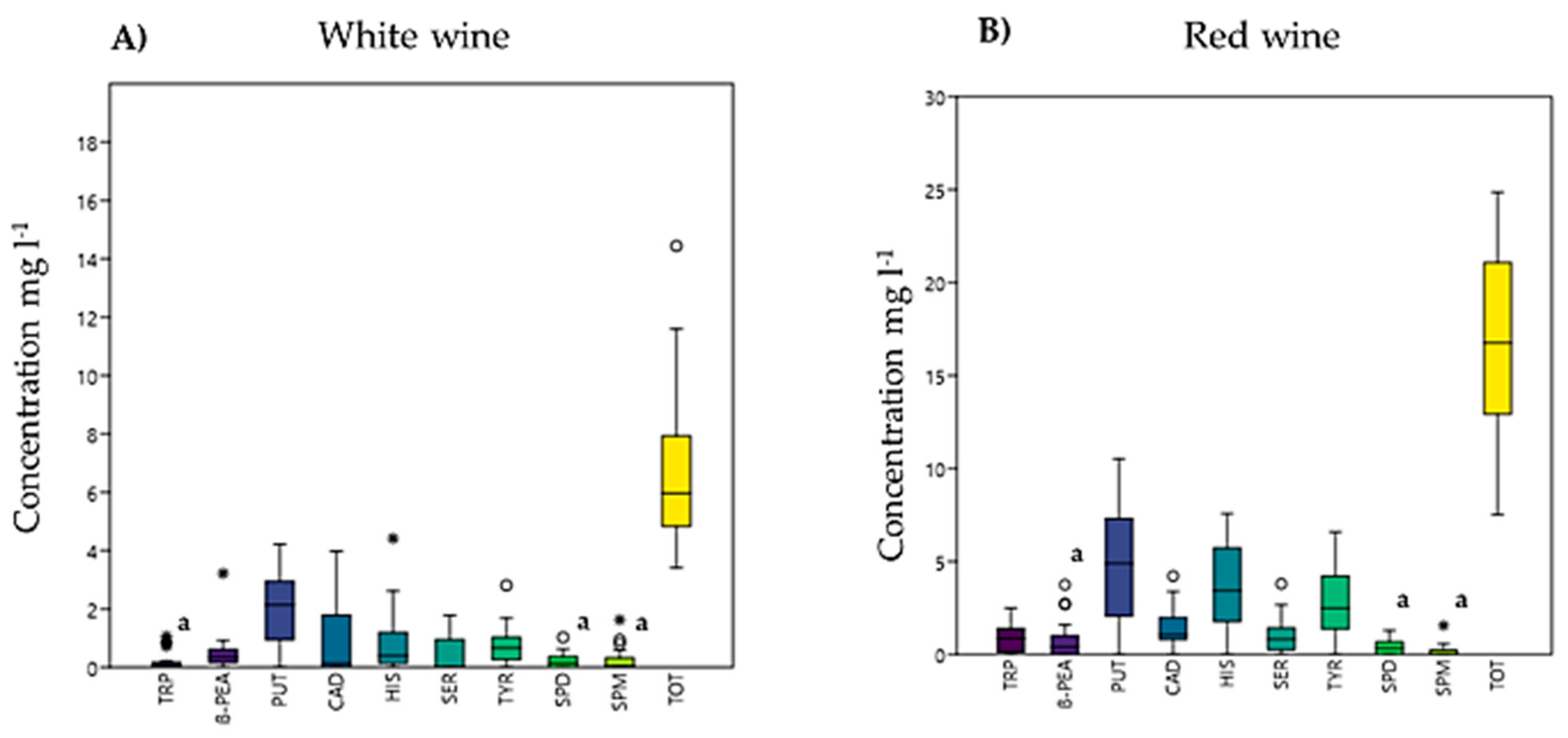
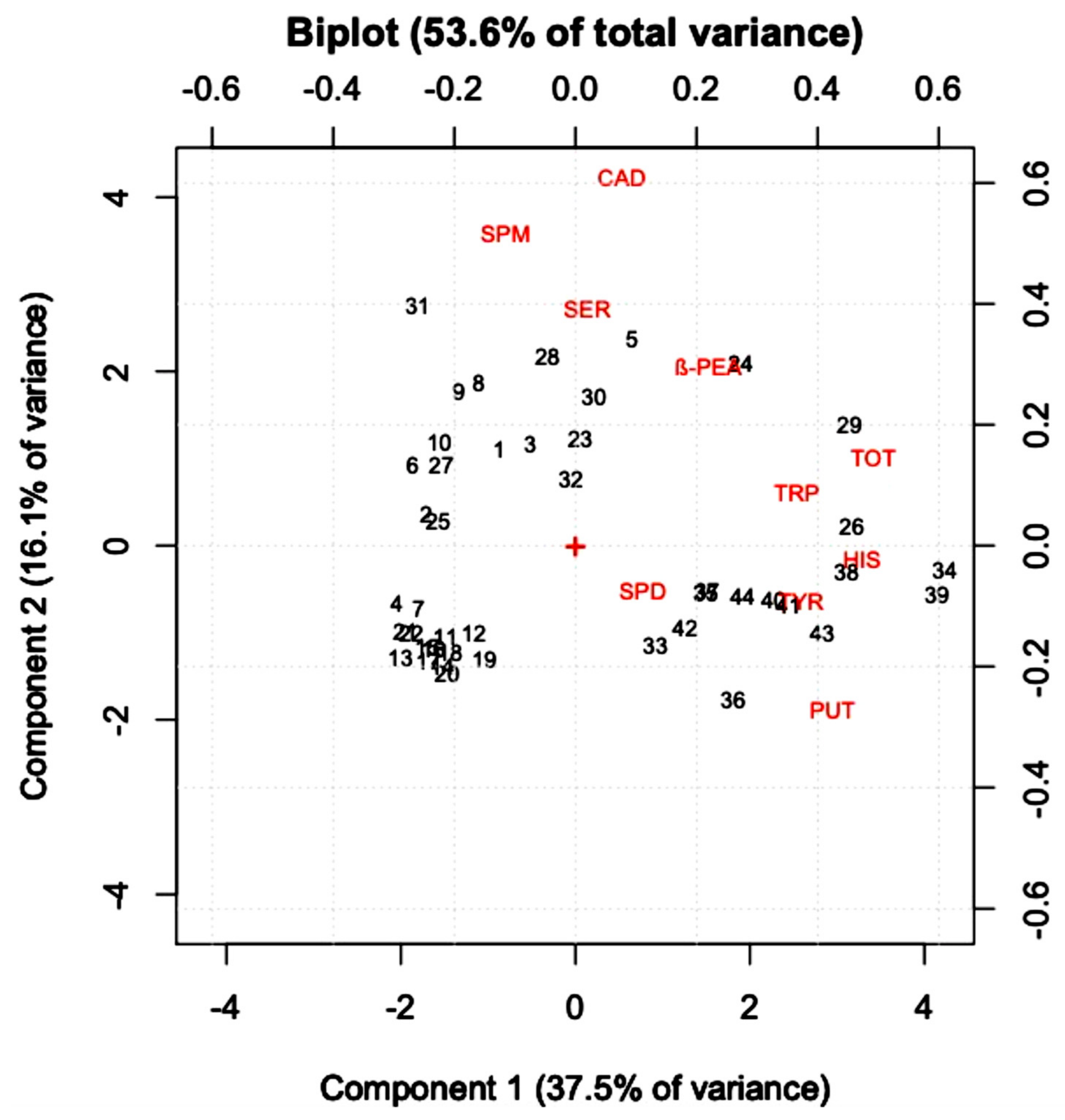
3.2. Biogenic Amines Determination in Wine Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Silla Santos, M.H. Biogenic amines: Their importance in foods. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1996, 29, 213–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Önal, A.; Serife, E.K.T.; Önal, C. A review of the liquid chromatographic methods for the determination of biogenic amines in foods. Food Chem. 2013, 139, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.A.; Poortvliet, E.; Stromberg, R.; Yngve, A. Polyamines in foods: Development of a food database. Food Nutr. Res. 2011, 55, 5572–5586. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, S.L.; Lieber, E.R. In vitro inhibition of rat intestinal histamine-metabolizing enzymes. Food Cosmet. Toxicol. 1979, 17, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinci, G.; Maddaloni, L. Biogenic Amines in Alcohol-Free Beverages. Beverages 2020, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maintz, L.; Novak, N. Histamine and histamine intolerance. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 1185–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.A. Interaction of Biogenic Amines with Ethanol. In Biochemical Pharmacology of Ethanol; Majchrowicz, E., Ed.; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1975; Volume 56. [Google Scholar]
- Martìnez-Pinilla, O.; Guadalupe, Z.; Hernàndez, Z.; Ayestaràn, B. Amino acids and biogenic amines in red varietal wines: The role of grape variety, malolactic fermentation and vintage. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2013, 237, 887–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulhussein, A.A.; Wallace, H.M. Polyamines and membrane transporters. Amino Acids 2014, 46, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortorella, V.; Masciari, P.; Pezzi, M.; Mola, A.; Tiburzi, S.P.; Zinzi, M.C.; Scozzafava, A.; Verre, M. Histamine Poisoning from Ingestion of Fish or Scombroid Syndrome. Case Rep. Emerg. Med. 2014, 2014, 482531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratta, P.; Badino, G. Scombroid poisoning. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2012, 184, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tofalo, R.; Perpetuini, G.; Schirone, M.; Suzzi, G. Biogenic Amines: Toxicology and Health Effect. Encycl. Food Health 2015, 71, 424–429. [Google Scholar]
- Shalaby, A.R. Changes in biogenic amines in mature and germinating legume seeds and their behavior during cooking. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2000, 44, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardoócz, S. Polyamines in food and their consequences for food quality and human health. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 6, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofalo, R.; Patrignani, F.; Lanciotti, R.; Perpetuini, G.; Schirone, M.; Di Gianvito, P.; Pizzoni, D.; Arfelli, G.; Suzzi, G. Aroma profile of Montepulciano d’Abruzzo wine fermented by single and co-culture starters of autochthonous Saccharomyces and non-saccharomyces yeasts. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 610, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickinson, G. Scombroid fish poisoning syndrome. Ann. Emerg. Med. 1982, 11, 487–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcobal, A.; de las Rivas, B.; Landete, J.M.; Tabera, L.; Munñoz, R. Tyramine and Phenylethylamine Biosynthesis by Food Bacteria. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 52, 448–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Del Rio, B.; Redruello, B.; Linares, D.M.; Ladero, V.; Ruas-Madiedo, P.; Fernandez, M.; Martin, M.C.; Alvarez, M.A. The biogenic amines putrescine and cadaverine show in vitro cytotoxicity at concentrations that can be found in foods. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ladero, V.; Calles-Enriquez, M.; Fernandez, M.A.; Alvarez, M. Toxicological Effects of Dietary Biogenic Amines. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2010, 6, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fankhauser, C.; Charieras, T.; Caille, D.; Rovei, V. Interaction of MAO inhibitors and dietary tyramine: A new experimental model in the conscious rat. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 1994, 32, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tittarelli, R.; Mannocchi, G.; Pantano, F.; Romolo, F.S. Recreational use, analysis and toxicity of tryptamines. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2015, 13, 26–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malaca, S.; Lo Faro, A.F.; Tamborra, A.; Pichini, S.; Busardò, F.P.; Huestis, M.A. Toxicology and Analysis of Psychoactive Tryptamines. Int. J. Mol. 2020, 21, 9279. [Google Scholar]
- Pegg, A.E. The function of spermine. IUBMB Life 2014, 66, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strasser, B.; Gostner, J.; Fuchs, D. Mood, food, and cognition. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2016, 19, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillén-Casla, V.; Rosales-Conrado, N.; León-González, M.E.; Pérez-Arribas, L.V.; Polo-Díez, L.M. Determination of serotonin and its precursors in chocolate samples by capillary liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1232, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özogul, Y.; Özogul, F. Chapter 1: Biogenic Amines Formation, Toxicity, Regulations in Food. In Biogenic Amines in Food: Analysis, Occurrence and Toxicity; Royal Society of Chemestry: London, UK, 2019; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Restuccia, D.; Loizzo, M.R.; Spizzirri, U.G. Accumulation of Biogenic Amines in Wine: Role of Alcoholic and Malolactic Fermentation. Ferment 2018, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caruso, M.; Fiorel, C.; Contursi, M.; Salzano, G.; Paparella, A.; Romano, P. Formation of biogenic amines as criteria for the selection of wine yeasts. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 18, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigentini, I.; Romano, A.; Compagno, C.; Merico, A.; Molinari, F.; Tirelli, A.; Foschino, R.; Volonterio, G. Physiological and oenological traits of differentDekkera/Brettanomycesbruxellensisstrains under wine-model conditions. FEMS Yeast Res. 2008, 8, 1087–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Del Prete, V.; Costantini, A.; Cecchini, F.; Morassut, M.; Garcia-Moruno, E. Occurrence of biogenic amines in wine: The role of grapes. Food Chem. 2009, 112, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, Á.; Calderón, F.; Palomero, F.; Benito, S. Combine use of selected Schizosaccharomyces pombe and Lachancea thermotolerans yeast strains as an alternative to the traditional malolactic fermentation in red wine production. Molecules 2015, 20, 9510–9523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benito, Á.; Jeffares, D.; Palomero, F.; Calderón, F.; Bai, F.-Y.; Bähler, J.; Benito, S. Selected Schizosaccharomyces pombe strains have characteristics that are beneficial for winemaking. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Álvarez, P.J.; Marcobal, Á.; Polo, C.; Moreno-Arribas, M.V. Influence of technological practices on biogenic amine contents in red wines. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2006, 222, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.P.; Leităo, M.C.; San Romăo, M.C. Biogenic amines in wines: Influence of oenological factors. Food Chem. 2008, 107, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfroi, L.; Silva, P.H.A.; Rizzon, L.A.; Sabaini, P.S. Influence of alcoholic and malolactic starter cultures on bioactive amines in Merlot wines. Food Chem. 2009, 116, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcobal, Á.; de las Rivas, B.; Muñoz, R. Methods for the detection of bacteria producing biogenic amines on foods: A survey. J. Consum. Prot. Food Saf. 2006, 1, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Preti, R.; Vieri, S.; Vinci, G. Biogenic amines profiles and antioxidant properties of Italian red wines from different price categories. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2016, 46, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinci, G.; Gobbi, L.; Maddaloni, L.; Prencipe, S.A. Simple and reliable determination of biogenic amines in Italian red wines. Direct analysis of non-derivatized biogenic amines by LC-ESI-MS. J. Adv. Mass. Spec. 2021, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Vinci, G.; Restuccia, D.; Antiochia, R. Determination of biogenic amines in wines by HPLC-UV and LC-ESI-MS: A comparative study. Sci. Technol. La Chim. l’Industria 2011, 9, 128–135. [Google Scholar]

| Biogenic Amines | Amino Acid Precursor | Physiological Effects | Pathological Effects | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Histamine | Histidine | Release of adrenaline and noradrenaline, Allergic processes, Stimulation of the smooth muscles of the uterus, intestine, and respiratory tract, Stimulation of sensory and motor neurons Control of gastric secretion | Allergic reaction (nausea, burning in the mouth, flushing of the face and body, abdominal cramps, diarrhea, swelling of the face and tongue) | [9,10,11,12,13] |
| Tyramine | Tryptamine | Peripheral vascularization Increase in cardiac output Increased lacrimation and salivation Increased breathing Increased blood sugar levels Noradrenaline release of the sympathetic nervous system Migraine | High blood pressure, Rapid heart rate, Tremors, Seizures, Hyperthermia | [11,14,15,16,17,18] |
| Putrescine | Ornithine | Hypotension Bradycardia Lockjaw Extremity paralysis | Cytotoxicity, Rule in tumors growth, Enhancement of the toxicity of other amines | [11,18,19,20] |
| Cadaverine | Lysine | |||
| Tryptamine | Tryptophan | Increase in blood pressure | Relaxations, Mild euphoria, Hallucinogens | [15,21,22] |
| ß-Phenylethylamine | Phenylalanine | Noradrenaline release of the sympathetic nervousIncrease in blood pressure Migraine | Migraine | [11] |
| Spermidine | Methionine | Hypotension, Bradycardia | Acute decrease in blood pressure, Respiratory symptoms, Nephrotoxicity, carcinogenesis, tumor invasion, and metastasis, Enhancement of the toxicity of other amines | [15,23,24,25,26] |
| Spermine | ||||
| Serotonin | Tryptophan | Modulation of anger, aggression, mood and sexuality, appetite, Physiological homeostasis Muscle contraction Blood pressure regulation | Altered behavior and neurochemical activities, cognitive decline, muscular inflammation, and immune activation | [24,25] |
| Fermentation | Microorganism | Biogenic Amines | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alcoholic | Spontaneous | HIS, MET, ETH, TYR, β-PEA, PUT, CAD, SPD, SPM, AGM | [8,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33] |
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae | AGM, ETA, ETH, PUT, TYR, CAD, β-PEA, HIS | [15,30] | |
| Dekkera/B. bruxellensis | ETA; MET; AGM; TRY; β-PEA; PUT; CAD; HIS; SPM | [28,29] | |
| Kloeckeraapiculata; Candida stellata; Metschnikowiapulcherrima | ETA; MET; AGM; TRY; β-PEA; PUT; CAD; HIS | [28] | |
| Kluyveromycesthermotolerans; Schizosaccharomyces pombe V2. Selected S. pombe; Non-Selected S. pombe | HIS; TYR; β-PEA; PUT; CAD | [31,32] | |
| Malolactic | Spontaneous, Oenococcus oeni, L. plantarum DSM 4361; Yeast | PUT; SPD; SPM; AGM; CAD; SER; HIS; TYR; β-PEA | [8,33,34,35] |
| Commercial malolactic bacteria | HIS; MET; ETH; TYR; β-PEA; PUT; CAD | [36] |
| Biogenic Amines | MW | Channel, m/z (Relative Abundance) | Cone Voltage (V) | Retention Window (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tyramine | 137.2 | 121.2 (30), 138.3 (100) | 30 | 0–12.85 |
| ß-Phenylethylamine | 121.2 | 105.1 (10), 122.3 (100) | 30 | 12.85–16.00 |
| Putrescine | 88.2 | 89.3 (100) | 40 | 0–12.85 |
| Cadaverine | 102.2 | 86.2 (10), 103.3 (100) | 30 | 0–12.85 |
| Histamine | 111.1 | 95.2 (30), 112.1 (100) | 40 | 0–12.85 |
| Serotonin | 176.2 | 160.3 (10), 177.2 (100) | 40 | 0–12.85 |
| Tryptamine | 160.2 | 144.3 (40), 161.2 (100) | 30 | 12.85–16.00 |
| Spermidine | 145.2 | 112.3 (10), 129.2 (10), 146.3 (100) | 40 | 12.85–16.00 |
| Spermine | 202.3 | 129.2 (20), 112.3 (10), 203.4 (100) | 40 | 12.85–16.00 |
| Wine | Sample | TRP | ß-PEA | PUT | CAD | HIS | SER | TYR | SPD | SPM | Total BAs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WHITE | Wine 1 | 0.72 ± 0.03 | 0.13 ± 0.17 | 0.90 ± 0.13 | 1.54 ± 0.31 | 2.61 ± 0.05 | 0.55 ± 0.20 | nd | 1.03 ± 0.08 | 0.94 ± 0.01 | 9.74 ± 0.98 |
| Wine 2 | nd | nd | 1.17 ± 0.19 | 1.79 ± 0.19 | nd | 1.78 ± 0.11 | 0.57 ± 0.09 | 0.62 ± 0.16 | nd | 6.49 ± 0.74 | |
| Wine 3 | 0.23 ± 0.02 | 0.16 ± 0.09 | 1.83 ± 0.11 | 2.76 ± 0.23 | 1.52 ± 0.07 | 0.96 ± 0.15 | 2.81 ± 0.04 | nd | 0.41 ± 0.04 | 11.59 ± 0.75 | |
| Wine 4 | nd | 0.24 ± 0.01 | nd | 0.51 ± 0.21 | nd | 0.34 ± 0.02 | nd | 0.52 ± 0.08 | nd | 7.37 ± 0.32 | |
| Wine 5 | 0.16 ± 0.05 | 3.22 ± 0.16 | 1.40 ± 0.12 | 3.97 ± 0.31 | 4.42 ± 0.40 | nd | 0.32 ± 0.11 | 0.42 ± 0.07 | 0.29 ± 0.02 | 14.44 ± 1.32 | |
| Wine 6 | nd | nd | 1.70 ± 0.15 | 2.73 ± 0.26 | 0.14 ± 0.03 | 1.05 ± 0.13 | 0.26 ± 0.09 | nd | 0.22 ± 0.10 | 6.87 ± 0.76 | |
| Wine 7 | 0.83 ± 0.02 | nd | 0.89 ± 0.12 | nd | nd | 0.95 ± 0.20 | 0.10 ± 0.03 | 0.21 ± 0.04 | nd | 5.16 ± 0.49 | |
| Wine 8 | 0.89 ± 0.15 | 0.85 ± 0.17 | 0.86 ± 0.19 | 2.36 ± 0.24 | 0.51 ± 0.08 | 1.37 ± 0.13 | 0.67 ± 0.18 | nd | 0.58 ± 0.13 | 9.03 ± 1.14 | |
| Wine 9 | nd | 0.92 ± 0.23 | 2.57 ± 0.34 | nd | 2.28 ± 0.29 | 1.37 ± 0.21 | 0.24 ± 0.09 | 0.26 ± 0.05 | 1.63 ± 0.14 | 9.79 ± 1.35 | |
| Wine 10 | 1.07 ± 0.17 | 0.66 ± 0.12 | 0.96 ± 0.25 | 1.80 ± 0.12 | nd | nd | 0.21 ± 0.02 | nd | 0.80 ± 0.21 | 6.76 ± 0.89 | |
| Wine 11 | nd | 0.88 ± 0.07 | 0.65 ± 0.21 | nd | 1.49 ± 0.16 | nd | 0.88 ± 0.14 | 0.52 ± 0.11 | nd | 5.02 ± 0.69 | |
| Wine 12 | nd | 0.27 ± 0.04 | 2.95 ± 0.33 | nd | 1.10 ± 0.24 | 0.88 ± 0.12 | 1.04 ± 0.18 | 0.35 ± 0.03 | nd | 7.57 ± 0.94 | |
| Wine 13 | nd | 0.41 ± 0.07 | 2.51 ± 0.27 | nd | 0.16 ± 0.01 | nd | 0.33 ± 0.09 | nd | nd | 3.41 ± 0.44 | |
| Wine 14 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.33 ± 0.09 | 3.51 ± 0.34 | nd | 0.41 ± 0.11 | nd | 0.85 ± 0.27 | 0.10 ± 0.03 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 5.25 ± 0.86 | |
| Wine 15 | nd | 0.24 ± 0.08 | 2.81 ± 0.39 | 0.32 ± 0.11 | 0.50 ±0.17 | nd | 0.67 ± 0.12 | 0.15 ± 0.02 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 4.74 ± 0.91 | |
| Wine 16 | nd | 0.38 ± 0.15 | 2.70 ± 0.41 | 0.30 ± 0.09 | 0.40 ± 0.13 | nd | 1.00 ± 0.09 | 0.08 ± 0.02 | nd | 4.86 ± 0.89 | |
| Wine 17 | nd | 0.22 ± 0.02 | 3.10 ± 0.23 | 0.08 ± 0.03 | 0.22 ± 0.04 | nd | 0.88 ± 0.14 | 0.15 ± 0.05 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 4.70 ± 0.52 | |
| Wine 18 | nd | 0.60 ± 0.21 | 2.96 ± 0.32 | nd | 0.45 ± 0.10 | nd | 1.20 ± 0.23 | 0.18 ± 0.09 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 5.45 ± 0.97 | |
| Wine 19 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.58 ± 0.18 | 4.22 ± 0.39 | nd | 0.50 ± 0.13 | nd | 1.38 ± 0.28 | 0.22 ± 0.06 | 0.08 ± 0.02 | 7.01 ± 0.78 | |
| Wine 20 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.15 ± 0.07 | 3.03 ± 0.44 | nd | 0.27 ± 0.03 | nd | 1.69 ± 0.12 | 0.08 ± 0.03 | nd | 5.26 ± 0.70 | |
| Wine 21 | nd | 0.55 ± 0.11 | 2.41 ± 0.21 | nd | 0.25 ± 0.07 | nd | 0.34 ± 0.06 | 0.12 ± 0.07 | 0.20 ± 0.05 | 3.87 ± 0.57 | |
| Wine 22 | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 0.42 ± 0.21 | 1.87 ± 0.19 | 0.20 ± 0.04 | 0.13 ± 0.02 | nd | 1.03 ± 0.17 | nd | 0.10 ± 0.03 | 3.85 ± 0.68 | |
| Wine 23 | 1.28 ± 0.11 | 1.58 ± 0.27 | 2.09 ± 0.23 | nd | 1.85 ± 0.25 | 2.41 ± 0.35 | 1.37 ± 0.22 | nd | 0.51 ± 0.11 | 12.26 ± 1.54 | |
| Wine 24 | 0.77 ± 0.21 | 2.75 ± 0.38 | 2.76 ± 0.27 | 4.22 ± 0.43 | 3.25 ± 0.35 | nd | 3.71 ± 0.35 | 0.20 ± 0.02 | 0.17 ± 0.05 | 18.82 ± 2.16 | |
| RED | Wine 25 | nd | nd | 1.57 ± 0.21 | 1.75 ± 0.19 | 0.51 ± 0.21 | 1.51 ± 0.17 | 0.38 ± 0.09 | 0.33 ± 0.05 | nd | 8.00 ± 0.92 |
| Wine 26 | nd | 2.68 ±0.37 | 3.39 ± 0.47 | nd | 6.51 ± 0.52 | 0.80 ± 0.13 | 6.59 ± 0.59 | 0.72 ± 0.31 | 0.39 ± 0.15 | 24.31 ± 2.54 | |
| Wine 27 | nd | nd | 1.65 ± 0.12 | 1.90 ± 0.23 | 1.23 ± 0.17 | 2.57 ± 0.37 | nd | nd | nd | 8.41 ± 0.89 | |
| Wine 28 | 0.47 ± 0.12 | 0.29 ± 0.01 | 2.47 ± 0.19 | 1.84 ± 0.19 | nd | 3.80 ± 0.31 | 2.68 ± 0.29 | 0.42 ± 0.12 | 0.56 ± 0.11 | 14.11 ± 1.34 | |
| Wine 29 | 1.41 ± 0.17 | 3.75 ± 0.38 | 7.59 ± 0.56 | 2.91 ± 0.31 | 3.10 ± 0.39 | nd | 1.99 ± 0.21 | nd | nd | 24.25 ± 2.02 | |
| Wine 30 | 1.83 ± 0.21 | nd | 1.52 ± 0.11 | 2.25 ± 0.21 | 1.52 ± 0.21 | 2.66 ± 0.19 | 1.20 ± 0.32 | 0.58 ± 0.21 | 0.30 ± 0.07 | 13.14 ± 1.53 | |
| Wine 31 | nd | 0.35 ± 0.07 | nd | 2.80 ± 0.31 | nd | 0.84 ± 0.23 | 2.22 ± 0.27 | 0.55 ± 0.12 | 1.56 ± 0.23 | 7.51 ± 1.23 | |
| Wine 32 | 0.80 ± 0.21 | nd | 1.96 ± 0.37 | 3.37 ± 0.27 | 3.61 ± 0.39 | 0.33 ± 0.11 | 0.86 ± 0.18 | nd | nd | 12.09 ± 1.53 | |
| Wine 33 | 0.15 ± 0.13 | nd | 4.42 ± 0.21 | 0.83 ± 0.21 | 2.22 ± 0.37 | nd | 5.19 ± 0.45 | 1.00 ± 0.13 | 0.21 ± 0.04 | 14.02 ± 1.54 | |
| Wine 34 | 2.49 ± 0.36 | 1.06 ± 0.31 | 10.52 ± 1.23 | 1.09 ± 0.19 | 7.57 ± 1.05 | 0.80 ± 0.24 | 1.33 ± 0.16 | nd | nd | 24.86 ± 3.54 | |
| Wine 35 | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 0.34 ± 0.10 | 5.88 ± 0.41 | 1.10 ± 0.29 | 3.25 ± 0.57 | 1.40 ± 0.35 | 4.28 ± 0.74 | 0.77 ± 0.21 | nd | 17.12 ± 2.69 | |
| Wine 36 | 1.05 ± 0.19 | nd | 5.23 ± 1.23 | nd | 4.54 ± 0.87 | nd | 3.38 ± 0.28 | 1.28 ± 0.38 | nd | 15.48 ± 2.95 | |
| Wine 37 | 0.85 ± 0.25 | 0.75 ± 0.18 | 6.76 ± 0.97 | 0.75 ± 0.43 | 4.03 ± 1.31 | 0.95 ± 0.23 | 2.29 ± 0.19 | nd | nd | 16.38 ± 3.56 | |
| Wine 38 | 1.24 ± 0.29 | 0.93 ± 0.23 | 8.54 ± 1.25 | 0.93 ± 0.27 | 5.61 ± 0.98 | 1.23 ± 0.24 | 2.87 ± 0.24 | 0.57 ± 0.15 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 22.00 ± 3.66 | |
| Wine 39 | 2.50 ± 0.12 | 0.18 ± 0.09 | 7.22 ± 1.11 | 0.81 ± 0.19 | 7.11 ± 1.23 | 1.00 ± 0.36 | 4.61 ± 0.46 | 0.33 ± 0.29 | nd | 23.76 ± 3.05 | |
| Wine 40 | 1.64 ± 0.23 | 0.24 ± 0.06 | 6.66 ± 1.03 | 0.88 ± 0.35 | 3.93 ± 0.59 | 0.78 ± 0.20 | 3.70 ± 0.34 | 0.24 ± 0.16 | 0.05 | 18.12 ± 2.96 | |
| Wine 41 | 0.57 ± 0.12 | 0.54 ± 0.24 | 10.04 ± 1.07 | 1.15 ± 0.37 | 6.06 ±0.65 | 0.84 ± 0.24 | 1.55 ± 0.37 | nd | nd | 20.75 ± 3.06 | |
| Wine 42 | 1.33 ± 0.34 | 0.61 ± 0.31 | 4.97 ± 0.87 | 0.89 ± 0.41 | 2.90 ± 0.37 | nd | 1.90 ± 0.23 | 1.11 ± 0.14 | nd | 13.71 ± 2.9 | |
| Wine 43 | 0.88 ± 0.27 | 0.47 ± 0.25 | 8.32 ± 0.77 | 1.05 ± 0.54 | 3.80 ± 0.59 | 0.54 ± 0.16 | 5.05 ± 0.53 | 0.66 ± 0.13 | nd | 20.77 ± 3.24 | |
| Wine 44 | 1.42 ± 0.25 | 1.00 ± 0.15 | 4.83 ± 0.44 | 0.80 ± 0.26 | 6.28 ± 0.35 | 0.60 ± 0.20 | 4.20 ± 0.32 | nd | nd | 9.13 ± 1.97 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vinci, G.; Maddaloni, L.; Prencipe, S.A.; Ruggieri, R. Natural Contaminants in Wines: Determination of Biogenic Amines by Chromatographic Techniques. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10159. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph181910159
Vinci G, Maddaloni L, Prencipe SA, Ruggieri R. Natural Contaminants in Wines: Determination of Biogenic Amines by Chromatographic Techniques. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(19):10159. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph181910159
Chicago/Turabian StyleVinci, Giuliana, Lucia Maddaloni, Sabrina A. Prencipe, and Roberto Ruggieri. 2021. "Natural Contaminants in Wines: Determination of Biogenic Amines by Chromatographic Techniques" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 19: 10159. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph181910159
APA StyleVinci, G., Maddaloni, L., Prencipe, S. A., & Ruggieri, R. (2021). Natural Contaminants in Wines: Determination of Biogenic Amines by Chromatographic Techniques. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(19), 10159. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph181910159







