Social Media Use and Body Dissatisfaction in Adolescents: The Moderating Role of Thin- and Muscular-Ideal Internalisation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Participants
2.2. Measures
2.2.1. Demographic Information
2.2.2. Social Media Use
2.2.3. Thin-Ideal Internalisation
2.2.4. Muscular-Ideal Internalisation
2.2.5. Body Dissatisfaction
2.3. Procedures
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
3.2. Correlations
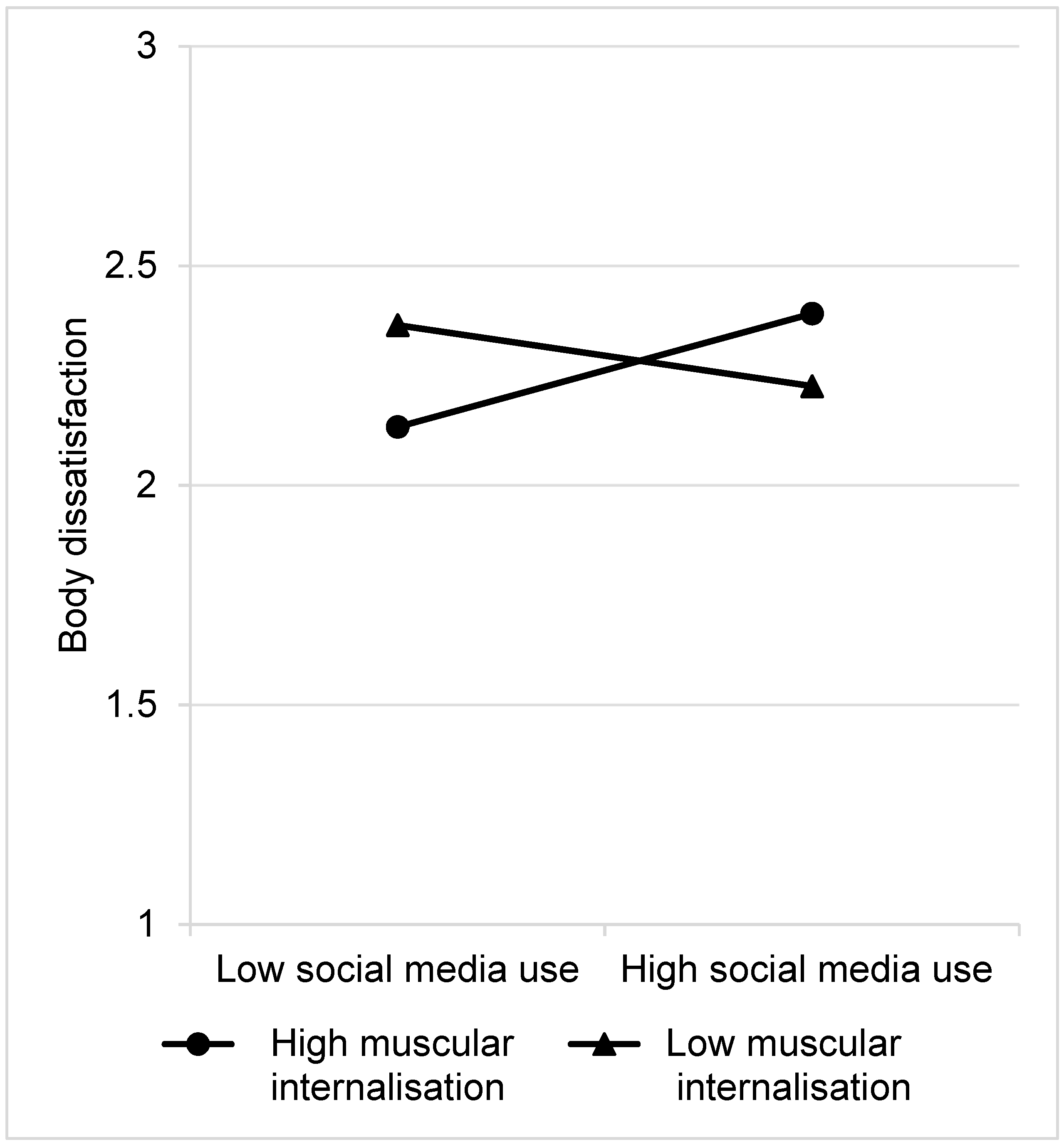
3.3. Moderation Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cash, T.F. Body-image attitudes: Evaluation, investment, and affect. Percept. Mot. Ski. 1994, 78, 1168–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohde, P.; Stice, E.; Marti, C.N. Development and predictive effects of eating disorder risk factors during adolescence: Implications for prevention efforts. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2015, 48, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Vries, D.A.; Peter, J.; de Graaf, H.; Nikken, P. Adolescents’ social network site use, peer appearance-related feedback, and body dissatisfaction: Testing a mediation model. J. Youth Adolesc. 2016, 45, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thompson, J.K.; Stice, E. Thin-ideal internalization: Mounting evidence for a new risk factor for body-image disturbance and eating pathology. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2001, 10, 181–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karazsia, B.T.; van Dulmen, M.H.M.; Wong, K.; Crowther, J.H. Thinking meta-theoretically about the role of internalization in the development of body dissatisfaction and body change behaviors. Body Image 2013, 10, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchôa, F.N.M.; Uchôa, N.M.; Daniele, T.M.D.C.; Lustosa, R.P.; Garrido, N.D.; Deana, N.F.; Aranha, Á.C.M.; Alves, N. Influence of the mass media and body dissatisfaction on the risk in adolescents of developing eating disorders. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, S.H.; Petrie, T.A.; Greenleaf, C.A.; Martin, S.B. Moderators of the internalization–body dissatisfaction relationship in middle school girls. Body Image 2012, 9, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullot, A.; Cave, L.; Fildes, J.; Hall, S.; Plummer, J. Mission Australia’s 2017 Youth Survey Report; Mission Australia: Sydney, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Franchina, V.; Coco, G.L. The influence of social media use on body image concerns. Int. J. Psychoanal. Educ. 2018, 10, 5–14. [Google Scholar]
- Grosick, T.L.; Talbert-Johnson, C.; Myers, M.J.; Angelo, R. Assessing the landscape: Body image values and attitudes among middle school boys and girls. Am. J. Health Educ. 2013, 44, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, S.C.; Kling, J.; Wängqvist, M.; Frisén, A.; Syed, M. Identity and the body: Trajectories of body esteem from adolescence to emerging adulthood. Dev. Psychol. 2018, 54, 1159–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacroix, E.; Atkinson, M.J.; Garbett, K.M.; Diedrichs, P.C. One size does not fit all: Trajectories of body image development and their predictors in early adolescence. Dev. Psychopathol. 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.B.; Haynos, A.F.; Wall, M.M.; Chen, C.; Eisenberg, M.E.; Neumark-Sztainer, D. Fifteen-year prevalence, trajectories, and predictors of body dissatisfaction from adolescence to middle adulthood. Clin. Psychol. Sci. 2019, 7, 1403–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aanesen, F.; Meland, E.; Torp, S. Gender differences in subjective health complaints in adolescence: The roles of self-esteem, stress from schoolwork and body dissatisfaction. Scand. J. Public Health 2017, 45, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxton, S.J.; Neumark-Sztainer, D.; Hannan, P.J.; Eisenberg, M.E. Body dissatisfaction prospectively predicts depressive mood and low self-esteem in adolescent girls and boys. J. Clin. Child Adolesc. Psychol. 2006, 35, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, M.P.; Ricciardelli, L.A. A longitudinal study of pubertal timing and extreme body change behaviors among adolescent boys and girls. Adolescence 2004, 39, 145–166. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Neumark-Sztainer, D.; Paxton, S.J.; Hannan, P.J.; Haines, J.; Story, M. Does body satisfaction matter? Five-year longitudinal associations between body satisfaction and health behaviors in adolescent females and males. J. Adolesc. Health 2006, 39, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esnaola, I.; Rodríguez, A.; Goñi, A. Body dissatisfaction and perceived sociocultural pressures: Gender and age differences. Salud Ment. 2010, 33, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- McCabe, M.P.; Ricciardelli, L.A. Parent, peer and media influences on body image and strategies to both increase and decrease body size among adolescent boys and girls. Adolescence 2001, 36, 225–240. [Google Scholar]
- Dye, H. Are there differences in gender, race, and age regarding body dissatisfaction? J. Hum. Behav. Soc. Environ. 2016, 26, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiphoo, A.N.; Vahedi, Z. A meta-analytic review of the relationship between social media use and body image disturbance. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2019, 101, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, M.P.; Ricciardelli, L.A. Body image and strategies to lose weight and increase muscle among boys and girls. Health Psychol. 2003, 22, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.D.; Barber, B.L. Embodied image: Gender differences in functional and aesthetic body image among Australian adolescents. Body Image 2010, 7, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzielska, A.; Kelly, C.; Ojala, K.; Finne, E.; Spinelli, A.; Furstova, J.; Dalmasso, P. Weight reduction behaviors among European adolescents—Changes from 2001/2002 to 2017/2018. J. Adolesc. Health 2020, 66, S70–S80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, J.M.; Bibbins-Domingo, K.; Garber, A.K.; Griffiths, S.; Vittinghoff, E.; Murray, S.B. Boys, bulk, and body ideals: Sex differences in weight-gain attempts among adolescents in the United States. J. Adolesc. Health 2019, 64, 450–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.K.; Heinberg, L.J.; Altabe, M.; Tantleff-Dunn, S. Exacting Beauty: Theory, Assessment, and Treatment of Body Image Disturbance; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Stice, E.; Nemeroff, C.; Shaw, H.E. Test of the dual pathway model of bulimia nervosa: Evidence for dietary restraint and affect regulation mechanisms. J. Soc. Clin. Psychol. 1996, 15, 340–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinsbekk, S.; Wichstrøm, L.; Stenseng, F.; Nesi, J.; Hygen, B.W.; Skalická, V. The impact of social media use on appearance self-esteem from childhood to adolescence—A 3-wave community study. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2021, 114, 106528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twenge, J.M.; Martin, G.N.; Spitzberg, B.H. Trends in U.S. Adolescents’ media use, 1976–2016: The rise of digital media, the decline of TV, and the (near) demise of print. Psychol. Pop. Media Cult. 2019, 8, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, J.; Das, P.; Muthiah, N.; Milanaik, R. New age technology and social media: Adolescent psychosocial implications and the need for protective measures. Curr. Opin. Pediatrics 2019, 31, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, J.P.; Krause, E.; Ohler, P. Every (Insta)Gram counts? Applying cultivation theory to explore the effects of Instagram on young users’ body image. Psychol. Pop. Media Cult. 2021, 10, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodyear, V. Narrative matters: Young people, social media and body image. Child Adolesc. Ment. Health 2019, 25, 48–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, S.S.; Lee, E.W.J.; Liao, Y. Social network sites, friends, and celebrities: The roles of social comparison and celebrity involvement in adolescents’ body image dissatisfaction. Soc. Media Soc. 2016, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McLean, S.A.; Jarman, H.K.; Rodgers, R.F. How do “selfies” impact adolescents’ well-being and body confidence? A narrative review. Psychol. Res. Behav. Manag. 2019, 12, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morgan, M.; Shanahan, J.; Signorielli, N. Growing up with television: Cultivation processes. In Media Effects: Advances in Theory and Research, 3rd ed.; Bryant, J., Oliver, M.B., Eds.; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2009; pp. 35–49. [Google Scholar]
- de Vries, D.A.; Vossen, H.G.M.; van der Kolk–van der Boom, P. Social media and body dissatisfaction: Investigating the attenuating role of positive parent–adolescent relationships. J. Youth Adolesc. 2019, 48, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fardouly, J.; Magson, N.R.; Rapee, R.M.; Johnco, C.J.; Oar, E.L. The use of social media by Australian preadolescents and its links with mental health. J. Clin. Psychol. 2020, 76, 1304–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryding, F.C.; Kuss, D.J. The use of social networking sites, body image dissatisfaction, and body dysmorphic disorder: A systematic review of psychological research. Psychol. Pop. Media 2020, 9, 412–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomon, I.; Brown, C.S. The selfie generation: Examining the relationship between social media use and early adolescent body image. J. Early Adolesc. 2018, 39, 539–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, A.; Eggermont, S.; Frison, E. The reciprocal and indirect relationships between passive Facebook use, comparison on Facebook, and adolescents’ body dissatisfaction. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2017, 73, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavender, J.M.; Brown, T.A.; Murray, S.B. Men, muscles, and eating disorders: An overview of traditional and muscularity-oriented disordered eating. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2017, 19, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Peng, W.; Ahn, S. When media become the mirror: A meta-analysis on media and body image. Media Psychol. 2021, 24, 437–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterna, A.; Alcaraz-Ibáñez, M.; Fuller-Tyszkiewicz, M.; Sicilia, Á. Internalization of body shape ideals and body dissatisfaction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2021, 54, 1575–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankauskiene, R.; Baceviciene, M. An exploration of the tripartite influence model of body image in Lithuanian sample of young adults: Does body weight make a difference? Eat. Weight. Disord. Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2021, 26, 1781–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Lee, H.H. A test of the expanded tripartite dual pathway model in physically active Korean men. Sex Roles 2020, 82, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davids, C.M.; Watson, L.B.; Gere, M.P. Objectification, masculinity, and muscularity: A test of objectification theory with heterosexual men. Sex Roles 2019, 80, 443–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, R.F.; Slater, A.; Gordon, C.S.; McLean, S.A.; Jarman, H.K.; Paxton, S.J. A biopsychosocial model of social media use and body image concerns, disordered eating, and muscle-building behaviors among adolescent girls and boys. J. Youth Adolesc. 2020, 49, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk, R.; Thompson, J.K. The effects of advertisements that sexually objectify women on state body dissatisfaction and judgments of women: The moderating roles of gender and internalization. Body Image 2015, 15, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, S.A.; Paxton, S.J.; Wertheim, E.H. Does media literacy mitigate risk for reduced body satisfaction following exposure to thin-ideal media? J. Youth Adolesc. 2016, 45, 1678–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahyad, S.; Pakdaman, S.; Shokri, O.; Saadat, S.H. The role of individual and social variables in predicting body dissatisfaction and eating disorder symptoms among Iranian adolescent girls: An expanding of the tripartite influence model. Eur. J. Transl. Myol. 2018, 28, 7277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, R.F.; McLean, S.A.; Paxton, S.J. Longitudinal relationships among internalization of the media ideal, peer social comparison, and body dissatisfaction: Implications for the tripartite influence model. Dev. Psychol. 2015, 51, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, A.E.; Sonneville, K.R.; Crosby, R.D.; Swanson, S.A.; Eddy, K.T.; Camargo, C.A.; Horton, N.J.; Micali, N. Prospective associations of concerns about physique and the development of obesity, binge drinking, and drug use among adolescent boys and young adult men. JAMA Pediatrics 2014, 168, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ricciardelli, L.A. Body Image Development–Adolescent Boys. In Encyclopedia of Body Image and Human Appearance; Cash, T.F., Ed.; Elsevier Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 180–186. [Google Scholar]
- Bearman, S.K.; Presnell, K.; Martinez, E.; Stice, E. The skinny on body dissatisfaction: A longitudinal study of adolescent girls and boys. J. Youth Adolesc. 2006, 35, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, S.; Warschburger, P. Prospective relations among internalization of beauty ideals, body image concerns, and body change behaviors: Considering thinness and muscularity. Body Image 2019, 28, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dye, H. Does internalizing society and media messages cause body dissatisfaction, in turn causing disordered eating? J. Evid. Inf. Soc. Work. 2016, 13, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.C.; Vigfusdottir, T.H.; Lee, Y. Body image and the appearance culture among adolescent girls and boys: An examination of friend conversations, peer criticism, appearance magazines, and the internalization of appearance ideals. J. Adolesc. Res. 2004, 19, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, P.; Paxton, S.J. Impact of exposure to idealised male images on adolescent boys’ body image. Body Image 2004, 1, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolak, L.; Stein, J.A. The relationship of drive for muscularity to sociocultural factors, self-esteem, physical attributes gender role, and social comparison in middle school boys. Body Image 2006, 3, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homan, K.; McHugh, E.; Wells, D.; Watson, C.; King, C. The effect of viewing ultra-fit images on college women’s body dissatisfaction. Body Image 2012, 9, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberga, A.S.; Withnell, S.J.; von Ranson, K.M. Fitspiration and thinspiration: A comparison across three social networking sites. J. Eat. Disord. 2018, 6, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, L.; Prichard, I.; Nikolaidis, A.; Drummond, C.; Drummond, M.; Tiggemann, M. Idealised media images: The effect of fitspiration imagery on body satisfaction and exercise behaviour. Body Image 2017, 22, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, M.; Rodgers, R.F.; Chabrol, H. Prospective predictors of body dissatisfaction, drive for thinness, and muscularity concerns among young women in France: A sociocultural model. Body Image 2018, 26, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmar, H.; Halliwell, E.; Stirling, E. Understanding the impact of thin media models on women’s body-focused affect: The roles of thin-ideal internalization and weight-related self-discrepancy activation in experimental exposure effects. J. Soc. Clin. Psychol. 2009, 28, 43–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Onis, M.; Onyango, A.W.; Borghi, E.; Siyam, A.; Nishida, C.; Siekmann, J. Development of a WHO growth reference for school-aged children and adolescents. Bull. World Health Organ. 2007, 85, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aparicio-Martinez, P.; Perea-Moreno, A.-J.; Martinez-Jimenez, M.P.; Redel-Macías, M.D.; Pagliari, C.; Vaquero-Abellan, M. Social Media, Thin-Ideal, Body Dissatisfaction and Disordered Eating Attitudes: An Exploratory Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marengo, D.; Longobardi, C.; Fabris, M.A.; Settanni, M. Highly-visual social media and internalizing symptoms in adolescence: The mediating role of body image concerns. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2018, 82, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, L.M.; Burke, N.L.; Thompson, J.K.; Dedrick, R.F.; Heinberg, L.J.; Calogero, R.M.; Bardone-Cone, A.M.; Higgins, M.K.; Frederick, D.A.; Kelly, M.; et al. Development and validation of the Sociocultural Attitudes Towards Appearance Questionnaire-4 (SATAQ-4). Psychol. Assess. 2015, 27, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schaefer, L.M.; Harriger, J.A.; Heinberg, L.J.; Soderberg, T.; Thompson, J.K. Development and validation of the sociocultural attitudes towards appearance questionnaire-4-revised (SATAQ-4R). Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2017, 50, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendelson, B.K.; Mendelson, M.J.; White, D.R. Body-esteem scale for adolescents and adults. J. Personal. Assess. 2001, 76, 90–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, J.J.; Tng, G.Y.; Yang, S. Effects of social media and smartphone use on body esteem in female adolescents: Testing a cognitive and affective model. Children 2020, 7, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Forbes, G.B.; Lee, Y.J. Body dissatisfaction and disordered eating among early adolescents from Korea and the US. Sex Roles 2009, 61, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, G.B.; Jung, J. Measures based on sociocultural theory and feminist theory as predictors of multidimensional measures of body dissatisfaction among Korean and U.S. college women. J. Soc. Clin. Psychol. 2008, 27, 70–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, R.J. A test of missing completely at random for multivariate data with missing values. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1988, 83, 1198–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalilzadeh, J.; Tasci, A.D.A. Large sample size, significance level, and the effect size: Solutions to perils of using big data for academic research. Tour. Manag. 2017, 62, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.H.; Bentler, P.M. Three likelihood-based methods for mean and covariance structure analysis with nonnormal missing data. Sociol. Methodol. 2000, 30, 165–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiken, L.S.; West, S.G.; Reno, R.R. Multiple Regression: Testing and Interpreting Interactions; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Biolcati, R.; Ghigi, R.; Mameli, C.; Passini, S. What can I do with my body? Boys and girls facing body dissatisfaction. Int. J. Adolesc. Youth 2017, 22, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klimek, P.; Murray, S.B.; Brown, T.; Gonzales, M., IV; Blashill, A.J. Thinness and muscularity internalization: Associations with disordered eating and muscle dysmorphia in men. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2018, 51, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawler, M.; Nixon, E. Body dissatisfaction among adolescent boys and girls: The effects of body mass, peer appearance culture and internalization of appearance ideals. J. Youth Adolesc. 2011, 40, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiklund, E.; Jonsson, E.; Coe, A.-B.; Wiklund, M. ‘Strong is the new skinny’: Navigating fitness hype among teenagers in northern Sweden. Sport Educ. Soc. 2019, 24, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knauss, C.; Paxton, S.J.; Alsaker, F.D. Body dissatisfaction in adolescent boys and girls: Objectified body consciousness, internalization of the media body ideal and perceived pressure from media. Sex Roles 2008, 59, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mostafa, E.S.M.; Eshak, E.S.; Seedhom, A.E.; Ghazawy, E.R. Media influence and body satisfaction among adolescent females, Minia, Egypt. J. Public Health 2018, 26, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumter, S.R.; Cingel, D.P.; Antonis, D. “To be able to change, you have to take risks #fitspo”: Exploring correlates of fitspirational social media use among young women. Telemat. Inform. 2018, 35, 1166–1175. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, H.S.; Donovan, C.L.; Ramme, R. Is athletic really ideal? An examination of the mediating role of body dissatisfaction in predicting disordered eating and compulsive exercise. Eat. Behav. 2016, 21, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, D.; Tiggemann, M. The effect of “Thin Ideal” television commercials on body dissatisfaction and schema activation during early adolescence. J. Youth Adolesc. 2003, 32, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presnell, K.; Bearman, S.K.; Stice, E. Risk factors for body dissatisfaction in adolescent boys and girls: A prospective study. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2004, 36, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrotte, E.R.; Prichard, I.; Lim, M.S.C. “Fitspiration” on social media: A content analysis of gendered images. J. Med. Internet Res. 2017, 19, e95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, M.; Lee, H.H. Can virtual makeovers using photo editing applications moderate negative media influences on SNS users’ body satisfaction? Can. J. Behav. Sci. Rev. Can. Des Sci. Du Comport. 2019, 51, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlmann, L.R.; Donovan, C.L.; Zimmer-Gembeck, M.J.; Bell, H.S.; Ramme, R.A. The fit beauty ideal: A healthy alternative to thinness or a wolf in sheep’s clothing? Body Image 2018, 25, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, R.; Newton-John, T.; Slater, A. The relationship between Facebook and Instagram appearance-focused activities and body image concerns in young women. Body Image 2017, 23, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Chock, T.M. Body image 2.0: Associations between social grooming on Facebook and body image concerns. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2015, 48, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, E.P.; Gray, J. Facebook photo activity associated with body image disturbance in adolescent girls. Cyberpsychology Behav. Soc. Netw. 2014, 17, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrew, R.; Tiggemann, M.; Clark, L. Predicting body appreciation in young women: An integrated model of positive body image. Body Image 2016, 18, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, M.; Chabrol, H.; Rodgers, R.F. Support for a modified Tripartite Dual Pathway model of body image concerns and risky body change behaviors in French young men. Sex Roles 2018, 78, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stice, E.; Marti, C.N.; Rohde, P.; Shaw, H. Testing mediators hypothesized to account for the effects of a dissonance-based eating disorder prevention program over longer term follow-up. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 2011, 79, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, T.A.; Forney, K.J.; Pinner, D.; Keel, P.K. A randomized controlled trial of The Body Project: More Than Muscles for men with body dissatisfaction. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2017, 50, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
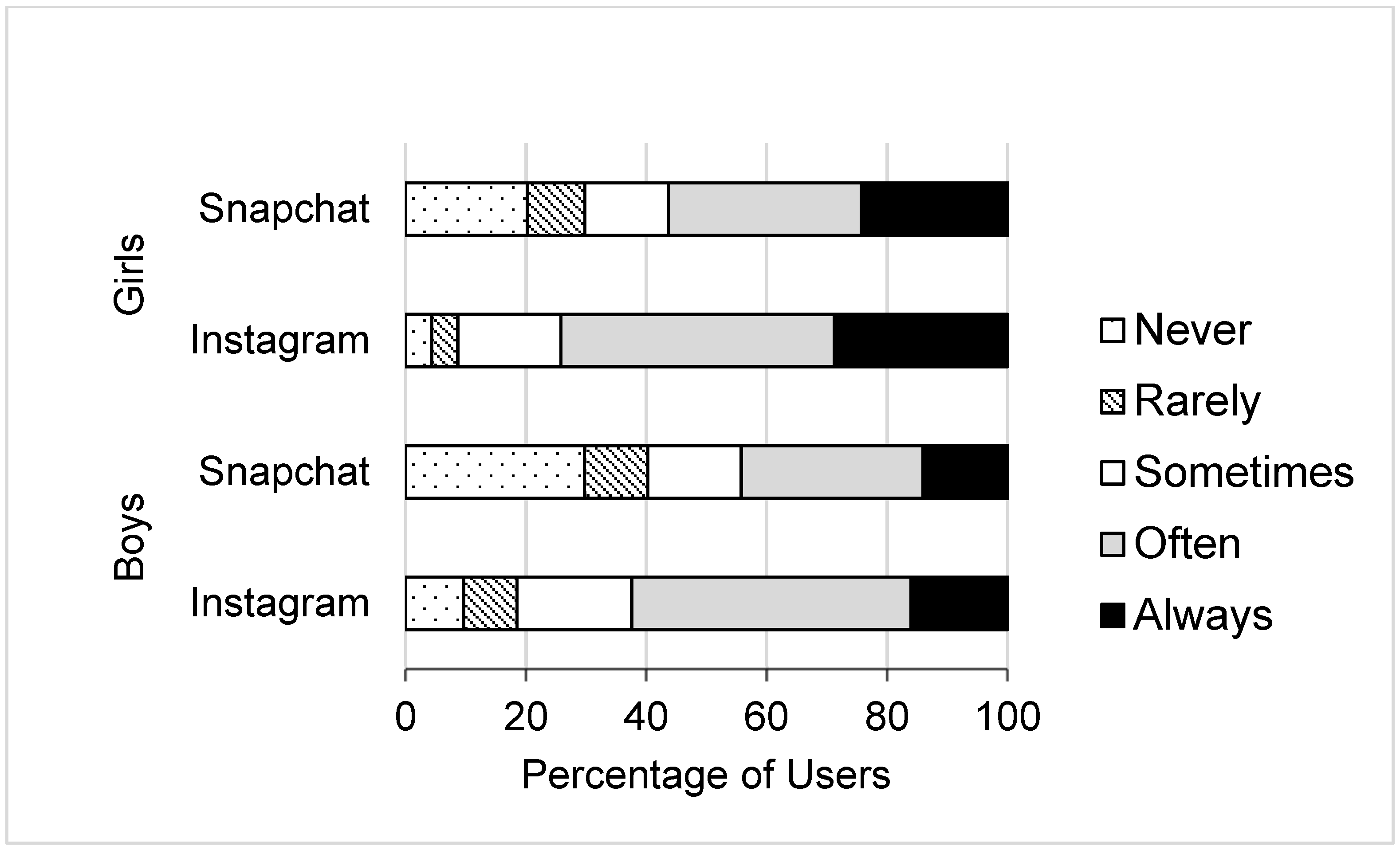
| Girls | Boys | Gender Differences | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SD | M | SD | p-Value | Cohen’s d | |
| Social Media Use | 3.60 | 1.02 | 3.19 | 1.11 | <0.001 | 0.36 |
| Thin-Ideal Internalisation | 2.87 | 1.11 | 2.18 | 0.93 | <0.001 | 0.67 |
| Muscular-Ideal Internalisation | 2.17 | 1.00 | 2.82 | 1.11 | <0.001 | 0.59 |
| Body Dissatisfaction | 2.76 | 0.87 | 2.29 | 0.81 | <0.001 | 0.57 |
| Social Media Use | Thin-Ideal Internalisation | Muscular-Ideal Internalisation | Body Dissatisfaction | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Social Media Use | _ | 0.21 ** | 0.06 | 0.20 ** |
| Thin-ideal Internalisation | 0.13 ** | _ | 0.27 ** | 0.64 ** |
| Muscular-ideal Internalisation | 0.26 ** | 0.47 ** | _ | 0.19 ** |
| Body Dissatisfaction | 0.10 * | 0.24 ** | 0.14 ** | _ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vuong, A.T.; Jarman, H.K.; Doley, J.R.; McLean, S.A. Social Media Use and Body Dissatisfaction in Adolescents: The Moderating Role of Thin- and Muscular-Ideal Internalisation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 13222. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182413222
Vuong AT, Jarman HK, Doley JR, McLean SA. Social Media Use and Body Dissatisfaction in Adolescents: The Moderating Role of Thin- and Muscular-Ideal Internalisation. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(24):13222. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182413222
Chicago/Turabian StyleVuong, An T., Hannah K. Jarman, Jo R. Doley, and Siân A. McLean. 2021. "Social Media Use and Body Dissatisfaction in Adolescents: The Moderating Role of Thin- and Muscular-Ideal Internalisation" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 24: 13222. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182413222
APA StyleVuong, A. T., Jarman, H. K., Doley, J. R., & McLean, S. A. (2021). Social Media Use and Body Dissatisfaction in Adolescents: The Moderating Role of Thin- and Muscular-Ideal Internalisation. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(24), 13222. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182413222






