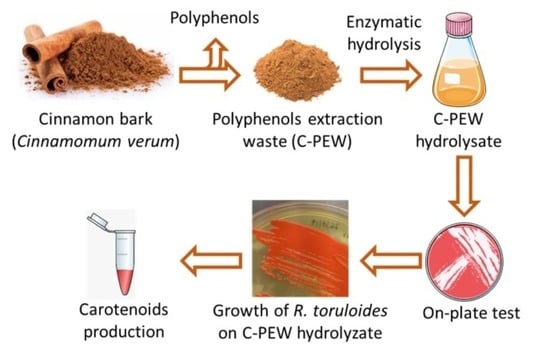
Enzymatic Hydrolysate of Cinnamon Waste Material as Feedstock for the Microbial Production of Carotenoids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Biomass: Feedstock Preparation and Composition
2.2. Pretreatment and Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Cinnamon Bark and Waste Material
2.3. Microbial Strains and Media
2.4. R. Toruloides Cultivation and Carotenoids Production
2.5. Analytical Methods
2.6. Calculations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Evaluation of Total Composition of the CB and C-PEW by Acid Hydrolysis
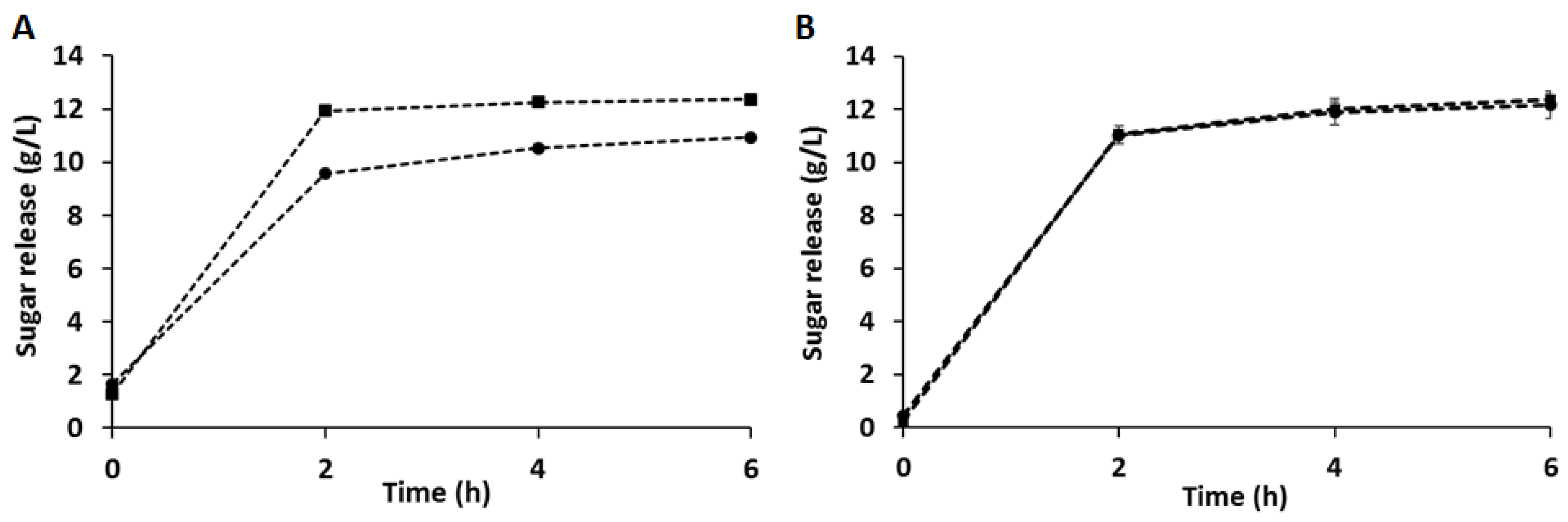
3.2. Enzymatic Hydrolysis of CB and C-PEW and Composition of the Hydrolysates
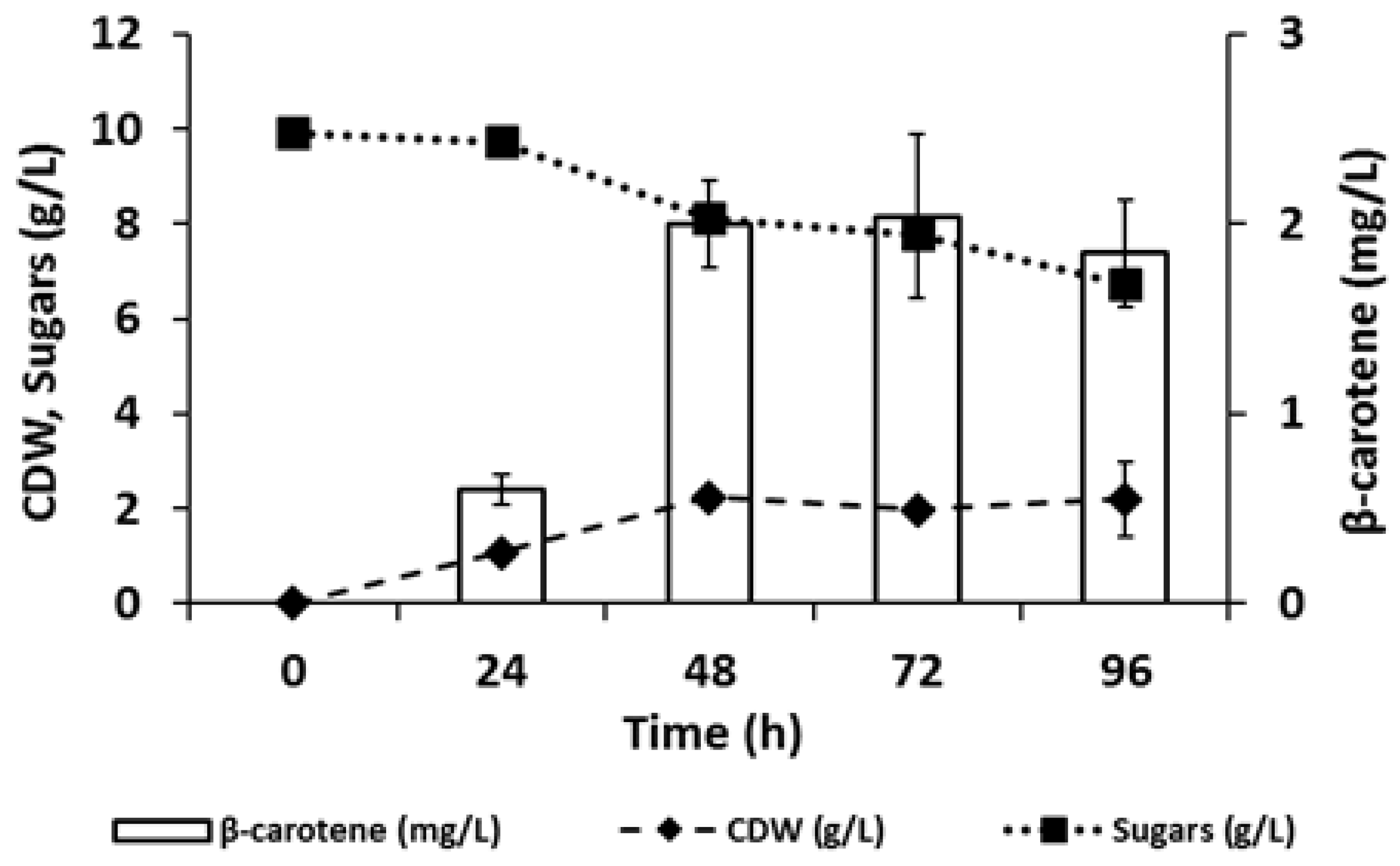
3.3. Production of Carotenoids from C-PEW Hydrolysate
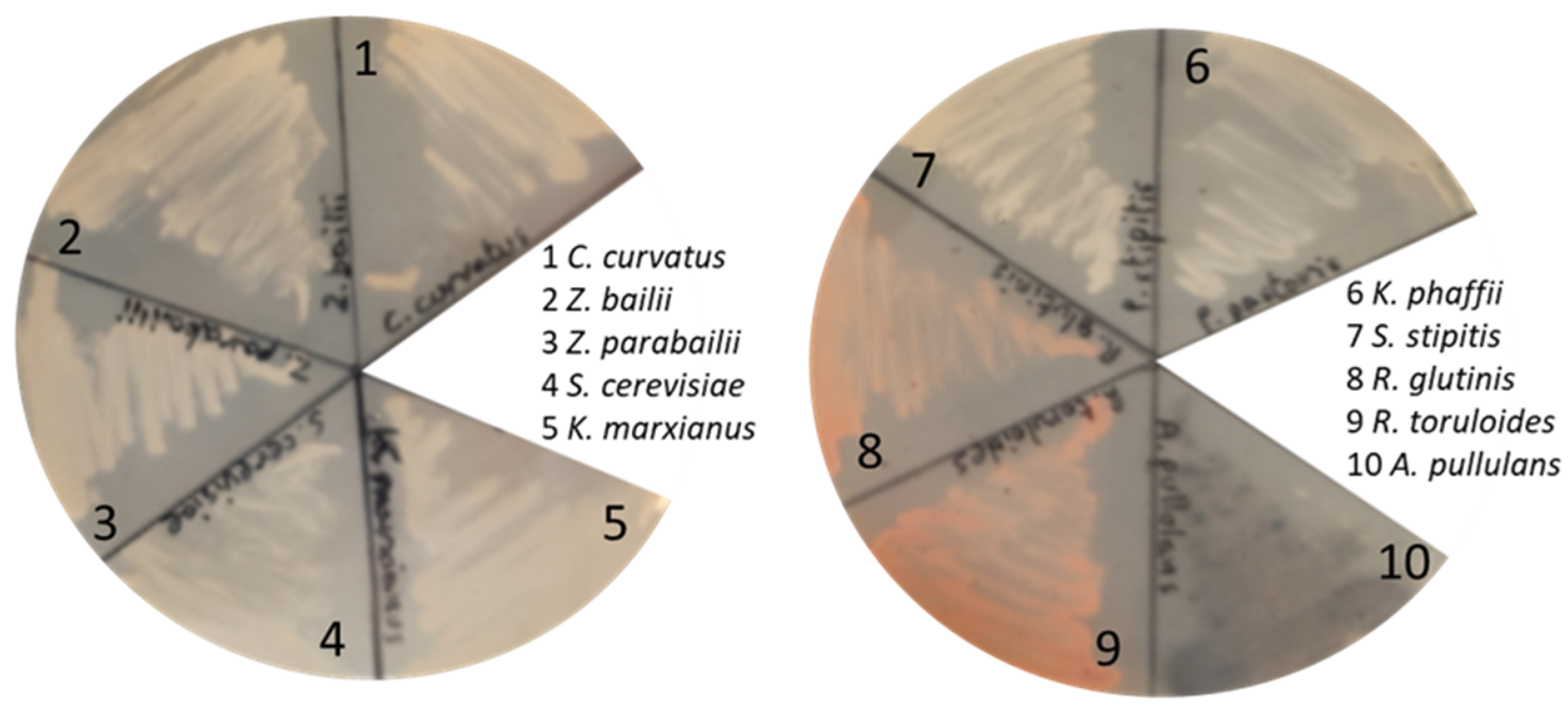
3.4. Testing the Growth of Other Fungal Cell Factories on C-PEW Hydrolysate
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bracco, S.; Calicioglu, O.; Juan, M.G.S.; Flammini, A. Assessing the contribution of bioeconomy to the total economy: A review of national frameworks. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEA Bioenergy Task42. Sustainable and Synergetic Processing of Biomass into Marketable Food & Feed Ingredients, Chemicals, Materials and Energy (Fuels, Power, Heat); IEA Bioenergy: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Dahiya, S.; Kumar, A.N.; Sravan, J.S.; Chatterjee, S.; Sarkar, O.; Mohan, S.V. Food waste biorefinery: Sustainable strategy for circular bioeconomy. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 248, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branduardi, P. Closing the loop: The power of microbial biotransformations from traditional bioprocesses to biorefineries, and beyond. Microb. Biotechnol. 2020, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoni, C.; Bruni, I.; Guzzetti, L.; Dell’Agli, M.; Sangiovanni, E.; Piazza, S.; Regonesi, M.E.; Maldini, M.; Spezzano, R.; Caruso, D.; et al. Valorizing coffee pulp by-products as anti-inflammatory ingredient of food supplements acting on IL-8 release. Food Res. Int. 2018, 112, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavini, S.; Guzzetti, L.; Givoia, F.; Regonesi, M.E.; Di Gennaro, P.; Magoni, C.; Campone, L.; Labra, M.; Bruni, I. Artichoke (Cynara cardunculus var. scolymus L.) by-products as a source of inulin: How to valorise an agricultural supply chain extracting an added-value compound. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, B.; Mishra, S. Medicinal and Nutritional Perspective of Cinnamon: A Mini-review. Eur. J. Med. Plants 2020, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, D.R.A.; Tuenter, E.; Patria, G.D.; Foubert, K.; Pieters, L.; Dewettinck, K. Phytochemical composition and antioxidant activity of Cinnamomum burmannii Blume extracts and their potential application in white chocolate. Food Chem. 2021, 340, 127983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, I.; Aznar, M.; Silva, F.; Nerín, C. Antimicrobial properties and mode of action of mustard and cinnamon essential oils and their combination against foodborne bacteria. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2016, 36, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabavi, S.F.; Di Lorenzo, A.; Izadi, M.; Sobarzo-Sánchez, E.; Daglia, M.; Nabavi, S.M. Antibacterial effects of cinnamon: From farm to food, cosmetic and pharmaceutical industries. Nutrients 2015, 7, 7729–7748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro-Santos, R.; Andrade, M.; Madella, D.; Martinazzo, A.P.; de Aquino Garcia Moura, L.; de Melo, N.R.; Sanches-Silva, A. Revisiting an ancient spice with medicinal purposes: Cinnamon. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 62, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, M.J.; Kumar, A. Green and Efficient Processing of Cinnamomum cassia Bark by Using Ionic Liquids: Extraction of Essential Oil and Construction of UV-Resistant Composite Films from Residual Biomass. Chem. Asian J. 2017, 12, 3150–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Kim, H.U.; Chae, T.U.; Cho, J.S.; Kim, J.W.; Shin, J.H.; Kim, D.I.; Ko, Y.-S.; Jang, W.D.; Jang, Y.-S. A comprehensive metabolic map for production of bio-based chemicals. Nat. Catal. 2019, 2, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, I.H.; Altameme, H.J.; Mohammed, G.J. Evaluation of antifungal and antibacterial activity and analysis of bioactive phytochemical compounds of Cinnamomum zeylanicum (Cinnamon bark) using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Orient. J. Chem. 2016, 32, 1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OuYang, Q.; Duan, X.; Li, L.; Tao, N. Cinnamaldehyde exerts its antifungal activity by disrupting the cell wall integrity of Geotrichum citri-aurantii. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Zhang, S.; Odoh, C.K.; Jin, M.; Zhao, Z.K. Rhodosporidium toruloides—A potential red yeast chassis for lipids and beyond. FEMS Yeast Res. 2020, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.-K.K.; Nicaud, J.-M.M.; Ledesma-Amaro, R. The Engineering Potential of Rhodosporidium toruloides as a Workhorse for Biotechnological Applications. Trends Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 304–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertacchi, S.; Bettiga, M.; Porro, D.; Branduardi, P. Camelina sativa meal hydrolysate as sustainable biomass for the production of carotenoids by Rhodosporidium toruloides. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2020, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.M.; Kuhn, P.; Poulev, A.; Rojo, L.E.; Lila, M.A.; Raskin, I. In vivo and in vitro antidiabetic effects of aqueous cinnamon extract and cinnamon polyphenol-enhanced food matrix. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 2994–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safafar, H.; Wagenen JVan Møller, P.; Jacobsen, C. Carotenoids, phenolic compounds and tocopherols contribute to the antioxidative properties of some microalgae species grown on industrial wastewater. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 7339–7356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.; Hao, E.; Deng, J.; Hou, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, J. Boost anti-oxidant activity of yogurt with extract and hydrolysate of cinnamon residues. Chin. Herb. Med. 2019, 11, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jönsson, L.J.; Martín, C. Pretreatment of lignocellulose: Formation of inhibitory by-products and strategies for minimizing their effects. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 199, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahlström, R.M.; Suurnäkki, A. Enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulosic polysaccharides in the presence of ionic liquids. Green Chem. R. Soc. Chem. 2015, 17, 694–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainane, A.; Elkouali, M. Cosmetic bio-product based on cinnamon essential oil “Cinnamomum verum” for the treatment of mycoses: Preparation, chemical analysis and antimicrobial activity. MOJ Toxicol. 2019, 5, 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Shreaz, S.; Wani, W.A.; Behbehani, J.M.; Raja, V.; Irshad, M.; Karched, M.; Ali, I.; Siddiqi, W.A.; Hun, L.T. Cinnamaldehyde and its derivatives, a novel class of antifungal agents. Fitoterapia 2016, 112, 116–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benkeblia, N. Free-radical scavenging capacity and antioxidant properties of some selected Onions (Allium cepa L.) and garlic (Allium sativum L.) extracts. Braz. Arch. Biol Technol. 2005, 48, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Settharaksa, S.; Jongjareonrak, A.; Hmadhlu, P.; Chansuwan, W.; Siripongvutikorn, S. Flavonoid, phenolic contents and antioxidant properties of thai hot curry paste extract and its ingredients as affected of pH, solvent types and high temperature. Int. Food Res. J. 2012, 19, 1581–1587. [Google Scholar]
- Bonturi, N.; Crucello, A.; Viana, A.J.C.; Miranda, E.A. Microbial oil production in sugarcane bagasse hemicellulosic hydrolysate without nutrient supplementation by a Rhodosporidium toruloides adapted strain. Process Biochem. 2017, 57, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, C.; Parreira, T.M.; Roseiro, J.; Reis, A.; Da Silva, T.L. Selecting low-cost carbon sources for carotenoid and lipid production by the pink yeast Rhodosporidium toruloides NCYC 921 using flow cytometry. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 158, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabaniotou, A. Redesigning a bioenergy sector in EU in the transition to circular waste-based Bioeconomy—A multidisciplinary review. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 177, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Financing the Green Transition: The European Green Deal Investment Plan and Just Transition Mechanism; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. Goal 9: Build Resilient Infrastructure, Promote Inclusive and Sustainable Industrialization, and Foster Innovation; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. A European Green Deal. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/strategy/priorities-2019-2024/european-green-deal_en (accessed on 10 December 2020).
- Ooi, L.S.M.; Li, Y.; Kam, S.L.; Wang, H.; Wong, E.Y.L.; Ooi, V.E.C. Antimicrobial activities of Cinnamon oil and cinnamaldehyde from the Chinese medicinal herb Cinnamomum cassia Blume. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2006, 34, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasongsuk, S.; Lotrakul, P.; Ali, I.; Bankeeree, W.; Punnapayak, H. The current status of Aureobasidium pullulans in biotechnology. Folia Microbiol. 2018, 63, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandy, S.K.; Srivastava, R.K. A review on sustainable yeast biotechnological processes and applications. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 207, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; Du, G.; Ledesma-Amaro, R.; Liu, L. Microbial Chassis Development for Natural Product Biosynthesis. Trends Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 779–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, J.E.; Glieder, A. Current advances in engineering tools for Pichia pastoris. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2019, 59, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Borodina, I. Application of synthetic biology for production of chemicals in yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Yeast Res. 2015, 15, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Varela, J.A.; Gethins, L.; Stanton, C.; Ross, P.; Morrissey, J.P. Applications of Kluyveromyces marxianus in Biotechnology. In Yeast Diversity in Human Welfare; Satyanarayana, T., Kunze, G., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 1–486. [Google Scholar]
- Kuanyshev, N.; Adamo, G.M.; Porro, D.; Branduardi, P. The spoilage yeast Zygosaccharomyces bailii: Foe or friend? Yeast 2017, 34, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, S.O.; Gujjari, P.; Beres, C.; Beck, B.; Zhou, J. Proposal of Zygosaccharomyces parabailii sp. nov. and Zygosaccharomyces pseudobailii sp. nov., novel species closely related to Zygosaccharomyces bailii. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 1922–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gao, M.; Cao, M.; Suástegui, M.; Walker, J.; Quiroz, N.R.; Wu, Y.; Tribby, D.; Okerlund, A.; Stanley, L.; Shanks, J.V.; et al. Innovating a nonconventional yeast platform for producing shikimate as the building block of high-value aromatics. ACS Synth. Biol. 2017, 6, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carsanba, E.; Papanikolaou, S.; Erten, H. Production of oils and fats by oleaginous microorganisms with an emphasis given to the potential of the nonconventional yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2018, 38, 1230–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreeharsha, R.V.; Mohan, S.V. Obscure yet Promising Oleaginous Yeasts for Fuel and Chemical Production. Trends Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 873–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donot, F.; Fontana, A.; Baccou, J.C.; Strub, C.; Schorr-Galindo, S. Single cell oils (SCOs) from oleaginous yeasts and moulds: Production and genetics. Biomass Bioenergy 2014, 68, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uemura, H. Synthesis and production of unsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids in yeast: Current state and perspectives. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 95, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frengova, G.I.; Beshkova, D.M. Carotenoids from Rhodotorula and Phaffia: Yeasts of biotechnological importance. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 36, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagarajan, J.; Ramanan, R.N.; Raghunandan, M.E.; Galanakis, C.M.; Krishnamurthy, N.P. Carotenoids. In Nutraceutical and Functional Food Components. Effects of Innovative Processing Techniques; Galanakis, C.M., Ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 259–296. [Google Scholar]
- IEA Bioenergy Task40. Cascading of Woody Biomass: Definitions, Policies and Effects on International Trade; IEA Bioenergy: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
| Total Acid Hydrolysis of Cinnamon | ||
|---|---|---|
| Component | Cinnamon Bark (CB) | Cinnamon Waste Material (C-PEW) |
| Water | 19.4 ± 1.34% | / |
| Insoluble fraction | 41.1 ± 1.26% | 44.5 ± 1.86% |
| Acetate | 1.5 ± 1.03% | 2.8 ± 0.13% |
| Sugars | 37.3 ± 0.83% | 41.5 ± 1.28% |
| of which | ||
| Glucose | 25.2 ± 0.53% | 27.2 ± 0.99% |
| Fructose | 9.1 ± 0.15% | 10.7 ± 0.32% |
| Arabinose | 3.0 ± 0.19% | 3.6 ± 0.04% |
| Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Cinnamon-Derived Biomasses | Cinnamon Bark (CB) | Cinnamon Waste Material (C-PEW) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Component Titer (g/L) | pH 4.5 | Yield | pH 6 | Yield | pH 3.5 | Yield | pH 6 | Yield |
| Sucrose | 0.9 ± 0.01 | - | 1.06 ± 0.00 | 0.8 ± 0.04 | - | 0.9 ± 0.01 | - | |
| Glucose | 7.5 ± 0.09 | 32.98% | 8.2 ± 0.08 | 36.07% | 8.8 ± 0.42 | 36.7% | 9.0 ± 0.12 | 35.9% |
| Fructose | 2.6 ± 0.05 | 30.73% | 2.4 ± 0.01 | 28.44% | 1.8 ± 0.05 | 18.6% | 1.8 ± 0.06 | 18.6% |
| Arabinose | - | - | 0.8 ± 0.01 | 25.65% | 0.8 ± 0.02 | 8.4% | 0.7 ± 0.06 | 5.6% |
| Total sugars | 10.9 ± 0.11 | 32.4% | 12.4 ± 0.10 | 36.67% | 12.2 ± 0.52 | 33% | 12.4 ± 0.23 | 32.5% |
| Aromatic Compounds in Cinnamon-Derived Hydrolysates | CB Hydrolysate ZZZ(W/O Autoclave Pre-Treatment) | CB Hydrolysate | C-PEW Hydrolysate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Component | Titer (mg/L) | Titer (mg/L) | Titer (mg/L) |
| 4-hydroxybenzoic acid | - | 1.8 ± 0.52 | 4.8 ± 0.47 |
| p-coumaric acid | 6.7 ± 0.24 | 2.5 ± 1.27 | 0.8 ± 0.16 |
| Cinnamic acid | 35.6 ± 0.51 | 23.2 ± 2.88 | 6.7 ± 1.29 |
| Cinnamaldehyde | 155.5 ± 12.55 | 73.4 ± 2.82 | 5.5 ± 0.96 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bertacchi, S.; Pagliari, S.; Cantù, C.; Bruni, I.; Labra, M.; Branduardi, P. Enzymatic Hydrolysate of Cinnamon Waste Material as Feedstock for the Microbial Production of Carotenoids. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1146. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18031146
Bertacchi S, Pagliari S, Cantù C, Bruni I, Labra M, Branduardi P. Enzymatic Hydrolysate of Cinnamon Waste Material as Feedstock for the Microbial Production of Carotenoids. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(3):1146. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18031146
Chicago/Turabian StyleBertacchi, Stefano, Stefania Pagliari, Chiara Cantù, Ilaria Bruni, Massimo Labra, and Paola Branduardi. 2021. "Enzymatic Hydrolysate of Cinnamon Waste Material as Feedstock for the Microbial Production of Carotenoids" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 3: 1146. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18031146
APA StyleBertacchi, S., Pagliari, S., Cantù, C., Bruni, I., Labra, M., & Branduardi, P. (2021). Enzymatic Hydrolysate of Cinnamon Waste Material as Feedstock for the Microbial Production of Carotenoids. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(3), 1146. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18031146