Effects of Facial Muscles Exercise on Mental Health: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Eligibility Criteria and Outcome Measures
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Data Analysis/Synthesis
3. Results
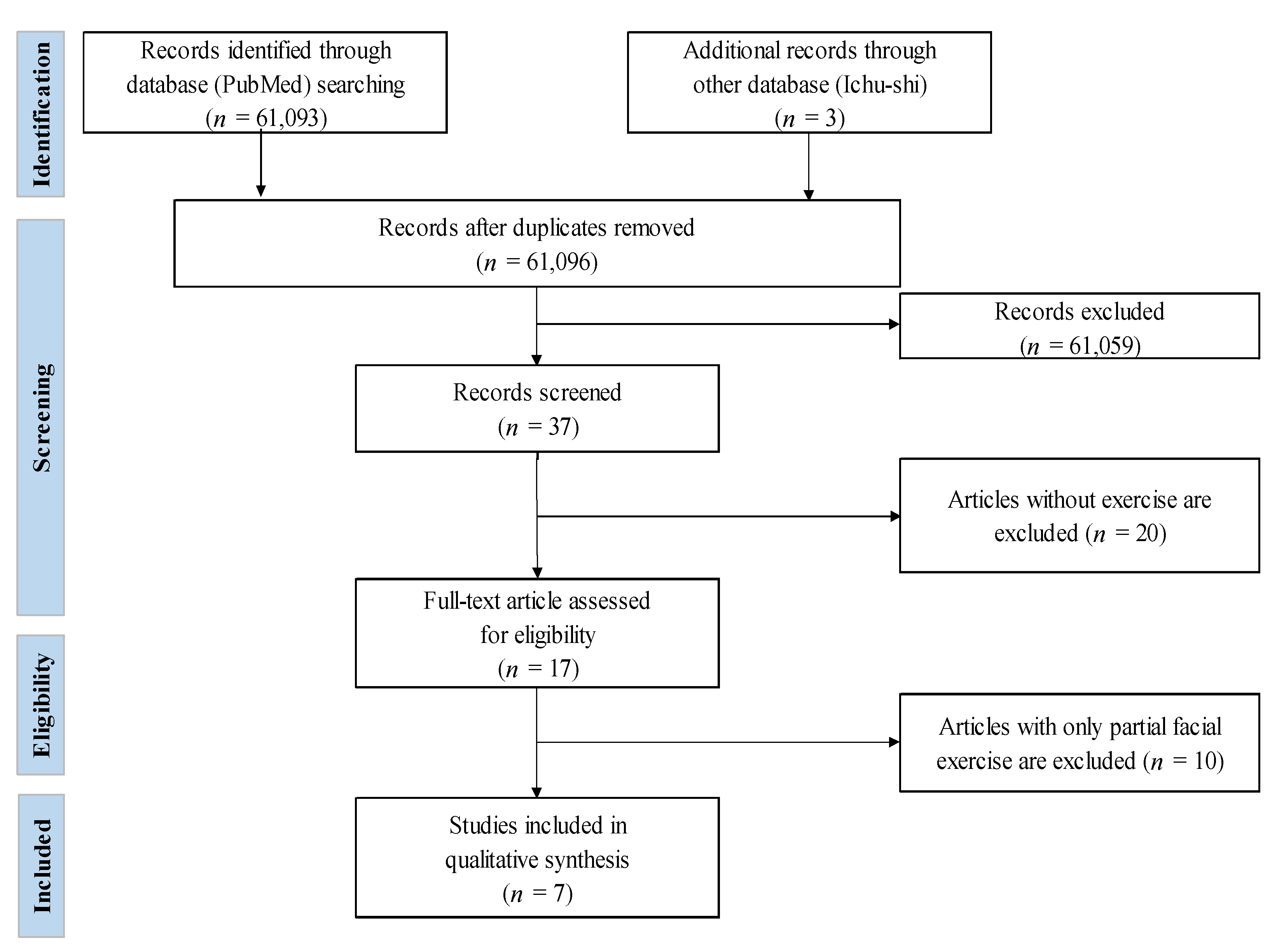
3.1. Study Selection and Characteristics
3.2. Interventions
3.3. Execise Program
3.4. Outcome Measurements
3.5. Risk of Bias and Quality Assessment
3.6. Effect of Facial Muscles Exercise on Mental Health
3.6.1. Depressive Symptoms
3.6.2. Mood
3.6.3. Stress
3.6.4. Humor
3.6.5. Immunological and Physiological Effects
3.6.6. Self-Reported
4. Discussion
4.1. Findings
4.2. Limitations of the Review
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weiss, D.S.; Marmar, C.R.; Metzler, T.J.; Ronfeldt, H.M. Predicting symptomatic distress in emergency services personnel. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 1995, 63, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalan, J.; Burgess, A.; Pergami, A.; Hulme, N.; Gazzard, B.; Phillips, R. The psychological impact on staff of caring for people with serious diseases: The case of HIV infection and oncology. J. Psychosom. Res. 1996, 40, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Liang, M.; Li, Y.; Guo, J.; Fei, D.; Wang, L.; He, L.; Shen, C.; Cai, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Mental health care for medical staff in China during the COVID-19 outbreak. Lancet Psychiatry 2020, 7, 15–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Investing in Treatment for Depression and Anxiety Leads to Fourfold Return. 2016. Available online: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/detail/13-04-2016-investing-in-treatment-for-depression-and-anxiety-leads-to-fourfold-return (accessed on 24 March 2019).
- Jong, E.Y. Therapeutic Benefits of Laughter in Mental Health: A Theoretical Review. TJEM 2016, 239, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vina, J.; Sanchis, G.F.; Martinez, B.V.; Gomez, C.M. Exercise acts as a drug; the pharmacological benefits of exercise. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 167, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izard, C. The Face of Emotion; Appleton-Century-Crofts: New York, NY, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Tomkins, S. Affect, Imagery, Consciousness: The Positive Affects; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1962; Volume I. [Google Scholar]
- Tourangeau, R.; Ellsworth, C. The role of facial response in the experience of emotion. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1979, 37, 1519–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekman, P.; Friesen, V. Unmasking the Face: A Guide to Recognizing Emotions from Facial Clues; Malor Books: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ekman, P.; Davidson, R.J.; Friesen, W.V. The Duchenne smile: Emotional expression and brain physiology. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1990, 58, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waller, B.M.; Vick, S.J.; Parr, L.A.; Bard, K.A.; Pasqualini, M.C.S.; Gothard, K.M.; Fuglevand, A.J. Intramuscular electrical stimulation of facial muscles in humans and chimpanzees: Duchenne revisited and extended. Emotion 2006, 6, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekman, P.; Davidson, J. Voluntary smiling changes regional brain activity. Psychol. Sci. 1993, 4, 342–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiswede, D.; Munte, T.F.; Kramer, U.M.; Russeler, J. Embodied emotion modulates neural signature of performance monitoring. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, 5754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, M.; Ekman, P. Physiologic effects of the smile. Dir. Psychiatry 1996, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Soussignan, R. Duchenne smile, emotional experience, and autonomic reactivity: A test of the facial feedback hypothesis. Emotion 2002, 2, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finzi, E.; Rosenthal, N.E. Emotional proprioception: Treatment of depression with afferent facial feedback. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2016, 80, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luigi, C.; Giovanni, P. The facial motor system. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2014, 38, 135–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruegsegger, G.N.; Booth, F.W. Health Benefits of Exercise. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a029694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fay, R.A.; Norgren, R. Identification of rat brainstem multisynaptic connections to the oral motor nuclei in the rat using pseudorabies virus. II. Facial muscle motor systems. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 1997, 25, 276–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porges, S.W. The Polyvagal Theory: Phylogenetic contributions to social behavior. Physiol. Behav. 2003, 79, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, M.B.; Erb, M.; Schmalzl, L.; Moonaz, S.; Noggle, T.J.; Porges, S.W. Yoga Therapy and Polyvagal Theory: The Convergence of Traditional Wisdom and Contemporary Neuroscience for Self-Regulation and Resilience. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, L.; Gue, M.; Fargeas, M.J.; Alvinerie, M.; Junien, J.L.; Fioramonti, J. Vagally mediated inhibition of acoustic stress-induced cortisol release by orally administered kappa-opioid substances in dogs. Endocrinology 1989, 124, 1788–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holstege, G. The emotional motor system. Eur. J. Morphol. 1992, 30, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holstege, G. Emotional innervation of facial musculature. Mov. Disord. 2002, 17 (Suppl. 2), 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emilou, N.; Andreas, W.; Ulrike, E. Are Psychosocial Resources Associated With Perceived Facial Aging in Men? Gerontol. Geriatr. Med. 2017, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapadia, N.; Zivanovic, B.; Moineau, B.; Downar, J.; Zariffa, J.; Popovic, R.M. Functional electrical stimulation of the facial muscles to improve symptoms in individuals with major depressive disorder: Pilot feasibility study. BioMed. Eng. OnLine 2019, 18, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japan Medical Abstracts Society: Ichu-Shi Web. Available online: http://search.jamas.or.jp/ (accessed on 8 June 2019).
- Nomura, K.; Shimamoto, K.; Iwatsuki, K. The effects of group facial muscle exercises on work stress for nursing care staff. J. Jpn. Nurs. Assoc. 2007, 38, 66–68. [Google Scholar]
- Uchida, M.; Arai, Y. The recovery of smile of Parkinson’s disease patient-Improvement the masked-face by smile making training. Jpn. Soc. Health Sci. Mind Body 2010, 6, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konecny, P.; Elfmark, M.; Urbanek, K. Facial paresis after stroke and ITS impact on patient’s facial movement and mental status. J. Rehabil. Med. 2011, 43, 73–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.; Tsai, G.; Hsieh, C.J. Psychological, Immunological and physiological effects of a Laughing Qigong Program (LQP) on adolescents. Complement. Ther. Med. 2016, 21, 660–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuchuen, U.; Pampiansil, P.; Busarakumtragul, P. Effects of Laughing Training on Stress Levels in Thai Private Office Workers. J. Med. Assoc. Thai. 2015, 98, 130–134. [Google Scholar]
- Hyoung, J.C.; Sang, H.S. Effects of a Facial Muscle Exercise Program Including Facial Massage for Patients with Facial Palsy. J. Korean Acad. Nurs. 2016, 46, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, R.; Mizukami, K. The effective of facial exercises on the mental health in elderly adults. Jpn. J. Geriat. 2018, 55, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Minds Ver.4; Japan Medical Function Evaluation Organization Medical Information Service. Available online: https://jcqhc.or.jp/htm1 (accessed on 8 June 2019).
- The Japanese Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. Stress Check System Implementation Manual 2015 Based on the Industrial Safety and Health Law. Available online: http://www.mhlw.go.jp/bunya/roudoukijun/anzeneisei12/pdf/150507–1.pdf (accessed on 28 April 2019).
- Zung, W.W.K. A self-rating depression scale. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1965, 12, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.; Steer, R.; Brown, G. Manual for the Beck Depression Inventory, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, C.J.; Hsia, Y.; Liu, S.; Chang, C. Positive psychological measure: Constructing and evaluating the reliability and validity of a Chinese Humor Scale applicable to professional nursing. J. Nurs. Res. 2005, 13, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahatnirunkul, S.; Pumpisanchai, W.; Tapanya, P. The construction of SuanPrung stress test for Thai population. J. Suanprung. Psychiatr. Hosp. 1997, 2540, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Radloff, L.S. The CES-D scale: A self-report depression scale for research in the general population. Appl. Psychol. Meas. 1977, 1, 385–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, D.P.; Gater, R.; Sartorius, N.; Ustun, T.B.; Piccinelli, M.; Gureje, O.; Rutter, C. The validity of two versions of the GHQ in the WHO study of mental illness in general health care. Psychol. Med. 1997, 27, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Level of Evidence | Intervention |
|---|---|
| Ⅰ | Meta-Analyses of Randomized Controlled Trials/Systematic Reviews |
| Ⅱ | Randomized Controlled Trials |
| Ⅲ | Controlled Clinical Trials |
| Ⅳa | Cohort Studies |
| Ⅳb | Case-Control Studies |
| Ⅴ | Case series/Case reports |
| Ⅵ | Expert Opinions/Non-EBM Guidelines |
| Authors (Year) | Country | Participant Characteristics | Intervention (Total Time) | Exercise Program | Study Design | Measuring Method | Outcome Measures | Results | Evidence Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nomura et al. (2007) [30] | Japan | n = 33 (Nursing care staff), Average age: 37.4 ± 5.33 years | 5 min/day, 5 days/week for a month (before morning meeting) (750 min) | Smile muscles exercise | Before–after | Psychological measures | (1) The Brief Job Stress Questionnaire; (2) Self- Restricted Type Behavior Traits Scale; (3) Emotional Support Network Scale | (1) The workload (one of subscales) score improved in the IG (p < 0.01); (2) Not statistically significant; (3) Not statistically significant | Ⅳb |
| Uchida and Arai (2010) [31] | Japan | n = 31 (females: 18, males: 13, Outpatients with Parkinson’s disease), Average age: 67.0 years, The Hoehn and Yahr Scale: Stage Ⅱ–Ⅴ, ICD10: F32 | a few min/day, every day for 2 months (at home) (1260 min) | (1) Facial muscles training; (2) Positive thinking training | Before–after | (1) Analysis of facial emotion; (2) Psychological measures | (1) FACS; (2) The Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS); (3) Self-Rating Depression Scale (SDS) | (1) The elevation of corners of mouth were significantly improved in the IG (p = 0.00003); (2) The UPDRS scores showed significantly improved between pretest 5.58 and posttest 1.55 (p = 0.00000); (3) The SDS scores showed significantly decreased between pretest 50.2 and posttest 41.6 (p = 0.00003) | Ⅳb |
| Konecny et al. (2011) [32] | Czech Republic | n = 99 (females: 46, males: 53, Facial palsy patients), Average age: 61.8 years | 20 min/day, for a month (720 min) | (1) Speech therapy; (2) Rehabilitation exercises; (3) Facial exercise therapy include breathing rehabilitation; (4) Speech therapy; (5) Rehabilitation exercises | RCT | (1) Analysis of facial movement; (2) Analysis of facial emotion; (3) Psychological measures | (1) House–Brackmann Grading Scale (HBGS); (2) 2D video analysis; (3) BDI-II | (1) A significant difference in the mean values on the HBGS before and after rehabilitation of 1.66 (SD 0.55) was observed in the experimental group and of 0.59 (SD 0.57) in the control group. (2) There were significant difference in the changes in distances between the corner of the mouth and the earlobe in the experimental group (11.5 mm (SD 3.50)) and in the control group (2.0 mm (SD 2.30)). (3) Statistically significant improvements in the experimental group can also be seen in the evaluation of depression according to the BDI-II. There was a significant difference in the mean values of the BDI-II before and after rehabilitation in the experimental group (14.3 (SD 5.1)) and in the control group (6.9 (SD 5.1)). | Ⅱ |
| Chang et al. (2013) [33] | Taiwan | n = 67 (females: 33, males: 34, students of a public junior high school, 7th grade) | 45 min/day, 8 sessions for 2 months (360 min) | (1) Facial tai chi; (2) Nothing | RCT | (1) Psychological measures; (2) Immunological measures | (1) Rosenberg’s Self-Esteem Scale (RSE); (2) The Chinese Humor Scale (CHS) (3) The Face Scale (FS); (4) ELISA; (5) Blood pressure, Heart rate variability, LF/HF | (1) Not statistically significant; (2) The CHS and Humor Creativity (one of subscales) scores improved in the IG (p = 0.004; p = 0.003); (3) Not statistically significant; (4) Cortisol showed significant differences between pretest 48.35 (SD 12.53) and posttest 38.50 (SD 13.10) in the IG (p = 0.001). (5) Not statistically significant | Ⅱ |
| Chuchun et al. (2015) [34] | Thailand | n = 38 (private office workers), Age: 25–60 years | 60 min/day, 3 days/week, 8 sessions for 2 months (480 min) | (1) Smile muscles training; (2) Nothing | RCT | Psychological measures | The Suanprung Stress Test-60 (SPST-60) | (1) Not statistically significant; (2) No significant difference was found in the mean scores of the level of stress between the CG and IG. However, the sensitivities to the arousal events in the IG had a tendency to decrease | Ⅱ |
| Hyoung and Sang (2016) [35] | Korea | n = 70 (females: 45, males: 25, Outpatients with Facial palsy), Age: < 40: n = 16, 40–49 years: n = 15, 50–59 years: n = 19, > 60: n = 2 | 20 min/day, 3 days/week, 2 weeks (120 min) | (1) Facial muscles exercises; (2) Facial massage (3) Nothing | Quasi-experimental | (1) Analysis of facial movement; (2) Psychological measures; (3) Reading measures | (1) House-Brackmann Grading Scale (HBGS); (2) Facial Nerve Grading Scale (FNGS); (3) Reading Time; (4) Palsy subjective symptoms; (5) CES-D | (1) Not statistically significant; (2) The FNGS scores were statistically significant in the IG (p < 0.001); (3) Not statistically significant. (4) The CES-D scores were statistically significant in the IG (p < 0.001) | Ⅲ |
| Okamoto and Mizukami (2018) [36] | Japan | n = 53 (females: 51, males: 2, Community-dwelling older adults), Average age 78.3 ± 5.3 years | 30 min/day, 2 days/week, 24 sessions for 3 months (720 min) | (1) Facial acupressure; (2) Facial muscles exercises; (3) Facial yoga; (4) Facial massage; (5) Nothing | RCT | (1) Psychological measures; (2) Tongue pressure; (3) Analysis of facial emotion | (1) GHQ-12; (2) PGC Moral Scale; (3) Tongue pressure (4) Face Reader™ | (1) The GHQ-12 scores were statistically significant in the IG (p = 0.003). There was a simple main effect; (2) Not statistically significant; (3) The tongue pressure scores were statistically significant in the IG (p = 0.036); (4) The happiness (smile) scores were significantly improved in the IG (p = 0.003) | Ⅱ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Okamoto, R.; Manabe, T.; Mizukami, K. Effects of Facial Muscles Exercise on Mental Health: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12216. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182212216
Okamoto R, Manabe T, Mizukami K. Effects of Facial Muscles Exercise on Mental Health: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(22):12216. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182212216
Chicago/Turabian StyleOkamoto, Rumiko, Toshie Manabe, and Katsuyoshi Mizukami. 2021. "Effects of Facial Muscles Exercise on Mental Health: A Systematic Review" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 22: 12216. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182212216
APA StyleOkamoto, R., Manabe, T., & Mizukami, K. (2021). Effects of Facial Muscles Exercise on Mental Health: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(22), 12216. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182212216






