Farmers’ Knowledge, Attitudes, and Perceptions Regarding Carcinogenic Pesticides in Fez Meknes Region (Morocco)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
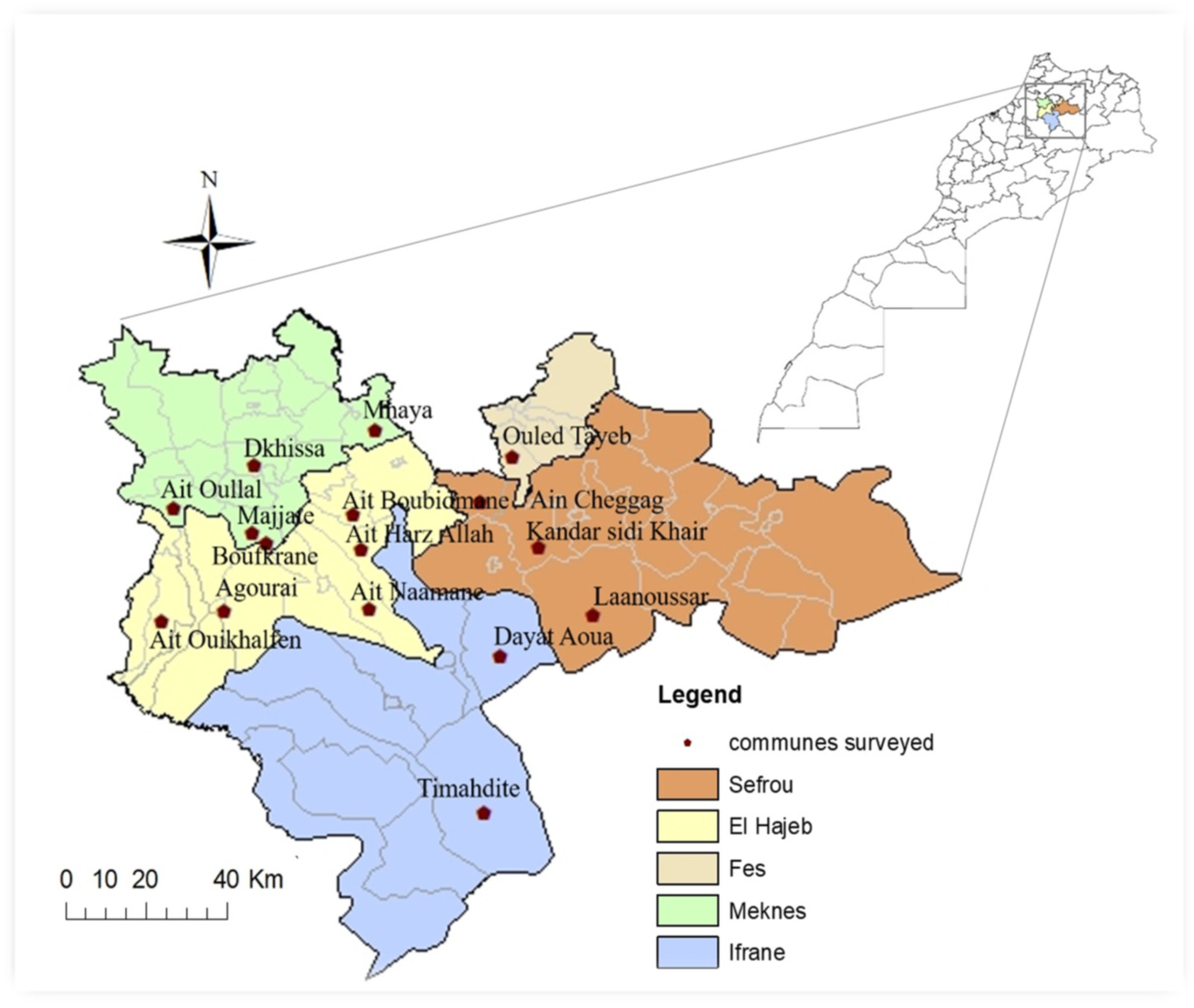
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling Method
2.3. Data Collection
- The first section dealt with socio-demographic issues (age, school level, family situation, a follow-up to training, and years of experience in agriculture).
- The second section focused on the phytosanitary assessment (crops and active ingredients used) and cancer risk.
- The third part was devoted to knowledge and behavior of farmers toward the use of pesticides, and the decision-making mechanisms relating to the use of phytosanitary products (the choice of active ingredients, concentration, and date of treatment), and the practices used for pesticide storage and elimination (the provision of a room fitted out for the storage of pesticides, compliance with the recommended used concentrations, the future packaging of pesticides and rinsing water from the sprayer after use). The individual protection measures taken by farmers during spraying (use of waterproof gloves, hat, boots, mask with filter cartridge, glasses, etc.), the consumption of food and drinks during the treatment, and the actions taken after application of pesticides, cleaning of clothes) were also examined.
- The last part of the questionnaire consecrated to the knowledge about the awareness and risk of pesticides to human health and the environment. Farmers were asked to select the adverse health effects experienced during or after exposure (short and/or long-term). These 10 symptoms were the most reported by farmers in several studies [41,42], as follows: dizziness, headache, excessive sweating, blurred vision, hands tremor, convulsion, loss of balance, excessive salivation, nausea/vomiting, and respiratory problems.
2.4. Data Treatment
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Information of the Sample
3.2. Phytosanitary Assessment and Cancer Risk
3.3. Farmer Knowledge and Behavior towards Pesticides Use
3.4. Socioeconomic Factors Influencing Farmers’ Protection Measures
3.5. Farmer Awareness of the Dangers of Pesticides to Human Health and Environment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maldani, M.; Dekaki, E.; Nassiri, L.; Ibijbijen, J.; Dekaki, M.; State, J. State of Art on the Use of Pesticides in Meknes Region, Morocco. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2017, 4, 138–148. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, C.L.F.; Volcão, L.M.; Ramires, P.F.; Moura, R.R.D.; Da Silva Júnior, F.M.R. Distribution of pesticides in agricultural and urban soils of Brazil: A critical review. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2020, 22, 256–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Kim, K.Y.; Hamm, S.-Y.; Kim, M.; Kim, H.K.; Oh, J.-E. Occurrence and distribution of pharmaceutical and personal care products, artificial sweeteners, and pesticides in groundwater from an agricultural area in Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjerps, R.M.A.; Kooij, P.J.F.; van Loon, A.; Van Wezel, A.P. Occurrence of pesticides in Dutch drinking water sources. Chemosphere 2019, 235, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bungau, S.; Behl, T.; Aleya, L.; Bourgeade, P.; Aloui-Sosse, B.; Purza, A.L.; Abid, A.; Samuel, A.D. Expatiating the impact of anthropogenic aspects and climatic factors on long-term soil monitoring and management. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, A.D.; Tit, D.M.; Melinte, C.E.; Iovan, C.; Purza, L.; Gitea, M.; Bungau, S. Enzymological and Physicochemical Evaluation of the Effects of Soil Management Practices. Rev. Chim. 2017, 68, 2243–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, A.D.; Bungau, S.; Tit, D.M.; Melinte (Frunzulica), C.E.; Purza, L.; Badea, G.E. Effects of long term application of organic and mineral fertilizers on soil enzymes. Rev. Chim. 2018, 69, 2608–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wołejko, E.; Jabłońska-Trypuć, A.; Wydro, U.; Butarewicz, A.; Łozowicka, B. Soil biological activity as an indicator of soil pollution with pesticides—A review. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 147, 103356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreux, F.; Scheunert, I.; Adrian, P.; Schiavon, M. The binding of pesticide residues to natural organic matter, their movement, and their bioavailability. In Fate and Prediction of Environmental Chemicals in Soils, Plants, and Aquatic Systems; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 133–148. [Google Scholar]
- Pirsaheb, M.; Hossini, H.; Asadi, F.; Janjani, H. A systematic review on organochlorine and organophosphorus pesticides content in water resources. Toxin Rev. 2017, 36, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climent, M.J.; Coscollà, C.; López, A.; Barra, R.; Urrutia, R. Legacy and current-use pesticides (CUPs) in the atmosphere of a rural area in central Chile, using passive air samplers. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Thakur, P.; Thakur, A.; Kumar, H.; Chawla, P.; Rohit, J.V.; Kaushik, R.; Kumar, N. Colorimetric sensing approaches of surface-modified gold and silver nanoparticles for detection of residual pesticides: A review. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerro, C.C.; Koutros, S.; Andreotti, G.; Sandler, D.P.; Lynch, C.F.; Louis, L.M.; Blair, A.; Parks, C.G.; Shrestha, S.; Lubin, J.H.; et al. Cancer incidence in the Agricultural Health Study after 20 years of follow-up. Cancer Causes Control. 2019, 30, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, T.T.; Zuo, A.J.; Wang, J.G.; Zhao, P. Organochlorine pesticides accumulation and breast cancer: A hospital-based case-control study. Tumour Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317699114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeng, F.; Lerro, C.; Lavoué, J.; Huang, H.; Siemiatycki, J.; Zhao, N.; Ma, S.; Deziel, N.C.; Friesen, M.C.; Udelsman, R.; et al. Occupational exposure to pesticides and other biocides and risk of thyroid cancer. Occup. Environ. Med. 2017, 74, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, F.W.; Zhao, G.P.; Ren, F.Z.; Pang, G.F.; Li, Y.X. Assessment of the endocrine-disrupting effects of diethyl phosphate, a nonspecific metabolite of organophosphorus pesticides, by in vivo and in silico approaches. Environ. Int. 2020, 135, 105383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueroa, Z.I.; Young, H.A.; Mumford, S.L.; Meeker, J.D.; Barr, D.B.; Gray, G.M.; Perry, M.J. Pesticide interactions and risks of sperm chromosomal abnormalities. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2019, 222, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- London, L.; Beseler, C.; Bouchard, M.F.; Bellinger, D.C.; Colosio, C.; Grandjean, P.; Harari, R.; Kootbodien, T.; Kromhout, H.; Little, F.; et al. Neurobehavioral and neurodevelopmental effects of pesticide exposures. Neurotoxicology 2012, 33, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jokanović, M. Neurotoxic effects of organophosphorus pesticides and possible association with neurodegenerative diseases in man: A review. Toxicology 2018, 410, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, D.; Lopes Alderete, B.; de Souza, C.T.; Ferraz Dias, J.; Niekraszewicz, L.; Cappetta, M.; Martínez-López, W.; Da Silva, J. DNA damage and epigenetic alteration in soybean farmers exposed to complex mixture of pesticides. Mutagenesis 2018, 33, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahyuni, E.L.; Harahap, U. The health belief model in prevention pesticide toxicity. Glob. J. Health Sci. 2020, 12, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesavachandran, C.N.; Fareed, M.; Pathak, M.K.; Bihari, V.; Mathur, N.; Srivastava, A.K. Adverse health effects of pesticides in agrarian populations of developing countries. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 200, 33–52. [Google Scholar]
- Badrane, N.; Ait Daoud, N.; Ghandi, M.; Fatima, Z.; el bouazzi, O.; Soulaymani, A.; Bencheikh, R. Quel role du laboratoire d’analyses toxicologiques dans l’evaluation du risque des produits de contrebande? Toxicol. Anal. Clin. 2017, 30, S79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, O.; Saint-Laurent, L. Guide de Prévention Pour les Utilisateurs de Pesticides en Agriculture Maraîchère. Available online: https://www.inspq.qc.ca/pdf/publications/045_pesticides_agriculture.pdf (accessed on 2 July 2021).
- Tolera, S. Systematic Review on Adverse Effect of Pesticide on Top Ten Importers of African Countries. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag. 2020, 24, 1607–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenko Nkontcheu Daniel, B.; Patricia Asanga Bi, F.; Ngameni Tchamadeu, N.; Mpoame, M. Environmental and Human Health Assessment in Relation to Pesticide Use by Local Farmers and the Cameroon Development Corporation (CDC), Fako Division, South-West Cameroon. Eur. Sci. J. ESJ 2017, 13, 454–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayadi-Hajji, H. Outils de Gestion de la Pollution Phytosanitaire Diffuse au Niveau d’un Territoire: Cas D’application Zone Humide Ramsar de la Merja Zerga au Maroc. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Paul Valéry-Montpellier III, Montpellier, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rezaei, R.; Damalas, C.; Abdollahzadeh, G. Understanding farmers’ safety behaviour towards pesticide exposure and other occupational risks: The case of Zanjan, Iran. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 616–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staudacher, P.; Fuhrimann, S.; Farnham, A.; Mora, A.M.; Atuhaire, A.; Niwagaba, C.; Stamm, C.; Eggen, R.I.L.; Winkler, M.S. Comparative Analysis of Pesticide Use Determinants Among Smallholder Farmers From Costa Rica and Uganda. Environ. Health Insights 2020, 14, 1178630220972417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapbamrer, R.; Thammachai, A. Factors affecting use of personal protective equipment and pesticide safety practices: A systematic review. Environ. Res. 2020, 185, 109444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, G.; Atreya, K.; Yang, X.; Fan, L.; Geissen, V. Factors affecting pesticide safety behaviour: The perceptions of Nepalese farmers and retailers. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 1560–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damte, T.; Tabor, G. Small-scale vegetable producers’ perception of pests and pesticide uses in East Shewa zone, Ethiopia. Int. J. Pest. Manag. 2015, 61, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppens, M. Understanding Limited Glove Use among Pesticide Applicators: A Qualitative Study on Java Island, Indonesia; Knowledge, Technology and Innovation; Wageningen University & Research: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Berni, I.; Menouni, A.; Ibrahim, E.G.; Duca, R.C.; Kestemont, M.P.; Godderis, L.; Jaafari, S. Understanding farmers’ safety behavior regarding pesticide use in Morocco. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 25, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HCP. Available online: https://www.hcp.ma/glossary/Recensement-General-de-la-Population-et-de-l-Habitat_gw115.html (accessed on 1 March 2020).
- Royaume du Maroc. 2015. Available online: http://www.equipement.gov.ma/Carte-Region/RegionFes/Presentation-de-la-region/Monographie/Pages/Monographie-de-la-region.aspx (accessed on 16 June 2020).
- Miller, G.J. Handbook of Research Methods in Public Administration; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1998; Volume 134. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, C. A Practical Guide to Research Methods: A User-friendly Manual for Mastering Research Techniques and Projects; Spring Hill House: Spring Hill, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Imane, B. Pesticide use pattern among farmers in a rural district of Meknes: Morocco. Open Access Libr. J. 2016, 3, 72593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa’ed, H.Z.; Sawalha, A.F.; Sweileh, W.M.; Awang, R.; Al-Khalil, S.I.; Al-Jabi, S.W.; Bsharat, N.M. Knowledge and practices of pesticide use among farm workers in the West Bank, Palestine: Safety implications. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2010, 15, 252–261. [Google Scholar]
- Lekei, E.E.; Ngowi, A.V.; London, L. Farmers’ knowledge, practices and injuries associated with pesticide exposure in rural farming villages in Tanzania. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oesterlund, A.H.; Thomsen, J.F.; Sekimpi, D.K.; Maziina, J.; Racheal, A.; Jørs, E. Pesticide knowledge, practice and attitude and how it affects the health of small-scale farmers in Uganda: A cross-sectional study. Afr. Health Sci. 2014, 14, 420–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wu, W.; Gao, X. Frequency recognition based on canonical correlation analysis for SSVEP-based BCIs. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 53, 2610–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, S.; Hammond, S. Investigating the multivariate relationship between impulsivity and psychopathy using canonical correlation analysis. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2017, 111, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Iarc Monographs on the Identification of Carcinogenic Hazards to Humans. Available online: https://monographs.iarc.who.int/list-of-classifications (accessed on 27 September 2021).
- Otrisal, P.; Bungau, C.; Obsel, V.; Melicharik, Z.; Tont, G. Selected Respiratory Protective Devices: Respirators and Significance of Some Markings. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Jara, J.P.; Córdova-Lepe, F.; Muñoz-Quezada, M.T.; Chowell, G. Susceptibility to organophosphates pesticides and the development of infectious-contagious respiratory diseases. J. Theor. Biol. 2020, 488, 110133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scammell, M.K.; Sennett, C.M.; Petropoulos, Z.E.; Kamal, J.; Kaufman, J.S. Environmental and occupational exposures in kidney disease. Semin. Nephrol. 2019, 39, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayour, C.; Ritz, B.; Langholz, B.; Mills, P.K.; Wu, A.; Wilson, J.P.; Shahabi, K.; Cockburn, M. A case–control study of breast cancer risk and ambient exposure to pesticides. Environ. Epidemiol. 2019, 3, e070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damalas, C.A.; Khan, M. Farmers’ attitudes towards pesticide labels: Implications for personal and environmental safety. Int. J. Pest. Manag. 2016, 62, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaosebikan, O.; Abdulrazaq, B.; Owoade, D.; Ogunade, A.; Aina, O.; Ilona, P.; Muheebwa, A.; Teeken, B.; Iluebbey, P.; Kulakow, P. Gender-based constraints affecting biofortified cassava production, processing and marketing among men and women adopters in Oyo and Benue States, Nigeria. Physiol. Mol. Plant. Pathol. 2019, 105, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, D.; Manfre, C.; Barett, K.N. Promoting Gender Equitable Opportunities in Agriculture Value Chains: A Handbookl; Produced for USAID Office of Women in Development by the GATE Project; Development & Training Services Inc.: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Salameh, P.; Baldi, I.; Brochard, P.; Saleh, B. Pesticides in Lebanon: A knowledge, attitude, and practice study. Environ. Res. 2004, 94, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondori, A.; Bagheri, A.; Sookhtanlou, M.; Allahyari, M.S.; Damalas, C.A. Pesticide use in cereal production in Moghan Plain, Iran: Risk knowledge and farmers’ attitudes. Crop Prot. 2018, 110, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijal, J.P.; Regmi, R.; Ghimire, R.; Puri, K.D.; Gyawaly, S.; Poudel, S. Farmers’ knowledge on pesticide safety and pest management practices: A case study of vegetable growers in Chitwan, Nepal. Agriculture 2018, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abang, A.; Kouame, C.; Abang, M.; Hannah, R.; Fotso, A. Vegetable growers perception of pesticide use practices, cost, and health effects in the tropical region of Cameroon. Int. J. Agron. Plant. Prod. 2013, 4, 873–883. [Google Scholar]
- Idowu, A.A.; Sowe, A.; Bah, A.K.; Kuyateh, M.; Anthony, A.; Oyelakin, O. Knowledge, attitudes and practices associated with pesticide use among horticultural farmers of Banjulinding and Lamin of the Gambia. Afr. J. Chem. Educ. 2017, 7, 2–17. [Google Scholar]
- Sharafi, K.; Pirsaheb, M.; Maleki, S.; Arfaeinia, H.; Karimyan, K.; Moradi, M.; Safari, Y. Knowledge, attitude and practices of farmers about pesticide use, risks, and wastes; a cross-sectional study (Kermanshah, Iran). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, A.; Emami, N.; Allahyari, M.S.; Damalas, C.A. Pesticide handling practices, health risks, and determinants of safety behavior among Iranian apple farmers. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2018, 24, 2209–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elibariki, R.; Maguta, M.M. Status of pesticides pollution in Tanzania–A review. Chemosphere 2017, 178, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damalas, C.A.; Khan, M. RETRACTED: Pesticide use in vegetable crops in Pakistan: Insights through an ordered probit model. Crop. Prot. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Normile, D. Vietnam turns back a’tsunami of pesticides’. Science 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaber, S.; Abdel-Latif, S.H. Effect of education and health locus of control on safe use of pesticides: A cross sectional random study. J. Occup. Med. Toxicol. 2012, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Recena, M.C.P.; Caldas, E.D.; Pires, D.X.; Pontes, E.R.J. Pesticides exposure in Culturama, Brazil—knowledge, attitudes, and practices. Environ. Res. 2006, 102, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, G.A. Attitudes and behaviours regarding use of crop protection products—A survey of more than 8500 smallholders in 26 countries. Crop Prot. 2008, 27, 834–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, S.; Meisner, C.; Wheeler, D.; Xuyen, K.; Lam, N.T. Pesticide poisoning of farm workers–implications of blood test results from Vietnam. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2007, 210, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohanty, M.K.; Behera, B.K.; Jena, S.K.; Srikanth, S.; Mogane, C.; Samal, S.; Behera, A.A. Knowledge attitude and practice of pesticide use among agricultural workers in Puducherry, South India. J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2013, 20, 1028–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, S.; Ball, A.; Pretty, J. Trends in pesticide use and drivers for safer pest management in four African countries. Crop Prot. 2008, 27, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngowi, A.V.; Maeda, D.N.; Partanen, T.J.; Sanga, M.P.; Mbise, G. Acute health effects of organophosphorus pesticides on Tanzanian small-scale coffee growers. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2001, 11, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- CAB Direct. Available online: https://www.cabdirect.org/?target=%2fcabdirect%2fabstract%2f20153213022 (accessed on 16 September 2021).
- Calaf, G.M.; Bleak, T.C.; Roy, D. Signs of carcinogenicity induced by parathion, malathion, and estrogen in human breast epithelial cells. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 45, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjitha, R.; Antony, A.; Shilpa, O.; Anupama, K.P.; Mallikarjunaiah, S.; Gurushankara, H.P. Malathion induced cancer-linked gene expression in human lymphocytes. Environ. Res. 2020, 182, 109131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crump, K. The potential effects of recall bias and selection bias on the epidemiological evidence for the carcinogenicity of glyphosate. Risk Anal. 2020, 40, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samsel, A.; Seneff, S. Glyphosate, pathways to modern diseases IV: Cancer and related pathologies. J. Biol. Phys. Chem. 2015, 15, 121–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, C. Glyphosate and cancer: The importance of the whole picture. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 2874–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, A.M.; Smith, M.T.; La Merrill, M.A.; Liaw, J.; Steinmaus, C. 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma: A meta-analysis accounting for exposure levels. Ann. Epidemiol. 2017, 27, 281–289.e284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Kumar, B.S.; Singh, B.; Sethi, R. Exposures to 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid with or without endotoxin upregulate small cell lung cancer pathway. J. Occup. Med. Toxicol. 2021, 16, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi, C.; Thompson, S.; Ritz, B.; Cockburn, M.; Heck, J.E. Residential proximity to pesticide application as a risk factor for childhood central nervous system tumors. Environ. Res. 2021, 197, 111078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, G.C.C.; Assmann, C.E.; Cadona, F.C.; Bonadiman, B.d.S.R.; de Oliveira Alves, A.; Machado, A.K.; Duarte, M.M.M.F.; da Cruz, I.B.M.; Costabeber, I.H. Immunomodulatory effect of mancozeb, chlorothalonil, and thiophanate methyl pesticides on macrophage cells. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 182, 109420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasumana, C.; Orantes, C.; Herrera, R.; Almaguer, M.; Lopez, L.; Silva, L.C.; Ordunez, P.; Siribaddana, S.; Gunatilake, S.; De Broe, M.E. Chronic interstitial nephritis in agricultural communities: A worldwide epidemic with social, occupational and environmental determinants. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2016, 32, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valcke, M.; Levasseur, M.-E.; da Silva, A.S.; Wesseling, C. Pesticide exposures and chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology: An epidemiologic review. Environ. Health 2017, 16, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Kamel, E.G.; El Minshawy, O. Environmental factors incriminated in the development of end stage renal disease in El-Minia governorate, upper Egypt. J. Nephro-Urol. Mon. 2010, 2, 431–437. [Google Scholar]
- Ganguli, A. Uddanam nephropathy/regional nephropathy in India: Preliminary findings and a plea for further research. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 68, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McClean, M.; Laws, R.; Rubio, O.R.; Brooks, D.; Kaufman, J.; Weiner, D.; Nicholson, S.; Miller, A.; Makey, C.; Collins, E. Industrial Hygiene/Occupational Health Assessment: Evaluating Potential Hazards Associated with Chemicals and Work Practices at the Ingenio San Antonio (Chichigalpa, Nicaragua); Boston University School of Public Health: Boston, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Jayasumana, C.; Gunatilake, S.; Siribaddana, S. Simultaneous exposure to multiple heavy metals and glyphosate may contribute to Sri Lankan agricultural nephropathy. BMC Nephrol. 2015, 16, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-Trabanino, R.; Jarquín, E.; Wesseling, C.; Johnson, R.; González-Quiroz, M.; Weiss, I.; Glaser, J.; José Vindell, J.; Stockfelt, L.; Roncal, C.; et al. Heat stress, dehydration, and kidney function in sugarcane cutters in El Salvador—A cross-shift study of workers at risk of Mesoamerican nephropathy. Environ. Res. 2015, 142, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Damalas, C.A.; Telidis, G.K.; Thanos, S.D. Assessing farmers’ practices on disposal of pesticide waste after use. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 390, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derafshi, M.; Black, C.; Agnew, R. Pesticide knowledge, attitudes, and clothing practices of Turkish farmers. Environ. Manag. Sustain. Dev. 2017, 6, 149–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gesesew, H.A.; Woldemichael, K.; Massa, D.; Mwanri, L. Farmers knowledge, attitudes, practices and health problems associated with pesticide use in rural irrigation villages, Southwest Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jallow, M.F.; Awadh, D.G.; Albaho, M.S.; Devi, V.Y.; Thomas, B.M. Pesticide knowledge and safety practices among farm workers in Kuwait: Results of a survey. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





| Province | Altitude (m) | Latitude (North) | Longitude (West) | Climate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Meknes | 552 | 33°53′ | 5°33′ | Mediterranean sub-floor temperate |
| Fez | 579 | 34°03′ | 4°58′ | Mediterranean sub-floor temperate |
| Sefrou | 823 | 33°49′ | 4°50′ | Continental |
| El Hajeb | 1000 | 33°41′ | 5°22′ | Semi-arid temperate winter |
| Ifrane | 1664 | 33°32′ | 5°06′ | Mediterranean |
| Variable | n | % |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) (mean 45.02; SD 9.59) | ||
| <30 | 35 | 6.7 |
| 30–40 | 153 | 29.1 |
| 41–50 | 185 | 35.2 |
| 51–60 | 121 | 23 |
| >60 | 32 | 6.1 |
| Farming experience (mean 11.56; SD 3.84) | ||
| 5–10 | 266 | 50.6 |
| 11–20 | 243 | 46.2 |
| >20 | 17 | 3.2 |
| Family situation | ||
| Single | 118 | 22.4 |
| Married | 396 | 75.3 |
| Widower | 7 | 1.3 |
| Divorced | 5 | 1 |
| Benefit from agricultural advisory services (ACS) | ||
| Yes | 63 | 12 |
| No | 463 | 88 |
| Training/Internship | ||
| Yes | 102 | 19.4 |
| No | 424 | 80.6 |
| Education study | ||
| Illiterate | 288 | 43.3 |
| Primary | 153 | 29.1 |
| College | 109 | 20.7 |
| Secondary | 31 | 5.9 |
| University | 5 | 1 |
| Name | Chemical Family | Class a | IARC | n | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deltamethrin | Pyrethroids | II | 3 | 301 | 57.2 |
| Carbendazim | Benzimidazoles | U | - | 232 | 44.1 |
| Glyphosate | Amino phosphanates | III | 2A | 232 | 44.1 |
| Malathion | Organophosphorus | III | 2A | 228 | 43.3 |
| Lambda cyhalothrin | Pyrethroids | II | - | 214 | 40.7 |
| Maneb | Dithiocarbamates | U | 3 | 181 | 34.4 |
| Methomyl | Carbamates | Ib | - | 168 | 31.9 |
| Mancozeb | Dithiocarbamates | U | - | 164 | 31.2 |
| Abamectin | Avermectins | Ib | - | 148 | 28.1 |
| Dimethoate | Organophosphorus | II | - | 141 | 26.8 |
| Dicofol | Carbinols | II | 3 | 136 | 25.9 |
| Cypermethrin | Pyrethroids | II | - | 131 | 24.9 |
| Captan | Phtalimides | U | 3 | 118 | 22.4 |
| Thiophanate methyl | Benzimidazoles | III | - | 104 | 19.8 |
| Ziram | Dithiocarbamates | II | 3 | 94 | 17.9 |
| Paraquat | Bipyridiles | II | - | 91 | 17.3 |
| Sulphur | Minerals | III | - | 82 | 15.6 |
| Thiram | Dithiocarbamates | II | 3 | 82 | 15.6 |
| Probinebe | Dithiocarbamates | U | - | 79 | 15 |
| Oxyfluorfen | Diphenyl ethers | U | - | 67 | 12.7 |
| Thiacloprid | Chloronicotiniles | II | - | 60 | 11.4 |
| Dodine | Guanidine | II | - | 58 | 11 |
| Fluazifop-P-butyl | Aryloxy phenoxy-propionates | III | - | 54 | 10.3 |
| Chloropyriphos ethyl | Organophosphorus | II | - | 48 | 9.1 |
| Difenoconazole | Triazoles | II | - | 47 | 8.9 |
| Azoxystrobine | Strobilurins | U | - | 44 | 8.4 |
| Iprodine | Dicarboximides | III | - | 42 | 8 |
| 2,4-D | A. phenoxy-alkanoic | II | 2B | 41 | 7.8 |
| Propargite | Sulfites | III | - | 41 | 7.8 |
| Indoxacarb | Indoxacarb | II | - | 36 | 6.8 |
| Copper oxychloride | Minerals | II | - | 43 | 8.1 |
| Copper hydroxide | Minerals | II | - | 30 | 5.7 |
| Imidoclopride | Neonicotinoids | II | - | 27 | 5.1 |
| Acétamipride | Chloronicotiniles | - | - | 25 | .8 |
| 2,4 MCPA | A. phenoxy-alkanoic | II | - | 24 | 4.6 |
| Dichlorovos | A. phenoxy-alkanoic | Ib | - | 16 | 3 |
| Chlorothalonil | Chloronitriles | U | 2B | 14 | 2.7 |
| Endosulfan | Triazole | II | - | 9 | 1.7 |
| Hexaconazole | Triazoles | III | - | 8 | 1.5 |
| Tau-fluvinate | A. phenoxy-alkanoic | III | - | 5 | 1 |
| Dicamba | Benzoic acids | II | - | 4 | 0.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ben Khadda, Z.; Fagroud, M.; El Karmoudi, Y.; Ezrari, S.; Berni, I.; De Broe, M.; Behl, T.; Bungau, S.G.; Sqalli Houssaini, T. Farmers’ Knowledge, Attitudes, and Perceptions Regarding Carcinogenic Pesticides in Fez Meknes Region (Morocco). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10879. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182010879
Ben Khadda Z, Fagroud M, El Karmoudi Y, Ezrari S, Berni I, De Broe M, Behl T, Bungau SG, Sqalli Houssaini T. Farmers’ Knowledge, Attitudes, and Perceptions Regarding Carcinogenic Pesticides in Fez Meknes Region (Morocco). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(20):10879. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182010879
Chicago/Turabian StyleBen Khadda, Zineb, Mustapha Fagroud, Yahya El Karmoudi, Said Ezrari, Imane Berni, Marc De Broe, Tapan Behl, Simona Gabriela Bungau, and Tarik Sqalli Houssaini. 2021. "Farmers’ Knowledge, Attitudes, and Perceptions Regarding Carcinogenic Pesticides in Fez Meknes Region (Morocco)" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 20: 10879. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182010879
APA StyleBen Khadda, Z., Fagroud, M., El Karmoudi, Y., Ezrari, S., Berni, I., De Broe, M., Behl, T., Bungau, S. G., & Sqalli Houssaini, T. (2021). Farmers’ Knowledge, Attitudes, and Perceptions Regarding Carcinogenic Pesticides in Fez Meknes Region (Morocco). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(20), 10879. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182010879









