Facial Expression Processing of Children Orphaned by Parental HIV/AIDS: A Cross-Sectional ERP Study with Rapid Serial Visual Presentation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Stimuli and Procedure
2.3. Apparatus
2.4. ERP Data Preprocessing and Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Behavioral Performance
3.2. ERP Data Analysis
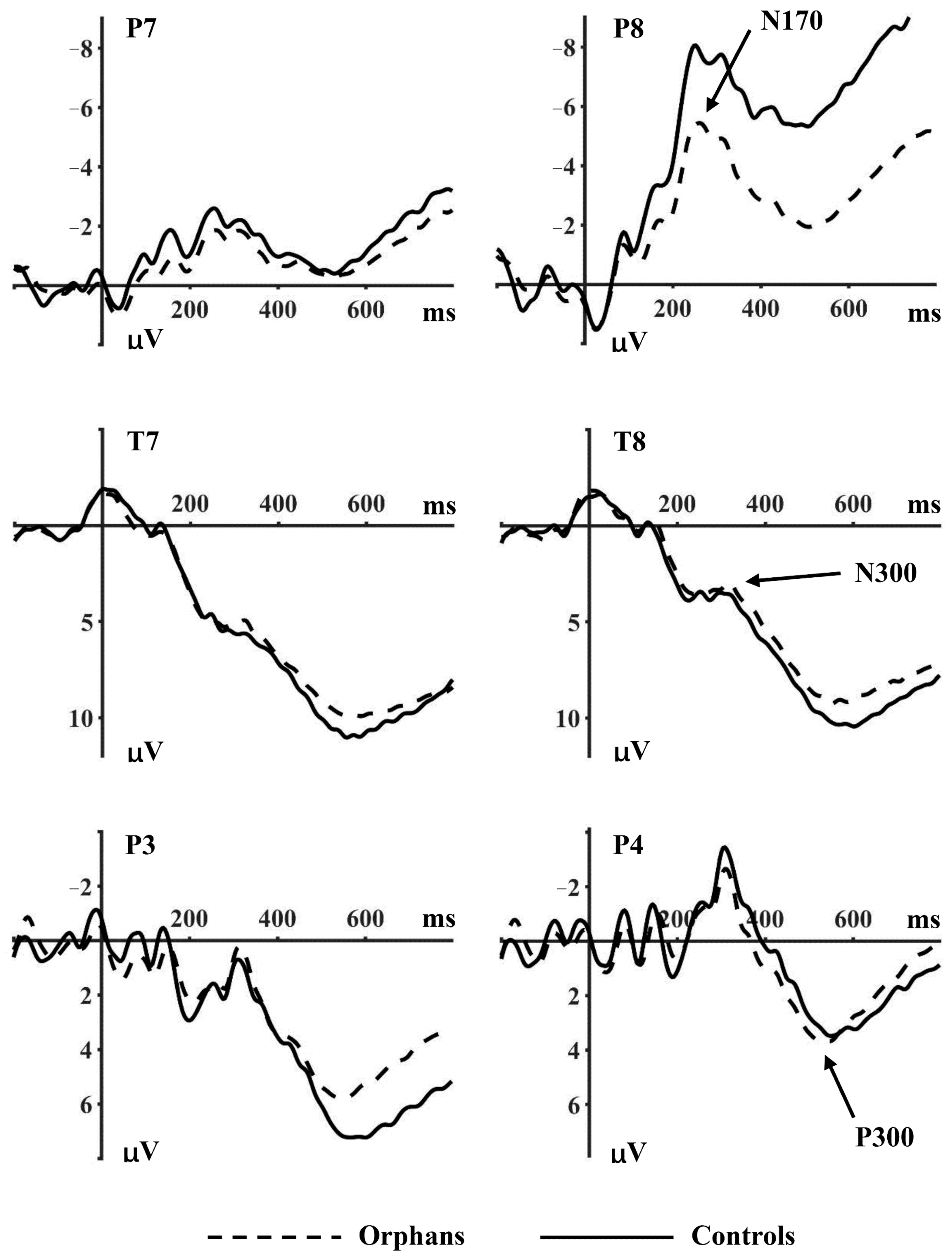
3.2.1. N170
3.2.2. N300
3.2.3. P300
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, Q.; Li, X.; Fang, X.; Zhao, G.; Zhao, J.; Lin, X.; Stanton, B. Difference in psychosocial well-being between paternal and maternal AIDS orphans in rural China. J. Assoc. Nurses AIDS Care 2010, 21, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atwine, B.; Cantor-Graae, E.; Bajunirwe, F. Psychological distress among AIDS orphans in rural Uganda. Soc. Sci. Med. 2005, 61, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, C.; Skovdal, M.; Mupambireyi, Z.; Gregson, S. Exploring children’s stigmatisation of AIDS-affected children in Zimbabwe through drawings and stories. Soc. Sci. Med. 2010, 71, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cluver, L.; Bowes, L.; Gardner, F. Risk and protective factors for bullying victimization among AIDS-affected and vulnerable children in South Africa. Child Abuse Neglect. 2010, 34, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Naar-King, S.; Barnett, D.; Stanton, B.; Fang, X.; Thurston, C. A developmental psychopathology framework of the psychosocial needs of children orphaned by HIV. J. Assoc. Nurses AIDS Care 2008, 19, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Skinner, D.; Tsheko, N.; Mtero-Munyati, S.; Segwabe, M.; Chibatamoto, P.; Mfecane, S.; Chandiwana, B.; Nkomo, N.; Tlou, S.; Chitiyo, G. Towards a definition of orphaned and vulnerable children. AIDS Behav. 2006, 10, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilton, S.M. Improving early childhood development outcomes for children affected by HIV and AIDS. AIDS 2014, 28 (Suppl. 3), S247–S248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chi, P.; Sherr, L.; Cluver, L.; Stanton, B. Psychological Resilience among Children Affected by Parental HIV/AIDS: A Conceptual Framework. Health Psychol. Behav. Med. 2015, 3, 217–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lovallo, W.R. Early life adversity reduces stress reactivity and enhances impulsive behavior: Implications for health behaviors. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2013, 90, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, D.W.; Anda, R.F.; Tiemeier, H.; Felitti, V.J.; Edwards, V.J.; Croft, J.B.; Giles, W.H. Adverse childhood experiences and the risk of premature mortality. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2009, 37, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, C.; Binder, E.B. Current research trends in early life stress and depression: Review of human studies on sensitive periods, gene-environment interactions, and epigenetics. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 233, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, S.J.; Arseneault, L.; Caspi, A.; Fisher, H.L.; Matthews, T.; Moffitt, T.E.; Odgers, C.L.; Stahl, D.; Teng, J.Y.; Danese, A. The epidemiology of trauma and post-traumatic stress disorder in a representative cohort of young people in England and Wales. Lancet Psychiat. 2019, 6, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dannlowski, U.; Kugel, H.; Huber, F.; Stuhrmann, A.; Redlich, R.; Grotegerd, D.; Dohm, K.; Sehlmeyer, C.; Konrad, C.; Baune, B.T.; et al. Childhood maltreatment is associated with an automatic negative emotion processing bias in the amygdala. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2013, 34, 2899–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enoch, M.A. The role of early life stress as a predictor for alcohol and drug dependence. Psychopharmacology 2011, 214, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petersen, I.T.; Hoyniak, C.P.; Bates, J.E.; Staples, A.D.; Molfese, D.L. A longitudinal, within-person investigation of the association between the P3 ERP component and externalizing behavior problems in young children. J. Child. Psychol. Psychiatry 2018, 59, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, S.J. Neurocognitive mechanisms of anxiety: An integrative account. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2007, 11, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosch, T.; Sander, D. Comment: The Appraising Brain: Towards a Neuro-Cognitive Model of Appraisal Processes in Emotion. Emot. Rev. 2013, 5, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McLaughlin, K.A.; Weissman, D.; Bitran, D. Childhood Adversity and Neural Development: A Systematic Review. Annu. Rev. Dev. Psychol. 2019, 1, 277–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pakulak, E.; Stevens, C.; Neville, H. Neuro-, Cardio-, and Immunoplasticity: Effects of Early Adversity. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2018, 69, 131–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Qin, S.; Yao, Z.; Zhang, K.; Wu, J. Long-term academic stress enhances early processing of facial expressions. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2016, 109, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rellecke, J.; Sommer, W.; Schacht, A. Does processing of emotional facial expressions depend on intention? Time-resolved evidence from event-related brain potentials. Biol. Psychol. 2012, 90, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.K.; Fung, P.C.; Chua, S.E.; McAlonan, G.M. Abnormal spatiotemporal processing of emotional facial expressions in childhood autism: Dipole source analysis of event-related potentials. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Chen, Q.; Xing, X.; Zhao, J.; Li, X. Facial emotion recognition in deaf children: Evidence from event-related potentials and event-related spectral perturbation analysis. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 703, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares, E.I.; Iglesias, J.; Saavedra, C.; Trujillo-Barreto, N.J.; Valdes-Sosa, M. Brain Signals of Face Processing as Revealed by Event-Related Potentials. Behav. Neurol. 2015, 2015, 514361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neath-Tavares, K.N.; Itier, R.J. Neural processing of fearful and happy facial expressions during emotion-relevant and emotion-irrelevant tasks: A fixation-to-feature approach. Biol. Psychol. 2016, 119, 122–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rossion, B. Understanding face perception by means of human electrophysiology. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2014, 18, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, M.E.; Class, Q.A.; Polich, J. Affective valence, stimulus attributes, and P300: Color vs. black/white and normal vs. scrambled images. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2009, 71, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carretie, L.; Iglesias, J.; Garcia, T.; Ballesteros, M. N300, P300 and the emotional processing of visual stimuli. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1997, 103, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, W.N.; Hu, W.; Luo, Y.J. Understanding the subliminal affective priming effect of facial stimuli: An ERP study. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 502, 182–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Feng, W.; He, W.; Wang, N.Y.; Luo, Y.J. Three stages of facial expression processing: ERP study with rapid serial visual presentation. Neuroimage 2010, 49, 1857–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Harrison, S.E.; Fairchild, A.J.; Chi, P.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, G. A randomized controlled trial of a resilience-based intervention on psychosocial well-being of children affected by HIV/AIDS: Effects at 6- and 12-month follow-up. Soc. Sci. Med. 2017, 190, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, P.; Slatcher, R.B.; Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, G.; Ren, X.; Zhu, J.; Stanton, B. Perceived Stigmatization, Resilience, and Diurnal Cortisol Rhythm Among Children of Parents Living With HIV. Psychol. Sci. 2015, 26, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cluver, L.D.; Gardner, F.; Operario, D. Effects of stigma on the mental health of adolescents orphaned by AIDS. J. Adolesc. Health 2008, 42, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ji, L.; Du, S.; Gu, H.; Zhao, Q.; Chi, P.; Li, X. Working memory impairment in children orphaned by parental HIV/AIDS: An event-related potentials study. Psychol. Health Med. 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quas, J.A.; Dickerson, K.L.; Matthew, R.; Harron, C.; Quas, C.M. Adversity, emotion recognition, and empathic concern in high-risk youth. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gu, H.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, J.X.; Zhao, J.F.; Ji, L.L.; Chi, P.L.; Li, X.M. EEG oscillation evidences of altered resting-state brain activity in children orphaned by parental HIV/AIDS. AIDS Care 2020, 32, S177–S182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, E.K.; Luck, S.J.; Shapiro, K.L. Electrophysiological evidence for a postperceptual locus of suppression during the attentional blink. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 1998, 24, 1656–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratton, G.; Coles, M.G.; Donchin, E. A new method for off-line removal of ocular artifact. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1983, 55, 468–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, M.J.; Aranda, D.; Ellgring, H.; Mueller, T.J.; Strik, W.K.; Heidrich, A.; Fallgatter, A.J. Face-specific event-related potential in humans is independent from facial expression. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2002, 45, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinojosa, J.A.; Mercado, F.; Carretie, L. N170 sensitivity to facial expression: A meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2015, 55, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krombholz, A.; Schaefer, F.; Boucsein, W. Modification of N170 by different emotional expression of schematic faces. Biol. Psychol. 2007, 76, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estes, Z.; Verges, M. Freeze or flee? Negative stimuli elicit selective responding. Cognition 2008, 108, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bramon, E.; Rabe-Hesketh, S.; Sham, P.; Murray, R.M.; Frangou, S. Meta-analysis of the P300 and P50 waveforms in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2004, 70, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euser, A.S.; Evans, B.E.; Greaves-Lord, K.; van de Wetering, B.J.; Huizink, A.C.; Franken, I.H. Multifactorial determinants of target and novelty-evoked P300 amplitudes in children of addicted parents. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klawohn, J.; Santopetro, N.J.; Meyer, A.; Hajcak, G. Reduced P300 in depression: Evidence from a flanker task and impact on ERN, CRN, and Pe. Psychophysiology 2020, 57, e13520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangal, R.B.; Sangal, J.M. Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: Use of cognitive evoked potential(P300) to predict treatment response. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2006, 117, 1996–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schupp, H.T.; Junghofer, M.; Weike, A.I.; Hamm, A.O. The selective processing of briefly presented affective pictures: An ERP analysis. Psychophysiology 2004, 41, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balconi, M.; Crivelli, D. FRN and P300 ERP effect modulation in response to feedback sensitivity: The contribution of punishment-reward system (BIS/BAS) and behaviour identification of action. Neurosci. Res. 2010, 66, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; He, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wei, Z. Deficits of unconscious emotional processing in patients with major depression: An ERP study. J. Affect. Disord. 2016, 199, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Orphan Group | Control Group | F or χ2 | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of subjects | 81 | 60 | |||
| Gender N(%) | Boys | 46 (65.7%) | 24 (34.3%) | 3.887 | 0.061 |
| Girls | 35 (49.3%) | 36 (50.7%) | |||
| age (years) | 14.64 ± 1.43 | 12.43 ± 1.62 | 87.372 | <0.001 | |
| Accuracy (%) | 0.87 ± 0.11 | 0.84 ± 0.13 | 9.674 | 0.002 | |
| Response time (ms) | 745.05 ± 256.72 | 904.32 ± 318.92 | 4.539 | 0.035 | |
| ERP Components | Facial Emotion | Electrode Point | Average Amplitudes (μV) | F or χ2 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Orphans | Controls | |||||
| N170 | Happy | P7 | −2.09 ± 3.94 | −1.75 ± 3.66 | 0.261 | 0.610 |
| P8 | −2.86 ± 8.60 | −5.29 ± 4.02 | 4.135 | 0.044 | ||
| Neutral | P7 | −1.71 ± 9.13 | −1.67 ± 7.35 | 0.001 | 0.978 | |
| P8 | −1.87 ± 5.23 | −4.15 ± 6.23 | 5.548 | 0.020 | ||
| Fearful | P7 | −1.45 ± 6.32 | −2.55 ± 5.87 | 1.094 | 0.298 | |
| P8 | −4.25 ± 8.14 | −5.24 ± 4.77 | 0.702 | 0.404 | ||
| N300 | Happy | T7 | 3.28 ± 5.20 | 4.33 ± 4.32 | 1.606 | 0.207 |
| T8 | 2.76 ± 4.42 | 2.52 ± 3.95 | 0.119 | 0.730 | ||
| Neutral | T7 | 3.50 ± 5.39 | 2.25 ± 8.28 | 1.177 | 0.280 | |
| T8 | 3.30 ± 5.93 | 1.31 ± 6.72 | 3.466 | 0.065 | ||
| Fearful | T7 | 2.49 ± 7.79 | 2.72 ± 6.80 | 0.032 | 0.858 | |
| T8 | 1.77 ± 6.24 | 1.93 ± 3.96 | 0.028 | 0.867 | ||
| P300 | Happy | P3 | 5.09 ± 10.44 | 8.16 ± 8.87 | 3.379 | 0.068 |
| P4 | 3.29 ± 10.53 | 5.01 ± 9.62 | 0.988 | 0.322 | ||
| Pz | 8.57 ± 9.90 | 9.83 ± 7.86 | 0.669 | 0.415 | ||
| Neutral | P3 | 5.60 ± 8.92 | 5.41 ± 10.80 | 0.013 | 0.909 | |
| P4 | 4.69 ± 7.55 | 3.41 ± 10.94 | 0.679 | 0.411 | ||
| Pz | 9.69 ± 10.09 | 6.94 ± 10.76 | 2.436 | 0.121 | ||
| Fearful | P3 | 6.18 ± 13.11 | 7.59 ± 11.14 | 0.455 | 0.501 | |
| P4 | 4.33 ± 10.59 | 4.96 ± 11.67 | 0.122 | 0.739 | ||
| Pz | 8.13 ± 18.17 | 8.87 ± 10.97 | 0.079 | 0.778 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Q.; He, H.; Gu, H.; Zhao, J.; Chi, P.; Li, X. Facial Expression Processing of Children Orphaned by Parental HIV/AIDS: A Cross-Sectional ERP Study with Rapid Serial Visual Presentation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9995. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18199995
Zhao Q, He H, Gu H, Zhao J, Chi P, Li X. Facial Expression Processing of Children Orphaned by Parental HIV/AIDS: A Cross-Sectional ERP Study with Rapid Serial Visual Presentation. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(19):9995. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18199995
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Qi, Hui He, Huang Gu, Junfeng Zhao, Peilian Chi, and Xiaoming Li. 2021. "Facial Expression Processing of Children Orphaned by Parental HIV/AIDS: A Cross-Sectional ERP Study with Rapid Serial Visual Presentation" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 19: 9995. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18199995
APA StyleZhao, Q., He, H., Gu, H., Zhao, J., Chi, P., & Li, X. (2021). Facial Expression Processing of Children Orphaned by Parental HIV/AIDS: A Cross-Sectional ERP Study with Rapid Serial Visual Presentation. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(19), 9995. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18199995






