Analysis of the Evolution of User Emotion and Opinion Leaders’ Information Dissemination Behavior in the Knowledge Q&A Community during COVID-19
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Basis and Concept Definition
2.1. Network Opinion Leaders
2.2. Knowledge Q&A Community
2.3. Emotional Cognition Theory
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Procedure
3.2. The Sample
3.3. Data Processing
3.4. Data Analysis
3.4.1. Variables and Instruments Used to Construct Networks
3.4.2. Identification and Measurement of Opinion Leaders
3.4.3. Measurement of Network Information Dissemination Ability
4. Results
4.1. Thematic Analysis
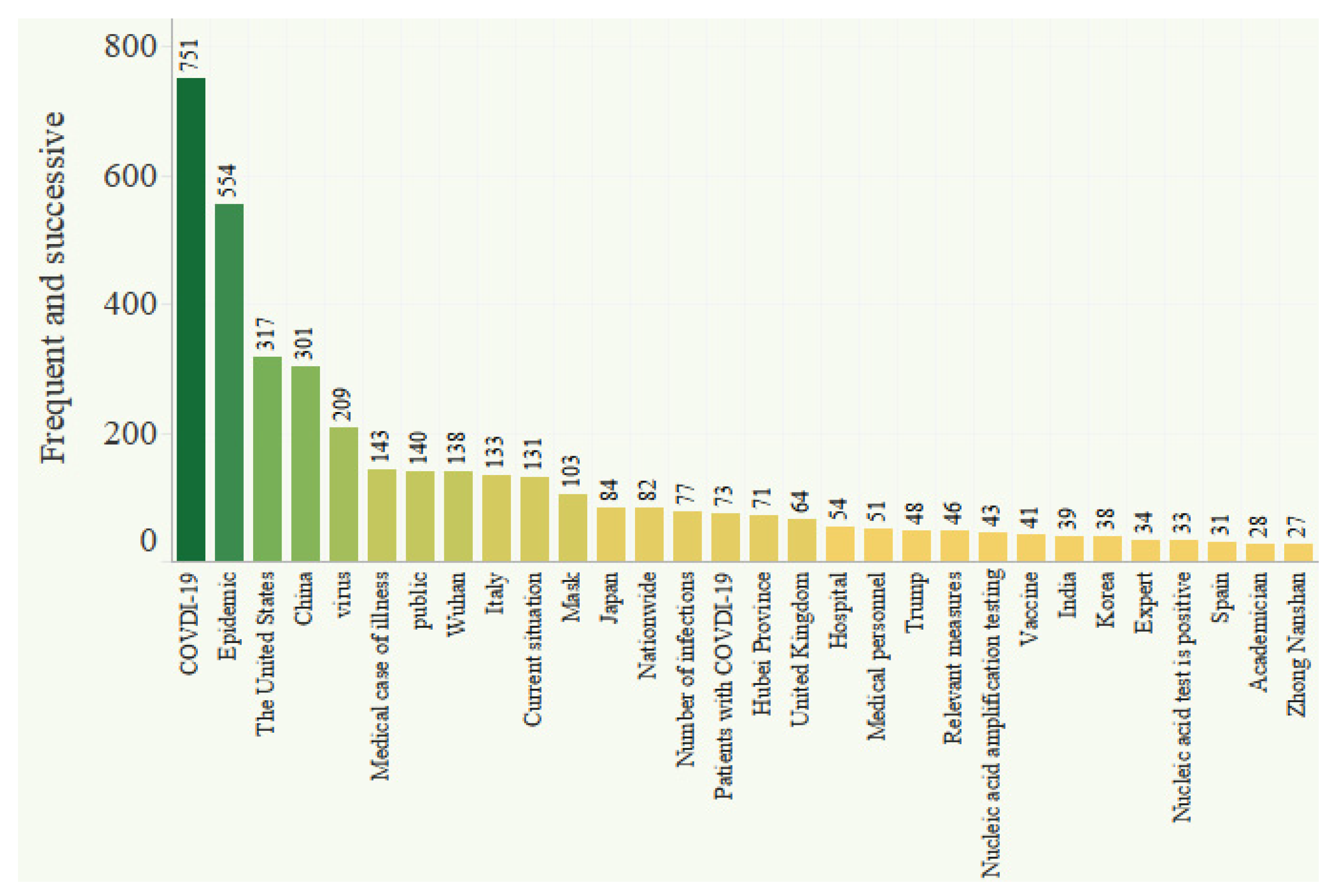
4.1.1. Word Cloud and Word Frequency
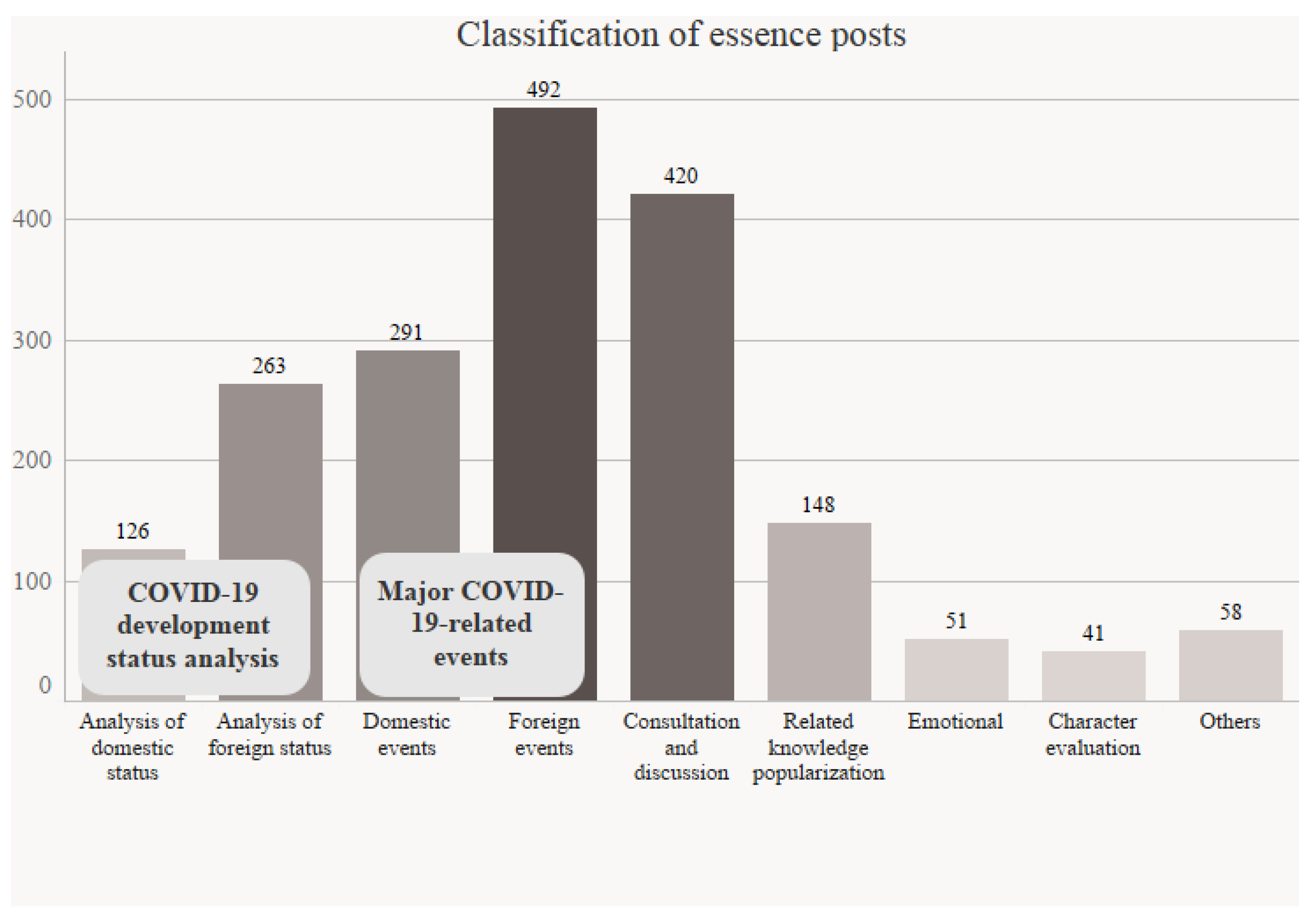
4.1.2. Classification of Essential Posts
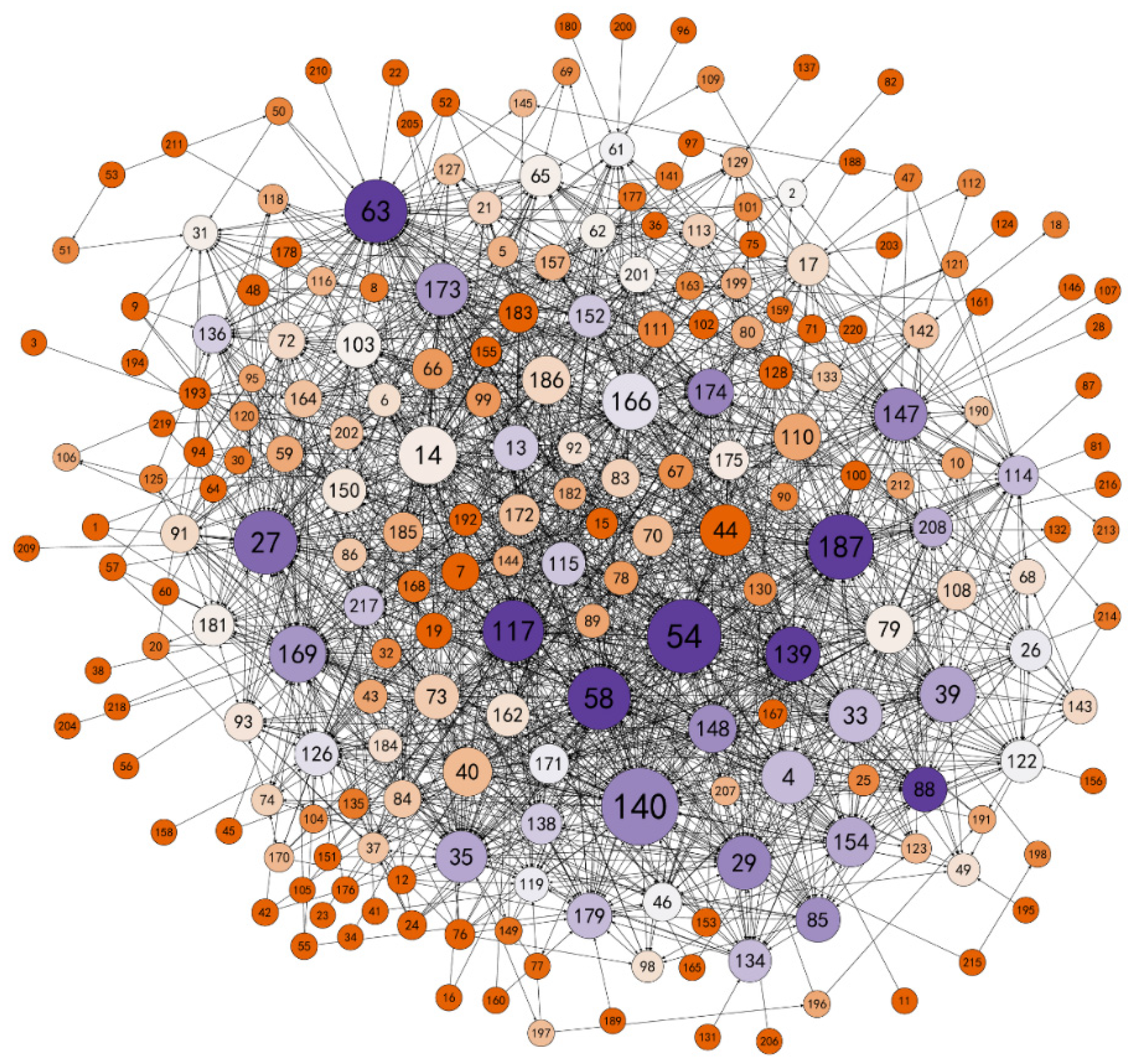
4.2. Identification of Opinion Leaders
4.3. Information Dissemination Network Analysis
4.3.1. Dissemination Efficiency
4.3.2. Dissemination Path
4.3.3. Degree of Control over Dissemination
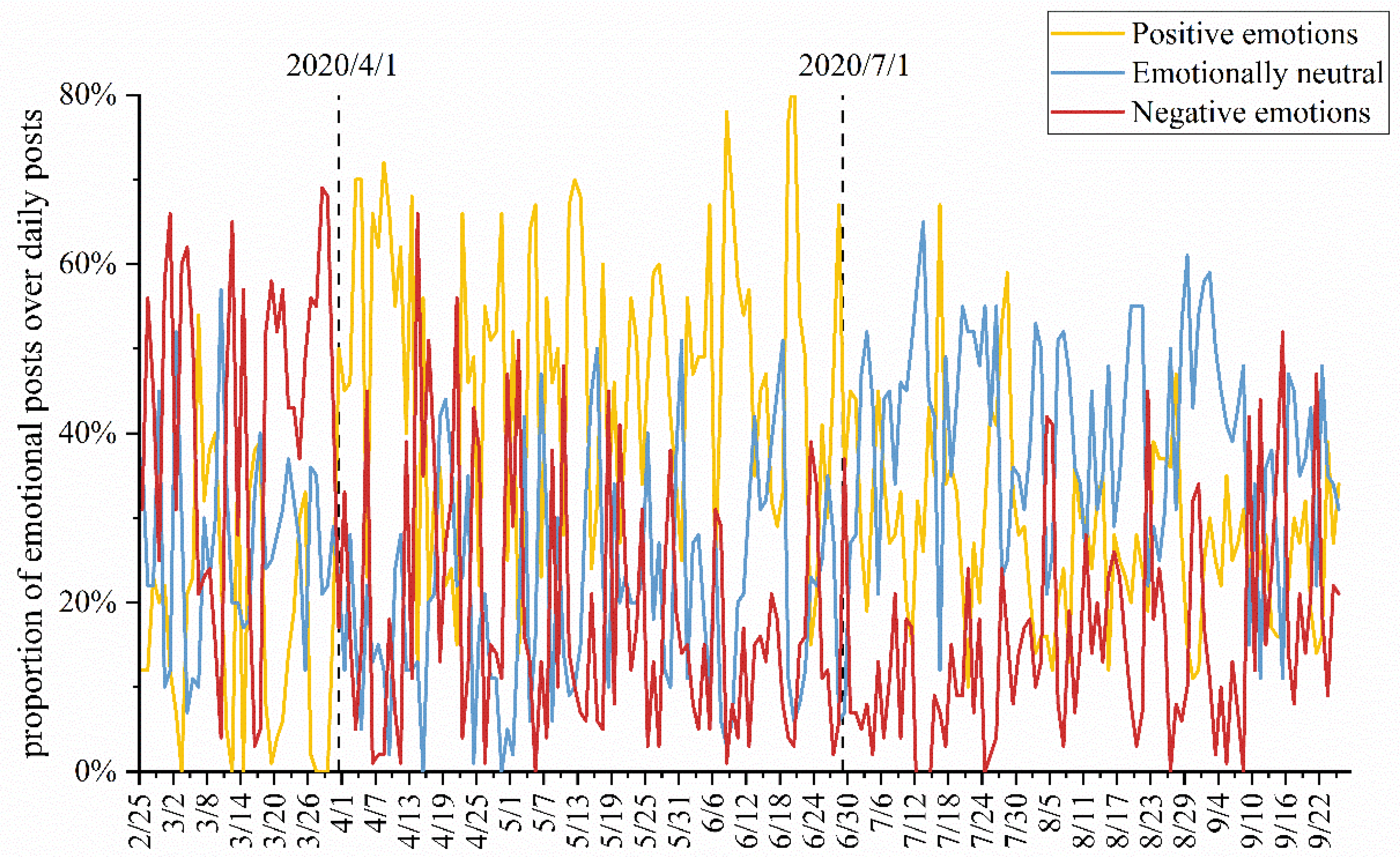
4.4. The Evolution of User Emotion
5. Discussion and Conclusion
5.1. Discussion
5.2. Implications for Research and Practice
5.3. Conclusions, Limitations, and Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Veer, M.; Kumar, A.M.; Ivanova, V. COVID-19 and the Cardiovascular System. Crit. Care Nurs. Q. 2020, 43, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartsch, S.M.; Ferguson, M.C.; McKinnell, J.A.; O’Shea, K.J.; Wedlock, P.; Siegmund, S.S.; Lee, B.Y. The Potential Health Care Costs and Resource Use Associated with COVID-19 in the United States. Health Aff. 2020, 39, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cerasti, D.; Ormitti, F.; Pardatscher, S.; Malchiodi, L.; Picetti, E.; Menozzi, R.; Rossi, S. Multiple Acute Ischemic Strokes in a COVID-19 Patient: A Case Report. SN Compr. Clin. Med. 2020, 2, 1213–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, E.E.; McMahon, D.E. Creating dermatology guidelines for COVID-19: The pitfalls of applying evidence-based medicine to an emerging infectious disease. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 82, e231–e232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Situation Report—11. Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/20200131-sitrep-11-ncov.pdf?sfvrsn=de7c0f7_4 (accessed on 21 February 2020).
- Tang, W.; Liao, H.; Marley, G.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, W.; Wu, D.; Yu, R. The Changing Patterns of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in China: A Tempogeographic Analysis of the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Epidemic. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanna, P.M.; Seagull, F.J.; Nagy, P. Online Social Networking: A Primer for Radiology. J. Digit. Imaging 2011, 24, 908–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, H.-C.; Ho, W.-H. Cultural Effects on Use of Online Social Media for Health-Related Information Acquisition and Sharing in Taiwan. Int. J. Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2018, 34, 1063–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, C.; Whittle, S.; Haghighi, P.D.; Burstein, F.; Sa’Adon, R.; Keen, H.I. Mining social media data to investigate patient perceptions regarding DMARD pharmacotherapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 1432–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Y.; Tu, Y.; Xie, K.; Ye, Y.; Shen, W. Internet Public Opinion Risk Grading under Emergency Event Based on AHPSort II-DEMATEL. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burhamah, W.; AlKhayyat, A.; Oroszlányová, M.; AlKenane, A.; Almansouri, A.; Behbehani, M.; Karimi, N.; Jafar, H.; AlSuwaidan, M. The psychological burden of the COVID-19 pandemic and associated lockdown measures: Experience from 4000 participants. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 277, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Meng, S.; Shi, J.; Lu, L. 2019-nCoV epidemic: Address mental health care to empower society. Lancet 2020, 395, e37–e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaligotla, C.; Yücesan, E.; Chick, S.E. Diffusion of competing rumours on social media. J. Simul. 2020, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, F.; Koura, Y.H.; Wang, H. Dynamic of interactive model for information propagation across social networks media. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2020, 2020, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shan, S.; Liu, M.; Xu, X. Analysis of the key influencing factors of haze information dissemination behavior and motivation in WeChat. Inf. Discov. Deliv. 2017, 45, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, T.; Jin, Z.; Su, N.; Zhao, C.; He, Y. The research on social networks public opinion propagation influence models and its controllability. China Commun. 2018, 15, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, A.; Bi, S.-B.; Wang, J.; Huang, T.; Wan, L. Spatial Structure and Characteristics of Information-Network Based on Network Public Opinion. China Sci. Technol. Forum 2017, 11, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, N.; Swim, J.K.; Glenna, L. Spread the Green Word: A Social Community Perspective into Environmentally Sustainable Behavior. Environ. Behav. 2019, 51, 561–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, H.; McMurray, J.R.; Kurz, T.; Lambert, F.H. Network analysis reveals open forums and echo chambers in social media discussions of climate change. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2015, 32, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirri, S.; Lorenzoni, V.; Andreozzi, G.; Mosca, M.; Turchetti, G. Topic Modeling and User Network Analysis on Twitter during World Lupus Awareness Day. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nip, J.Y.M.; Fu, K.-W. Networked framing between source posts and their reposts: An analysis of public opinion on China’s microblogs. Inf. Commun. Soc. 2015, 19, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Yu, N.; Song, Y. User Engagement in Public Discourse on Genetically Modified Organisms: The Role of Opinion Leaders on Social Media. Sci. Commun. 2018, 40, 691–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Song, Y. Viral misinformation and echo chambers: The diffusion of rumors about genetically modified organisms on social media. Internet Res. 2020, 30, 1547–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, H.; Lin, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Liu, C.; Wang, Z.; Gifu, D.; Xia, J. Investigation in the influences of public opinion indicators on vegetable prices by corpora construction and WeChat article analysis. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020, 102, 876–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chen, B.; Ai, C.; He, L.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, X.; Lu, X. The Influence of Geographic Factors on Information Dissemination in Mobile Social Networks in China: Evidence from WeChat. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joshi, G.C.; Paul, M.; Kalita, B.K.; Ranga, V.; Rawat, J.S.; Rawat, P.S. Mapping the social landscape through social media. J. Inf. Sci. 2020, 46, 776–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keelan, J.; Pavri, V.; Balakrishnan, R.; Wilson, K. An analysis of the Human Papilloma Virus vaccine debate on MySpace blogs. Vaccine 2010, 28, 1535–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massey, P.M.; Kearney, M.D.; Hauer, M.K.; Selvan, P.; Koku, E.; Leader, A.E. Dimensions of Misinformation About the HPV Vaccine on Instagram: Content and Network Analysis of Social Media Characteristics. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e21451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xie, Z.; Sun, L.; Xu, C.; Li, D. Electronic Cigarette–Related Contents on Instagram: Observational Study and Exploratory Analysis. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2020, 6, e21963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vo, T.T.; Xiao, X.; Ho, S.Y. How Does Corporate Social Responsibility Engagement Influence Word of Mouth on Twitter? Evidence from the Airline Industry. J. Bus. Ethics 2019, 157, 525–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, P.; Sharma, N.; Sikka, G. The emergence of social media data and sentiment analysis in election prediction. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2021, 12, 2601–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babac, M.B.; Podobnik, V. What social media activities reveal about election results? The use of Facebook during the 2015 general election campaign in Croatia. Inf. Technol. People 2018, 31, 327–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.-H.; Fu, K.-W. The Relationship Between Cyberbalkanization and Opinion Polarization: Time-Series Analysis on Facebook Pages and Opinion Polls During the Hong Kong Occupy Movement and the Associated Debate on Political Reform. J. Comput. Commun. 2017, 22, 266–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; McKee, M.; Torbica, A.; Stuckler, D. Systematic Literature Review on the Spread of Health-related Misinformation on Social Media. Soc. Sci. Med. 2019, 240, 112552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Guo, H.; Zhuang, J. Social Media Behavior and Emotional Evolution during Emergency Events. Health 2021, 9, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Dimitroff, A. A study on health care consumers’ diabetes term usage across identified categories. Aslib J. Inf. Manag. 2014, 66, 443–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, N. Opinion leaders as intermediaries in audience building for independent films in the Internet age. Converg. Int. J. Res. New Media Technol. 2014, 21, 450–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, J.W.; Kim, E.M.; Suk, K.H. Exploring Online Opinion Leadership. Korean J. Commun. Stud. 2007, 51, 358–384. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Liang, E.; Wu, Y. Accumulation mechanism of opinion leaders’ social interaction ties in virtual communities: Empirical evidence from China. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2018, 82, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhu, F.; Liu, S.; Zhu, B. Identifying opinion leaders by improved algorithm based on Leader—Rank. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2015, 51, 110. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; He, H.; Cao, B. Identifying and evaluating the internet opinion leader community based on k-clique clustering. Neural Comput. Appl. 2014, 25, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, X.; He, H.; Wang, X. Identifying Network Public Opinion Leaders Based on Markov Logic Networks. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-M.; You, Z.-L. Community detection with opinion leaders’ identification for promoting collaborative problem-based learning performance. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2018, 50, 1846–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Liu, Y. SuperedgeRank algorithm and its application in identifying opinion leader of online public opinion supernetwork. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 1357–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Jansen, B.J. Identifying and predicting the desire to help in social question and answering. Inf. Process. Manag. 2017, 53, 490–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Oh, J.S.; Shah, C. The use of information sources by internet users in answering questions. Proc. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2008, 45, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recode. Yes, Quora Still Exists, and It’s Now Worth Billion. 2019. Available online: https://carmona.mx/2019/05/18/yes-quora-still-exists-and-its-now-worth-2-billion/ (accessed on 23 December 2019).
- Chen, Y.; Dong, T.; Ban, Q.; Li, Y. What Concerns Consumers about Hypertension? A Comparison between the Online Health Community and the Q&A Forum. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2021, 14, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazan, R. Microcollaborations in a social Q&A community. Inf. Process. Manag. 2010, 46, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.L.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Lee, M.K.O.; Cheung, C.M.K. Why users keep answering questions in online question answering communities: A theoretical and empirical investigation. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2013, 33, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Chen, L.; Gillenson, M.L. How to keep brand fan page followers? The lens of person-environment fit theory. Inf. Technol. People 2018, 31, 927–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Peng, X.; Liu, Z.; Song, S.; Hansen, P. Factors that affect asker’s pay intention in trilateral payment-based social Q&A platforms: From a benefit and cost perspective. J. Assoc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2020, 71, 516–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.L. Emotional Psychology; Peking University Press: Beijing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, T.; Wang, L.; Jin, J.; Song, X. Knowledge contribution behavior in online Q&A communities: An empirical investigation. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2018, 81, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Li, Y.; Zhong, X.; Zhai, L. Why users contribute knowledge to online communities: An empirical study of an online social Q&A community. Inf. Manag. 2015, 52, 840–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.A. Social capital and the search for information: Examining the role of social capital in information seeking behavior in Mongolia. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. 2007, 58, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osatuyi, B.; Passerini, K.; Turel, O. Diminishing returns of information quality: Untangling the determinants of best answer selection. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2022, 126, 107009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.; Milkman, K.L. What Makes Online Content Viral? J. Mark. Res. 2012, 49, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhihu Product Analysis Report. Available online: http://www.woshipm.com/evaluating/5041779.html (accessed on 17 August 2021).
- He, L.; He, C.; Reynolds, T.L.; Bai, Q.; Huang, Y.; Li, C.; Zheng, K.; Chen, Y. Why do people oppose mask wearing? A comprehensive analysis of U.S. tweets during the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2021, 28, 1564–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Dong, J.; Zhang, Y.; He, Z.; Shi, L.; Cai, Y. A content analysis of e-cigarette related calls to the Shanghai health hotline, for the period 2014–2019. Tob. Induc. Dis. 2021, 19, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teasdale, E.; Clarke, H.; Chen, N.; Everitt, H. Online forum users’ views and experiences of managing irritable bowel syndrome: A qualitative analysis of discussion content. BJGP Open 2020, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivlighan, I.D.M.; Adams, M.C.; Deng, K.; Ye, X.; Menninga, E.J. A Social Network Analysis of International Collaboration in Counseling Psychology. Couns. Psychol. 2018, 46, 274–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getchell, M.C.; Sellnow, T.L. A network analysis of official Twitter accounts during the West Virginia water crisis. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 54, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- File, K.; Valente, T.; McLaws, M.-L. Hygiene and Health: Who Do Mothers in Vanuatu Communicate with about Health? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J. Overall Network Analysis Lecture: UCINET Software Practical Guide; Shanghai People’s Publishing House: Shanghai, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Xu, X. Analysis of Network Structure and Doctor Behaviors in E-Health Communities from a Social-Capital Perspective. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burt, R.S.; Kilduff, M.; Tasselli, S. Social Network Analysis: Foundations and Frontiers on Advantage. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2013, 64, 527–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulgar, J.; Candia, C.; Leonardi, P.M. Social networks and academic performance in physics: Undergraduate cooperation enhances ill-structured problem elaboration and inhibits well-structured problem solving. Phys. Rev. Phys. Educ. Res. 2020, 16, 010137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grodzinski, N.; Grodzinski, B.; Davies, B.M. Can co-authorship networks be used to predict author research impact? A machine-learning based analysis within the field of degenerative cervical myelopathy research. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yie, K.-Y.; Chien, T.-W.; Chen, C.-H.; Yeh, Y.-T.; Lin, J.-C.J.; Lai, F.-J. Suitability of h- and x-indices for evaluating authors’ individual research achievements in a given short period of years. Medicine 2021, 100, e25016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Yang, C.C. Ranking User Influence in Healthcare Social Media. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2012, 3, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.; Shim, H.; Kim, J.; Lee, C.; Lee, D. The effects of popularity metrics in news comments on the formation of public opinion: Evidence from an internet portal site. Soc. Sci. J. 2020, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wu, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J. Efficient Information Dissemination in Dynamic Networks. In Proceedings of the 2013 42nd International Conference on Parallel Processing, Lyon, France, 1–4 October 2013; pp. 603–610. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Lv, G.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Chen, E.; Qiao, L. Understanding the mechanism of social tie in the propagation process of social network with communication channel. Front. Comput. Sci. 2019, 13, 1296–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, S.; Babu, L.D.D. Interest aware influential information disseminators in social networks. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, S.; Hossain, L.; Crawford, J.W.; Bossomaier, T. Quantifying Network Dynamics and Information Flow Across Chinese Social Media During the African Ebola Outbreak. Disaster Med. Public Health Prep. 2018, 12, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO Director-General’s Opening Remarks at the Media Briefing on COVID-19—13 March 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-remarks-at-the-mission-briefing-on-covid-19---13-march-2020 (accessed on 13 March 2020).
- Guedes Farias, M.G.; de Andrade Maia, F.C. Proposition of Scientific Observatory for Popularization of Science. Inf. Soc. Estud. 2020, 30, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, S.; Ren, J.; Li, C. The dynamic evolution of social ties and user-generated content: A case study on a Douban group. Enterp. Inf. Syst. 2016, 11, 1462–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.L. Research on Network Structure Optimization of Shared Medical Stakeholders. Ph.D. Thesis, Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rushmore, J.; Caillaud, D.; Matamba, L.; Stumpf, R.M.; Borgatti, S.P.; Altizer, S. Social network analysis of wild chimpanzees provides insights for predicting infectious disease risk. J. Anim. Ecol. 2013, 82, 976–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercellone-Smith, P.; Jablokow, K.; Friedel, C. Characterizing communication networks in a web-based classroom: Cognitive styles and linguistic behavior of self-organizing groups in online discussions. Comput. Educ. 2012, 59, 222–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lwin, M.O.; Lu, J.; Sheldenkar, A.; Schulz, P.J.; Shin, W.; Gupta, R.; Yang, Y. Global Sentiments Surrounding the COVID-19 Pandemic on Twitter: Analysis of Twitter Trends. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2020, 6, e19447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, J.; Luo, X.; Wu, X.; Bao, H. Dynamic Evolution of Public’s Positive Emotions and Risk Perception for the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Case Study of Hubei Province of China. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Zheng, B.; Agostini, M.; Bélanger, J.J.; Gützkow, B.; Kreienkamp, J.; Reitsema, A.M.; van Breen, J.A.; PsyCorona Collaboration; Leander, N.P. Associations of risk perception of COVID-19 with emotion and mental health during the pandemic. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 284, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bruin, Y.B.; Lequarre, A.-S.; McCourt, J.; Clevestig, P.; Pigazzani, F.; Jeddi, M.Z.; Colosio, C.; Goulart, M. Initial impacts of global risk mitigation measures taken during the combatting of the COVID-19 pandemic. Saf. Sci. 2020, 128, 104773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chena, Q.; Min, C.; Zhangd, W.; Wange, G.; Maa, X.; Evansf, R. Unpacking the black box: How to promote citizen engagement through government social media during the COVID-19 crisis. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2020, 110, 106380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, M.; Zhu, Y.-C. Does government information release really matter in regulating contagion-evolution of negative emotion during public emergencies? From the perspective of cognitive big data analytics. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 50, 498–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Node | Answers | Questions | Articles | Ideas | Approvals | Likes | Favorites | Followed | Followers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 187 | 775 | 7 | 311 | 1064 | 4,427,729 | 876,161 | 3,371,310 | 308 | 2,961,288 |
| 117 | 3653 | 0 | 1212 | 642 | 7,632,933 | 944,971 | 2,205,389 | 127 | 2,776,704 |
| 17 | 214 | 8 | 22 | 32 | 498,041 | 317,217 | 925,781 | 905 | 89,391 |
| 129 | 14,243 | 0 | 830 | 982 | 3,491,598 | 365,752 | 921,719 | 38 | 264,810 |
| 173 | 1854 | 2 | 428 | 61 | 6,303,481 | 492,862 | 854,182 | 254 | 1,641,516 |
| 169 | 1508 | 6 | 40 | 949 | 5,476,721 | 535,175 | 840,646 | 79 | 799,315 |
| 201 | 249 | 0 | 455 | 0 | 2,183,119 | 240,481 | 806,312 | 19 | 298,173 |
| 212 | 2050 | 1 | 282 | 137 | 2,214,365 | 342,510 | 792,615 | 13 | 1,401,030 |
| 179 | 1897 | 297 | 1661 | 4758 | 999,646 | 164,500 | 665,398 | 1385 | 1,311,450 |
| 35 | 10,388 | 1390 | 160 | 2089 | 2,843,875 | 374,544 | 601,155 | 242 | 2,167,282 |
| 126 | 11,203 | 17 | 27 | 2603 | 3,375,730 | 35,792 | 584,300 | 257 | 304,892 |
| 186 | 163 | 0 | 86 | 12 | 759,608 | 132,906 | 533,675 | 552 | 334,760 |
| 54 | 1572 | 153 | 147 | 964 | 2,895,881 | 325,269 | 481,453 | 1141 | 1,016,351 |
| 13 | 751 | 8 | 47 | 1253 | 1,101,697 | 159,888 | 480,228 | 582 | 412,234 |
| 182 | 911 | 5 | 6 | 40 | 1,223,316 | 206,001 | 415,743 | 139 | 194,479 |
| 92 | 2400 | 1 | 25 | 13 | 1,155,062 | 163,414 | 399,878 | 44 | 198,812 |
| 174 | 829 | 4 | 18 | 33 | 929,442 | 157,933 | 374,313 | 118 | 403,985 |
| 63 | 447 | 17 | 333 | 514 | 2,536,188 | 172,221 | 374,150 | 193 | 949,990 |
| 68 | 741 | 19 | 40 | 721 | 916,109 | 122,278 | 365,038 | 273 | 513,848 |
| 58 | 252 | 0 | 31 | 137 | 770,716 | 123,994 | 345,119 | 95 | 875,600 |
| Node | Freeman’s Degree | Freeman’s Betweenness | Closeness | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Out-Degree | In-Degree | Out-Closeness | In-Closeness | ||
| 4 | 32 | 25 | 931.471 | 1.141 | 42.442 |
| 7 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 1.153 | 0.455 |
| 14 | 40 | 27 | 1329.821 | 1.142 | 38.830 |
| 19 | 22 | 0 | 0 | 1.153 | 0.455 |
| 27 | 16 | 61 | 2250.844 | 1.140 | 48.667 |
| 29 | 19 | 39 | 1008.740 | 1.139 | 46.300 |
| 35 | 6 | 47 | 659.184 | 1.135 | 44.785 |
| 39 | 28 | 34 | 1100.431 | 1.141 | 44.603 |
| 40 | 39 | 9 | 735.769 | 1.142 | 37.694 |
| 44 | 52 | 0 | 0 | 1.183 | 0.455 |
| 53 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1.166 | 0.455 |
| 54 | 38 | 59 | 3147.564 | 1.142 | 50.345 |
| 58 | 2 | 73 | 941.889 | 1.131 | 53.545 |
| 63 | 15 | 60 | 2071.452 | 1.138 | 48.026 |
| 79 | 32 | 15 | 552.177 | 1.141 | 37.889 |
| 110 | 37 | 7 | 573.174 | 1.142 | 34.488 |
| 117 | 4 | 68 | 1182.808 | 1.135 | 51.529 |
| 139 | 12 | 47 | 785.077 | 1.137 | 48.451 |
| 140 | 59 | 45 | 4782.494 | 1.143 | 47.198 |
| 147 | 15 | 41 | 1439.679 | 1.138 | 46.300 |
| 148 | 18 | 28 | 889.609 | 1.139 | 45.436 |
| 152 | 14 | 21 | 1055.198 | 1.139 | 38.693 |
| 166 | 37 | 27 | 2035.962 | 1.142 | 41.243 |
| 169 | 7 | 56 | 1146.631 | 1.138 | 46.695 |
| 173 | 10 | 45 | 758.197 | 1.137 | 45.342 |
| 174 | 1 | 41 | 408.984 | 1.123 | 47.505 |
| 183 | 29 | 0 | 0 | 1.154 | 0.455 |
| 186 | 30 | 17 | 440.518 | 1.141 | 38.153 |
| 187 | 21 | 59 | 1391.886 | 1.139 | 49.213 |
| 215 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1.162 | 0.455 |
| 220 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 1.174 | 0.455 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, R.; Zhao, L. Analysis of the Evolution of User Emotion and Opinion Leaders’ Information Dissemination Behavior in the Knowledge Q&A Community during COVID-19. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12252. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182212252
Xu X, Li Z, Wang R, Zhao L. Analysis of the Evolution of User Emotion and Opinion Leaders’ Information Dissemination Behavior in the Knowledge Q&A Community during COVID-19. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(22):12252. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182212252
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Xu, Zhigang Li, Rui Wang, and Li Zhao. 2021. "Analysis of the Evolution of User Emotion and Opinion Leaders’ Information Dissemination Behavior in the Knowledge Q&A Community during COVID-19" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 22: 12252. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182212252
APA StyleXu, X., Li, Z., Wang, R., & Zhao, L. (2021). Analysis of the Evolution of User Emotion and Opinion Leaders’ Information Dissemination Behavior in the Knowledge Q&A Community during COVID-19. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(22), 12252. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182212252





