Outpatient Assessment of Mechanical Load, Heat Strain and Dehydration as Causes of Transitional Acute Kidney Injury in Endurance Trail Runners
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Materials and Procedures
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
6. Practical Applications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scheer, V. Participation Trends of Ultra Endurance Events. Sports Med. Arthrosc. Rev. 2019, 27, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, L.; Walter, E.; Venn, R.M.; Galloway, R.; Pitsiladis, Y.; Sardat, F.; Forni, L.G. Acute kidney injury associated with endurance events—Is it a cause for concern? A systematic review. BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2017, 3, e000093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rojas-Valverde, D.; Sánchez-Ureña, B.; Crowe, J.; Timón, R.; Olcina, G.J. Exertional rhabdomyolysis and acute kidney injury in endurance sports: A systematic review. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2021, 21, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovanelli, N.; Taboga, P.; Rejc, E.; Simunic, B.; Antonutto, G.; Lazzer, S. Effects of an Uphill Marathon on Running Mechanics and Lower-Limb Muscle Fatigue. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2016, 11, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheer, V.; Basset, P.; Giovanelli, N.; Vernillo, G.; Millet, G.P.; Costa, R.J.S. Defining Off-road Running: A Position Statement from the Ultra Sports Science Foundation. Int. J. Sports Med. 2020, 41, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernillo, G.; Giandolini, M.; Edwards, W.B.; Morin, J.-B.; Samozino, P.; Horvais, N.; Millet, G. Biomechanics and Physiology of Uphill and Downhill Running. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 615–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez-Vargas, R.; Martín-Rodríguez, S.; Sánchez-Ureña, B.; Rodríguez-Montero, A.; Salas-Cabrera, J.; Gutiérrez-Vargas, J.C.; Simunic, B.; Rojas-Valverde, D. Biochemical and Muscle Mechanical Postmarathon Changes in Hot and Humid Conditions. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2020, 34, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipman, G.S.; Krabak, B.J.; Waite, B.L.; Logan, S.B.; Menon, A.; Chan, G.K. A Prospective Cohort Study of Acute Kidney Injury in Multi-stage Ultramarathon Runners: The Biochemistry in Endurance Runner Study (BIERS). Res. Sports Med. 2014, 22, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.-A.; Park, K.D.; Ahn, J.; Park, Y.; Kim, Y.-J. Comparison of Changes in Biochemical Markers for Skeletal Muscles, Hepatic Metabolism, and Renal Function after Three Types of Long-distance Running. Medicine 2016, 95, e3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheer, V.; Tiller, N.; Doutrleau, S.; Khodaee, M.; Knechtle, B.; Pasternak, A.; Rojas-Valverde, D. Potential Long-Term Health Problems Associated with Ultra- Endurance Running: A Narrative Review. Sport Med. 2021. in Press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Valverde, D.; Sánchez-Ureña, B.; Pino-Ortega, J.; Gómez-Carmona, C.; Gutierrez-Vargas, R.; Timón, R.; Olcina, G. External Workload Indicators of Muscle and Kidney Mechanical Injury in Endurance Trail Running. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopes, J.A.; Jorge, S. The RIFLE and AKIN classifications for acute kidney injury: A critical and comprehensive review. Clin. Kidney J. 2013, 6, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCullough, P.A.; Shaw, A.D.; Haase, M.; Bouchard, J.; Waikar, S.S.; Siew, E.D.; Murray, P.T.; Mehta, R.L.; Ronco, C. Diagnosis of Acute Kidney Injury Using Functional and Injury Biomarkers: Workgroup Statements from the Tenth Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative Consensus Conference. In CKD-Associated Complications: Progress in the Last Half Century; S. Karger AG: Basel, Switzerland, 2013; Volume 182, pp. 13–29. [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft, D.W.; Gault, H. Prediction of Creatinine Clearance from Serum Creatinine. Nephron 1976, 16, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Castro, A.F., 3rd; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T.; et al. A New Equation to Estimate Glomerular Filtration Rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas-Valverde, D.; Olcina, G.; Gutierrez-Vargas, R.; Crowe, J. Heat Strain, External Workload, and Chronic Kidney Disease in Tropical Settings: Are Endurance Athletes Exposed? Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giandolini, M.; Horvais, N.; Rossi, J.; Millet, G.; Morin, J.-B.; Samozino, P. Effects of the foot strike pattern on muscle activity and neuromuscular fatigue in downhill trail running. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2016, 27, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easthope, C.S.; Hausswirth, C.; Louis, J.; Lepers, R.; Vercruyssen, F.; Brisswalter, J. Effects of a trail running competition on muscular performance and efficiency in well-trained young and master athletes. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2010, 110, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bongers, C.C.W.G.; Alsady, M.; Nijenhuis, T.; Tulp, A.D.M.; Eijsvogels, T.M.H.; Deen, P.M.T.; Hopman, M.T.E. Impact of acute versus prolonged exercise and dehydration on kidney function and injury. Physiol. Rep. 2018, 6, e13734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupferman, J.; Ramírez-Rubio, O.; Amador, J.J.; López-Pilarte, D.; Wilker, E.H.; Laws, R.L.; Sennett, C.; Robles, N.V.; Lau, J.L.; Salinas, A.J.; et al. Acute Kidney Injury in Sugarcane Workers at Risk for Mesoamerican Nephropathy. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2018, 72, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipman, G.S.; Krabak, B.J.; Rundell, S.; Shea, K.M.; Badowski, N.; Little, C. Incidence and Prevalence of Acute Kidney Injury During Multistage Ultramarathons. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2016, 26, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheer, V.; Rojas-Valverde, D. Long-term health issues in ultraendurance runners: Should we be concerned? BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2021, 7, e001131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Valverde, D. Potential Role of Cannabidiol on Sports Recovery: A Narrative Review. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, M.D.; Stuempfle, K.J.; Fogard, K.; Hew-Butler, T.; Winger, J.; Weiss, R.H. Urine dipstick analysis for identification of runners susceptible to acute kidney injury following an ultramarathon. J. Sports Sci. 2013, 31, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyness, S.P.; Hunsaker, J.J.; Snow, T.M.; Genzen, J.R. Evaluation and analytical validation of a handheld digital refractometer for urine specific gravity measurement. Pr. Lab. Med. 2016, 5, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Casa, U.J.; Armstrong, L.E.; Hillman, S.K.; Montain, S.J.; Reiff, R.V.; Rich, B.S.E.; Roberts, W.O.; Stone, J.A. National athletic trainers’ association position statement: Fluid replacement for athletes. J. Athl. Train. 2000, 35, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rico-González, M.; Arcos, A.L.; Rojas-Valverde, D.; Clemente, F.M.; Pino-Ortega, J. A Survey to Assess the Quality of the Data Obtained by Radio-Frequency Technologies and Microelectromechanical Systems to Measure External Workload and Collective Behavior Variables in Team Sports. Sensors 2020, 20, 2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gómez-Carmona, C.D.; Pino-Ortega, J.; Sánchez-Ureña, B.; Ibáñez, S.J.; Rojas-Valverde, D. Accelerometry-Based External Load Indicators in Sport: Too Many Options, Same Practical Outcome? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 5101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rojas-Valverde, D.; Pino-Ortega, J.; Timon, R.; Gutiérrez-Vargas, R.; Sánchez-Ureña, B.; Olcina, G. Agreement and Reliability of Magnetic, Angular Rate, and Gravity (MARG) Sensors to Assess Multiple Body Segment´s External Loads during off-Road Running. Part P J. Sport Eng. Technol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, D.; McGrath, P.A.; Rafii, A.; Buckingham, B. The validation of visual analogue scales as ratio scale measures for chronic and experimental pain. Pain 1983, 17, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratz, A.; Ferraro, M.; Sluss, P.; Lewandowski, K. Laboratory Reference Values. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosten, A.O. BUN and Creatinine. In Clinical Methods: The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations; Walker, H.K., Hall, W.D., Hurst, J.W., Eds.; Butterworths: Boston, MA, USA, 1990; ISBN 978-0-409-90077-4. [Google Scholar]
- Coca, S.G.; Singanamala, S.; Parikh, C.R. Chronic kidney disease after acute kidney injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Kidney Int. 2012, 81, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, R.; Hsu, C.-Y. The Role of Acute Kidney Injury in Chronic Kidney Disease. Semin. Nephrol. 2016, 36, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boulter, J.; Noakes, T.D.; Hew-Butler, T. Acute renal failure in four Comrades Marathon runners ingesting the same electrolyte supplement: Coincidence or causation? S. Afr. Med. J. 2011, 101, 876–878. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Poussel, M.; Touzé, C.; Allado, E.; Frimat, L.; Hily, O.; Thilly, N.; Rousseau, H.; Vauthier, J.-C.; Chenuel, B. Ultramarathon and Renal Function: Does Exercise-Induced Acute Kidney Injury Really Exist in Common Conditions? Front. Sports Act. Living 2020, 1, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castenfors, J. Renal Function during Prolonged Exercise. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1977, 301, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas-Valverde, D.; Timón, R.; Sánchez-Ureña, B.; Pino-Ortega, J.; Martínez-Guardado, I.; Olcina, G. Potential Use of Wearable Sensors to Assess Cumulative Kidney Trauma in Endurance Off-Road Running. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2020, 5, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khwaja, A. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Acute Kidney Injury. Nephron 2012, 120, c179–c184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Trabanino, R.; Jarquín, E.; Wesseling, C.; Johnson, R.J.; González-Quiroz, M.; Weiss, I.; Glaser, J.; Vindell, J.J.; Stockfelt, L.; Roncal, C.; et al. Heat stress, dehydration, and kidney function in sugarcane cutters in El Salvador—A cross-shift study of workers at risk of Mesoamerican nephropathy. Environ. Res. 2015, 142, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jouffroy, R.; Lebreton, X.; Mansencal, N.; Anglicheau, D. Acute kidney injury during an ultra-distance race. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

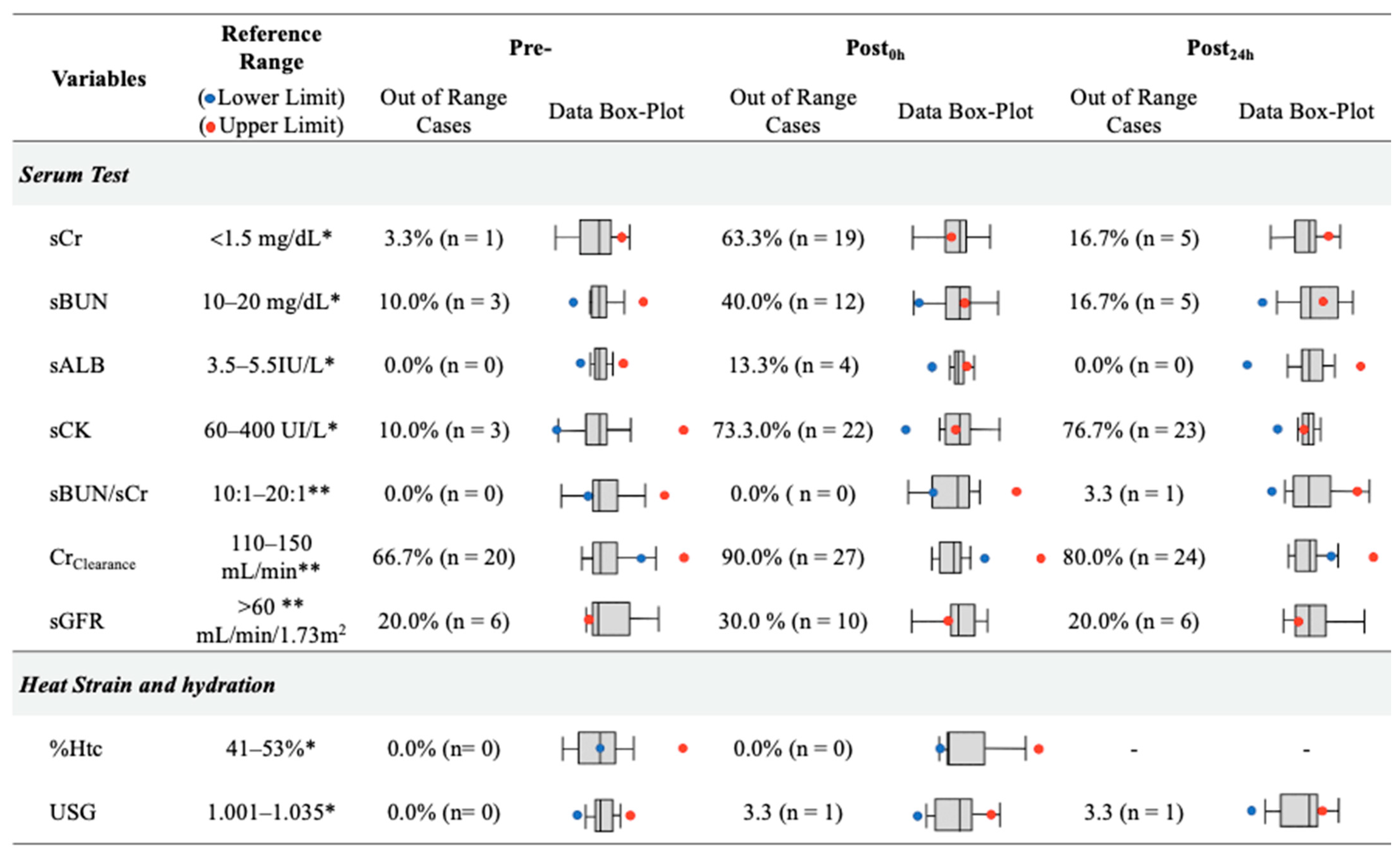
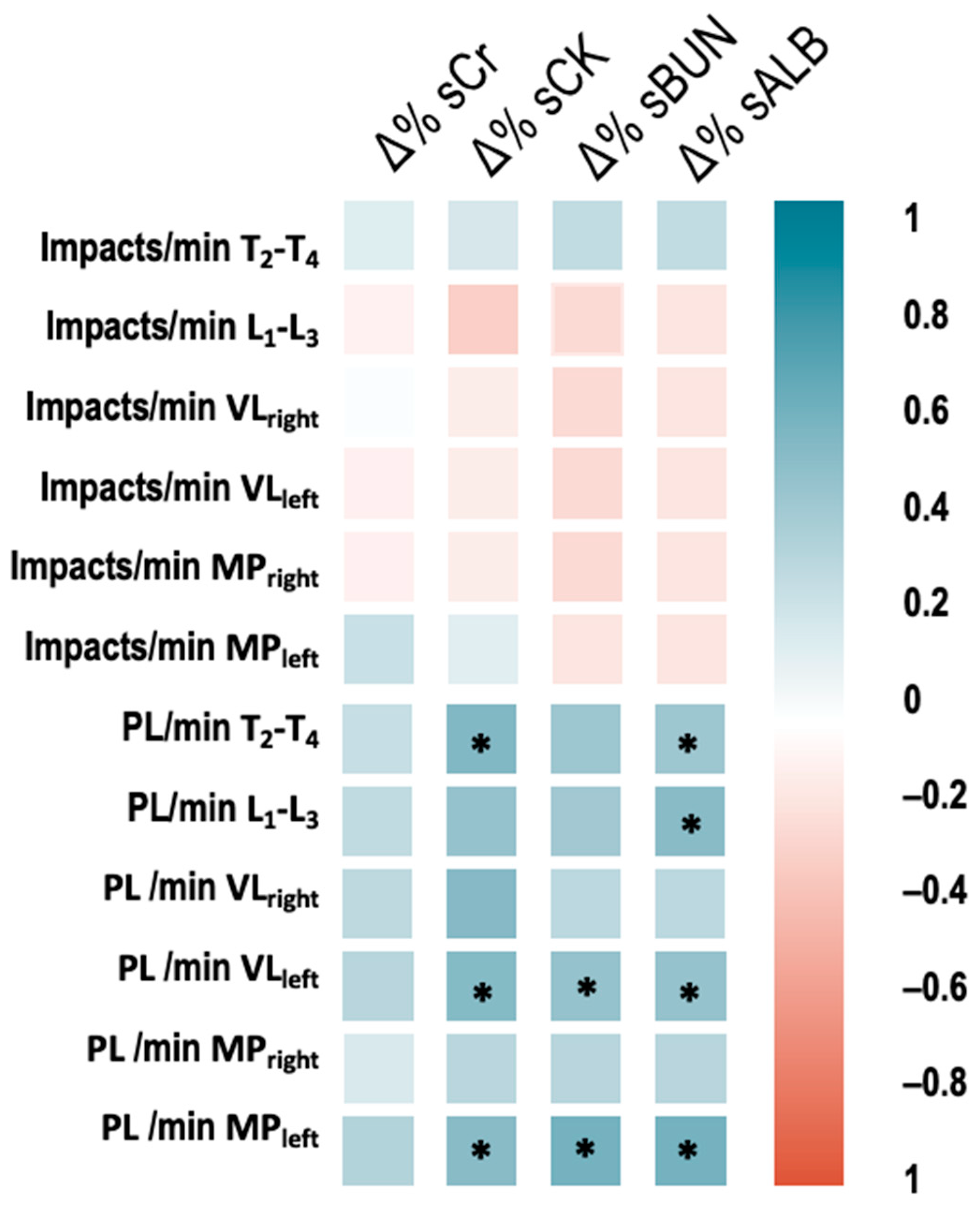
| Variable | Pre- | -Post0h | -Post24h | F/t Value | p-Value | ωp2/d Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serum test | ||||||
| sCr (mg/dL) | 1.2 ± 0.3 (1.1 to 1.3) | 1.6 ± 0.3 * (1.5 to 1.8) | 1.3 ± 0.3 † (1.2 to 1.4) | 34.5 | <0.01 | 0.5 large |
| sCK (IU/L) | 187.3 ± 182.2 (106.5 to 268.0) | 528.0 ± 345.2 * (374.9 to 680.9) | 677.0 ± 534.2 * (440.1 to 913.8) | 16.3 | <0.01 | 0.3 large |
| sBUN (mg/dL) | 14.5 ± 4.1 (12.7 to 16.3) | 19.4 ± 4.6 * (17.3 to 21.4) | 18.9 ± 4.2 * (17.0 to 20.8) | 26.9 | <0.01 | 0.5 large |
| sALB (IU/L) | 4.5 ± 0.7 (4.2 to 4.9) | 5.1 ± 0.8 * (4.7 to 5.4) | 4.7 ± 0.2 (4.6 to 4.8) | 7.8 | <0.01 | 0.2 large |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73m2) | 80.5 ± 24.7 (69.5 to 91.4) | 69.9 ± 18.5 * (61.7 to 78.1) | 74.7 ± 21.3 (65.3 to 84.1) | 5.4 | <0.01 | 0.1 moderate |
| CrClearance (mL/min) | 87.4 ± 30.0 (74.1 to 100.7) | 60.9 ± 25.9 * (49.4 to 72.4) | 78.1 ± 30.8 *† (64.4 to 91.7) | 43.8 | <0.01 | 0.6 large |
| sBUN/sCr ratio | 12.2 ± 3.3 (10.8 to 13.7) | 12.0 ± 2.7 (10.8 to 13.3) | 15.3 ± 4.0 *† (13.5 to 17.1) | 15.7 | <0.01 | 0.3 large |
| Heat Strain and Hydration | ||||||
| USG | 1.02 ± 0.02 (1.0 to 1.0) | 1.02 ± 0.01 (1.0 to 1.0) | 1.02 ± 0.01 (1.0 to 1.0) | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0 trivial |
| USol | 3.7 ± 2 (2.6 to 4.8) | 5.4 ± 2 * (4.3 to 6.5) | 4.7 ± 2.3 (3.5 to 6.0) | 4.5 | 0.01 | 0.1 moderate |
| Htc (%) | 41.2 ± 2.9 (40 to 42.4) | 42.4 ± 3.7 (41 to 43.8) | - | −1.4 | 0.2 | 0.3 small |
| BW (kg) | 71.7 ± 10.8 (67.6 to 75.8) | 67.8 ± 15.8 * (61.7 to 73.9) | - | 2.3 | 0.03 | 0.5 moderate |
| Variable | Pre- | -Post0h | χ2 | p-Value | Pre- | -Post24h | χ2 | p-Value | -Post0h | -Post24h | χ2 | p-Value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | |||||||
| pH ≤ 5 | 18 | 60.0% | 13 | 43.3% | 2.3 | 0.1 | 18 | 60.0% | 12 | 40.0% | 6.4 | 0.04 | 13 | 43.3% | 12 | 40% | 1.7 | 0.44 |
| Proteinuria 1+ or higher | 1 | 3.3% | 13 | 43.3% | 10.3 | <0.01 | 1 | 3.3% | 1 | 3.3% | 0.0 | 1.0 | 13 | 43.3% | 1 | 3.3% | 10.3 | <0.01 |
| Glucosuria 1+ or higher | 0 | 0.0% | 0 | 0.0% | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0 | 0.0% | 0 | 0.0% | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0 | 0.0% | 0 | 0.0% | 0.0 | 1.0 |
| Hematuria 1+ or higher | 1 | 3.3% | 8 | 26.7% | 12.2 | <0.01 | 1 | 3.3% | 3 | 6.7% | 1.3 | 0.5 | 8 | 26.7% | 3 | 6.7% | 6.0 | 0.04 |
| USG > 1.020 | 10 | 33.3% | 20 | 66.7% | 3.2 | 0.1 | 10 | 33.3% | 14 | 46.7% | 2.2 | 0.3 | 20 | 66.7% | 14 | 46.7% | 5.3 | 0.07 |
| Variable | Pre- | 1st Lap | 2nd Lap | Post0h | F Value | p-Value | ωp2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RPE | 0.0 ± 0.0 (0.0 to 0.0) | 6.4 ± 2.2 * (5.5 to 7.2) | 7.6 ± 2.0 * (6.8 to 8.4) | 8.8 ± 1.2 *†¶ (8.3 to 9.2) | 176.4 | <0.01 | 0.9 large |
| Lumbar Pain | 0.0 ± 0.0 (0.0 to 0.0) | 0.0 ± 0.0 (0.0 to 0.0) | 1.0 ± 1.8 *† (0.3 to 1.7) | 0.9 ± 2.1 *† (0.1 to 1.8) | 4.2 | <0.01 | 0.1 moderate |
| Squat Pain | 0.1 ± 0.4 (0.08 to 0.2) | 0.4 ± 1.1 (0.1 to 0.8) | 2.7 ± 3.4 *† (1.3 to 4.1) | 2.5 ± 3.2 *† (1.2 to 3.7) | 11.7 | <0.01 | 0.3 large |
| One-leg squat Pain | 0.1 ± 0.4 (0.08 to 0.2) | 0.3 ± 1.0 (0.1 to 0.7) | 1.7 ± 2.8 * (0.5 to 2.8) | 1.9 ± 3.0 *† (0.7 to 3.2) | 6.8 | <0.01 | 0.2 large |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rojas-Valverde, D.; Martínez-Guardado, I.; Sánchez-Ureña, B.; Timón, R.; Scheer, V.; Pino-Ortega, J.; Olcina, G. Outpatient Assessment of Mechanical Load, Heat Strain and Dehydration as Causes of Transitional Acute Kidney Injury in Endurance Trail Runners. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph181910217
Rojas-Valverde D, Martínez-Guardado I, Sánchez-Ureña B, Timón R, Scheer V, Pino-Ortega J, Olcina G. Outpatient Assessment of Mechanical Load, Heat Strain and Dehydration as Causes of Transitional Acute Kidney Injury in Endurance Trail Runners. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(19):10217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph181910217
Chicago/Turabian StyleRojas-Valverde, Daniel, Ismael Martínez-Guardado, Braulio Sánchez-Ureña, Rafael Timón, Volker Scheer, José Pino-Ortega, and Guillermo Olcina. 2021. "Outpatient Assessment of Mechanical Load, Heat Strain and Dehydration as Causes of Transitional Acute Kidney Injury in Endurance Trail Runners" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 19: 10217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph181910217
APA StyleRojas-Valverde, D., Martínez-Guardado, I., Sánchez-Ureña, B., Timón, R., Scheer, V., Pino-Ortega, J., & Olcina, G. (2021). Outpatient Assessment of Mechanical Load, Heat Strain and Dehydration as Causes of Transitional Acute Kidney Injury in Endurance Trail Runners. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(19), 10217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph181910217











