Contamination Transport in the Coastal Unconfined Aquifer under the Influences of Seawater Intrusion and Inland Freshwater Recharge—Laboratory Experiments and Numerical Simulations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
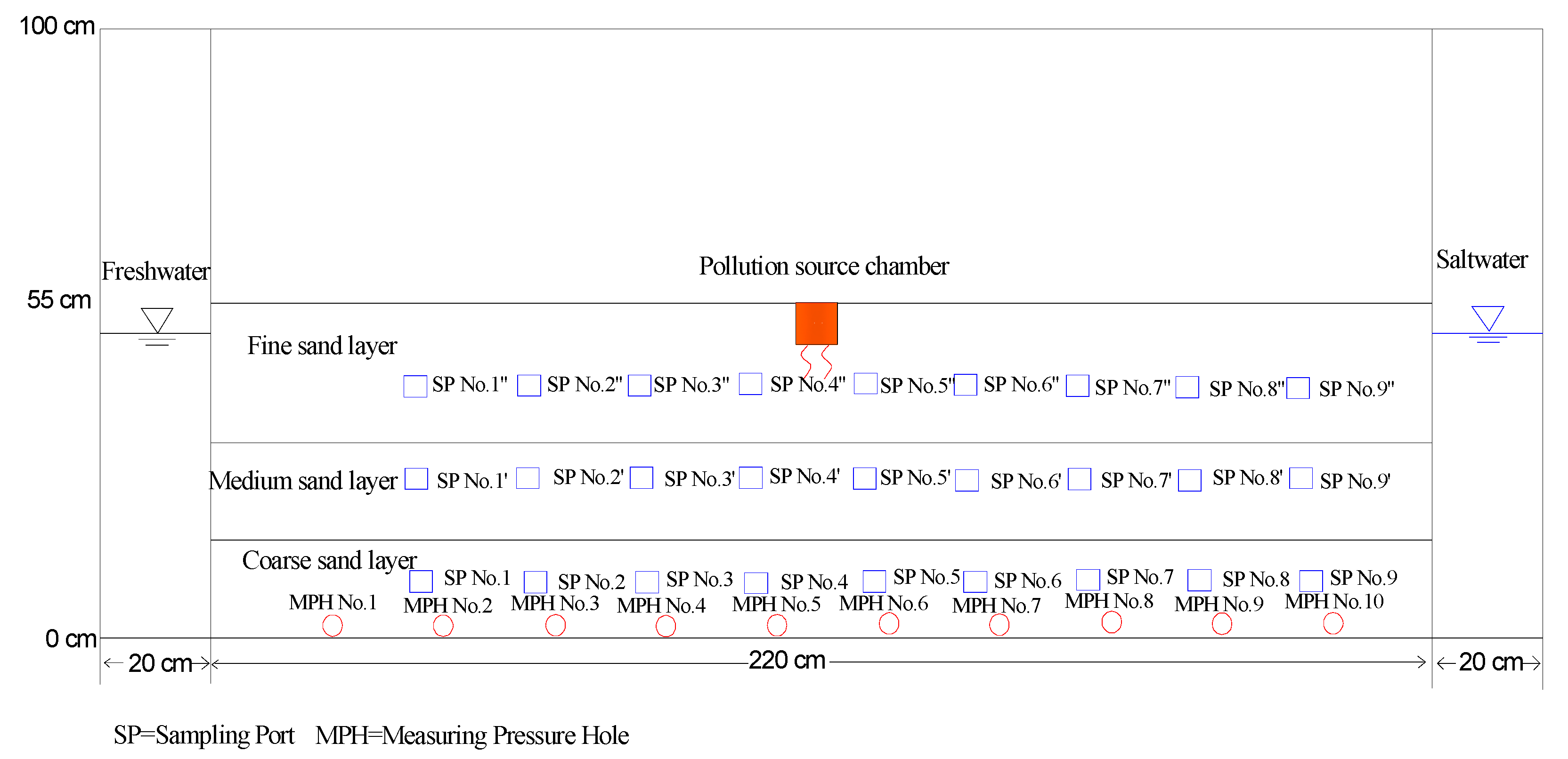
2.1. Laboratory Experiment
2.2. Numerical Model and Procedure
3. Results and Discussions
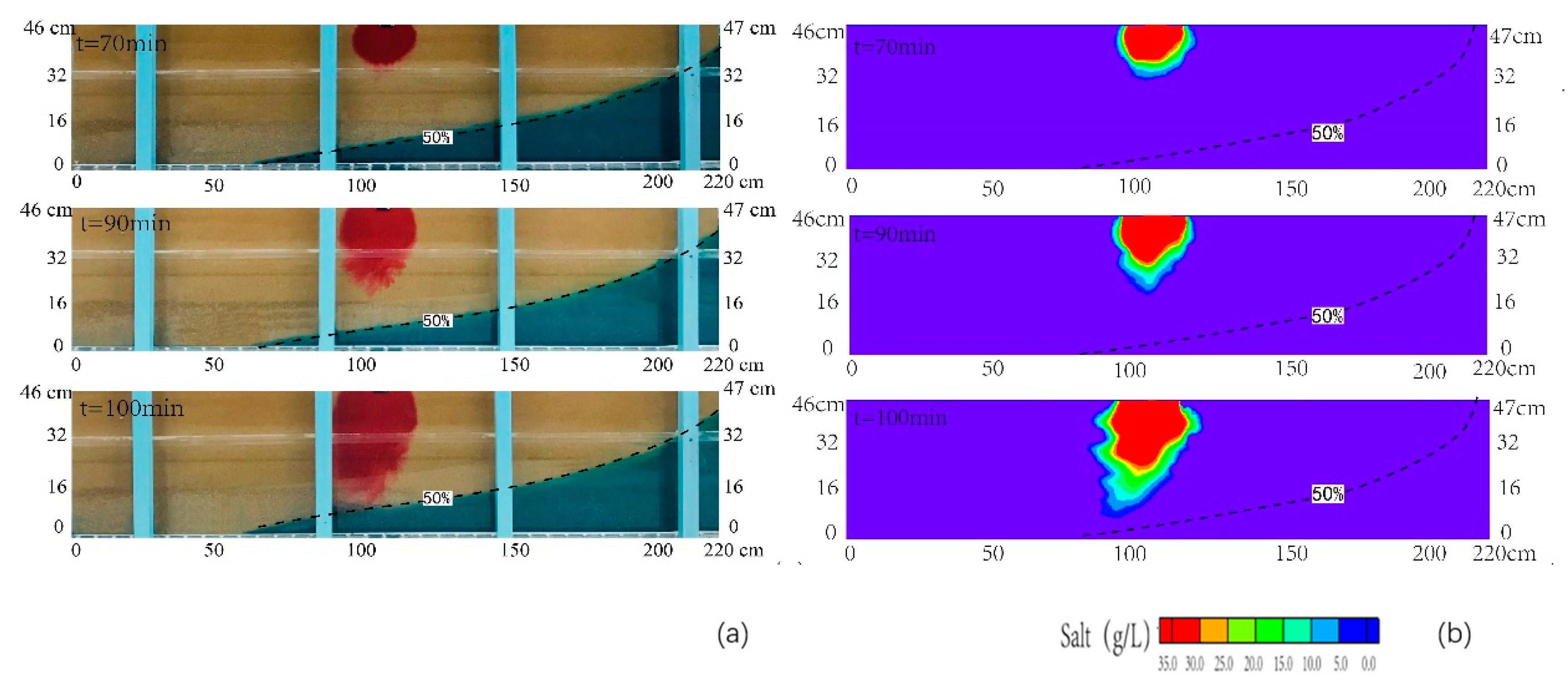
3.1. Salinity of Basic Scenarios
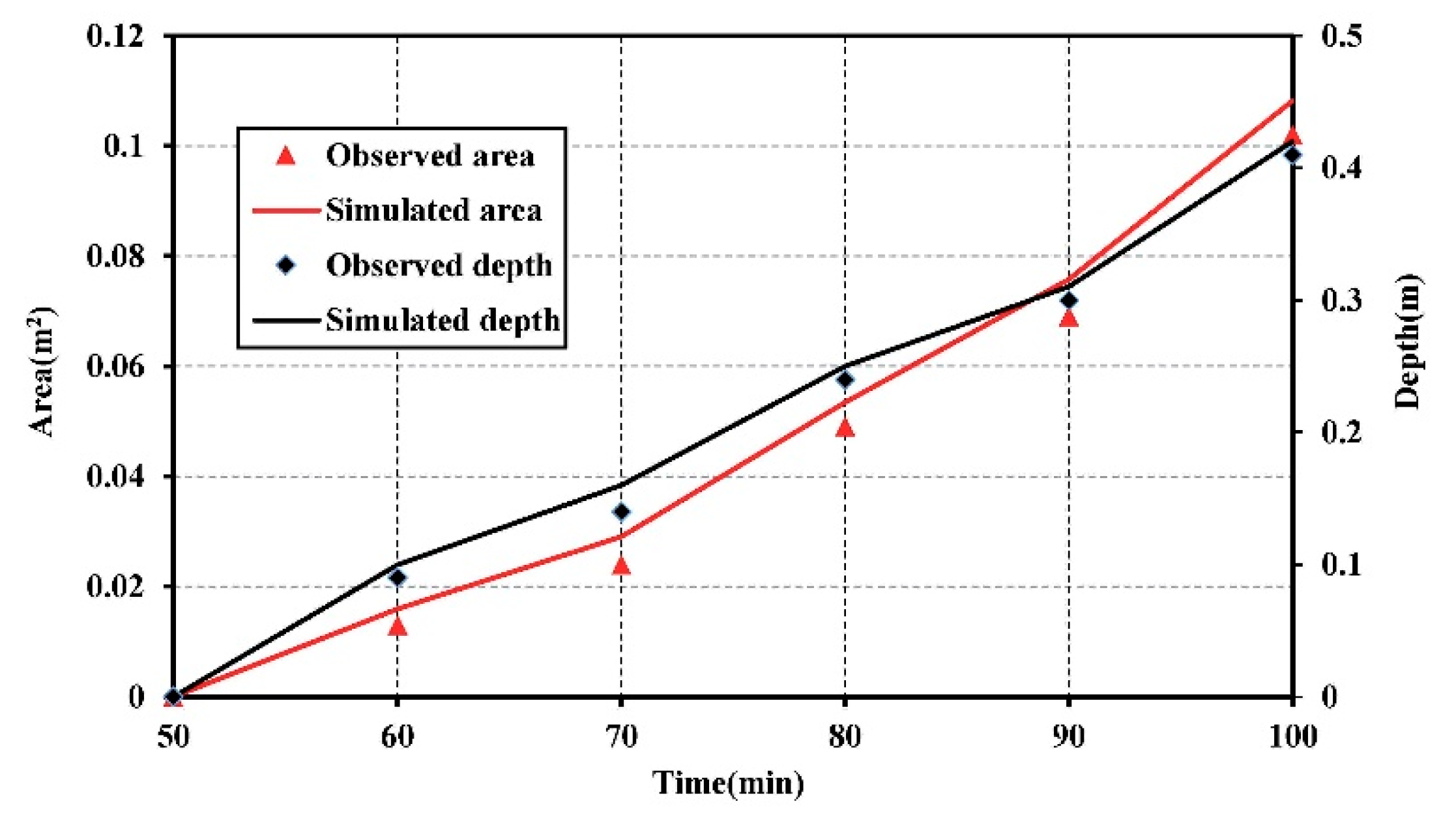
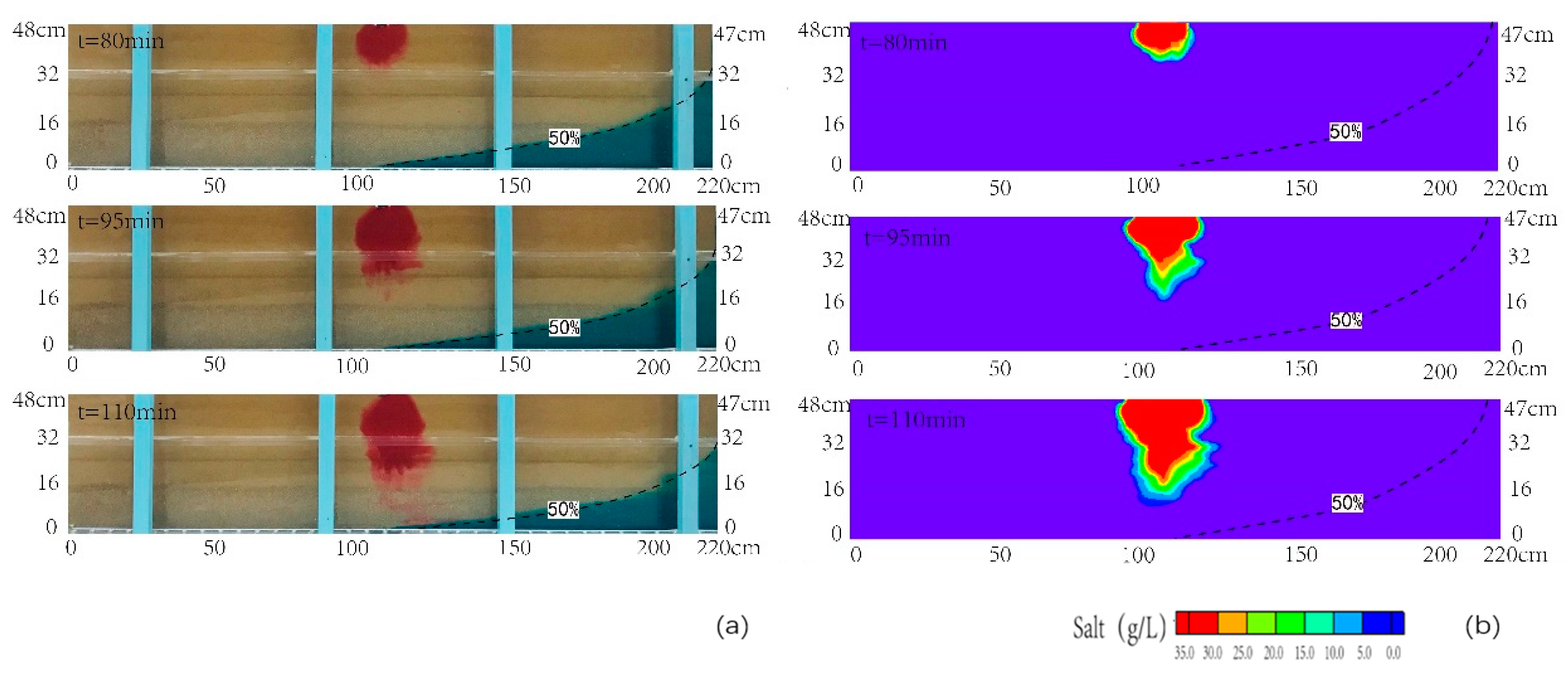
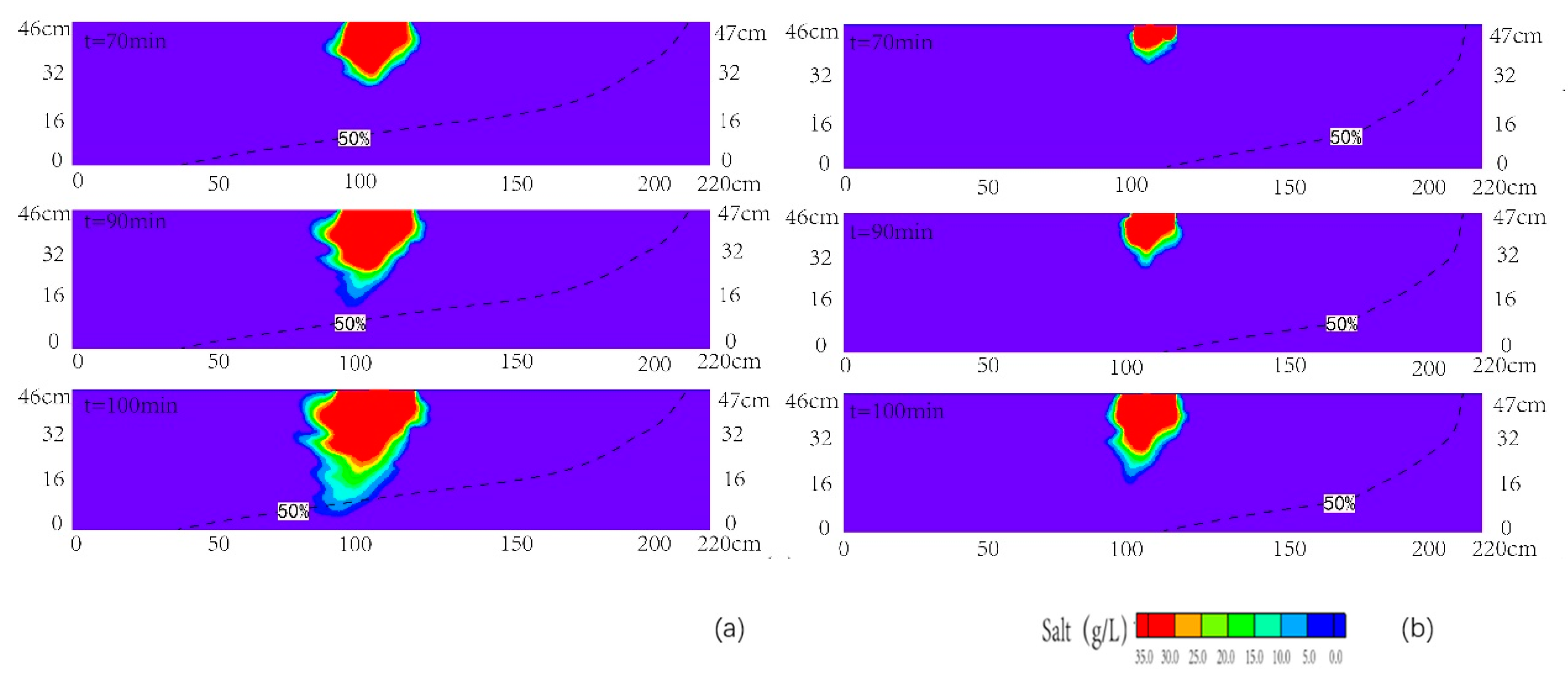
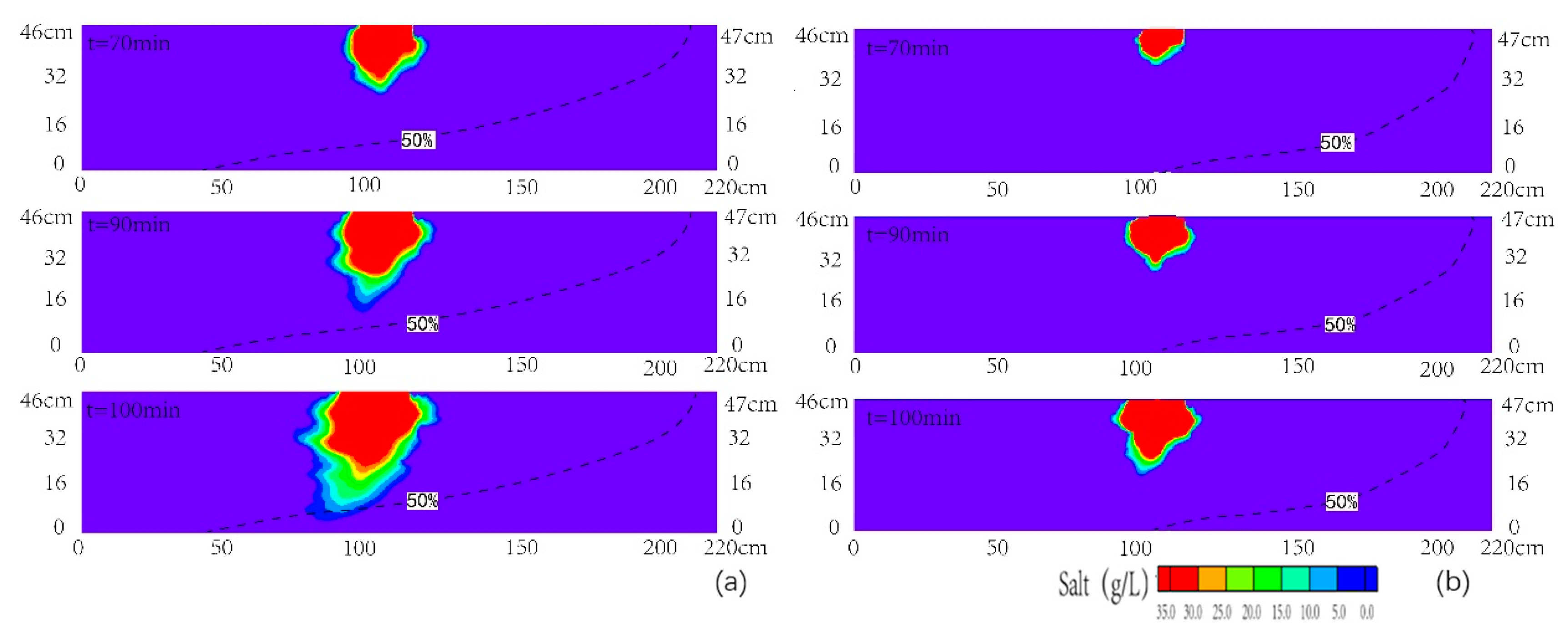
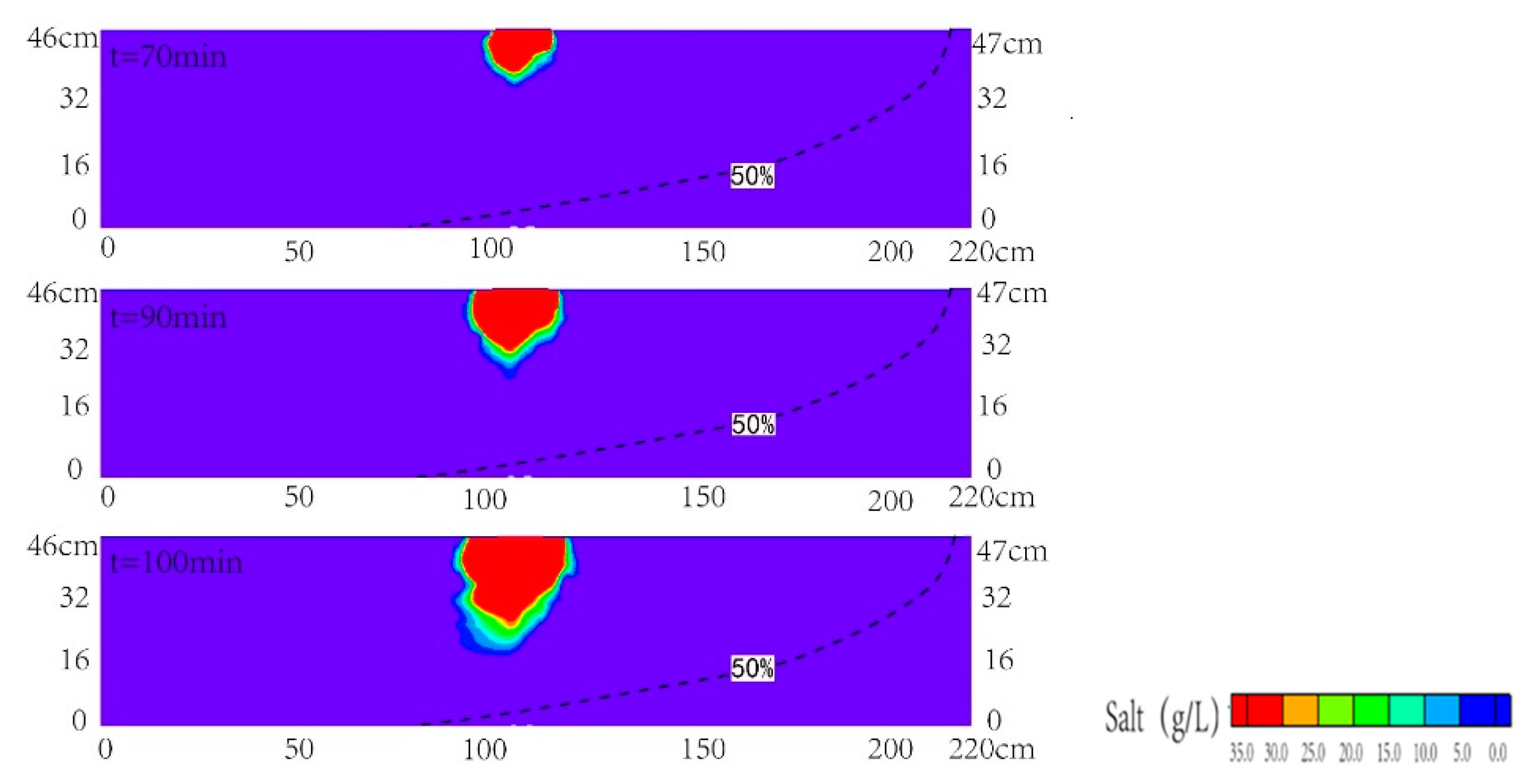
3.2. Transport of Contamination in Heterogeneous Aquifer
3.3. Sensitivity Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Post, V. Fresh and saline groundwater interaction in coastal aquifers: Is our technology ready for the problems ahead? Hydrogeol. J. 2005, 13, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherif, M.; Sefelnasr, A.; Javadi, A. Incorporating the concept of equivalent freshwater head in successive horizontal simulations of seawater intrusion in the Nile Delta aquifer, Egypt. J. Hydrol. 2012, 464, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, A.D.; Bakker, M.; Post, V.E.A.; Vandenbohede, A.; Lu, C.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Simmons, C.T.; Barry, D. Seawater intrusion processes, investigation and management: Recent advances and future challenges. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sefelnasr, A.; Sherif, M. Impacts of Seawater Rise on Seawater Intrusion in the Nile Delta Aquifer, Egypt. Ground Water 2014, 52, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Huang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, J. Experiment and Numerical Simulation of Seawater Intrusion under the Influences of Tidal Fluctuation and Groundwater Exploitation in Coastal Multilayered Aquifers. Geofluids 2019, 2019, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farrell, E.R. Analysis of groundwater flow through leaky marine retaining structures. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Géoméch. Abstr. 1995, 32, A35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oki, D.S.; Souza, W.R.; Bolke, E.L.; Bauer, G.R. Numerical analysis of the hydrogeologic controls in a layered coastal aquifer system, Oahu, Hawaii, USA. Hydrogeol. J. 1998, 6, 243–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koohbor, B.; Fahs, M.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Simmons, C.T.; Younes, A. Semianalytical solutions for contaminant transport under variable velocity field in a coastal aquifer. J. Hydrol. 2018, 560, 434–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, M.; Luo, X.; Jiao, J.J.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Gao, J.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, K. Nutrients and heavy metals mediate the distribution of microbial community in the marine sediments of the Bohai Sea, China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Xiao, K.; Qu, W. Evaluations of submarine groundwater discharge and associated heavy metal fluxes in Bohai Bay, China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 695, 133873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Michael, H.A. Mechanisms, configuration typology, and vulnerability of pumping-induced seawater intrusion in heterogeneous aquifers. Adv. Water Resour. 2019, 128, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Michael, H.A. Offshore Pumping Impacts Onshore Groundwater Resources and Land Subsidence. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 2553–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-H.; Wang, W.; Han, T.-T.; Liu, D.-H.; Fang, J.-G.; Jiang, Z.-J.; Liu, X.-J.; Zhang, X.-J.; Lian, Y. The distributions of dissolved nutrients in spring of Sungo Bay and potential reason of outbreak of red tide. J. Fish. China 2012, 36, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbeck, L.S.; Unger, D.; Wu, Y.; Jennerjahn, T.C. Effluent, nutrient and organic matter export from shrimp and fish ponds causing eutrophication in coastal and back-reef waters of NE Hainan, tropical China. Cont. Shelf Res. 2013, 57, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Volker, R.; Lockington, D. Tidal effects on sea water intrusion in unconfined aquifers. J. Hydrol. 1999, 216, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elhamid, H.F.; Javadi, A.A. Impact of sea level rise and over-pumping on seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2011, 2, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Werner, A.D.; Simmons, C.T.; Morgan, L.K.; Lu, C. How important is the impact of land-surface inundation on seawater intrusion caused by sea-level rise? Hydrogeol. J. 2013, 21, 1673–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, N.; Robinson, C.E.; Barry, D. Influence of tides and waves on the fate of nutrients in a nearshore aquifer: Numerical simulations. Adv. Water Resour. 2014, 73, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Xin, P.; Li, L.; Luo, J. Seawater intrusion in response to sea-level rise in a coastal aquifer with a general-head inland boundary. J. Hydrol. 2015, 522, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketabchi, H.; Mahmoodzadeh, D.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Simmons, C.T. Sea-level rise impacts on seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers: Review and integration. J. Hydrol. 2016, 535, 235–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Dong, J.; Wang, D.; Wu, J.; Zhu, X.; Xu, S.; Zheng, X.; Xin, J. Identifying key factors of the seawater intrusion model of Dagu river basin, Jiaozhou Bay. Environ. Res. 2018, 165, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, C.; Luo, J. Steady-state freshwater—Seawater mixing zone in stratified coastal aquifers. J. Hydrol. 2013, 505, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Xin, P.; Kong, J.; Li, L.; Luo, J. Analytical solutions of seawater intrusion in sloping confined and unconfined coastal aquifers. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 6989–7004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Shi, W.; Xin, P.; Wu, J.; Werner, A.D. Replenishing an unconfined coastal aquifer to control seawater intrusion: Injection or infiltration? Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 4775–4786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, M.K.; Ginn, T.R. Impact of numerical artifact of the forward model in the inverse solution of density-dependent flow problem. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 6322–6338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.; Li, H.; Wan, L.; Wang, X.; Jiang, X.-W. Numerical simulations of steady-state salinity distribution and submarine groundwater discharges in homogeneous anisotropic coastal aquifers. Adv. Water Resour. 2014, 74, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.; Fahs, M.; Hoteit, H.; Carrera, J.; Ackerer, P.; Younes, A. A 3-D Semianalytical Solution for Density-Driven Flow in Porous Media. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 10094–10116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bear, J. Hydraulics of groundwater. Adv. Water Resour. 1980, 3, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, M. Analytic solutions for interface flow in combined confined and semi-confined, coastal aquifers. Adv. Water Resour. 2005, 29, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacimov, A.R.; Sherif, M.M. Sharp interface, one-dimensional seawater intrusion into a confined aquifer with controlled pumping: Analytical solution. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42, 10094–10116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strack, O.D.L. Salt water interface in a layered coastal aquifer: The only published analytic solution is in error. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 1502–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajabi, M.M.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Simmons, C.T. Polynomial chaos expansions for uncertainty propagation and moment independent sensitivity analysis of seawater intrusion simulations. J. Hydrol. 2015, 520, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Hu, B.X.; Ye, M. Numerical modeling and sensitivity analysis of seawater intrusion in a dual-permeability coastal karst aquifer with conduit networks. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diersch, H.J.G. WASY Software-FEFLOW: Finite Element Subsurface Flow & Transport Simulation System; Reference Manual, WASY; WASY Institue for Water Resources Planning and Systems Research Ltd.: Berlin, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Volker, R.E.; Lockington, D.A. Experimental investigation of contaminant transport in coastal groundwater. Adv. Environ. Res. 2002, 6, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataie-Ashtiani, B. MODSharp: Regional-scale numerical model for quantifying groundwater flux and contaminant discharge into the coastal zone. Environ. Model. Softw. 2007, 22, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-S.; Lai, K.-H.; Liu, C.-W.; Ni, C.-F. A novel method for analytically solving multi-species advective–dispersive transport equations sequentially coupled with first-order decay reactions. J. Hydrol. 2012, 420, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayek, M.; Kosakowski, G.; Jakob, A.; Churakov, S.V. A class of analytical solutions for multidimensional multispecies diffusive transport coupled with precipitation-dissolution reactions and porosity changes. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, S.W.; Clement, T.P. Laboratory and numerical investigation of transport processes occurring above and within a saltwater wedge. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2013, 147, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.T.; Dawson, C.N.; Farthing, M.W.; Hou, T.Y.; Huang, J.; Kees, C.E.; Kelley, C.; Langtangen, H.P. Numerical simulation of water resources problems: Models, methods, and trends. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 405–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Li, H.; Boufadel, M.C.; Liu, J. A field experiment and numerical modeling of a tracer at a gravel beach in Prince William Sound, Alaska. Hydrogeol. J. 2014, 22, 1795–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Mao, X.; Chen, J.; Barry, D.A. Influence of a coarse interlayer on seawater intrusion and contaminant migration in coastal aquifers. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 5162–5175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oz, I.; Shalev, E.; Yechieli, Y.; Gvirtzman, H. Saltwater circulation patterns within the freshwater–saltwater interface in coastal aquifers: Laboratory experiments and numerical modeling. J. Hydrol. 2015, 530, 734–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.C.; Kim, U. An upscaled approach for transport in media with extended tailing due to back-diffusion using analytical and numerical solutions of the advection dispersion equation. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2015, 182, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shahkarami, P.; Liu, L.; Moreno, L.; Neretnieks, I. Radionuclide migration through fractured rock for arbitrary-length decay chain: Analytical solution and global sensitivity analysis. J. Hydrol. 2015, 520, 448–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Zhang, C.; Kong, J.; Xin, P.; Lu, C.; Zhao, Z.; Li, L. Solute transport influenced by unstable flow in beach aquifers. Adv. Water Resour. 2019, 125, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Volker, R.E.; Lockington, D.A. Influence of seaward boundary condition on contaminant transport in unconfined coastal aquifers. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2001, 49, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boufadel, M.C.; Xia, Y.; Li, H. Modeling solute transport and transient seepage in a laboratory beach under tidal influence. Environ. Model. Softw. 2011, 26, 899–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Volker, R.E.; Lockington, D.A. Contaminant Transport in the Aquifers Influenced by Tide; Australian Civil Engineering Transactions, Institution of Engineering: Canberra, Australia, 2002; Volume CE43, pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, X.; Enot, P.; Barry, D.; Li, L.; Binley, A.; Jeng, D.-S. Tidal influence on behaviour of a coastal aquifer adjacent to a low-relief estuary. J. Hydrol. 2006, 327, 110–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brovelli, A.; Mao, X.; Barry, D. Numerical modeling of tidal influence on density-dependent contaminant transport. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bakhtyar, R.; Brovelli, A.; Barry, D.; Robinson, C.E.; Li, L. Transport of variable-density solute plumes in beach aquifers in response to oceanic forcing. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 53, 208–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Boufadel, M.C. Numerical study of solute transport in shallow beach aquifers subjected to waves and tides. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2015, 120, 1409–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, E.; He, W.; Savoy, H.; Dietrich, P.; Kolditz, O.; Rubin, Y.; Schüth, C.; Kalbacher, T. Identifying the influential aquifer heterogeneity factor on nitrate reduction processes by numerical simulation. Adv. Water Resour. 2017, 99, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jiao, J.J.; Luo, X. Effects of inland water level oscillation on groundwater dynamics and land-sourced solute transport in a coastal aquifer. Coast. Eng. 2016, 114, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Hu, Z. Transport of Contamination under the Influence of Sea Level Rise in Coastal Heterogeneous Aquifer. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Langevin, C.D. User’s Guide to SEAWAT: A Computer Program for Simulation of Three-Dimensional Variable-Density Groundwater Flow. 2002; pp. 1–434. Available online: https://fl.water.usgs.gov/PDF_files/twri_6_A7_guo_langevin.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- Langevin, C.D. Simulation of Submarine Ground Water Discharge to a Marine Estuary: Biscayne Bay, Florida. Ground Water 2003, 41, 758–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, M. A Dupuit formulation for modeling seawater intrusion in regional aquifer systems. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, B.X.; Burnett, W.C.; Santos, I.R.; Chanton, J.P. Submarine Ground Water Discharge Driven by Tidal Pumping in a Heterogeneous Aquifer. Ground Water 2009, 47, 558–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Hu, B.X.; Xu, Z.; Li, X.; Tong, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Miao, J.; Liu, H.; Ma, Z. Numerical simulation of seawater intrusion to coastal aquifers and brine water/freshwater interaction in south coast of Laizhou Bay, China. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2018, 215, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Q.; Zheng, T.; Zheng, X.; Chang, Q.; Walther, M. Influence of a subsurface cut-off wall on nitrate contamination in an unconfined aquifer. J. Hydrol. 2019, 575, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Definition | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| K | Hydraulic conductivity | m/d | 4.0 (fine sand layer) |
| 25.0 (medium sand layer) | |||
| 60.0 (coarse sand layer) | |||
| μ | Specific yield | - | 0.2 (fine sand layer) |
| 0.25 (medium sand layer) | |||
| 0.30 (coarse sand layer) | |||
| SS | Specific storage | 1/m | 10−5 |
| ρf | Density of the freshwater | kg/m3 | 1.0 × 103 |
| ρ | Density of the seawater | kg/m3 | 1.02 × 103 |
| n | porosity | - | 0.3 |
| αT | Longitudinal dispersivity | m | 0.1 |
| Transverse dispersivity | m | 0.01 | |
| τDm | Molecular diffusion coefficient in porous media | m2/s | 10−9 |
| t | Time period | min | 100 for scenario 1 |
| 110 for scenario 2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, Z.; Li, M. Contamination Transport in the Coastal Unconfined Aquifer under the Influences of Seawater Intrusion and Inland Freshwater Recharge—Laboratory Experiments and Numerical Simulations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18020762
Guo Q, Zhao Y, Hu Z, Li M. Contamination Transport in the Coastal Unconfined Aquifer under the Influences of Seawater Intrusion and Inland Freshwater Recharge—Laboratory Experiments and Numerical Simulations. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(2):762. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18020762
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Qiaona, Yue Zhao, Zili Hu, and Mengjun Li. 2021. "Contamination Transport in the Coastal Unconfined Aquifer under the Influences of Seawater Intrusion and Inland Freshwater Recharge—Laboratory Experiments and Numerical Simulations" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 2: 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18020762
APA StyleGuo, Q., Zhao, Y., Hu, Z., & Li, M. (2021). Contamination Transport in the Coastal Unconfined Aquifer under the Influences of Seawater Intrusion and Inland Freshwater Recharge—Laboratory Experiments and Numerical Simulations. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(2), 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18020762




