Characteristics of and Influencing Factors of Hydrochemistry and Carbon/Nitrogen Variation in the Huangzhouhe River Basin, a World Natural Heritage Site
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
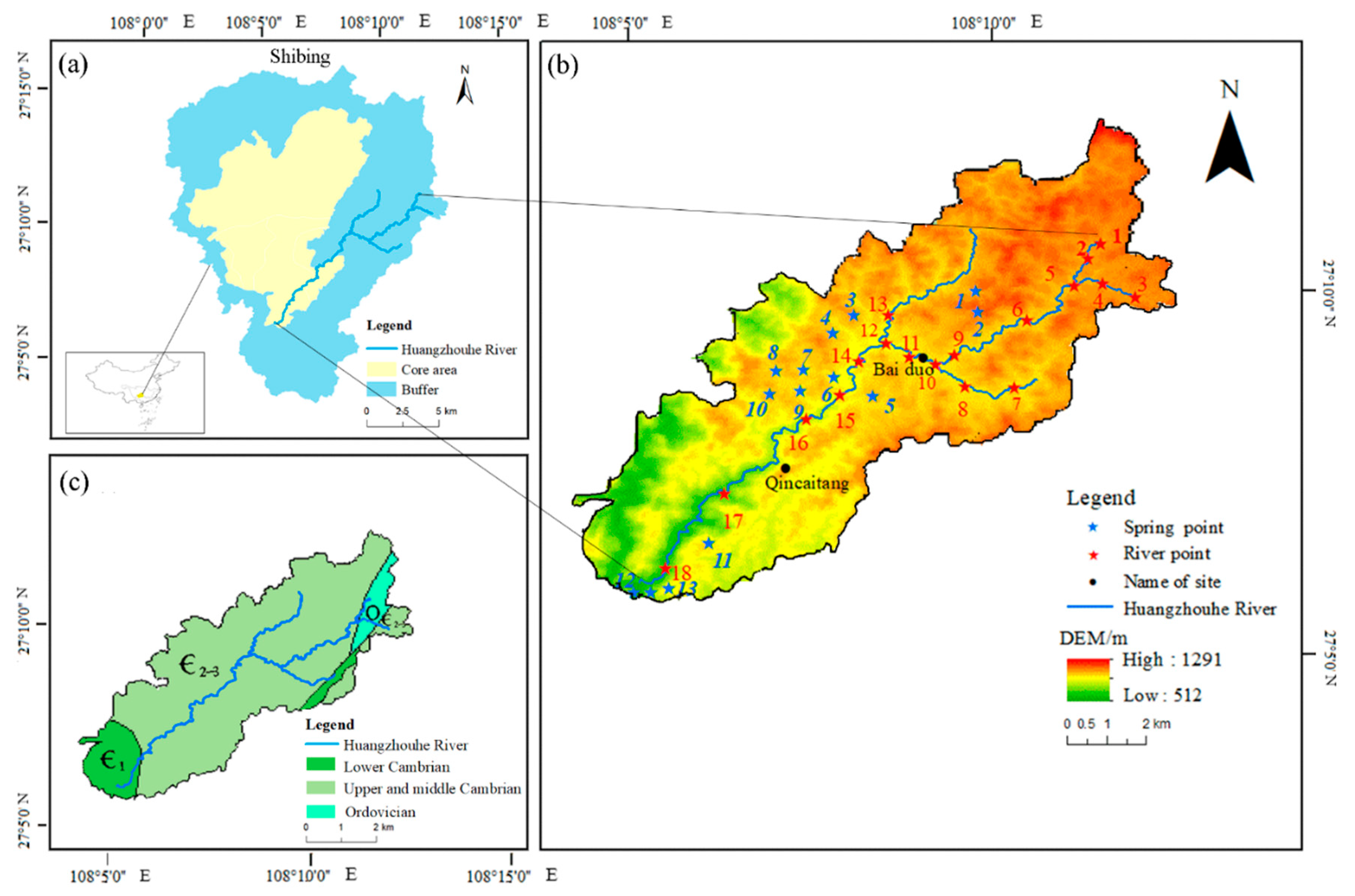
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Water Sampling and Analysis
2.3. Data Processing
3. Results
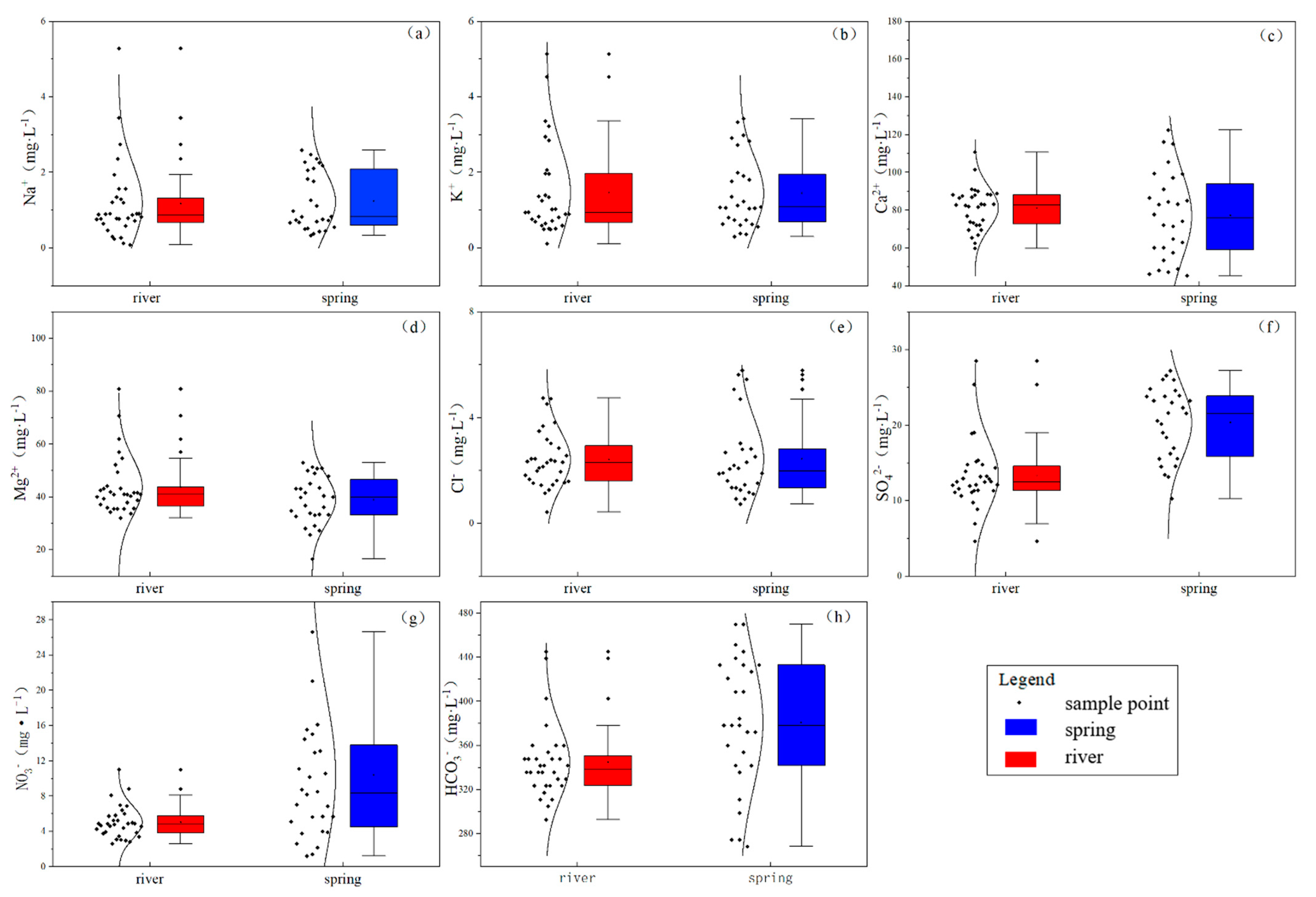
3.1. Physicochemical Parameters and Hydrochemical Type
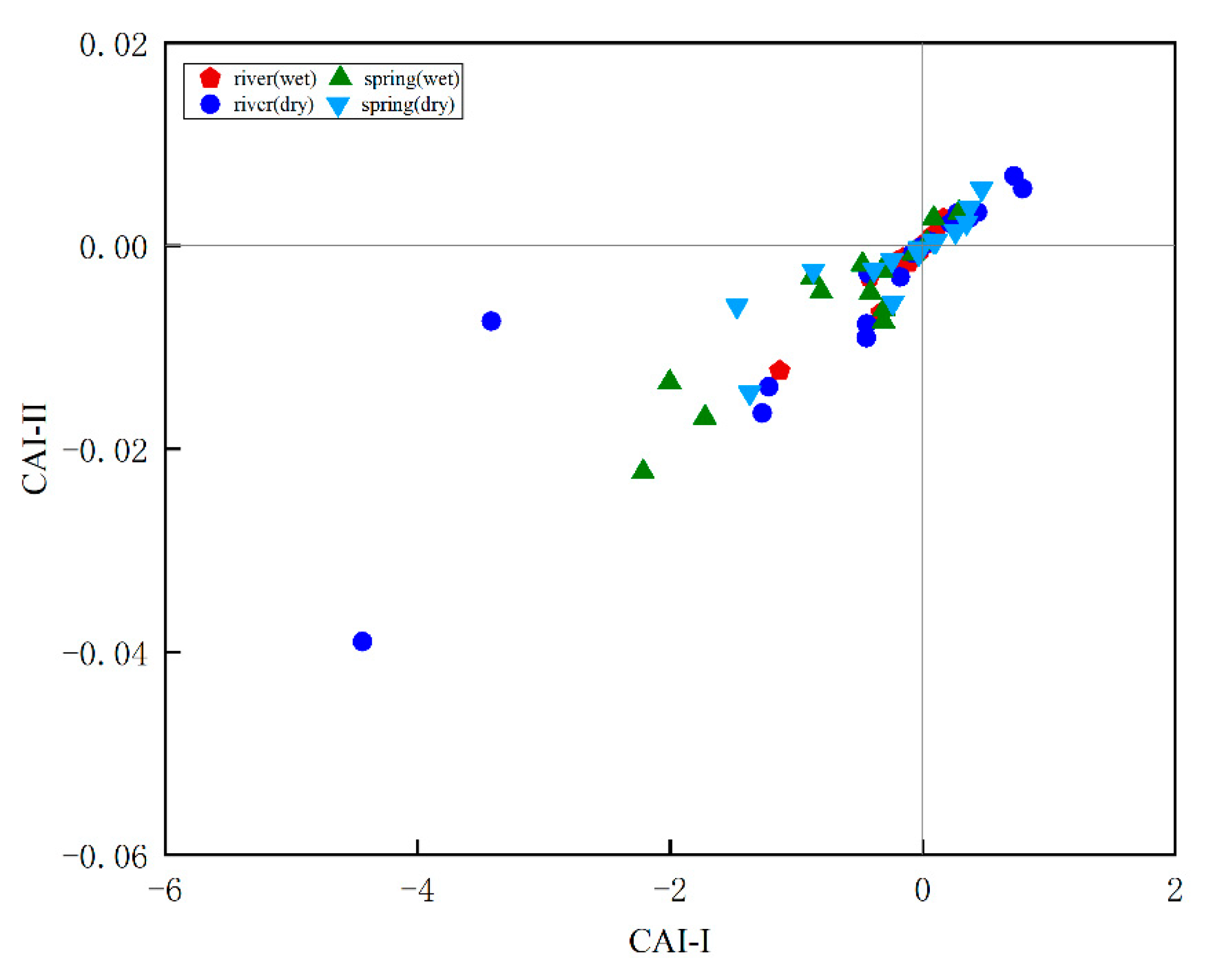
3.2. C and N Types and Distribution
4. Discussion
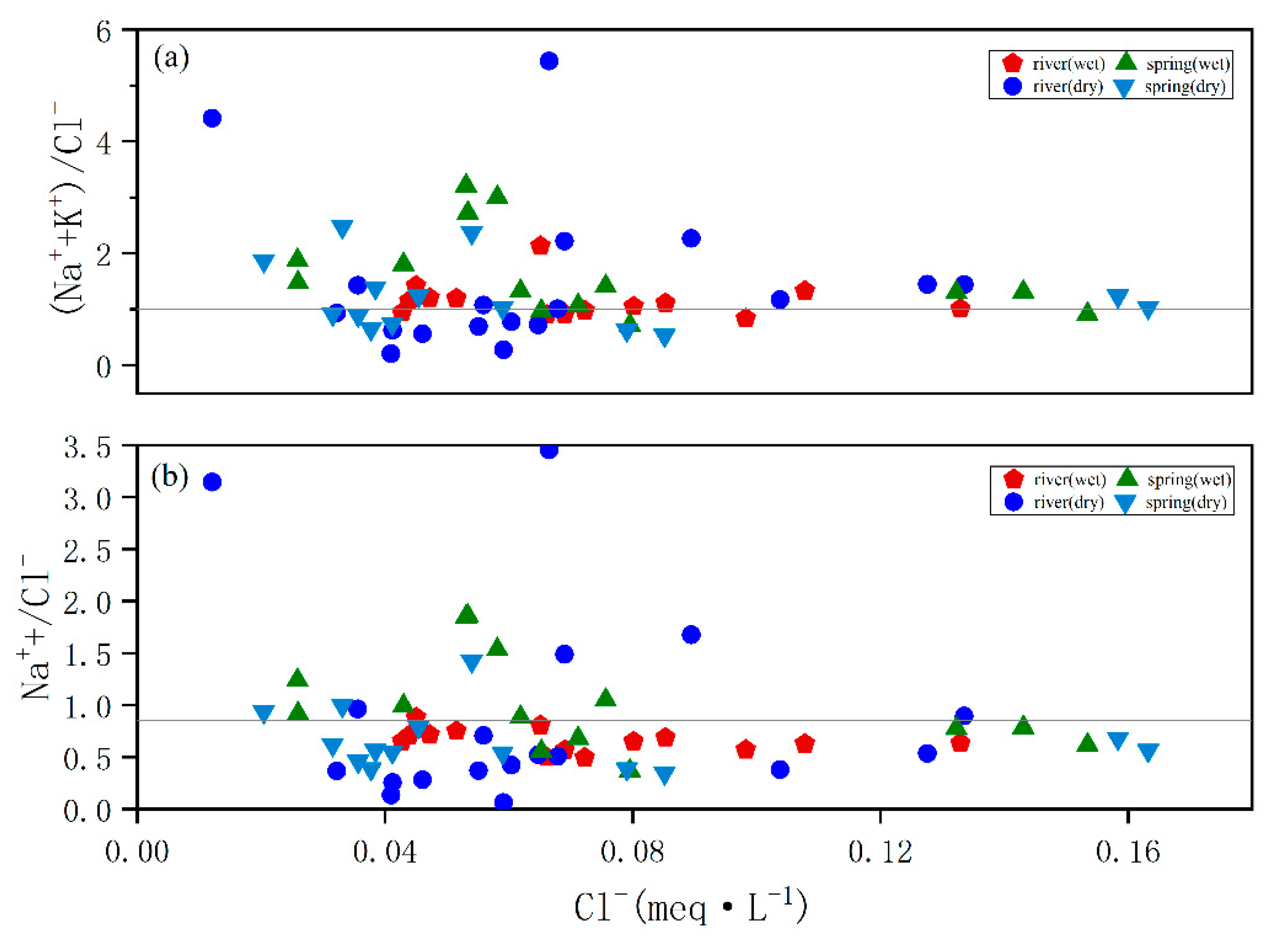
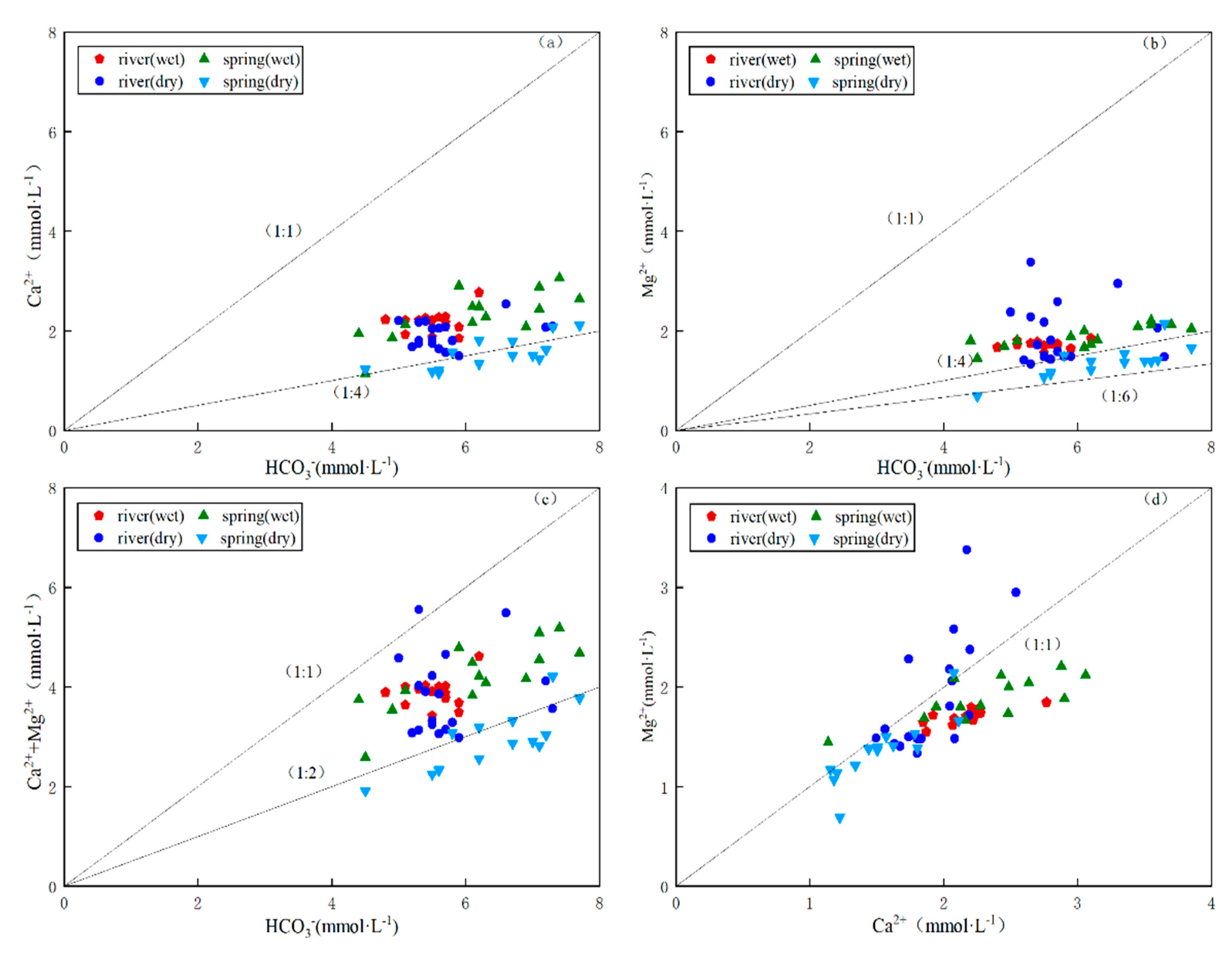
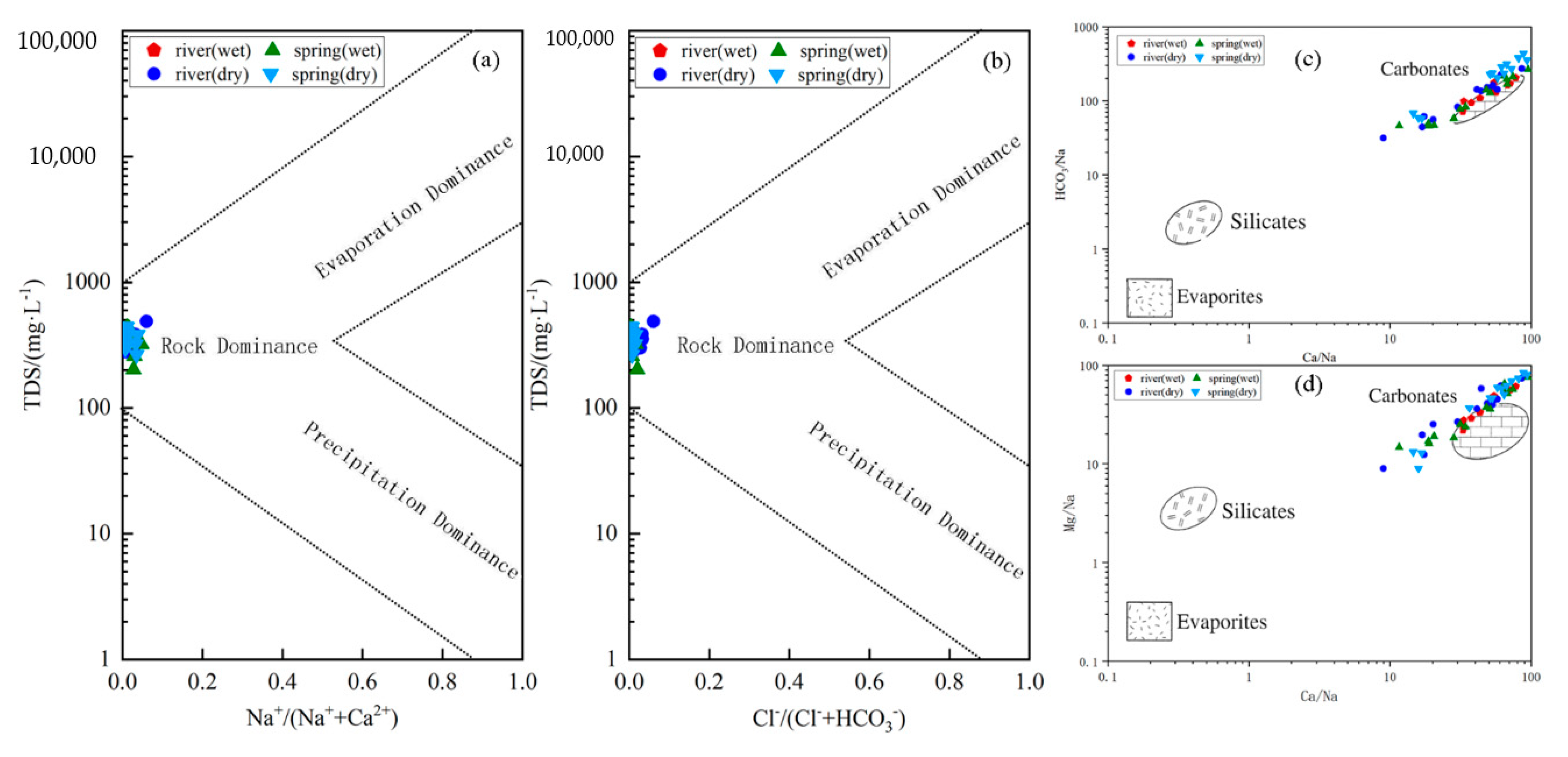
4.1. Analysis of Major Ion Sources
4.2. Water Chemistry Evolutionary Processes
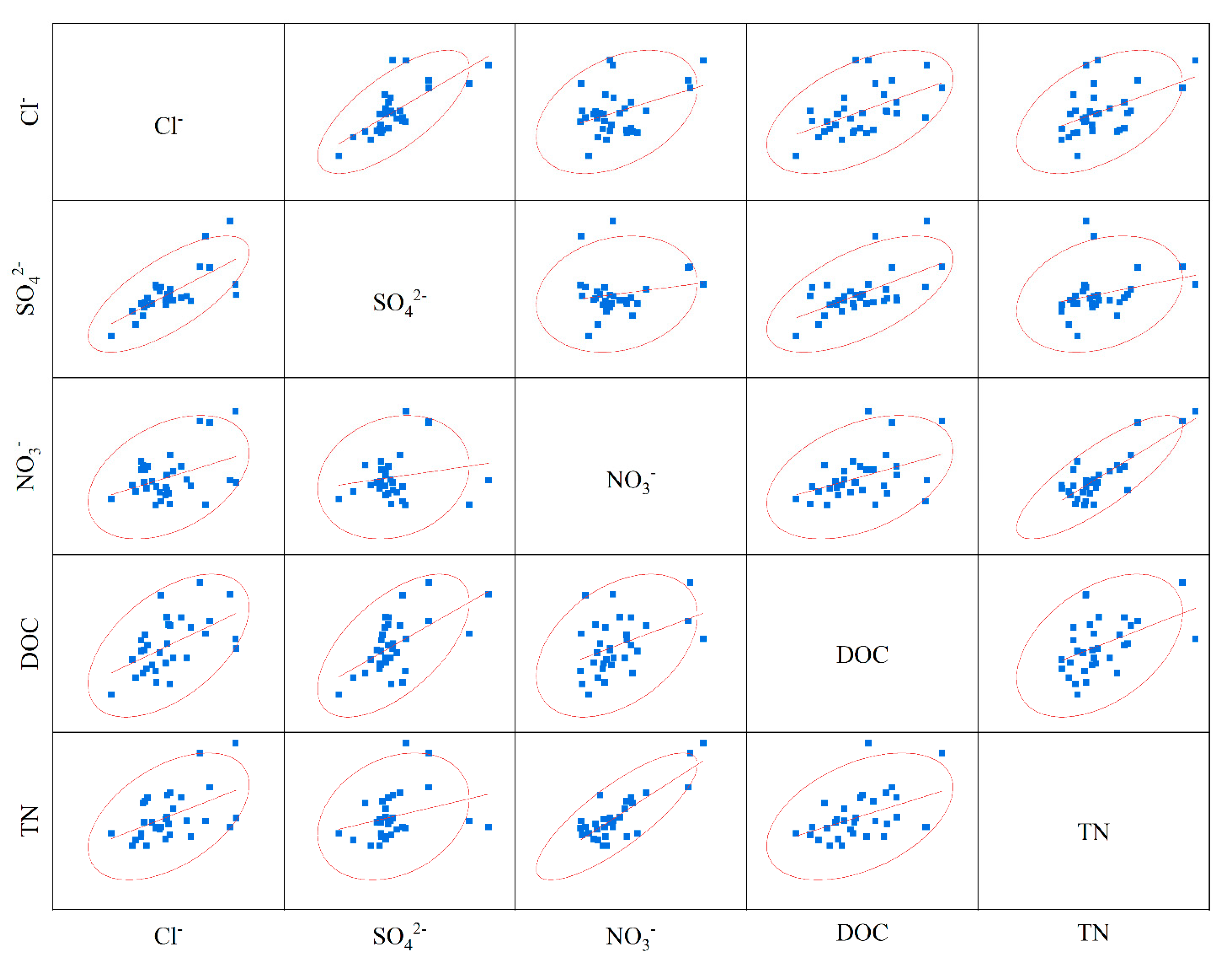
4.3. Impacts of Human Activities on Water Chemistry and Carbon and Nitrogen Contents
4.4. Relationship between C and N
4.5. Water Quality Assessments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- White, A.F.; Blum, A.E. Effects of climate on chemical weathering in watersheds. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 1729–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, J.D.; Gazis, C.; Jacobson, A.D.; Chamberlain, C. Carbonate versus silicate weathering in the Raikhot watershed within the High Himalayan Crystalline Series. Geology 1998, 26, 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, A.J.; Galy, A.; Bickle, M. Tectonic and climatic controls on silicate weathering. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2005, 235, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riebe, C.S.; Kirchner, J.W.; Finkel, R. Erosional and climatic effects on long-term chemical weathering rates ingranitic land-scapes spanning diverse climate regimes. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2004, 224, 547–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillardet, J.; Dupré, B.; Louvat, P.; Allegre, C.J. Global silicate weathering and CO2 consumption rates deduced from the chemistry of large rivers. Chem. Geol. 1999, 159, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipper, E.T.; Galy, A.; Bickle, M.J. Riverine evidence for a fractionated reservoir of Ca and Mg on the continents: Implications for the oceanic Ca cycle. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2006, 247, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, Z.; Ahmad, S. Seasonal Variations of Streams Hydrochemistry and Relationships with Morphometric/Landcover Parameters in the Bhagirathi Watersheds, Garhwal Himalaya, India. J. Geol. Soc. India 2019, 94, 93–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Liu, C. Chemical weathering in the upper reaches of Xijiang River draining the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau, Southwest China. Chem. Geol. 2007, 239, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, C.T.; Whitall, D.; Aber, J.D.; Boyer, E.W.; Castro, M.; Cronan, C.; Goodale, C.L.; Groffman, P.M.; Hopkinson, C.; Lambert, K.; et al. Nitrogen pollution in the northeastern United States: Sources, effects, and management options. Bioscience 2003, 53, 357–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, P.C.; Larson, J.H.; Johnston, C.A.; Young, K.C.; Maurice, P.A.; Lamberti, G.A.; Bridgham, S.D. Landscape predictors of stream dissolved organic matter concentration and physicochemistry in a Lake Superior river watershed. Aquat. Sci. 2006, 68, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neff, J.C.; Chapin III, F.S.; Vitousek, P.M. Breaks in the cycle: Dissolved organic nitrogen in terrestrial ecosystems. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2003, 1, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, D.P.; Hood, R.R. Comparative simulations of dissolved organic matter cycling in idealizedoceanic, astal, and estuarine surface waters. Mar. Syst. 2013, 109, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badr, E.S.A. Spatio-temporal variability of dissolved organic nitrogen (DON), carbon (DOC), and nutrients in the Nile River, Egypt. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 88, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitousek, P.M.; Aber, J.D.; Howarth, R.W.; Likens, G.E.; Matson, P.A.; Schindler, D.W.; Schlesinger, W.H.; Tilman, D.G. Human alteration of the global nitrogen cycle: Sources and consequences. Ecol. Appl. 1997, 7, 737–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eshleman, K.N.; Hemond, H.F. The role of organic acids in the acid-base status of surface waters at Bickford Watershed, Massachusetts. Water Resour. Res. 1985, 21, 1503–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.L.; Campbell, P.G.C. Decreased toxicity of Al to juvenile atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) in acidic soft water containing natural organic matter: A test of the free-ion model. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1997, 16, 1962–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawlor, A.J.; Tipping, E. Metals in bulk deposition and surface waters at two upland locations in northern England. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 121, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCartney, A.G.; Harriman, R.; Watt, A.W.; Moore, D.W.; Taylor, E.M.; Collen, P.; Keay, E.J. Long-term trends in pH, aluminium and dissolved organic carbon in Scottish fresh waters; implications for brown trout(Salmo trutta) survival. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 310, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, J.A.C.; Cronin, A.A.; Dunlop, J.; Kalin, R.M. Influence of carbonates on the riverine carbon cycle in an anthropogenically dominated catchment basin: Evidence from major elements and stable carbon isotopes in the Lagan River (N. Irel). Chem. Geol. 2003, 200, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, J.A.; Larsson, A.; Wallin, M.B.; Nilsson, M.B.; Laudon, H. Twelve years interannual and seasonal variability of stream carbon export from a boreal peatland catchment. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2016, 121, 1851–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomas, G.H.; William, B.; George, R.A.; Justin, S.; Li, F.L.; Collin, S.R.; Philip, C. Climate change and dissolved organic carbon export to the Gulf of Mainecarbon export to the Gulf of Maine. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2016, 121, 2700–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, C.D.; Monteith, D.T.; Cooper, D.M. Long-term increases in surface water dissolved organic carbon: Observations, possible causes and environmental impacts. Environ. Pollut. 2005, 137, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorite-Herrera, M.; Hiscock, K.; Jiménez-Espinosa, R. Distribution of dissolved inorganic and organic nitrogen in river water and groundwater in an agriculturally-dominated catchment, south-East Spain. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2009, 198, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetelat, B.; Liu, C.Q.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Wang, Q.L.; Li, S.L.; Li, J.; Wang, B.L. Geochemistry of the dissolved load of the Changjiang Basin rivers: Anthropogenic impacts and chemical weathering. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 4254–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Qu, X.; Zhang, M.; Yu, Y.; Peng, W.Q. Distinct Bacterial Communities in Wet and Dry Seasons during a Seasonal Water Level Fluctuation in the Largest Freshwater Lake (Poyang Lake) in China. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Li, F.; Tan, Q. Effects of land use on water chemistry in a river draining karst terrain, south west China. Hydrol. Sci. 2014, 59, 1063–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaushal, S.S.; Duan, S.; Doody, T.R.; Haq, S.; Smith, R.M.; Newcomer, T.A.; Delaney, K.; Gorman, J.; Bowman, N.; Mayer, P.M.; et al. Human-accelerated weathering increases salinization, major ions, and alkalinization in fresh water across land use. Appl. Geochem. 2017, 83, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christophe, R.; Fred, T.M.; Leah, M.V. Influence of the human perturbation on carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen biogeochemical cycles in the global coastal ocean. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2001, 65, 3615–3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Lu, X.X.; Sun, H.; Han, J.; Laurence, D. Major ion chemistry and dissolved inorganic carbon cycling in a human-disturbed mountainous river (the Luodingjiang River) of the Zhujiang (Pearl River), China. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 2796–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Bao, H.Y.; Unger, D.; Herbeck, L.S.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Zhang, J.; Jennerjahn, T.C. Biogeochemical behavior of organic carbon in a small tropical river and estuary, Hainan, China. Cont. Shelf Res. 2013, 57, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinka, O.M.; Loiskandl, W.; Ndambuki, J.M. Hydrochemical characterization of various surface water and groundwater resources available in Matahara areas, Fantalle Woreda of Oromiya region. Hydrol Reg Stud. 2015, 3, 444–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dinka, O.M. Hydrochemical composition and origin of surface water and groundwater in the Matahara area, Ethiopia. Inland Waters 2017, 7, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.Z. Chemical Weathering Rate and Karst Carbon Sink of Typical Dolomite Catchment in Subtropical Area: With a Special Reference to Shanmuhe Catchment in Shibing of Guizhou. Ph.D. Thesis, Southwest University, Chongqing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.Q.; Lan, F.N.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.Q.; Liu, P.; Hou, S.T.; Wei, M.J.; Yue, X.F. Hydrochemical characteristics and causes of Nandong karst water system in Yunnan Province. Yangtze River 2021, 52, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, I.D.; Fritz, P. Environmental Isotopes in Hydrogeology; Lewis Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 1–352. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Liu, C.; Ma, Y.; Wang, X.L. Land-based dissolved organic nitrogen dynamics and bioavailability in Jiaozhou Bay, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 220, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.E.; Wang, T.; Lin, Q.Q.; Han, B.P. Spatial pattern and temporal dynamics of limnological variables in Liuxihe Reservoir, Guangdong. J. Lake Sci. 2009, 21, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, B.; Yang, X.; Rioual, P.; Qin, X.; Liu, Z.; Xiong, H.; Yu, J. Hydrogeochemistry of three watersheds (the Erlqis, Zhungarer and Yili) in northern Xinjiang, NW China. Appl. Geochem. 2011, 26, 1535–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.N.; Guo, H.M.; Zhan, Y.H. Groundwater hydrochemical characteristics and processes along flow paths in the North China Plain. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2013, 70–71, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Guerrero, A. Origin and geochemical evolution of groundwater in a closed-basin clayey aquitard, Northern Mexico. J. Hydrol. 2003, 284, 26–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Wu, J.; He, X.; Elumalai, V. Temporal Changes of Groundwater Quality within the Groundwater Depression Cone and Prediction of Confined Groundwater Salinity Using Grey Markov Model in Yinchuan Area of Northwest China. Expo. Health 2020, 12, 447–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeller, H. Les Eaux Souterraines; Masson: Paris, France, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs, R.J. Mechanisms Controlling World Water Chemistry. Science 1970, 170, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y. The contribution of human activities to dissolved inorganic carbon fluxes in a karst underground river system: Evidence from major elements and δ13C-DIC in Nandong, Southwest China. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2013, 152, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.; Huh, Y. Chemical weathering in the Hong (Red) River basin: Rates of silicate weathering and their controlling factors. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2007, 71, 1411–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meybeck, M. Carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus transport by world rivers. Am. J. Sci. 1982, 282, 401–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Q.; Han, G.L.; Liu, M.; Song, C.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y.G.; Liu, J.K. Hydrochemistry and Dissolved Inorganic Carbon (DIC) Cycling in a Tropical Agricultural River, Mun River Basin, Northeast Thailand. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, W.J.; Lee, K.S.; Park, Y.; Lee, D.; Yu, E.J. Tracing anthropogenic DIC in urban streams based on isotopic and geochemical tracers. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 2707–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchman, D.L.; Wheeler, P.A. Uptake of ammonium and nitrate by heterotrophic bacteria and phytoplankton in the sub-Arctic Pacific. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 1998, 45, 347–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middelburg, J.J.; Nieuwenhuize, J. Uptake of dissolved inorganic nitrogen in turbid, tidal estuaries. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 192, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.Y. River Water Environment Quality Monitoring and Health Evaluation Index System Construction in Karst Area. Master’s Thesis, Guizhou Normal University, Guizhou, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Satoh, H.; Okabe, S.; Norimatsu, N.; Watanabe, Y. Significance of Substrate C/N Ratio on structure and activity of nitrifying biofilms determined by in situ hybridization and the use of microelectrodes. J. Jpn. Soc. Water Environ. 2000, 41, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dila, D.K.; Biddanda, B.A. From land to lake: Contrasting microbial processes across a Great Lakes gradient of organic carbon and inorganic nutrient inventories. J. Great Lakes Res. 2015, 41, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, J. The Influence of Biogeochemical Behavior of Aquatic Plants on Karst Carbon Sink. Master’s Thesis, Southwest University, Chongqing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Telmer, K.; Veizer, J. Chemical dynamics of the “St. Lawrence” riverine system:δDH2O, δ18OH2O, δ13CDIC, δ34Ssulfate, and dissolved 87Sr/86Sr. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 851–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.N.; An, S.Q.; Yan, Z.B.; Ren, J.P.; Lu, X.Q.; Ge, F.Y.; Han, W.X. Variation and potential influence factors of foliar pH in land-water ecozones of three small plateau lakes. Plant Ecol. 2021, 14, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitton, B.A.; Potts, M. The Ecology of Cyanobacteria; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 149–194. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.F.; Zhu, W.; Mo, M.X. Effects of submerged macrophytes on pH values and nitrogen removal. Water Resour. Prot. 2008, 24, 64–67. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, L.L.; Shi, X.L.; Wu, X.D.; Li, D.M.; Yu, Y.; Kong, M.F. The effect of cyanobacteria on dissolved organic carbon post the bloom in autumn in Western Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Sci. 2011, 31, 131–136. [Google Scholar]
- Rui, Y.L. Pilot-Scale Study on Denitrification Technology of Shallow Groundwater in the Lakeside of Lake Dianchi. Master’s Thesis, Yunnan University, Kunming, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Redfield, A.C.; Ketchum, B.H.; Richards, F.A. The influence of organisms on the composition of sea-water. Sea 1963, 2, 26–77. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China Standardization Administration. Standards for Drinking Water Quaity (GB5749-2006); Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2007.


| Dry | pH | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | K+ | Na+ | Cl− | NO3− | SO42− | HCO3− | TDS |
| Minimum | 6.98 | 46.15 | 16.56 | 0.11 | 0.08 | 0.43 | 1.20 | 4.63 | 274.50 | 265.60 |
| Maximum | 8.19 | 101.57 | 80.94 | 5.13 | 5.29 | 5.79 | 8.51 | 28.53 | 469.70 | 488.50 |
| Average | 7.46 | 70.25 | 40.12 | 1.40 | 1.10 | 2.27 | 3.68 | 16.19 | 367 | 348.58 |
| SD | 0.29 | 13.69 | 13.30 | 1.26 | 1.11 | 1.31 | 1.99 | 6.05 | 48.71 | 51.01 |
| Wet | pH | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | K+ | Na+ | Cl− | NO3− | SO42− | HCO3− | TDS |
| Minimum | 7.19 | 45.47 | 34.66 | 0.49 | 0.55 | 0.92 | 2.61 | 8.84 | 268.4 | 202.30 |
| Maximum | 8.99 | 122.40 | 52.93 | 3.37 | 2.59 | 5.45 | 26.64 | 26.08 | 469.7 | 440.20 |
| Average | 8.16 | 89.71 | 43.10 | 1.52 | 1.31 | 2.60 | 8.84 | 17.12 | 355.3 | 338.40 |
| SD | 0.48 | 15.54 | 4.40 | 0.87 | 0.62 | 1.20 | 7.67 | 5.44 | 51.53 | 54.69 |
| Parameter | Upper Huangzhouhe | Middle Huangzhouhe | Lower Huangzhouhe | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range | Mean Value | Range | Mean Value | Range | Mean Value | ||
| River (dry) | DOC | 2.46–4.52 | 3.33 | 2.34–3.77 | 2.90 | 2.04–3.54 | 2.79 |
| DIC | 305–445.3 | 351.36 | 317.2–439.2 | 356.85 | 323.3–329.4 | 326.35 | |
| NO3-N | 0.49–0.79 | 0.63 | 0.76–1.19 | 0.92 | 0.64–0.7 | 0.67 | |
| TN | 0.62–1.33 | 0.9 | 1.04–1.91 | 1.26 | 0.89–0.93 | 0.91 | |
| River (wet) | DOC | 2.57–4.81 | 3.38 | 2.82–3.96 | 3.37 | 2.86 | 2.86 |
| DIC | 323.3–378.2 | 347.7 | 311.1–347.7 | 324.83 | 292.87 | 292.8 | |
| NO3-N | 0.85–1.99 | 1.20 | 0.77–1.29 | 1.01 | 0.90 | 0.90 | |
| TN | 1.22–3.23 | 1.89 | 1.29–1.97 | 1.54 | 1.06 | 1.06 | |
| Spring (dry) | DOC | 1.56–1.93 | 1.75 | 1.77–4.85 | 3.09 | 1.48–1.8 | 1.70 |
| DIC | 378.2–433.1 | 405.65 | 335.5–469.7 | 407.16 | 274.5–408.7 | 341.6 | |
| NO3-N | 0.15–1.92 | 1.04 | 0.27–1.4 | 1 | 0.7–0.88 | 0.81 | |
| TN | 0.59–2.99 | 1.44 | 0.62–2.63 | 1.50 | 0.83–1.55 | 1.17 | |
| Spring (wet) | DOC | 1.90–2.33 | 2.11 | 2.11–4.23 | 3.36 | 1.66–1.86 | 1.75 |
| DIC | 420.9–433.1 | 427 | 274.5–469.7 | 390.4 | 268.4–372.1 | 312.63 | |
| NO3-N | 0.59–1.55 | 1.07 | 0.89–6.01 | 3.54 | 1.15–4.75 | 2.43 | |
| TN | 1.84–2.16 | 2 | 1.62–3.78 | 2.97 | 1.99–3.32 | 2.70 | |
| Parameters | T | PH | EC | TDS | DIC | DOC | NO3-N | TN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | 1 | |||||||
| pH | 0.83 ** | 1 | ||||||
| EC | 0.46 * | −0.31 | 1 | |||||
| TDS | −0.17 | −0.32 | 0.36 * | 1 | ||||
| DIC | −0.17 | −0.10 | 0.71 | 0.58 ** | 1 | |||
| DOC | 0.20 | 0.77 | 0.32 | 0.35 * | −0.08 | 1 | ||
| NO3-N | 0.64 ** | 0.33 | 0.61 ** | 0.29 | 0.003 | 0.39 * | 1 | |
| TN | 0.67 ** | 0.42 | 0.56 ** | 0.27 | 0.14 | 0.42 * | 0.96 ** | 1 |
| Parameter | pH | Cl− | NO3−N | SO42− | TDS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard range | 6.5-8.5 | <250 | <10 | <250 | <1000 |
| Water sample | 6.98–8.99 | 0.43–5.79 | 0.15–3.05 | 4.62–28.53 | 202.3–488.5 |
| Unqualified | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, C.; Liu, Z.; Xiong, K.; Lyu, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, R. Characteristics of and Influencing Factors of Hydrochemistry and Carbon/Nitrogen Variation in the Huangzhouhe River Basin, a World Natural Heritage Site. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 13169. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182413169
Hu C, Liu Z, Xiong K, Lyu X, Li Y, Zhang R. Characteristics of and Influencing Factors of Hydrochemistry and Carbon/Nitrogen Variation in the Huangzhouhe River Basin, a World Natural Heritage Site. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(24):13169. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182413169
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Chenpeng, Ziqi Liu, Kangning Xiong, Xiaoxi Lyu, Yuan Li, and Renkai Zhang. 2021. "Characteristics of and Influencing Factors of Hydrochemistry and Carbon/Nitrogen Variation in the Huangzhouhe River Basin, a World Natural Heritage Site" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 24: 13169. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182413169
APA StyleHu, C., Liu, Z., Xiong, K., Lyu, X., Li, Y., & Zhang, R. (2021). Characteristics of and Influencing Factors of Hydrochemistry and Carbon/Nitrogen Variation in the Huangzhouhe River Basin, a World Natural Heritage Site. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(24), 13169. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182413169






