Electric and Manual Oral Hygiene Routines Affect Plaque Index Score Differently
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
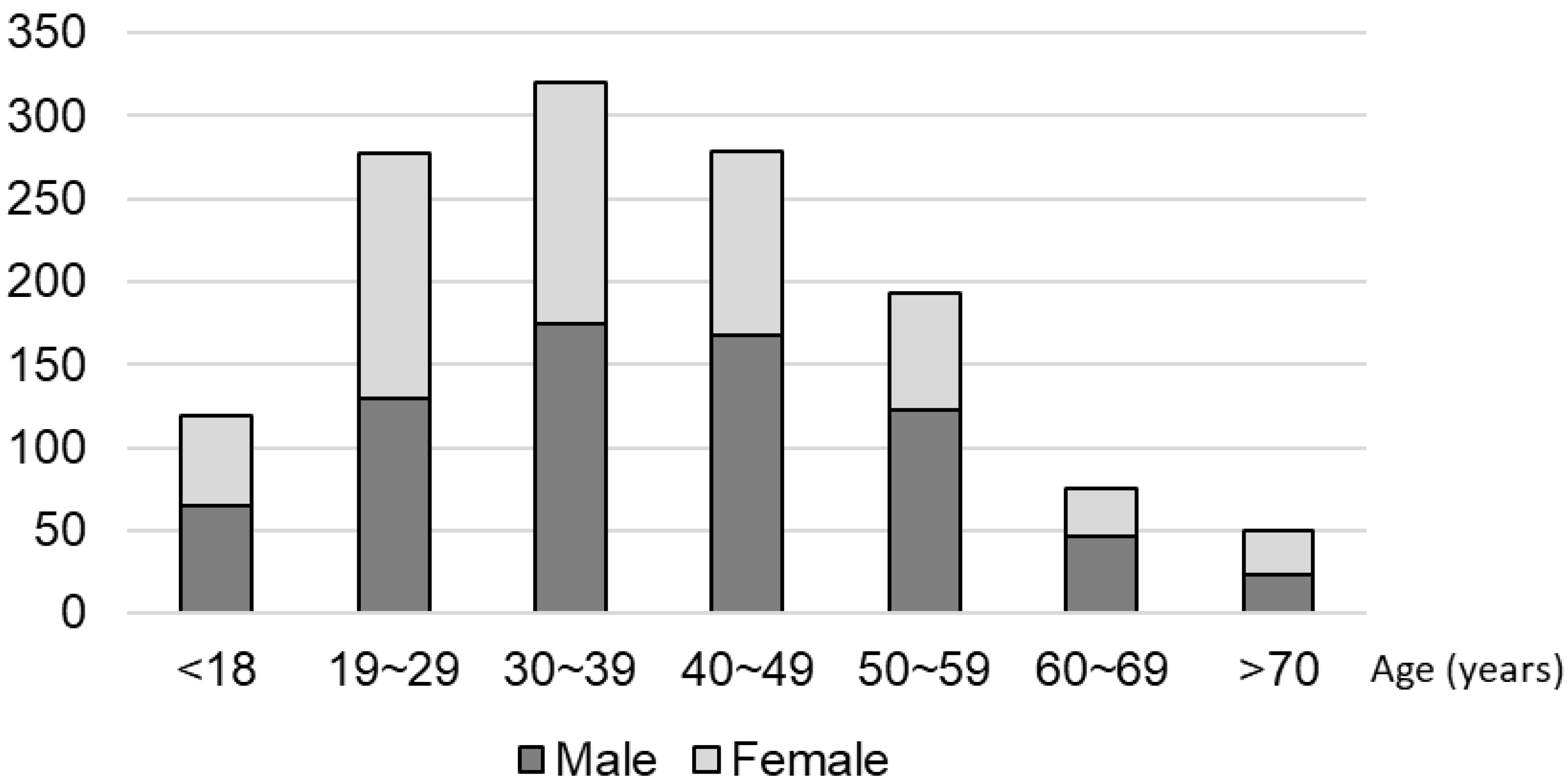
2.1. Participants
2.2. Survey
2.3. Status of Dental Treatment
2.4. Plaque Index Score (PIS)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Oral Hygiene Routines for All Participants
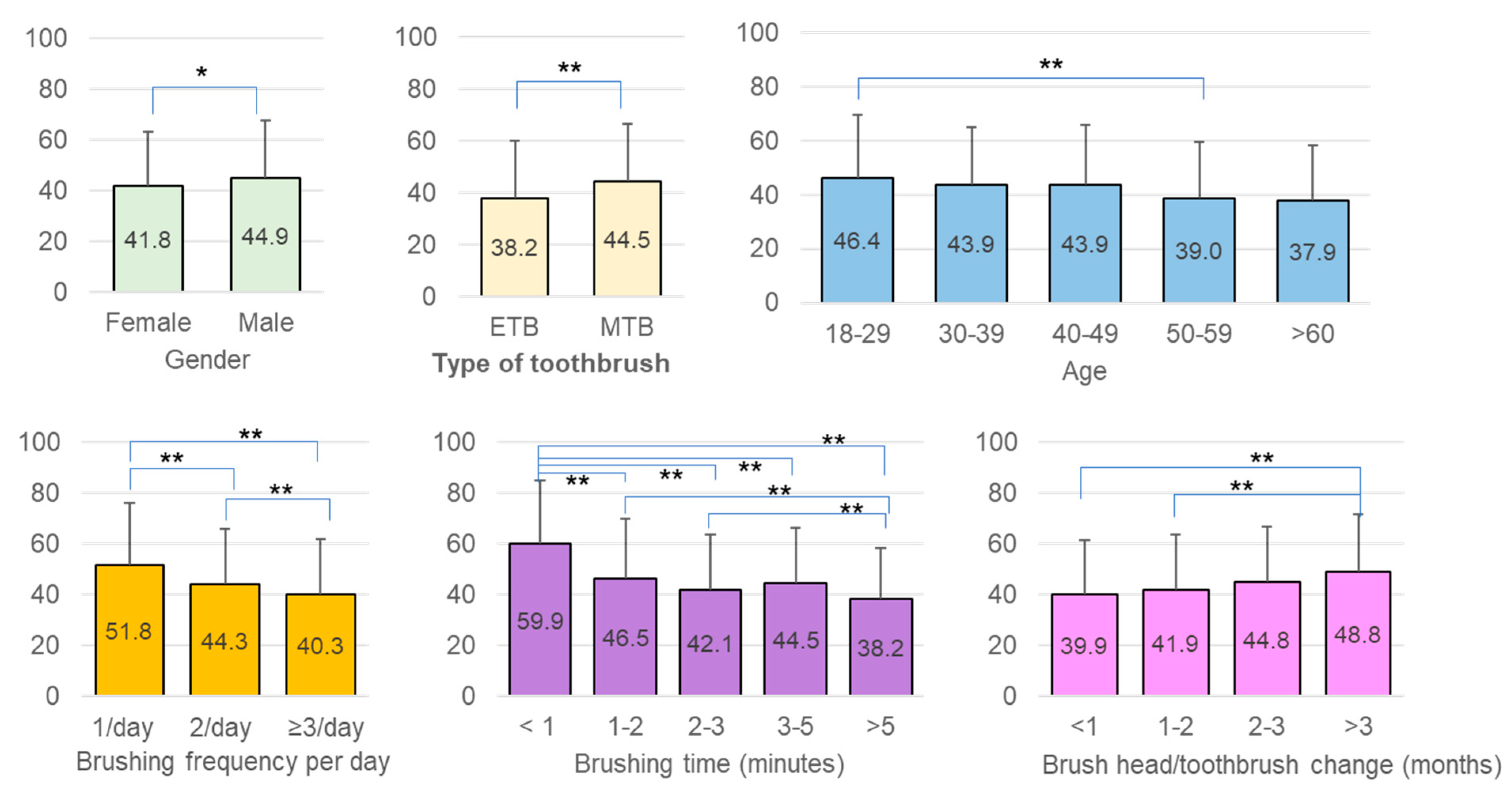
3.2. Factors Affecting Overall Oral Hygiene Behaviors
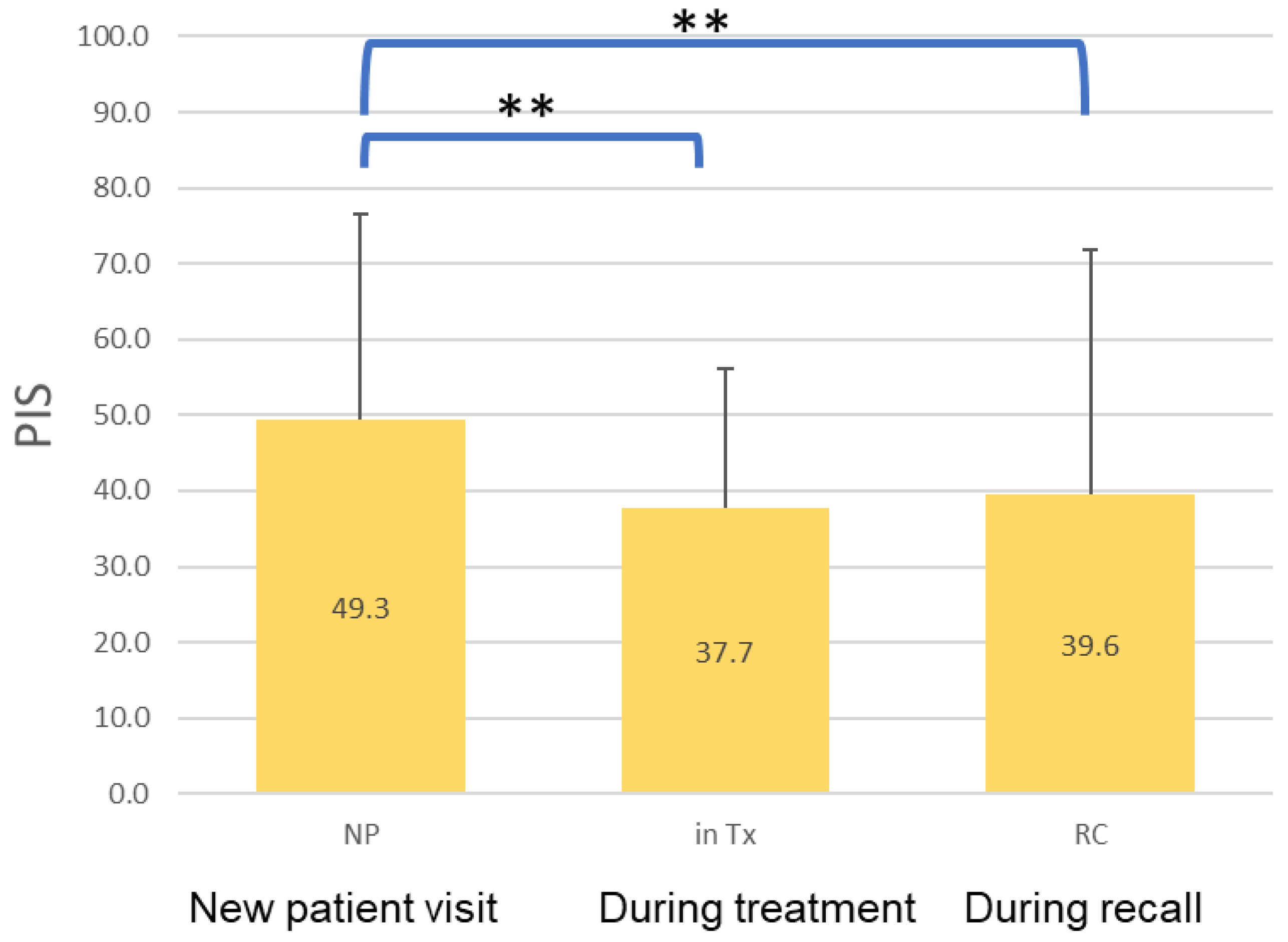
3.3. Association among PIS, Oral Hygiene Behaviors, and Status of Dental Treatment
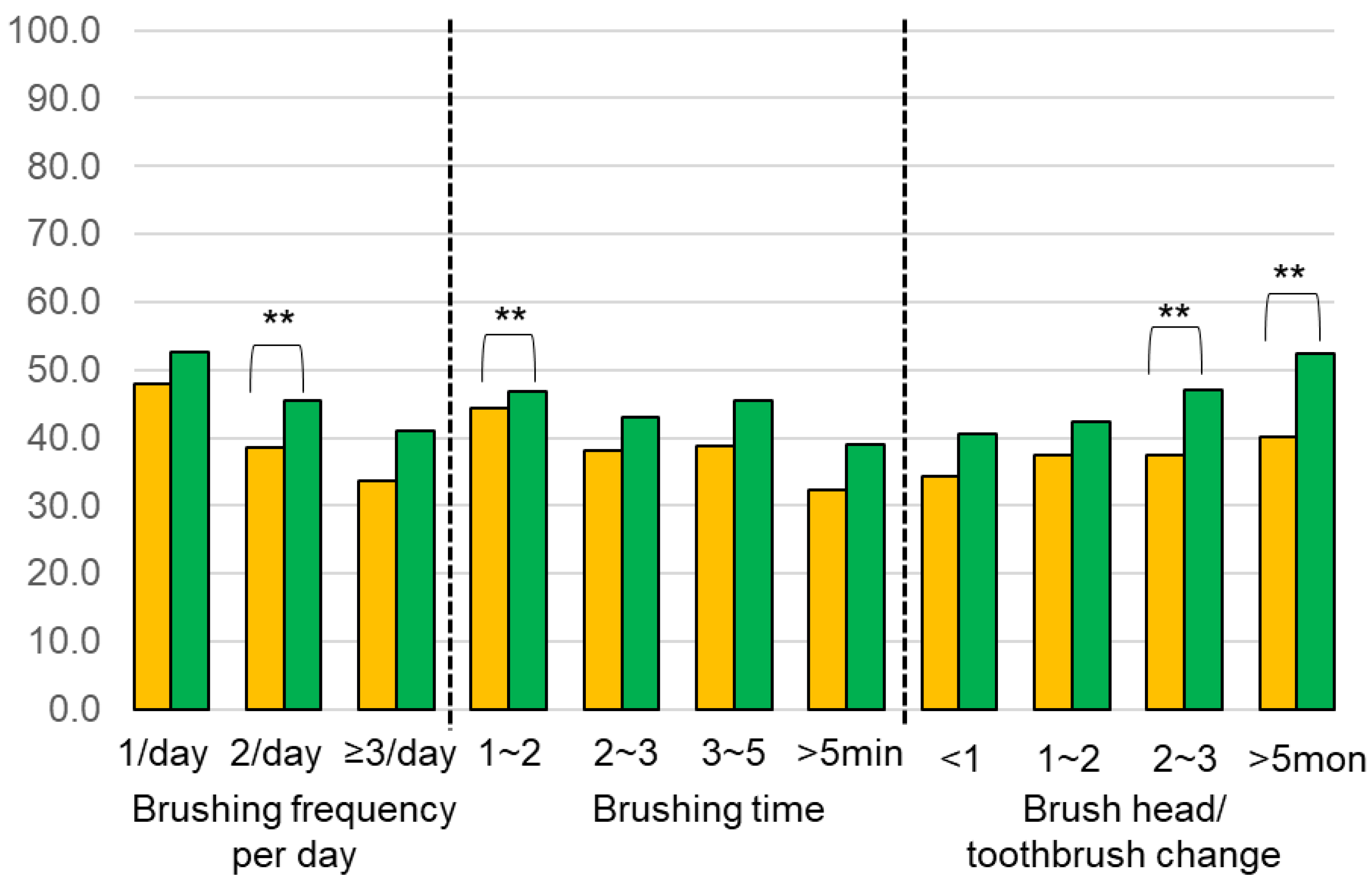
3.4. Differences between the Manual (MTB) and Electric Toothbrush (ETB)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seneviratne, C.J.; Zhang, C.F.; Samaranayake, L.P. Dental plaque biofilm in oral health and disease. Chin. J. Dent. Res. Off. J. Sci. Sect. Chin. Stomatol. Assoc. (CSA) 2011, 14, 87–94. [Google Scholar]
- Marsh, P.D. Dental plaque as a biofilm and a microbial community—Implications for health and disease. BMC Oral Health 2006, 6 (Suppl. S1), S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- White, D.A.; Tsakos, G.; Pitts, N.B.; Fuller, E.; Douglas, G.V.A.; Murray, J.J.; Steele, J.G. Adult Dental Health Survey 2009: Common oral health conditions and their impact on the population. Br. Dent. J. 2012, 213, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demmer, R.T.; Papapanou, P.N.; Jacobs, D.R.; Desvarieux, M. Bleeding on probing differentially relates to bacterial profiles: The Oral Infections and Vascular Disease Epidemiology Study. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2008, 35, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugoson, A.; Norderyd, O.; Slotte, C.; Thorstensson, H. Oral hygiene and gingivitis in a Swedish adult population 1973, 1983 and 1993. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1998, 25, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loe, H.; Theilade, E.; Jensen, S.B. Experimental gingivitis in man. J. Periodontol. 1965, 36, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, P.D.; Moter, A.; Devine, D.A. Dental plaque biofilms: Communities, conflict and control. Periodontology 2000 2011, 55, 16–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, N.P.; Schätzle, M.A.; Löe, H. Gingivitis as a risk factor in periodontal disease. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2009, 36 (Suppl. S10), 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Weijden, F.; Slot, D.E. Oral hygiene in the prevention of periodontal diseases: The evidence. Periodontology 2000 2011, 55, 104–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westfelt, E. Rationale of mechanical plaque control. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1996, 23, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khocht, A.; Spindel, L.; Person, P. A comparative clinical study of the safety and efficacy of three toothbrushes. J. Periodontol. 1992, 63, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Comprehensive History of Dentistry and Dental Care. Available online: https://www.thoughtco.com/history-of-dentistry-and-dental-care-1991569#brushpaste (accessed on 29 November 2021).
- Erbe, C.; Klees, V.; Ferrari-Peron, P.; Ccahuana-Vasquez, R.A.; Timm, H.; Grender, J.; Cunningham, P.; Adam, R.; Farrell, S.; Wehrbein, H. A comparative assessment of plaque removal and toothbrushing compliance between a manual and an interactive power toothbrush among adolescents: A single-center, single-blind randomized controlled trial. BMC Oral Health 2018, 18, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erbe, C.; Klees, V.; Braunbeck, F.; Ferrari-Peron, P.; Ccahuana-Vasquez, R.A.; Timm, H.; Grender, J.; Cunningham, P.; Adam, R.; Wehrbein, H. Comparative assessment of plaque removal and motivation between a manual toothbrush and an interactive power toothbrush in adolescents with fixed orthodontic appliances: A single-center, examiner-blind randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2019, 155, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grossman, E.; Proskin, H. A comparison of the efficacy and safety of an electric and a manual children’s toothbrush. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 1997, 128, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vandana, K.L.; Tatuskar, P.V.; Valavalkar, N.N. A comparative evaluation of manual and powered brushing on oral health and microbial status of mentally challenged individuals. J. Indian Soc. Periodontol. 2020, 24, 362–368. [Google Scholar]
- Elkerbout, T.A.; Slot, D.E.; Rosema, N.A.M.; Van der Weijden, G.A. How effective is a powered toothbrush as compared to a manual toothbrush? A systematic review and meta-analysis of single brushing exercises. Int. J. Dent. Hyg. 2020, 18, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosema, N.; Slot, D.E.; van Palenstein Helderman, W.H.; Wiggelinkhuizen, L.; Van der Weijden, G.A. The efficacy of powered toothbrushes following a brushing exercise: A systematic review. Int. J. Dent. Hyg. 2016, 14, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Liang, W.; Liu, X.; Xian, J.; Xie, H. Comparison of the effectiveness between power toothbrushes and manual toothbrushes for oral health: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2020, 78, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaacob, M.; Worthington, H.V.; Deacon, S.A.; Deery, C.; Walmsley, A.D.; Robinson, P.G.; Glenny, A.-M. Powered versus manual toothbrushing for oral health. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 2014, CD002281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strippoli, G.F.; Palmer, S.C.; Ruospo, M.; Natale, P.; Saglimbene, V.; Craig, J.C.; Pellegrini, F.; Petruzzi, M.; De Benedittis, M.; Ford, P.; et al. Oral disease in adults treated with hemodialysis: Prevalence, predictors, and association with mortality and adverse cardiovascular events: The rationale and design of the ORAL Diseases in hemodialysis (ORAL-D) study, a prospective, multinational, longitudinal, observational, cohort study. BMC Nephrol. 2013, 14, 90. [Google Scholar]
- Skorupka, W.; Zurek, K.; Kokot, T.; Nowakowska-Zajdel, E.; Fatyga, E.; Niedworok, E.; Muc-Wierzgon, M. Assessment of oral hygiene in adults. Cent. Eur. J. Public Health 2012, 20, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, L.; Petersen, P.E.; Wang, H.Y.; Bian, J.Y.; Zhang, B.X. Oral health knowledge, attitudes and behaviour of adults in China. Int. Dent. J. 2005, 55, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O′Leary, T.J.; Drake, R.B.; Naylor, J.E. The Plaque Control Record. J. Periodontol. 1972, 43, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Market, Research, ASMARQ. Available online: https://www.asmarq.co.jp/global/ (accessed on 29 November 2021).
- Creeth, J.E.; Gallagher, A.; Sowinski, J.; Bowman, J.; Barrett, K.; Lowe, S.; Patel, K.; Bosma, M.L. The effect of brushing time and dentifrice on dental plaque removal in vivo. J. Dent. Hyg. 2009, 83, 111–116. [Google Scholar]
- Gallob, J.; Mateo, L.R.; Chaknis, P.; Morrison, B.M.; Panagakos, F. Randomized controlled trial comparing a powered toothbrush with distinct multi-directional cleaning action to a manual flat trim toothbrush. Am. J. Dent. 2015, 28, 351–356. [Google Scholar]
- Ghassemi, A.; Vorwerk, L.; Hooper, W.; Patel, V.; Milleman, J.L.; Milleman, K.R. Comparative plaque removal efficacy of two new powered toothbrushes and a manual toothbrush. J. Clin. Dent. 2014, 25, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Klukowska, M.; Grender, J.M.; Timm, H. A single-brushing study to compare plaque removal efficacy of a new power brush to an ADA reference manual toothbrush. Am. J. Dent. 2012, 25 Spec No A(A), 10A–13A. [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni, P.; Singh, D.K.; Jalaluddin, M. Comparison of Efficacy of Manual and Powered Toothbrushes in Plaque Control and Gingival Inflammation: A Clinical Study among the Population of East Indian Region. J. Int. Soc. Prev. Community Dent. 2017, 7, 168–174. [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz, B.; Reise, M.; Klukowska, M.; Grender, J.M.; Timm, H.; Sigusch, B.W. A randomized clinical trial comparing plaque removal efficacy of an oscillating-rotating power toothbrush to a manual toothbrush by multiple examiners. Int. J. Dent. Hyg. 2016, 14, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzo, G.; Licata, M.E.; Pizzo, I.; D’Angelo, M. Plaque removal efficacy of power and manual toothbrushes: A comparative study. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2010, 14, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorwerk, L.; Ghassemi, A.; Hooper, W.; Patel, V.; Milleman, J.; Milleman, K. Comparative Plaque Removal Efficacy of a New Powered Toothbrush and a Manual Toothbrush. J. Clin. Dent. 2016, 27, 76–79. [Google Scholar]
- Graetz, C.; Plaumann, A.; Heinevetter, N.; Sälzer, S.; Bielfeldt, J.; Dörfer, C.E. Bristle splaying and its effect on pre-existing gingival recession-a 12-month randomized controlled trial. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2017, 21, 1989–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Leeuwen, M.P.C.; Van der Weijden, F.A.; Slot, D.E.; Rosema, M.A.M. Toothbrush wear in relation to toothbrushing effectiveness. Int. J. Dent. Hyg. 2019, 17, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van der Weijden, G.A.; Timmerman, M.F.; Nijboer, A.; Lie, M.A.; Van der Velden, U. A comparative study of electric toothbrushes for the effectiveness of plaque removal in relation to toothbrushing duration. Timerstudy. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1993, 20, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, K.; Ferrante, A.; Dockter, K.; Haun, J.; Biesbrock, A.R.; Bartizek, R.D. One- and 3-minute plaque removal by a battery-powered versus a manual toothbrush. J. Periodontol. 2004, 75, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slot, D.E.; Wiggelinkhuizen, L.; Rosema, N.A.M.; Van der Weijden, G.A. The efficacy of manual toothbrushes following a brushing exercise: A systematic review. Int. J. Dent. Hyg. 2012, 10, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheikh-Al-Eslamian, S.M.; Youssefi, N.; Monir, S.E.S.; Kadkhodazadeh, M. Comparison of Manual and Electric Toothbrush in Dental Plaque Removal: A Clinical Trial. Avicenna J. Dent. Res. 2014, 6, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deery, C.; Heanue, M.; Deacon, S.; Robinson, P.G.; Walmsley, A.D.; Worthington, H.; Shaw, W.; Glenny, A.M. The effectiveness of manual versus powered toothbrushes for dental health: A systematic review. J. Dent. 2004, 32, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grender, J.; Williams, K.; Walters, P.; Klukowska, M.; Reick, H. Plaque removal efficacy of oscillating-rotating power toothbrushes: Review of six comparative clinical trials. Am. J. Dent. 2013, 26, 68–74. [Google Scholar]
- McCracken, G.I.; Janssen, J.; Swan, M.; Steen, N.; de Jager, M.; Heasman, P.A. Effect of brushing force and time on plaque removal using a powered toothbrush. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2003, 30, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N.C.; Goyal, C.R.; Qaqish, J.G.; Cugini, M.A.; Thompson, M.C.; Warren, P.R. Single-use plaque removal efficacy of three power toothbrushes. J. Dent. 2005, 33 (Suppl. S1), 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

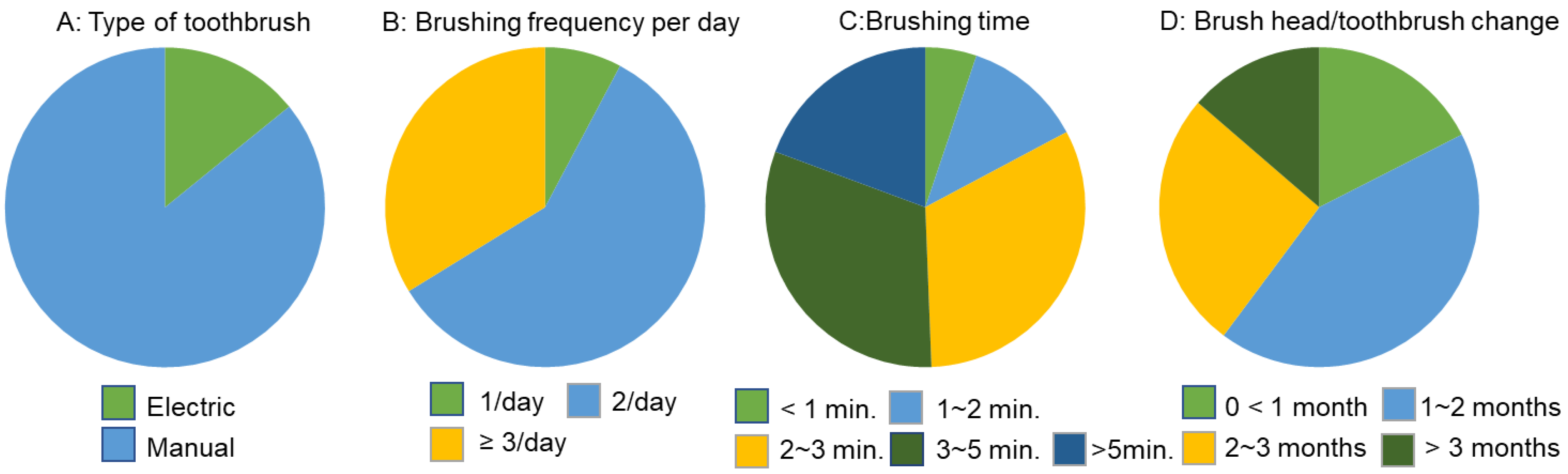

| Type of Toothbrush | Frequency/Day | Brushing Time | Brush Head/Toothbrush Change | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | The chi-square | 26.6906 | 75.7634 | 1.4543 | 14.6999 |
| p value | <0.00001 | <0.00001 | Not significant | <0.01 | |
| Age | The chi-square | 22.7229 | 20.9302 | 79.1158 | 26.373 |
| p value | <0.001 | <0.01 | <0.001 | <0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bahammam, S.; Chen, C.-Y.; Ishida, Y.; Hayashi, A.; Ikeda, Y.; Ishii, H.; Kim, D.M.; Nagai, S. Electric and Manual Oral Hygiene Routines Affect Plaque Index Score Differently. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 13123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182413123
Bahammam S, Chen C-Y, Ishida Y, Hayashi A, Ikeda Y, Ishii H, Kim DM, Nagai S. Electric and Manual Oral Hygiene Routines Affect Plaque Index Score Differently. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(24):13123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182413123
Chicago/Turabian StyleBahammam, Shaima, Chia-Yu Chen, Yoshiki Ishida, Akito Hayashi, Yutaka Ikeda, Hiroaki Ishii, David M. Kim, and Shigemi Nagai. 2021. "Electric and Manual Oral Hygiene Routines Affect Plaque Index Score Differently" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 24: 13123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182413123
APA StyleBahammam, S., Chen, C.-Y., Ishida, Y., Hayashi, A., Ikeda, Y., Ishii, H., Kim, D. M., & Nagai, S. (2021). Electric and Manual Oral Hygiene Routines Affect Plaque Index Score Differently. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(24), 13123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182413123







