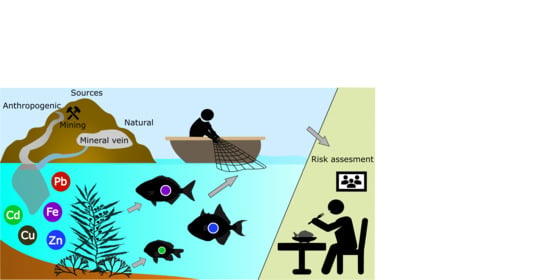
Cadmium, Lead, Copper, Zinc, and Iron Concentration Patterns in Three Marine Fish Species from Two Different Mining Sites inside the Gulf of California, Mexico
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Analyses of Trace Metals
2.4. Analyses of Stable Isotopes
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Multiple Categorial Regression
2.7. Health Risk
3. Results
3.1. Locations and Seasons
3.2. Fish Species
3.3. Multiple Categorical Regression
3.4. Health Risk Assessment
4. Discussion
Health Risk Assessment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marín-Guirao, L.; Lloret, J.; Marin, A. Carbon and Nitrogen Stable Isotopes and Metal Concentration in Food Webs from a Mining-Impacted Coastal Lagoon. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 393, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Cadmium in Food-Scientific Opinion of the Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain. EFS2 2009, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Scientific Opinion on Lead in Food. EFSA J. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Auger, C.; Castonguay, Z.; Appanna, V.P.; Thomas, S.C.; Appanna, V.D. The Unravelling of Metabolic Dysfunctions Linked to Metal-Associated Diseases by Blue Native Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 1821–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manea, D.N.; Ienciu, A.A.; Ştef, R.; Şmuleac, I.L.; Gergen, I.I.; Nica, D.V. Health Risk Assessment of Dietary Heavy Metals Intake from Fruits and Vegetables Grown in Selected Old Mining Areas—A Case Study: The Banat Area of Southern Carpathians. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedepohl, K.H. The Composition of the Continental Crust. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 1217–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, F.Â.; Hauser-Davis, R.A.; Soares, L.; Mazzuco, A.C.A.; Rocha, R.C.C.; Saint Pierre, T.D.; Saggioro, E.; Correia, F.V.; Ferreira, T.O.; Bernardino, A.F. Contamination and Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Estuarine Fish Following a Mine Tailing Disaster. PeerJ 2020, 8, e10266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnandi, K.; Tchangbedji, G.; Killi, K.; Baba, G.; Abbe, K. The Impact of Phosphate Mine Tailings on the Bioaccumulation of Heavy Metals in Marine Fish and Crustaceans from the Coastal Zone of Togo. Mine Water Environ. 2006, 25, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Ni, H.-G.; Chen, F.; Luo, Z.-X.; Shen, H.; Liu, L.; Wu, P. Metal Accumulation in the Tissues of Grass Carps (Ctenopharyngodon Idellus) from Fresh Water around a Copper Mine in Southeast China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 4289–4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servicio Geológico Mexicano. Panorama Minero Del Estado de Baja California Sur; Servicio Geológico Mexicano: Ciudad de México, Mexico, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Figueroa, G.M.; Shumilin, E.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, I. Heavy Metal Pollution Monitoring Using the Brown Seaweed Padina durvillaei in the Coastal Zone of the Santa Rosalía Mining Region, Baja California Peninsula, Mexico. J. Appl. Phycol. 2009, 21, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumilin, E.N.; Rodríguez-Figueroa, G.; Bermea, O.M.; Baturina, E.L.; Hernández, E.; Meza, G.D.R. Anomalous Trace Element Composition of Coastal Sediments near the Copper Mining District of Santa Rosalía, Peninsula of Baja California, Mexico. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2000, 65, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshahri, F.; Alqahtani, M. Chemical Fertilizers as a Source of 238U, 40K, 226Ra, 222Rn, and Trace Metal Pollutant of the Environment in Saudi Arabia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 8339–8348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jara-Marini, M.E.; Molina-García, A.; Martínez-Durazo, Á.; Páez-Osuna, F. Trace Metal Trophic Transference and Biomagnification in a Semiarid Coastal Lagoon Impacted by Agriculture and Shrimp Aquaculture. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 5323–5336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez-Castillo, A.; Torre-Cosío, J.; Rojo-Amaya, M.; Fernández-Rivera Melo, F.; Talamantes, C.; Figueroa-Carranza, A.; Mariano-Meléndez, E.; Urciaga-García, J.; Cabrera, A.; Sáenz-Arroyo, A. Valoración Económica de los Servicios Ecosistémicos de los Bosques de Sargassum En El Golfo de California, México. Desarro. Reg. En Baja Calif. Sur Una Perspect. De Los Serv. Ecosistémicos. Univ. Auton. De Baja Calif. Surla Paz 2014, 79–111. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, G.R.; Robertson, R. An Annotated Checklist of the Fishes of Clipperton Atoll, Tropical Eastern Pacific. Rev. De Biol. Trop. 1997, 45, 813–843. [Google Scholar]
- Clements, K.D.; Choat, J.H. Comparison of Herbivory in the Closely-Related Marine Fish Genera Girella and Kyphosus. Mar. Biol. 1997, 127, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streit, R.P.; Hoey, A.S.; Bellwood, D.R. Feeding Characteristics Reveal Functional Distinctions among Browsing Herbivorous Fishes on Coral Reefs. Coral Reefs 2015, 34, 1037–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choat, J.H.; Clements, K.; Robbins, W. The Trophic Status of Herbivorous Fishes on Coral Reefs. Mar. Biol. 2002, 140, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Escalona, V.; Águila-Ramírez, R.N.; Abitia-Cárdenas, L.A. Food of Kyphosus elegans (Perciformes: Khyposidae) in Loreto, Baja California Sur, Mexico. Cicimar Oceánides 2009, 24, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatsuya, K.; Kiyomoto, S.; Yoshimura, T. Seasonal Changes in Dietary Composition of the Herbivorous Fish Kyphosus bigibbus in Southwestern Japan. Fish. Sci. 2015, 81, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, W.L. Comparative Feeding Ecology of Two Herbivorous Damselfishes (Pomacentridae: Teleostei) from the Gulf of California, Mexico. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1980, 47, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Sánchez, X.G.; Abitia-Cárdenas, L.A.; Escobar-Sánchez, O.; Palacios-Salgado, D.S. Diet of the Cortez Damselfish Stegastes rectifraenum (Teleostei: Pomacentridae) from the Rocky Reef at Los Frailes, Baja California Sur, Mexico. Mar. Biodivers. Rec. 2011, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier, D.; Lepoint, G.; Aguilar-Medrano, R.; Díaz, A.H.R.; Sánchez-González, A.; Sturaro, N. Ecomorphology, Trophic Niche, and Distribution Divergences of Two Common Damselfishes in the Gulf of California. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2019, 342, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abitia Cárdenas, L.; Rodríguez Romero, J.; Galván Magaña, F. Observaciones Tróficas de Tres Especies de Peces de Importancia Comercial de Bahía Concepción, Baja California Sur, México. Investig. Mar. Cicimar 1990, 5, 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- Hobson, E.S. Diurnal-nocturnal activity of some inshore fishes in the Gulf of California. Copeia 1965, 1965, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.-S.; Swenson, C.; Yanagihara, K.; Li, Q.X. Polychlorinated Biphenyls and Metals in Marine Species from French Frigate Shoals, North Pacific Ocean. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2000, 38, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, K.M.; Hamil, A.M.; Al-Houni, A.Q.A.; Ackacha, M.A. Determination of Heavy Metals in Fish Species of the Mediterranean Sea (Libyan Coastline) Using Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. Int. J. Pharm. Tech. Res. 2010, 2, 1350–1354. [Google Scholar]
- Denton, G.R.W.; Burdon-Jones, C. Trace Metals in Fish from the Great Barrier Reef. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1986, 17, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.-G.; Lin, Q.; Wang, X.-H.; Du, F.-Y.; Yu, Z.-L.; Huang, H.-H. Heavy Metal Concentrations in Wild Fishes Captured from the South China Sea and Associated Health Risks. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 96, 508–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sun, C.; Zheng, L.; Jiang, F.; Wang, S.; Zhuang, Z.; Wang, X. Determination of Trace Metals and Analysis of Arsenic Species in Tropical Marine Fishes from Spratly Islands. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 122, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metian, M.; Warnau, M.; Chouvelon, T.; Pedraza, F.; Rodriguez y Baena, A.M.; Bustamante, P. Trace Element Bioaccumulation in Reef Fish from New Caledonia: Influence of Trophic Groups and Risk Assessment for Consumers. Mar. Environ. Res. 2013, 87–88, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hilal, A.A.; Ismail, N.S. Heavy Metals in Eleven Common Species of Fish from the Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea. Jordan J. Biol. Sci. 2008, 1, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Maestre, R.; Johnson-Restrepo, B.; Olivero-Verbel, J. Heavy Metals in Sediments and Fish in the Caribbean Coast of Colombia: Assessing the Environmental Risk. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2018, 12, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Sierra, D.; Bergés-Tiznado, M.E.; Márquez-Farías, F.; Torres-Rojas, Y.E.; Ruelas-Inzunza, J.R.; Páez-Osuna, F. Trace Metals in Target Tissues and Stomach Contents of the Top Predator Sailfish Istiophorus platypterus from the Eastern Pacific: Concentrations and Contrasting Behavior of Biomagnification. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 23791–23803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonathan, M.P.; Aurioles-Gamboa, D.; Villegas, L.E.C.; Bohórquez-Herrera, J.; Hernández-Camacho, C.J.; Sujitha, S.B. Metal Concentrations in Demersal Fish Species from Santa Maria Bay, Baja California Sur, Mexico (Pacific Coast). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 99, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordiano-Flores, A.; Galván-Magaña, F.; Sánchez-González, A.; Páez-Osuna, F. Evidence for Interrupted Biomagnification of Cadmium in Billfish Food Chain Based on Stable Carbon and Nitrogen Isotopes from Southwestern of Gulf of California. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 195, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinone, S.G.; Parés-Sierra, A.; Castro, R.; Mascarenhas, A. Correction to “Temporal and Spatial Variation of the Surface Winds in the Gulf of California” Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L10305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salinas-Zavala, C.; Lluch-Belda, D.; Hernández-Vázquez, S.; Lluch-Cota, D.B. La Aridez en el Noreste de México. Un Análisis de su Variabilidad Espacial y Temporal. Atmósfera 1998, 11, 29–44. [Google Scholar]
- Salinas-Zavala, C.; Lluch-Cota, D.; Hernández-Vázquez, S.; Lluch-Belda, D. Anomalías de Precipitación. En Baja California Sur Durante 1990. Posibles Causas. Atmósfera 1992, 5, 79–93. [Google Scholar]
- Herrera-Cervantes, H.; Lluch-Cota, S.E.; Cortés-Ramos, J.; Farfán, L.; Morales-Aspeitia, R. Interannual Variability of Surface Satellite-Derived Chlorophyll Concentration in the Bay of La Paz, Mexico, during 2003–2018 Period: The ENSO Signature. Cont. Shelf Res. 2020, 209, 104254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Cervantes, H. Sea Surface Temperature, Ocean Color and Wind Forcing Patterns in the Bay of La Paz, Gulf of California: Seasonal Variability. Atmósfera 2019, 32, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, J.P.; Chester, R. Introducción a la Química Marina; AGT: Ciudad de Mexico, Mexico, 1989; ISBN 978-968-463-053-6. [Google Scholar]
- Cadena-Cárdenas, L.; Méndez-Rodríguez, L.; Zenteno-Savín, T.; García-Hernández, J.; Acosta-Vargas, B. Heavy Metal Levels in Marine Mollusks from Areas With, or Without, Mining Activities Along the Gulf of California, Mexico. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 57, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrera-García, A.; O’Hara, T.; Galván-Magaña, F.; Méndez-Rodríguez, L.C.; Castellini, J.M.; Zenteno-Savín, T. Oxidative Stress Indicators and Trace Elements in the Blue Shark (Prionace glauca) off the East Coast of the Mexican Pacific Ocean. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2012, 156, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Post, D.M.; Pace, M.L.; Hairston, N.G. Ecosystem Size Determines Food-Chain Length in Lakes. Nature 2000, 405, 1047–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, B.J.; Fry, B. Stable Isotopes in Ecosystem Studies. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1987, 18, 293–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, D.M.; Layman, C.A.; Arrington, D.A.; Takimoto, G.; Quattrochi, J.; Montaña, C.G. Getting to the Fat of the Matter: Models, Methods and Assumptions for Dealing with Lipids in Stable Isotope Analyses. Oecologia 2007, 152, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farnham, I.M.; Singh, A.K.; Stetzenbach, K.J.; Johannesson, K.H. Treatment of Nondetects in Multivariate Analysis of Groundwater Geochemistry Data. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2002, 60, 265–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofukany, A.F.A.; Wassenaar, L.I.; Bond, A.L.; Hobson, K.A. Defining Fish Community Structure in Lake Winnipeg Using Stable Isotopes (δ13C, δ15N, δ34S): Implications for Monitoring Ecological Responses and Trophodynamics of Mercury & Other Trace Elements. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 497–498, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zar, J.H. Biostatistical Analysis, 5th ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-0-321-65686-5. [Google Scholar]
- Gil-Manrique, B.; Nateras-Ramírez, O.; Martínez-Salcido, A.I.; Ruelas-Inzunza, J.; Páez-Osuna, F.; Amezcua, F. Cadmium and Lead Concentrations in Hepatic and Muscle Tissue of Demersal Fish from Three Lagoon Systems (SE Gulf of California). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 12927–12937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandkumar, A.; Nagarajan, R.; Prabakaran, K.; Bing, C.H.; Rajaram, R.; Li, J.; Du, D. Bioaccumulation of Trace Metals in the Coastal Borneo (Malaysia) and Health Risk Assessment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 145, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñón-Gimate, A.; Jakes-Cota, U.; Tripp-Valdez, A.; Casas-Valdez, M.; Almendarez-Hernández, L.C. Assessment of Human Health Risk: Copper and Lead Concentrations in Stone Scorpionfish (Scorpaena mystes) from the Coastal Region of Santa Rosalia in the Gulf of California, Mexico. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2020, 34, 101003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trumbo, P.; Yates, A.A.; Schlicker, S.; Poos, M. Dietary Reference Intakes. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2001, 101, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine; Committee on the Development of Guiding Principles for the Inclusion of Chronic Disease Endpoints in Future Dietary Reference Intakes; Food and Nutrition Board; Health and Medicine Division. Guiding Principles for Developing Dietary Reference Intakes Based on Chronic Disease; Kumanyika, S., Oria, M.P., Eds.; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; p. 24828. ISBN 978-0-309-46256-3. [Google Scholar]
- Bat, L.; Öztekin, A.; Arici, E.; Şahin, F. Health Risk Assessment: Heavy Metals in Fish from the Southern Black Sea. Foods Raw Mater. 2020, 8, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SNIIM. Sistema Nacional de Información e Integración de Mercados. 2020. Available online: http://www.economia-sniim.gob.mx/ (accessed on 15 November 2020).
- Erisman, B.; Mascareñas, I.; Paredes, G.; Sadovy de Mitcheson, Y.; Aburto-Oropeza, O.; Hastings, P. Seasonal, Annual, and Long-Term Trends in Commercial Fisheries for Aggregating Reef Fishes in the Gulf of California, Mexico. Fish. Res. 2010, 106, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo Guerrero, J.M.; Rivera, M.G. Organización y transformaciones de la pesca comercial ribereña en el Parque Nacional Bahía de Loreto (Baja California Sur, México). Ager. Rev. De Estud. Sobre Despoblación Y Desarro. Rural 2017, 59–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Bonilla, H.; Calderon-Aguilera, L.E. Population Density, Distribution and Consumption Rates of Three Corallivores at Cabo Pulmo Reef, Gulf of California, Mexico. Mar. Ecol. 1999, 20, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germain, N.; Hartmann, H.J.; Melo, F.J.F.-R.; Reyes-Bonilla, H. Ornamental Reef Fish Fisheries: New Indicators of Sustainability and Human Development at a Coastal Community Level. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2015, 104, 136–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Medrano, R.; Calderon-Aguilera, L.E. Redundancy and Diversity of Functional Reef Fish Groups of the Mexican Eastern Pacific. Mar. Ecol. 2016, 37, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FishBase. A Global Information System on Fishes. 2019. Available online: https://www.fishbase.in/ (accessed on 15 November 2020).
- Pérez-Tribouillier, H.; Shumilin, E.; Rodríguez-Figueroa, G.M. Trace Elements in the Marine Sediments of the La Paz Lagoon, Baja California Peninsula, Mexico: Pollution Status in 2013. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 95, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Almaraz, P.; Méndez-Rodríguez, L.; Zenteno-Savín, T.; O’Hara, T.M.; Harley, J.R.; Serviere-Zaragoza, E. Concentrations of Trace Elements in Sea Urchins and Macroalgae Commonly Present in Sargassum Beds: Implications for Trophic Transfer. Ecol. Res. 2016, 31, 785–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agah, H.; Leermakers, M.; Elskens, M.; Fatemi, S.M.R.; Baeyens, W. Accumulation of Trace Metals in the Muscle and Liver Tissues of Five Fish Species from the Persian Gulf. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 157, 499–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalman, Ö.; Demirak, A.; Balcı, A. Determination of Heavy Metals (Cd, Pb) and Trace Elements (Cu, Zn) in Sediments and Fish of the Southeastern Aegean Sea (Turkey) by Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. Food Chem. 2006, 95, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mille, T.; Cresson, P.; Chouvelon, T.; Bustamante, P.; Brach-Papa, C.; Bruzac, S.; Rozuel, E.; Bouchoucha, M. Trace Metal Concentrations in the Muscle of Seven Marine Species: Comparison between the Gulf of Lions (North-West Mediterranean Sea) and the Bay of Biscay (North-East Atlantic Ocean). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 135, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elnabris, K.J.; Muzyed, S.K.; El-Ashgar, N.M. Heavy Metal Concentrations in Some Commercially Important Fishes and Their Contribution to Heavy Metals Exposure in Palestinian People of Gaza Strip (Palestine). J. Assoc. Arab Univ. Basic Appl. Sci. 2013, 13, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruelas-Inzunza, J.; Páez-Osuna, F.; García-Flores, D. Essential (Cu) and Nonessential (Cd and Pb) Metals in Ichthyofauna from the Coasts of Sinaloa State (SE Gulf of California). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 162, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jara-Marini, M.E.; Soto-Jiménez, M.F.; Páez-Osuna, F. Trophic Relationships and Transference of Cadmium, Copper, Lead and Zinc in a Subtropical Coastal Lagoon Food Web from SE Gulf of California. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 1366–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deycard, V.N.; Schäfer, J.; Blanc, G.; Coynel, A.; Petit, J.C.J.; Lanceleur, L.; Dutruch, L.; Bossy, C.; Ventura, A. Contributions and Potential Impacts of Seven Priority Substances (As, Cd, Cu, Cr, Ni, Pb, and Zn) to a Major European Estuary (Gironde Estuary, France) from Urban Wastewater. Mar. Chem. 2014, 167, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.E.L.; Floeter, S.R.; Gasparini, J.L.; Ferreira, B.P.; Joyeux, J.C. Trophic Structure Patterns of Brazilian Reef Fishes: A Latitudinal Comparison. J. Biogeogr. 2004, 31, 1093–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Macías, C.; Schifter, I.; Lluch-Cota, D.B.; Méndez-Rodríguez, L.; Hernández-Vázquez, S. Distribution, Enrichment and Accumulation of Heavy Metals in Coastal Sediments of Salina Cruz Bay, México. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2006, 118, 211–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero-Alvarez, J.M.; Soto-Jiménez, M.F.; Amezcua, F.; Voltolina, D.; Frías-Espericueta, M.G. Cadmium and Lead Concentrations in the Fish Tissues of a Coastal Lagoon System of the SE Gulf of California. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 89, 820–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canli, M.; Atli, G. The Relationships between Heavy Metal (Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Pb, Zn) Levels and the Size of Six Mediterranean Fish Species. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 121, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikemoto, T.; Tu, N.P.C.; Okuda, N.; Iwata, A.; Omori, K.; Tanabe, S.; Tuyen, B.C.; Takeuchi, I. Biomagnification of Trace Elements in the Aquatic Food Web in the Mekong Delta, South Vietnam Using Stable Carbon and Nitrogen Isotope Analysis. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 54, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bebianno, M.J.; Langston, W.J. Metallothionein Induction in Mytilus edulis Exposed to Cadmium. Mar. Biol. 1991, 108, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espejo, W.; Padilha, J.D.A.; Kidd, K.A.; Dorneles, P.R.; Barra, R.; Malm, O.; Chiang, G.; Celis, J.E. Trophic Transfer of Cadmium in Marine Food Webs from Western Chilean Patagonia and Antarctica. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 137, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza-Chaffai, A.; Cosson, R.P.; Amiard-Triquet, C.; El Abed, A. Physico-Chemical Forms of Storage of Metals (Cd, Cu and Zn) and Metallothionein-like Proteins in Gills and Liver of Marine Fish from the Tunisian Coast: Ecotoxicological Consequences. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Pharmacol. Toxicol. Endocrinol. 1995, 111, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.T. Zooplankton Fecal Pellets, Marine Snow, Phytodetritus and the Ocean’s Biological Pump. Prog. Oceanogr. 2015, 130, 205–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, C.C.; Cohen, P.J.; Graham, N.A.J.; Nash, K.L.; Allison, E.H.; D’Lima, C.; Mills, D.J.; Roscher, M.; Thilsted, S.H.; Thorne-Lyman, A.L. Harnessing Global Fisheries to Tackle Micronutrient Deficiencies. Nature 2019, 574, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joint FAO/WHO Codex Alimentarius Commission. Codex Alimentarius. International Food Standards. General Standard for Contaminants and Toxins in Food and Feed; Codex Stan 193-1995; FAO Headquarters: Rome, Italy, 2015; p. 59. [Google Scholar]
- Sanaei, F.; Amin, M.M.; Alavijeh, Z.P.; Esfahani, R.A.; Sadeghi, M.; Bandarrig, N.S.; Fatehizadeh, A.; Taheri, E.; Rezakazemi, M. Health Risk Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements Intake via Food Crops Consumption: Monte Carlo Simulation-Based Probabilistic and Heavy Metal Pollution Index. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Species | n | Size (cm) | Cadmium | Lead | Copper | Zinc | Iron | Locality | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kyphosus | |||||||||
| K. cinerascens | - | 35–42 | - | - | 0.63–1.1 | 16.0–41.8 | - | Great Barrier Reef, Australia | [29] |
| K. cinerascens * | 14 | - | 3.56 ± 0.10 ** | 23.21 ± 0.72 ** | 1.13 ± 0.017 | 6.88 ± 0.08 | 22.99 ± 0.28 | South China Sea | [30] |
| K. vaigiensis (as K. lembus) * | 15 | - | 1.57 ± 0.04 ** | 16.43 ± 0.46 ** | 0.68 ± 0.012 | 5.23 ± 0.12 | 16.02 ± 0.22 | South China Sea | [30] |
| K. vaigiensis (as K. lembus) | - | - | 0.016 | 0.039 | 1.549 | 33.860 | 23.060 | Spratly islands, China | [31] |
| K. vaigiensis | 5 | 31.7 ± 5.0 | - | <0.08 | <0.83 | 24.1 ± 8.51 | 8.69 ± 1.06 | New Caledonia | [32] |
| K. sp. | - | - | 0.50 | 4.00 | 0.80 | 28.30 | 6.00 | Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea | [33] 1 |
| K. sp. | 3 | 29 | 0.002 | 0.017 | - | 0.97 | - | Caribbean Sea, Colombia | [34] |
| K. vaigiensis | 42 | 31.82 ± 1.32 | 0.18 ± 0.03 | 0.59 ± 0.16 | 1.60 ± 0.20 | 42.45 ± 3.01 | 33.24 ± 3.67 | Gulf of California, Santa Rosalía | Present study |
| K vaigiensis | 27 | 23.70 ± 1.42 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 1.02 ± 0.39 | 0.83 ± 0.19 | 43.39 ± 3.30 | 18.24 ± 2.58 | Gulf of California, Bahía de La Paz | Present study |
| Stegastes | |||||||||
| S. fasciolatus | 3 | NA | 0.8–1.7 | 13.00–16.00 | - | - | - | Tern Island, North Pacific | [27] |
| S. rectifraenum | 40 | 11.09 ± 0.16 | 0.24 ± 0.02 | 0.90 ± 0.22 | 0.53 ± 0.10 | 21.19 ± 0.42 | 18.51 ± 2.48 | Gulf of California, Santa Rosalía | Present study |
| S. rectifraenum | 28 | 12.47 ± 0.13 | 0.17 ± 0.06 | 2.76 ± 0.49 | 0.60 ± 0.10 | 23.88 ± 0.77 | 26.24 ± 4.90 | Gulf of California, Bahía de La Paz | Present study |
| Balistes | |||||||||
| B. capriscus | - | - | 2.615 | 0.995 | 0.013 | - | 0.253 | Libya, Mediterranean Sea | [28] |
| B. polylepis * | 524 | - | 5.282 ± 1.020 | 0.023 ± 0.001 | 1.29 ± 0.10 | 64.2 ± 2.72 | - | Mazatlán, Mexico | [35] 2 |
| B. polylepis | 3 | 15.5 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 0.073 | 2.65 | 3.80 | Pacific Baja California | [36] |
| B. polylepis | 2 | - | 2.57 ± 1.03 | - | - | - | - | Gulf of California | [37] 3 |
| B. polylepis | 2 | - | 2.94 ± 0.41 | - | - | - | - | Gulf of California | [37] 4 |
| B. polylepis | 40 | 22.97 ± 0.89 | 0.19 ± 0.03 | 0.89 ± 0.25 | 1.55 ± 0.68 | 93.72 ± 14.77 | 27.97 ± 2.80 | Gulf of California, Santa Rosalía | Present study |
| B. polylepis | 28 | 26.62 ± 1.05 | 0.11 ± 0.05 | 1.33 ± 0.36 | 1.66 ± 0.71 | 36.16 ± 1.60 | 23.98 ± 7.80 | Gulf of California, Bahía de La Paz | Present study |
| Location | Santa Rosalía | La Paz | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Season | Dry | Rainy | Annual Average | Dry | Rainy | Annual Average |
| Kyphosus vaigiensis | ||||||
| cadmium | 0.17 ± 0.05 | 0.20 ± 0.04 | 0.19 ± 0.03 A | 0.06 ± 0.03 a | <0.01 b | 0.03 ± 0.01 B |
| lead | 0.58 ± 0.17 | 0.60 ± 0.27 | 0.59 ± 0.16 | 2.08 ± 0.71 a | <0.07 b | 1.02 ± 0.39 |
| copper | 1.23 ± 0.26 | 1.92 ± 0.30 | 1.57 ± 0.20 A | 1.71 ± 0.21 a | <0.017 b | 0.83 ± 0.20 B |
| zinc | 47.90 ± 5.27 | 36.01 ± 1.86 | 42.09 ± 2.96 | 55.01 ± 4.72 a | 32.60 ± 2.09 b | 43.39 ± 3.30 |
| iron | 47.70 ± 5.14 a | 16.78 ± 1.93 b | 32.60 ± 3.65 A | 13.30 ± 2.68 | 22.83 ± 4.04 | 18.24 ± 2.59 B |
| Stegastes rectifraenum | ||||||
| cadmium | 0.20 ± 0.03 | 0.27 ± 0.03 | 0.24 ± 0.02 | 0.12 ± 0.04 | 0.21 ± 0.11 | 0.17 ± 0.06 |
| lead | 1.01 ± 0.31 | 0.80 ± 0.31 | 0.90 ± 0.22 A | 4.16 ± 0.43 a | 1.37 ± 0.71 b | 2.76 ± 0.49 B |
| copper | 1.05 ± 0.12 a | 0.05 ± 0.03 b | 0.53 ± 0.10 | 0.88 ± 0.14 a | 0.33 ± 0.10 b | 0.60 ± 0.10 |
| zinc | 20.97 ± 0.63 | 21.39 ± 0.57 | 21.19 ± 0.42 A | 24.11 ± 0.94 | 23.66 ± 1.26 | 23.88 ± 0.77 B |
| iron | 17.16 ± 2.62 | 19.72 ± 4.14 | 18.51 ± 2.48 | 17.53 ± 2.63 | 34.96 ± 9.02 | 26.24 ± 4.90 |
| Balistes polylepis | ||||||
| cadmium | 0.14 ± 0.05 | 0.21 ± 0.04 | 0.19 ± 0.03 | 0.09 ± 0.04 | 0.14 ± 0.09 | 0.11 ± 0.05 |
| lead | 1.91 ± 0.56 a | 0.31 ± 0.14 b | 0.89 ± 0.25 | 1.44 ± 0.48 | 1.23 ± 0.56 | 1.33 ± 0.36 |
| copper | 1.49 ± 0.89 | 1.59 ± 0.95 | 1.55 ± 0.68 | 2.73 ± 1.33 | 0.59 ± 0.40 | 1.66 ± 0.71 |
| zinc | 41.55 ± 3.00 a | 123.54 ± 20.58 b | 93.72 ± 14.77 A | 33.71 ± 2.15 | 38.62 ± 2.25 | 36.16 ± 1.60 B |
| iron | 39.16 ± 3.86 a | 21.57 ± 3.07 b | 27.97 ± 2.80 | 11.96 ± 2.86 | 29.13 ± 10.82 | 23.98 ± 7.80 |
| Scientific Name | Kyphosus vaigiensis | Stegastes rectifraenum | Balistes polylepis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fish Photo |  |  |  |
| Common name | Blue-bronze chub/Brassy chub | Cortez damselfih | Finescale triggerfish |
| Common local name | Chopa rayada | Jaqueta de Cortés | Cochi/Cochito |
| Commercial value [58] | 1.5 USD/k—artisanal fisheries [59,60] | 18 USD/k—ornamental reef fishery [61,62] | 1.3 USD/k—artisanal fisheries [59] |
| Feeding habits | Herbivore [17] | Omnivore [35,63] | Carnivore [25] |
| Trophic level [64] | 2.0 ± 0.00 | 2.0 ± 0.00 | 3.3 ± 0.37 |
| Sample size | 70 | 68 | 61 |
| Lenght (cm) | 28.69 ± 1.08 a (14.30–54.00) | 11.66 ± 0.14 b (8.50–14.20) | 24.64 ± 0.71 a,b (15.30–38.50) |
| cadmium | 0.13 ± 0.02 a (<0.01–0.68) | 0.21 ± 0.03 b (<0.01–1.0) | 0.15 ± 0.03 a,b (<0.01–1.00) |
| lead | 0.75 ± 0.18 a (<0.04–7.41) | 1.67 ± 0.26 b (<0.04–6.45) | 1.09 ± 0.22 a,b (0.04–6.04) |
| copper | 1.28 ± 0.15 a (<0.017–5.19) | 0.56 ± 0.07 b (<0.017–1.95) | 1.60 ± 0.49 a,b (<0.017–20.50) |
| zinc | 42.59 ± 2.21 a (22.34–114.22) | 22.30 ± 0.43 b (17.17–33.08) | 67.30 ± 8.79 c (23.34–217.64) |
| iron | 27.06 ± 2.58 a (2.60–103.34) | 21.69 ± 2.51 a (2.09–141.15) | 26.46 ± 3.16 a (0.64–146.76) |
| δ13C | −13.66 ± 0.26 a (−20.13–−9.75) | −14.99 ± 0.19 b (−18.39–−12.31) | −16.25 ± 0.21 c (−18.46–−11.92) |
| δ15N | 16.77 ± 0.16 a (13.33–18.57) | 18.12 ± 0.13 b (15.99–19.91) | 17.73 ± 0.17 b (14.03–19.52) |
| Statistics | Cadmium | Lead | Cooper | Zinc | Iron | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coeff | SE | t-Value | Coeff | SE | t-Value | Coeff | SE | t-Value | Coeff | SE | t-Value | Coeff | SE | t-Value | |
| Intercept | −6.75 | 2.65 | −2.55 * | −1.35 | 2.86 | −0.47 | −0.33 | 3.48 | −0.10 | 1.24 | 0.64 | 1.95 | 5.31 | 1.21 | 4.37 * |
| Location_STR | 1.59 | 0.30 | 5.37 * | −0.19 | 0.32 | −0.60 | 1.43 | 0.39 | 3.69 * | 0.08 | 0.07 | 1.17 | 0.40 | 0.14 | 2.86 * |
| Season_Rainy | 0.07 | 0.30 | 0.23 | −1.30 | 0.33 | −3.98 * | −2.12 | 0.40 | −5.33 * | 0.26 | 0.09 | 3.55 * | −0.18 | 0.14 | −1.34 |
| Sp_K. vaigiensis | 0.05 | 0.37 | 0.14 | −0.87 | 0.40 | −2.17 * | 0.59 | 0.49 | 1.20 | −0.10 | 0.11 | −1.13 | −0.25 | 0.17 | −1.48 |
| Sp_S. rectifraenum | 0.14 | 0.48 | 0.29 | 2.09 | 0.52 | 4.05 * | −0.25 | 0.63 | −0.39 | −0.56 | 0.01 | −4.90 * | 0.29 | 0.22 | 1.28 |
| L_std | −0.03 | 0.02 | −1.49 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 4.67 * | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.34 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 2.99 * | 0.03 | 0.01 | 2.50 * |
| δ13C | −0.05 | 0.09 | −0.61 | −0.11 | 0.09 | −1.16 | −0.17 | 0.11 | −1.51 | −0.07 | 0.02 | −3.24 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.22 |
| δ15N | 0.15 | 0.13 | 1.15 | −0.23 | 0.14 | −1.68 | −0.22 | 0.17 | −1.33 | 0.06 | 003 | 1.91 | −0.17 | 0.06 | −2.91 * |
| Model R2 | 0.17 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.44 | 0.07 | ||||||||||
| Model p< | 8.07e−10 | 1.25e−10 | 1.73e−11 | <2.2e−16 | 9.56e−4 | ||||||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Serviere-Zaragoza, E.; Lluch-Cota, S.E.; Mazariegos-Villarreal, A.; Balart, E.F.; Valencia-Valdez, H.; Méndez-Rodríguez, L.C. Cadmium, Lead, Copper, Zinc, and Iron Concentration Patterns in Three Marine Fish Species from Two Different Mining Sites inside the Gulf of California, Mexico. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18020844
Serviere-Zaragoza E, Lluch-Cota SE, Mazariegos-Villarreal A, Balart EF, Valencia-Valdez H, Méndez-Rodríguez LC. Cadmium, Lead, Copper, Zinc, and Iron Concentration Patterns in Three Marine Fish Species from Two Different Mining Sites inside the Gulf of California, Mexico. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(2):844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18020844
Chicago/Turabian StyleServiere-Zaragoza, Elisa, Salvador E. Lluch-Cota, Alejandra Mazariegos-Villarreal, Eduardo F. Balart, Hugo Valencia-Valdez, and Lia Celina Méndez-Rodríguez. 2021. "Cadmium, Lead, Copper, Zinc, and Iron Concentration Patterns in Three Marine Fish Species from Two Different Mining Sites inside the Gulf of California, Mexico" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 2: 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18020844
APA StyleServiere-Zaragoza, E., Lluch-Cota, S. E., Mazariegos-Villarreal, A., Balart, E. F., Valencia-Valdez, H., & Méndez-Rodríguez, L. C. (2021). Cadmium, Lead, Copper, Zinc, and Iron Concentration Patterns in Three Marine Fish Species from Two Different Mining Sites inside the Gulf of California, Mexico. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(2), 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18020844