Profiling Persistent Asthma Phenotypes in Adolescents: A Longitudinal Diagnostic Evaluation from the INSPIRERS Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Study Design and Procedures
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Population
3.2. Classes of Persistent Asthma
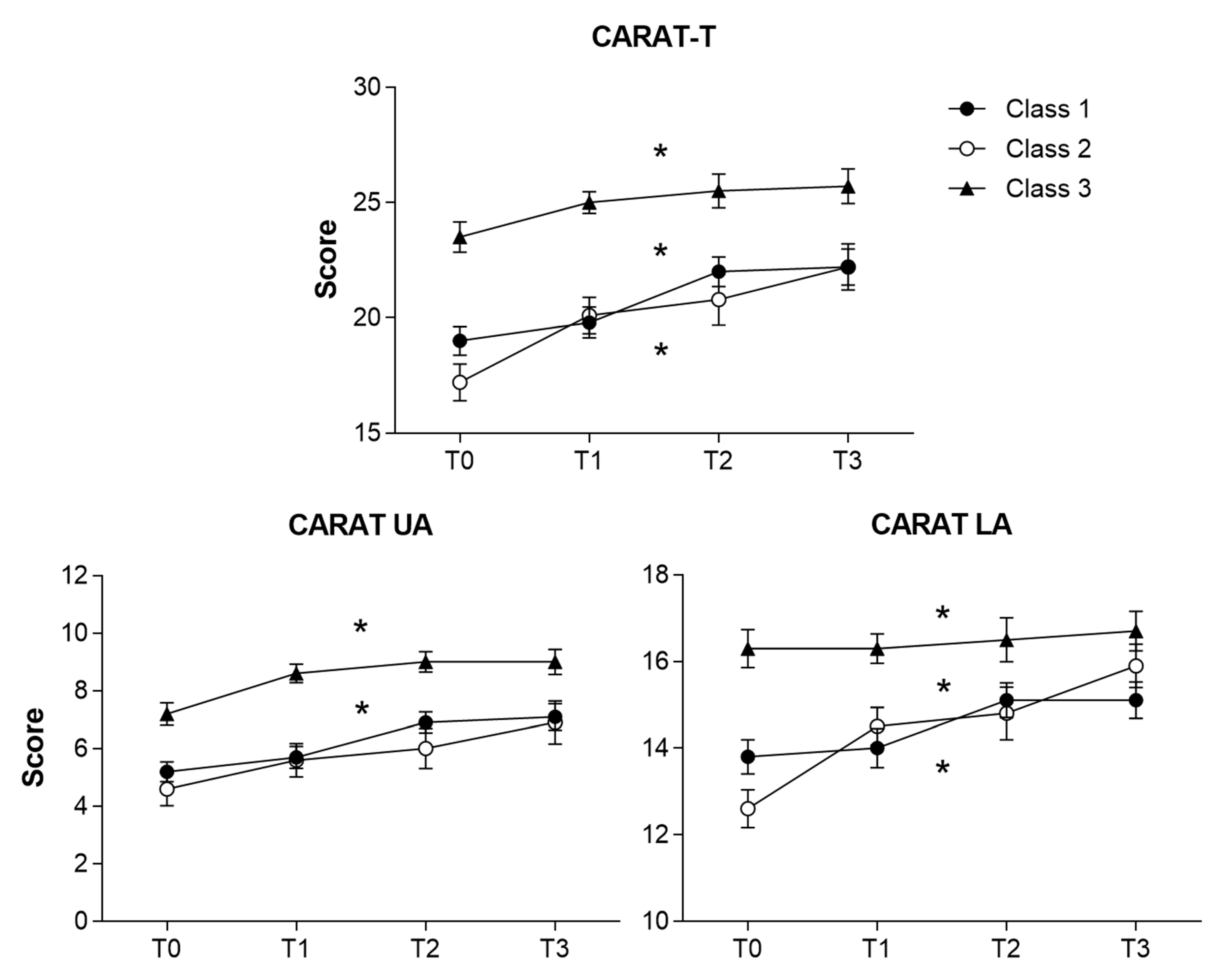
3.3. Longitudinal Assessment of Latent Classes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Asher, I.; Pearce, N. Global burden of asthma among children. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2014, 18, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Initiative for Asthma. Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention. 2019. Available online: https://www.ginasthma.org (accessed on 29 October 2020).
- Guilbert, T.W.; Garris, C.; Jhingran, P.; Bonafede, M.; Tomaszewski, K.J.; Bonus, T.; Hahn, R.M.; Schatz, M. Asthma that is not well-controlled is associated with increased healthcare utilization and decreased quality of life. J. Asthma 2011, 48, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira-Magalhães, M.; Pereira, A.M.; Sá-Sousa, A.; Morais-Almeida, M.; Azevedo, I.; Azevedo, L.F.; Fonseca, J.A. Asthma control in children is associated with nasal symptoms, obesity and health insurance: A nationwide survey. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2015, 26, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira-Magalhães, M.; Sá-Sousa, A.; Morais-Almeida, M.; Azevedo, L.F.; Azevedo, I.; Pereira, A.M.; Fonseca, J.A. High prevalence of hospitalisation for asthma in a population-based paediatric sample. Arch. Dis Child. 2015, 100, 507–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.; Sorensen, K. Enabling and hindering factors influencing adherence to asthma treatment among adolescents: A systematic literature review. J. Asthma 2016, 53, 862–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, T.B. Is a longitudinal trajectory helpful in identifying phenotypes in asthma? Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2018, 10, 571–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Lee, S.H.; Kwon, J.W.; Kim, Y.H.; Yoon, J.; Cho, H.J.; Yang, S.I.; Jung, Y.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Seo, J.H.; et al. Persistent asthma phenotype related with late-onset, high atopy, and low socioeconomic status in school-aged Korean children. BMC Pulm. Med. 2017, 17, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; He, X.Y.; Baines, K.J.; Gunawardhana, L.P.; Simpson, J.L.; Li, F.; Gibson, P.G. Different inflammatory phenotypes in adults and children with acute asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 38, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Owora, A.H.; Becker, A.B.; Chan-Yeung, M.; Chan, E.S.; Chooniedass, R.; Ramsey, C.; Watson, W.T.A.; Azad, M.B. Wheeze trajectories are modifiable through early-life intervention and predict asthma in adolescence. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 29, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jácome, C.; Guedes, R.; Almeida, R.; Teixeira, J.F.; Pinho, B.; Vieira-Marques, P.; Vilaça, R.; Fernandes, J.; Ferreira, A.; Couto, M.; et al. Minspirers—Estudo da exequibilidade de uma aplicação móvel para medição e melhoria da adesão à medicação inalada de controlo em adolescentes e adultos com asma persistente. Protocolo de um estudo observacional multicêntrico. Rev. Port. Imunoalergol. 2018, 26, 47–61. [Google Scholar]
- Jácome, C.; Almeida, R.; Amaral, R.; Pereira, A.M.; Vidal, C.; Freire, S.; Brea, P.; Antolin-Amerigo, D.; Caballer, B.; Castro, A.; et al. Feasibility of a mobile app to improve inhaler adherence in real-world patients with asthma: A multicentre observational study in Portugal and Spain. Allergy 2020, 75, 307–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jácome, C.; Pereira, A.M.; Almeida, R.; Ferreira-Magalhaes, M.; Couto, M.; Araujo, L.; Pereira, M.; Correia, M.A.; Loureiro, C.C.; Catarata, M.J.; et al. Patient-physician discordance in assessment of adherence to inhaled controller medication: A cross-sectional analysis of two cohorts. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e031732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vandenbroucke, J.P.; Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Pocock, S.J.; Poole, C.; Schlesselman, J.J.; Egger, M.; for the STROBE Initiative. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE): Explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med. 2007, 12, e297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loymans, R.J.B.; Ter Riet, G.; Sterk, P.J. Definitions of asthma exacerbations. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 11, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, J.A.; Nogueira-Silva, L.; Morais-Almeida, M.; Azevedo, L.; Sa-Sousa, A.; Branco-Ferreira, M.; Fernandes, L.; Bousquet, J. Validation of a questionnaire (CARAT10) to assess rhinitis and asthma in patients with asthma. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 65, 1042–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, P.; Correia de Sousa, J.; Bousquet, J.; Bugalho-Almeida, A.; Del Giacco, S.R.; Demoly, P.; Haahtela, T.; Jacinto, T.; Garcia-Larsen, V.; van der Molen, T.; et al. Control of Allergic Rhinitis and Asthma Test (CARAT): Dissemination and applications in primary care. Prim. Care Respir. J. 2013, 22, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Multicentre growth reference study Group WHO child growth standards based on length/height, weight and age. Acta Paediatr. Suppl. 2006, 45, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henson, J.M.; Reise, S.P.; Kim, K.H. Detecting mixtures from structural model differences using latent variable mixture modeling: A comparison of relative model fit statistics. Struct. Equ. Model. 2007, 14, 202–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savenije, O.E.; Granell, R.; Caudri, D.; Koppelman, G.H.; Smit, H.A.; Wijga, A.; de Jongste, J.C.; Brunekreef, B.; Sterne, J.A.; Postma, D.S.; et al. Comparison of childhood wheezing phenotypes in 2 birth cohorts: ALSPAC and PIAMA. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 1505–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, A.M.; Teague, W.G.; Meyers, D.A.; Peters, S.P.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Wenzel, S.E.; Aujla, S.; Castro, M.; Bacharier, L.B.; et al. National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Severe Asthma Research Program. Heterogeneity of severe asthma in childhood: Confirmation by cluster analysis of children in the National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Severe Asthma Research Program. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howrylak, J.A.; Fuhlbrigge, A.L.; Strunk, R.C.; Zeiger, R.S.; Weiss, S.T.; Raby, B.A. Classification of childhood asthma phenotypes and long-term clinical responses to inhaled anti-inflammatory medications. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 33, 1289–1300.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zoratti, E.M.; Krouse, R.Z.; Babineau, D.C.; Pongracic, J.A.; O’Connor, G.T.; Wood, R.A.; Khurana Hershey, G.K.; Kercsmar, C.M.; Gruchalla, R.S.; Kattan, M.; et al. Asthma phenotypes in inner-city children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 1016–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Der Leeuw, S.; Van Der Molen, T.; Dekhuijzen, P.; Fonseca, J.; Van Gemert, F.; Frederik, A.; Van Wijk, R.G.; Kocks, J.; Janwillem, W.; Oosterom, H.; et al. The minimal clinically important difference of the control of allergic rhinitis and asthma test (CARAT): Cross-cultural validation and relation with pollen counts. NPJ Prim. Care Resp. Med. 2015, 25, 14107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miles, C.; Arden-Close, E.; Thomas, M.; Bruton, A.; Yardley, L.; Hankins, M.; Kirby, S.E. Barriers and facilitators of effective self-management in asthma: Systematic review and thematic synthesis of patient and healthcare professional views. NPJ Prim. Care Respir. Med. 2017, 27, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrman, C.; Dubus, J.C.; Marguet, C.; Delacourt, C.; Thumerelle, C.; de Blic, J.; Delmas, M.C. Hospitalizations for asthma in children are linked to undertreatment and insufficient asthma education. J. Asthma 2011, 48, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jácome, C.; Almeida, R.; Pereira, A.M.; Araújo, L.; Correia, M.A.; Pereira, M.; Couto, M.; Lopes, C.; Chaves Loureiro, C.; Catarata, M.J.; et al. Asthma App Use and Interest among Patients with Asthma: A Multicenter Study. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 30, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matricardi, P.M.; Dramburg, S.; Alvarez-Perea, A.; Antolín-Amérigo, D.; Apfelbacher, C.; Atanaskovic-Markovic, M.; Berger, U.; Blaiss, M.S.; Blank, S.; Boni, E.; et al. The role of mobile health technologies in allergy care: An EAACI position paper. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 75, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jácome, C.; Almeida, R.; Teixeira, J.P.; Vieira Marques, P.; Vilaça, R.; Fernandes, J.M.; Ferreira, A.; Fonseca, J.A. Inspirers: An app to measure and improve adherence to inhaled treatment. In Proceedings of the International Conference on E-Health, Eh 2017—Part of the Multi Conference on Computer Science and Information Systems 2017; International Assn for Development of the Information Society (IADIS): Lisbon, Portugal, 2017; pp. 135–139. [Google Scholar]
- Bousquet, J.; Arnavielhe, S.; Bedbrook, A.; Bewick, M.; Laune, D.; Mathieu-Dupas, E.; Murray, R.; Onorato, G.L.; Pépin, J.L.; Picard, R.; et al. MASK 2017: ARIA digitally-enabled, integrated, person-centred care for rhinitis and asthma multimorbidity using real-world-evidence. Clin. Transl. Allergy 2018, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holt, P.G.; Sly, P.D. Viral infections and atopy in asthma pathogenesis: New rationales for asthma prevention and treatment. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everitt, B.S.; Landau, S.; Leese, M.; Stahl, D. Cluster Analysis. In Cluster Analysis, 5th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]

| Characteristics | Total n = 162 | Male n = 83 | Female n = 79 | p Value 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, median (P25–P75) | 15 (14–16) | 14 (13–16) | 15 (14–16) | 0.061 |
| Age of Symptom’s onset, median (P25–P75) | 6 (3–10) | 5.5 (3–10) | 7.0 (3–10) | 0.538 |
| BMI classification, n (%): | ||||
| Underweight (<5th percentile) | 3 (2) | 1 (1) | 2 (3) | 0.537 |
| Healthy weight (5th–85th percentile) | 117 (76) | 62 (80) | 55 (73) | 0.370 |
| Overweight (85th–95th percentile | 21 (14) | 9 (11) | 12 (16) | 0.443 |
| Obesity (≥95th percentile) | 12 (8) | 6 (8) | 6 (8) | 0.944 |
| Pre-BD FEV1% predicted, mean (sd) | 95.6 (16.2) | 95.0 (16.8) | 95.9 (15.7) | 0.735 |
| Exposure to ETS, n (%) | 71 (47) | 36 (43) | 35 (47) | 0.888 |
| Comorbidities 1, n (%) | 111 (68) | 59 (64) | 58 (73) | 0.190 |
| Single inhaler, n (%) | 104 (64) | 57 (69) | 47 (59) | 0.223 |
| Inhaled medication, n (%): | ||||
| ICS/LABA | 114 (72) | 57 (70) | 57 (74) | 0.608 |
| SABA | 52 (33) | 22 (27) | 30 (39) | 0.115 |
| ICS | 45 (28) | 24 (30) | 21 (27) | 0.743 |
| LAMA | 4 (2) | 2 (2) | 2 (3) | 0.959 |
| Asthma control (GINA), n (%) | ||||
| Controlled | 74 (46) | 42 (51) | 32 (41) | 0.223 |
| Partly controlled | 62 (38) | 33 (40) | 29 (37) | 0.737 |
| Uncontrolled | 25 (16) | 8 (10) | 17 (22) | 0.033 |
| CARAT-T, median (P25–P75) | 21 (16–24) | 22 (17–25) | 18 (14–23) | 0.010 |
| CARAT-UA, median (P25–P75) | 6 (3–8) | 6 (4–8) | 5 (2–7) | 0.101 |
| CARAT-LA, median (P25–P75) | 15 (12–17) | 16 (13–18) | 14 (11–16) | 0.003 |
| Exacerbations, n (%) | 91 (58) | 44 (55) | 47 (61) | 0.443 |
| Unscheduled healthcare visits, n (%) | 39 (31) | 24 (34) | 15 (27) | 0.395 |
| Variables | Class 1 n = 87 | Class 2 n = 32 | Class 3 n = 43 | 1 vs. 2 p Value 1 | 1 vs. 3 p Value 1 | 2 vs. 3 p Value 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 44 (50) | 6 (20) | 33 (76) | 0.004 | 0.006 | <0.001 |
| BMI ≥ 85th percentile | 16 (19) | 8 (25) | 8 (19) | 0.637 | 0.925 | 0.625 |
| Exposure to ETS | 41 (48) | 11 (39) | 18 (47) | 0.413 | 0.933 | 0.513 |
| Comorbidities | 63 (72) | 17 (57) | 32 (76) | 0.797 | 0.379 | 0.647 |
| Symptom’s onset, before age of 6 years | 45 (52) | 10 (33) | 20 (50) | 0.073 | 0.808 | 0.163 |
| Pre-BD FEV1 < 80% | 11 (17) | 0 (0) | 8 (23) | 0.041 | 0.517 | 0.022 |
| CARAT-T, uncontrolled | 70 (81) | 30 (97) | 23 (56) | 0.035 | 0.003 | <0.001 |
| CARAT-UA, uncontrolled | 71 (82) | 28 (90) | 26 (63) | 0.292 | 0.023 | 0.011 |
| CARAT-LA, uncontrolled | 52 (60) | 31 (100) | 6 (15) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Exacerbations, last year | 81 (97) | 3 (11) | 3 (8) | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.669 |
| Unscheduled healthcare visits, last year | 49 (57) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.999 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amaral, R.; Jácome, C.; Almeida, R.; Pereira, A.M.; Alves-Correia, M.; Mendes, S.; Rodrigues, J.C.C.; Carvalho, J.; Araújo, L.; Costa, A.; et al. Profiling Persistent Asthma Phenotypes in Adolescents: A Longitudinal Diagnostic Evaluation from the INSPIRERS Studies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18031015
Amaral R, Jácome C, Almeida R, Pereira AM, Alves-Correia M, Mendes S, Rodrigues JCC, Carvalho J, Araújo L, Costa A, et al. Profiling Persistent Asthma Phenotypes in Adolescents: A Longitudinal Diagnostic Evaluation from the INSPIRERS Studies. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(3):1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18031015
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmaral, Rita, Cristina Jácome, Rute Almeida, Ana Margarida Pereira, Magna Alves-Correia, Sandra Mendes, José Carlos Cidrais Rodrigues, Joana Carvalho, Luís Araújo, Alberto Costa, and et al. 2021. "Profiling Persistent Asthma Phenotypes in Adolescents: A Longitudinal Diagnostic Evaluation from the INSPIRERS Studies" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 3: 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18031015
APA StyleAmaral, R., Jácome, C., Almeida, R., Pereira, A. M., Alves-Correia, M., Mendes, S., Rodrigues, J. C. C., Carvalho, J., Araújo, L., Costa, A., Silva, A., Teixeira, M. F., Ferreira-Magalhães, M., Alves, R. R., Moreira, A. S., Fernandes, R. M., Ferreira, R., Pinto, P. L., Neuparth, N., ... Fonseca, J. A. (2021). Profiling Persistent Asthma Phenotypes in Adolescents: A Longitudinal Diagnostic Evaluation from the INSPIRERS Studies. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(3), 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18031015









