Simulating Land-Use Changes and Predicting Maize Potential Yields in Northeast China for 2050
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
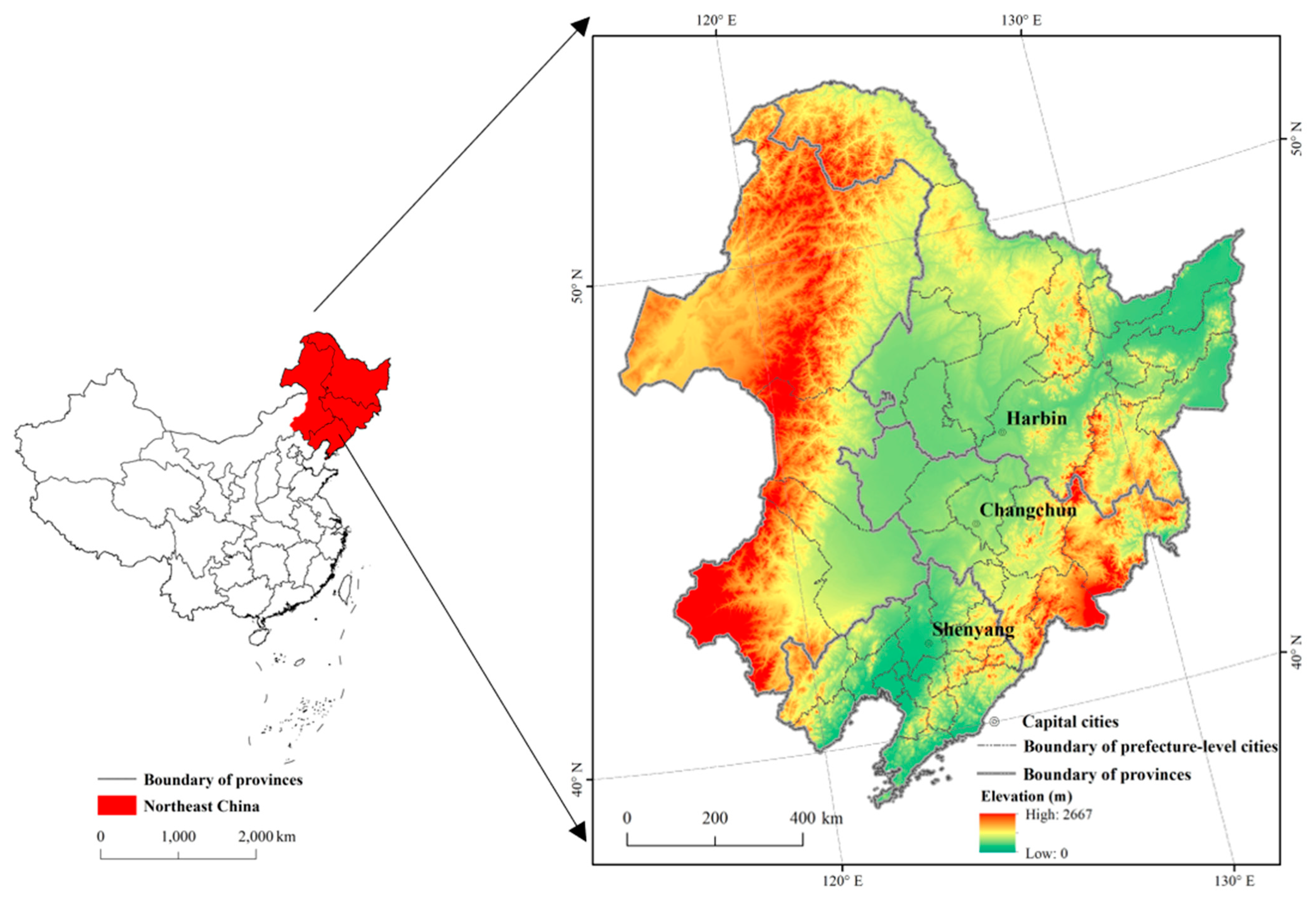
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Preprocessing
2.2.1. Data for Future Land-Use Simulation
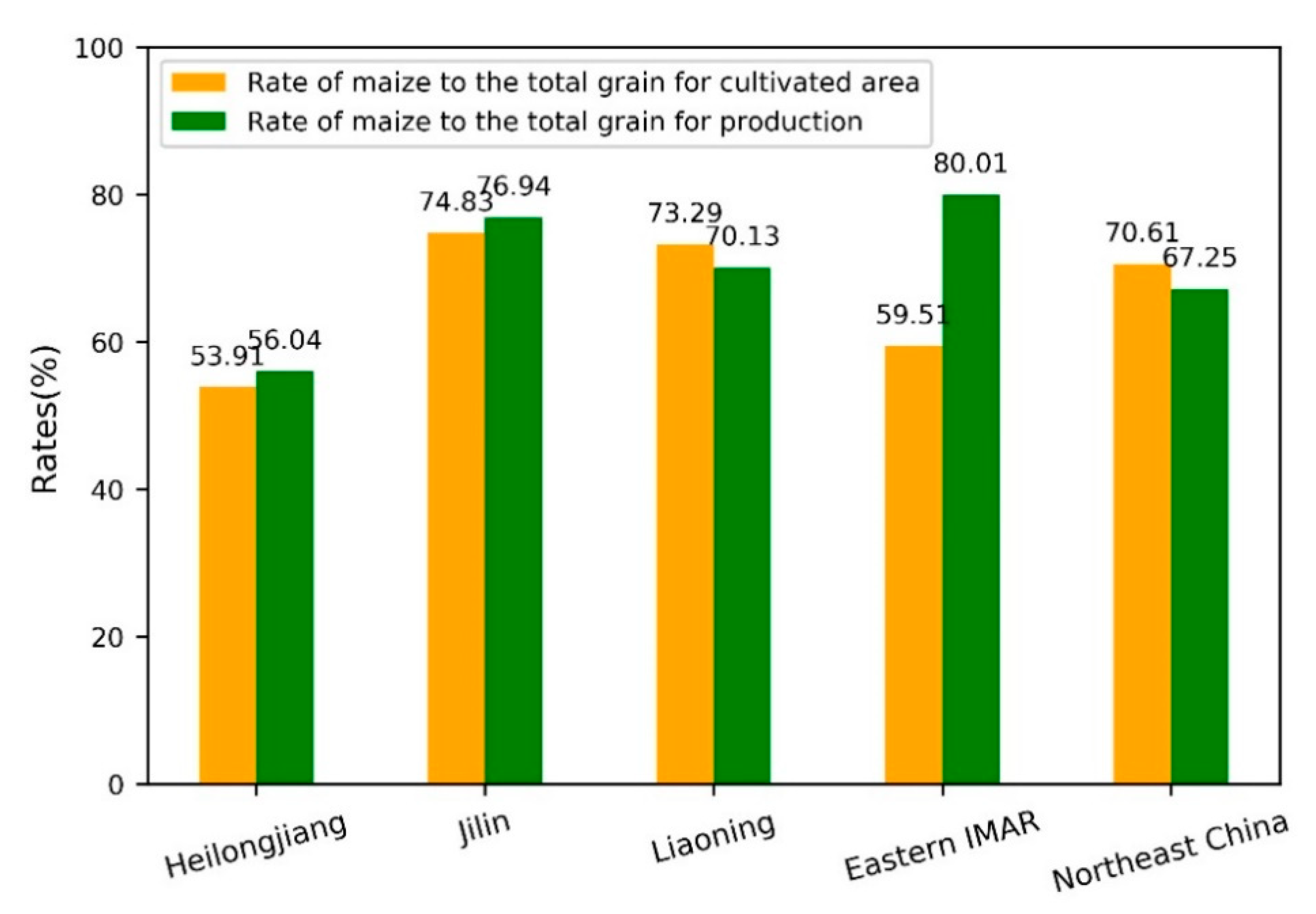
2.2.2. Data for Maize Potential Yields Prediction
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Future Land-Use Simulation
2.3.2. Analysis of Future Land-Use Changes
2.3.3. Prediction of Maize Potential Yields
2.3.4. Analysis of Maize Potential Yields Changes
3. Results
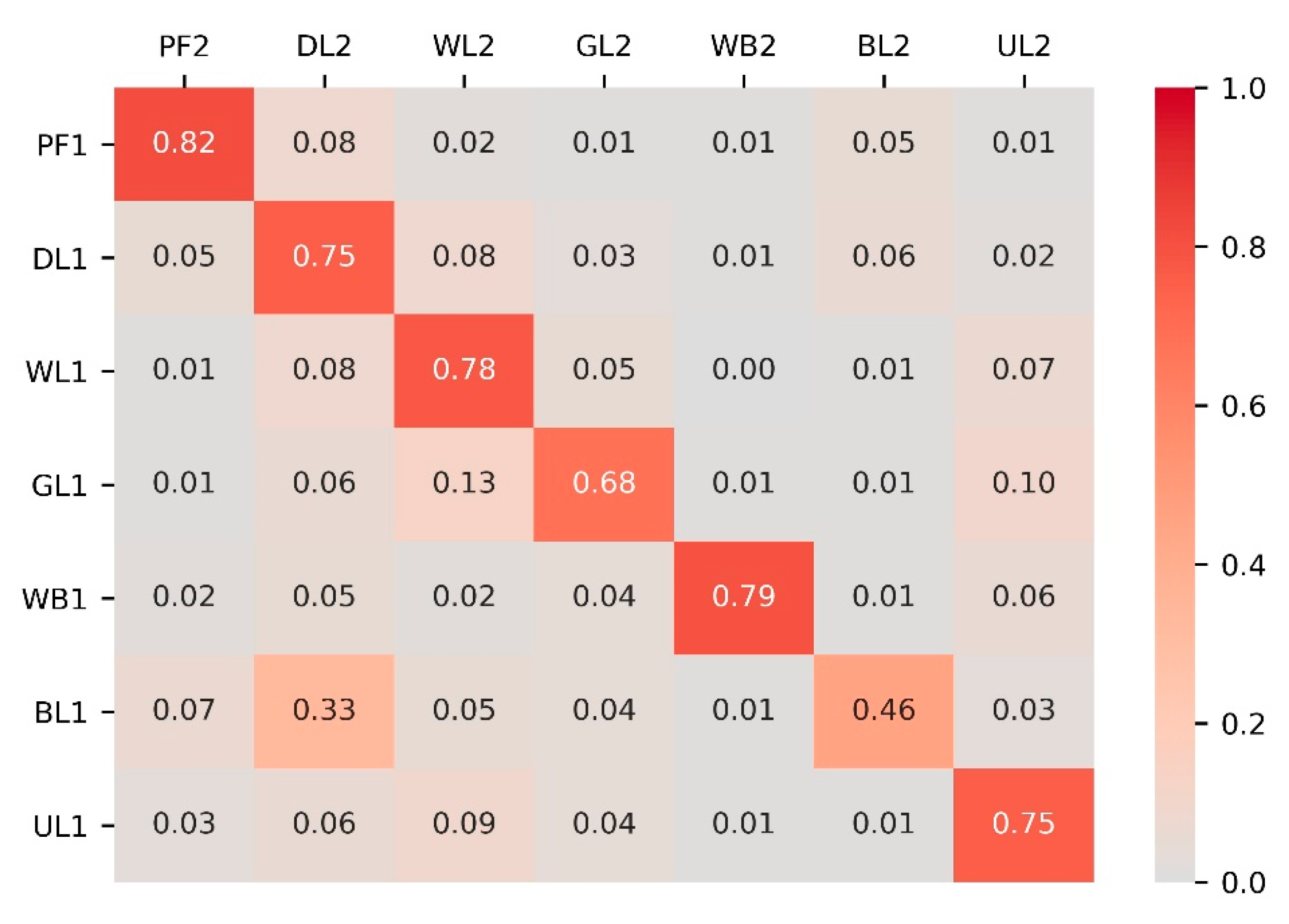
3.1. Accuracy Verification of the CA-Markov Model
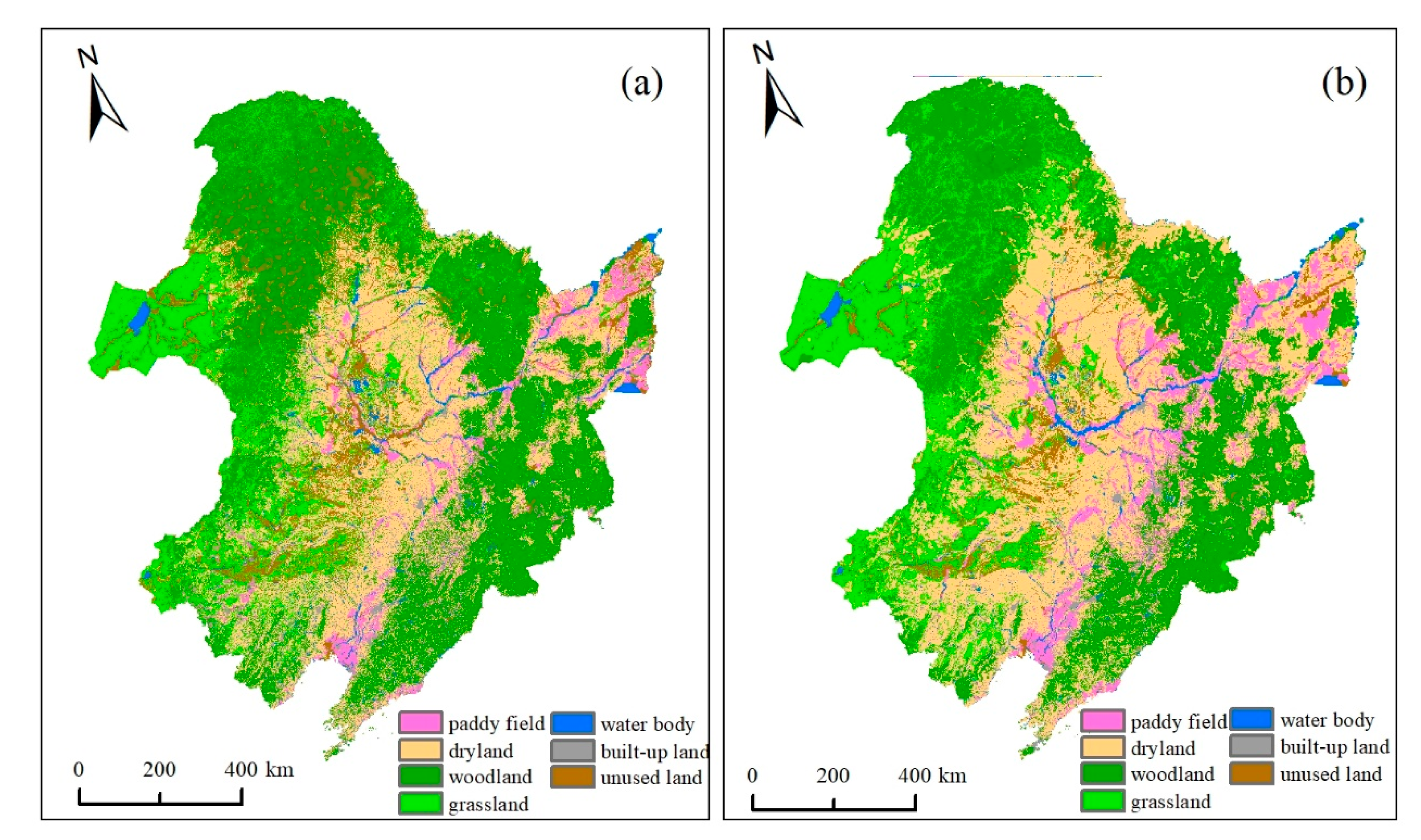
3.2. Land-Use Changes During 2015–2050
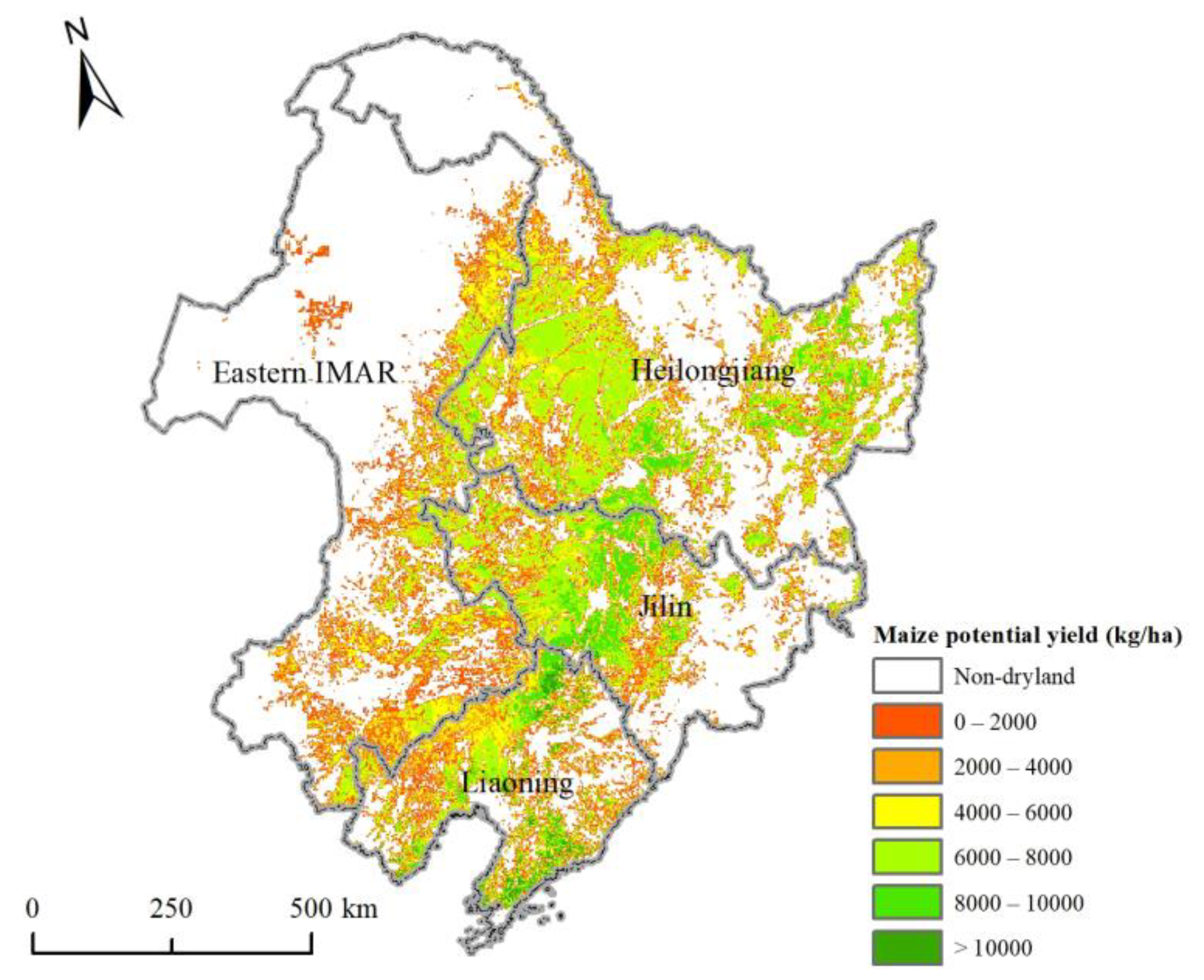
3.3. Maize Potential Yields in 2050
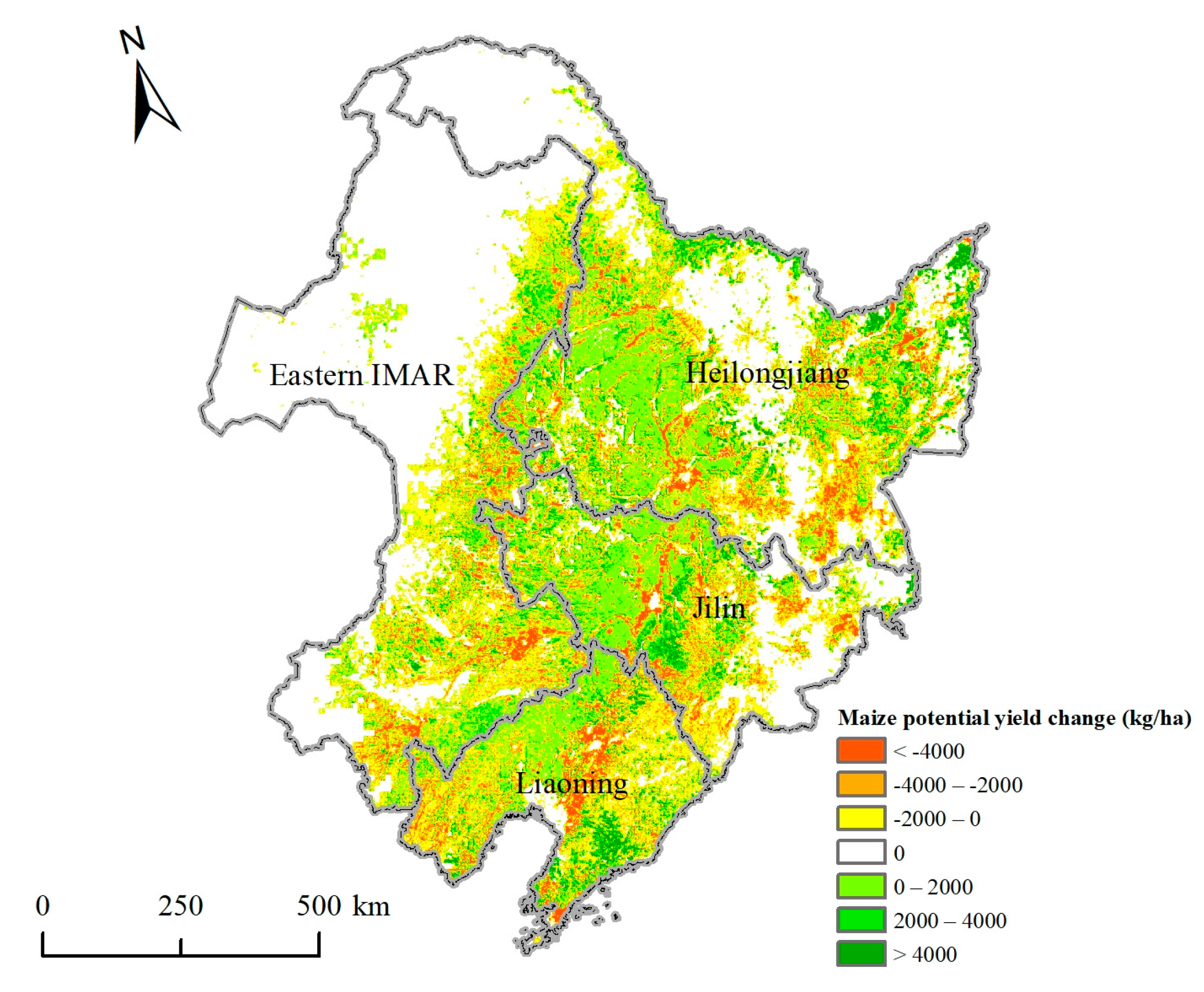
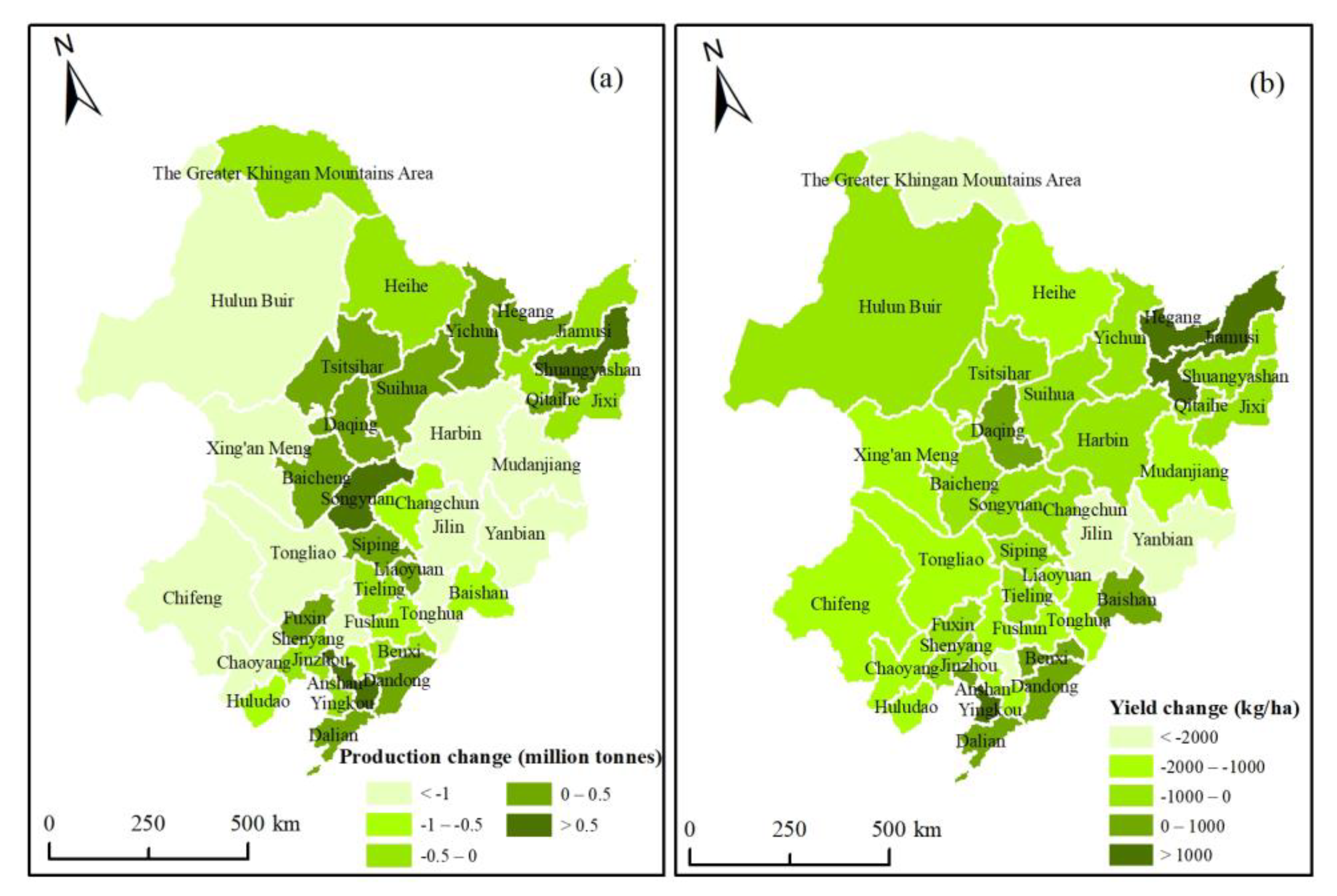
3.4. Temporal and Spatial Changes of Maize Potential Yields
3.4.1. Temporal Changes of Maize Potential Yields during 2015–2050
3.4.2. Spatial Changes of Maize Potential Yields during 2015–2050
4. Discussion
4.1. Kappa Index Method
4.2. More Work Needed in Considering Driving Factors and Constraints
4.3. Impact of Accuracy Verification of Land-Use Simulations on Maize Potential Yields Prediction
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, Y. Spatio-Temporal Change of Cultivated land Use in China and Its Impact on Grain Production Capacity. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, P.; Yang, G.; Su, W. Progress on effects of land use change on land productivity. Prog. Geogr. 2012, 31, 539–550. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Kong, X.; Xiang, H. Progress and enlightenment on potential productivity of China’s arable land. J. China Agric. Univ. 2013, 18, 198–202. [Google Scholar]
- Song, W.; Pijanowski, B. The effects of China’s cultivated land balance program on potential land productivity at a national scale. Appl. Geogr. 2014, 46, 158–170. [Google Scholar]
- Verburg, P.H.; Schot, P.P.; Dijst, M.J.; Veldkamp, A. Land use change modelling: Current practice and research priorities. Geojournal 2004, 61, 309–324. [Google Scholar]
- Aaviksoo, K. Simulating vegetation dynamics and land use in a mire landscape using a Markov model. Landsc. Urban. Plan. 1995, 31, 129–142. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, R.; Li, H.; Juergen, P.; He, Y.; Wang, B. Statistical properties of Markov chain in land use and landscape study. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2006, 17, 434. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelkader, A.; Saad, A.; Abdulla, A.; Reem, A.K. Land Use Change at the Historical Tourist Attractions of Umm Qais, Jordan: GIS and Markov Chain Analyses. Int. J. Hist. Archaeol. 2019, 23, 235–259. [Google Scholar]
- Gobin, A.; Campling, P.; Feyen, J. Logistic modelling to derive agricultural land use determinants: A case study from southeastern Nigeria. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 89, 213–228. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Li, G.; Chen, G. Driving force analysis of land use change based on Logistic regression model in mining area. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2012, 28, 247–255. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Brown, D.; An, L.; Yang, S.; Ligmann-Zielinska, A. Comparative performance of logistic regression and survival analysis for detecting spatial predictors of land-use change. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. 2013, 27, 1960–1982. [Google Scholar]
- Batty, M.; Xie, Y.; Sun, Z. Modeling urban dynamics through GIS-based cellular automata. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 1999, 23, 205–233. [Google Scholar]
- Nuno, N.; Antonio, P. Cellular automata and urban studies: A literature survey. Archit. City Environ. 2007, 1, 368–399. [Google Scholar]
- Verburg, P.; Soepboer, W.; Limpiada, R.; Espaldon, M.; Sharifa, M.; Veldkamp, A. Land use change modelling at the regional scale: The CLUE-S model. Environ. Manag. 2002, 30, 391–405. [Google Scholar]
- Han, H.; Yang, C.; Song, J. Scenario simulation and the prediction of land use and land cover change in Beijing, China. Sustainability 2015, 7, 4260–4279. [Google Scholar]
- Nouri, J.; Gharagozlou, A.; Arjmandi, R.; Faryadi, S.; Adl, M. Predicting urban land use changes using a CA-Markov model. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2014, 39, 5565–5573. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, M.; Sharma, N.; Garg, P.; Kappas, M. Statistical independence test and validation of CA-Markov land use land cover (LULC) prediction results. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2016, 19, 259–272. [Google Scholar]
- Eastman, J.R.; He, J. A Regression-Based Procedure for Markov Transition Probability Estimation in Land Change Modeling. Land 2020, 9, 407. [Google Scholar]
- Mansour, S.; Al-Belushi, M.; Al-Awadhi, T. Monitoring land use and land cover changes in the mountainous cities of Oman using GIS and CA-Markov modelling techniques. Land Use Policy 2020, 91, 104414. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G. Land Use Change and Simulation in Shenzhen Based on FLUS Model. Master’s Thesis, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X. The Simulation Study of the Land Use Pattern of Hunchun City Based on the Model of ANN-CA. Master’s Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X. The Simulation of Land Use Evolution in Nanning City Center Based on GIS and Model of ANN-CA. Master’s Thesis, Guangxi Teach. Educ. University, Nanning, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.; Lai, R.; Luo, W.; Yu, L.; Lai, Z.; Li, H. Analysis and prediction of land use changes in Jinjiang City based on LCM model. For. Resour. Manag. 2018, 1, 96–102. [Google Scholar]
- Hamad, R.; Balzter, H.; Kolo, K. Predicting Land Use/Land Cover Changes Using a CA-Markov Model under Two Different Scenarios. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3421. [Google Scholar]
- Karimi, H.; Jafarnezhad, J.; Khaledi, J.; Ahmadi, P. Monitoring and prediction of land use/land cover changes using CA-Markov model: A case study of Ravansar County in Iran. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontius, J.R.G.; Millones, M. Death to Kappa: Birth of quantity disagreement and allocation disagreement for accuracy assessment. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 4407–4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, J. Prediction and Analysis of Land Use Change Based on CA-Markov Model in Ganzhou District. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2017, 33, 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, W.; Du, P. Dynamic Change of Land Use in Dalian Development Zone Based on CA-Markov Model. Resour. Dev. Mark. 2019, 35, 1347–1350. [Google Scholar]
- Pontius, J.R.G.; Peethambaram, S.; Castella, J.C. Comparison of three maps at multiple resolutions: A case study of land change simulation in Cho Don District, Vietnam. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2011, 101, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Pontius, J.R.G. Diagnostic tools to evaluate a spatial land change projection along a gradient of an explanatory variable. Landsc. Ecol. 2010, 25, 1319–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Pontius, J.R.G. Sensitivity of a land change model to pixel resolution and precision of the independent variable. Environ. Modeling Assess. 2011, 16, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Zhang, L.; Xu, X.; Wang, J. Spatial-temporal characteristics of maize production potential change under the background of climate change in Northeast China over the past 50 years. Geogr. Res. 2016, 35, 864–874. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, D.; Wang, Z.; Luo, L.; Ren, C.-Y. Integrating AVHRR and MODIS data to monitor NDVI changes and their relationships with climatic parameters in Northeast China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geo. Inf. 2012, 18, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, L.; Zhang, S.; Yang, J.; Chang, L.; Xiao, X. Assessing the impact of climate changes on the potential yields of maize and paddy rice in Northeast China by 2050. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2020, 140, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ren, C.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Z.; Liu, M. Quantifying urban land sprawl and its driving forces in Northeast China from 1990 to 2015. Sustainability 2018, 10, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, G.; Wang, J.; Fan, W.; Ying, T.-Y. Vegetation net primary productivity in Northeast China in 2000–2008: Simulation and seasonal change. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2011, 22, 621. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Ren, B.; Zhuo, Z.; Gao, C.; Zhou, G. Faunal composition of grasshopper in different habitats of Northeast China. Chin. J. Ecol. 2006, 25, 286–289. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Liu, M.; Deng, X.; Zhuang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, D. The land use and land cover change database and its relative studies in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2002, 12, 275–282. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Liu, M.; Tian, H.; Zhuang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Tang, X.; Deng, X. Spatial and temporal patterns of China’s cropland during 1990–2000: An analysis based on Landsat TM data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 98, h442–h456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, M.; Zhuang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, X. Study on spatial pattern of land-use change in china during 1995–2000. Sci. China Ser. Darth Sci. 2003, 46, 373–384. [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson, M. Interpolating mean rainfall using thin plate smoothing splines. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 1995, 9, 385–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, M. Interpolation of rainfall data with thin plate smoothing splines—Part I: Two dimensional smoothing of data with short range correlation. J. Geogr. Inf. Decis. Anal. 1998, 2, 139–151. [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson, M. Interpolation of rainfall data with thin plate smoothing splines—Part II: Analysis of topographic dependence. J. Geogr. Inf. Decis. Anal. 1998, 2, 152–167. [Google Scholar]
- Tifafi, M.; Guenet, B.; Hatté, C. Large Differences in Global and Regional Total Soil Carbon Stock Estimates Based on SoilGrids, HWSD, and NCSCD: Intercomparison and Evaluation Based on Field Data from USA, England, Wales, and France. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2018, 32, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastman, J. Idrisi Taiga Guide to Gis and Image Processing; Clark Labs-Clark University: Worcester, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, G.; Zhang, F.; Kong, X. Determining conversion direction of the rural residential land consolidation in Beijing mountainous areas. Trans. CSAE 2009, 25, 214–221. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, C. Spatial pattern change of land use in China in recent 40 years. ACTA Geogr. Sin. 2002, 5, 523–530. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Li, X. Discussion on the index method of regional land use change. ACTA Geogr. Sin. 2003, 5, 643–650. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, X.; Chang, B.; Yu, X. Land use change in Hexi corridor based on CA-Markov methods. Trans. CSAE 2004, 20, 286–291. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Z. Analysis and simulation of land use temporal and spatial pattern based on CA–Markov model. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2007, 32, 414–418. [Google Scholar]
- Wickramasuriya, R.; Bregt, A.; Delden, H.; Hagen-Zanker, A. The dynamics of shifting cultivation captured in an extended constrained cellular automata land use model. Ecol. Model. 2009, 220, 2302–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfram, S. Cellular automata as models of complexity. Nature 1984, 311, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Zhang, H. Simulation of Land-use change in Poyang Lake region based on CA-Markov model. Resour. Environ. Yangtze River 2018, 27, 1207–1219. [Google Scholar]
- Pontius, R. Quantification Error versus Location Error in Comparison of Categorical Maps. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2000, 66, 1011–1016. [Google Scholar]
- Pontius, R.; Schneider, L. Land-cover change model validation by an ROC method for the ipswich watershed, massachusetts, USA. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2001, 85, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, O.G.; Pontius, R.G.J.; Singh, S.K.; Szabó, S. Intensity Analysis and the Figure of Merit’s components for assessment of a Cellular automata-Markov simulation model. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 101, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Y. Study on Spatial Reconstruction of Historical Land Use in Zhenlai County, Jilin Province, China. Ph.D. Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, R.; Pereira, L.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper No. 56; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1990; pp. 31–74. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, G.; van Velthuizen, H.T.; Nachtergaele, F.O.; Medow, S. Global Agro-Ecological Zones Assessment: Methodology and Results; Interim Report; International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis: Laxenburg, Austria, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, G.; Velthuizen, H.; Shah, M.; Nachtergaele, F.O. Global Agro-Ecological Assessment for Agriculture in the 21st Century: Methodology and Results; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2002; pp. 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Xu, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Ning, J. Impact of farmland changes on production potential in China during 1990–2010. J. Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pu, L.; Zhang, S.; Yang, J.; Chang, L.; Bai, S. Spatio-temporal dynamics of maize potential yield and yield gaps in Northeast China from 1990 to 2015. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, F.; Zhang, S.; Xu, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, Q.; Bu, K.; Chang, L. The Response of grain potential productivity to land use change: A case study in Western Jilin, China. Sustainability 2015, 7, 14729–14744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pontius, J.R.G.; Boersma, W.; Castella, J.C.; Clarke, K.; De Nijs, T.; Dietzel, C.; Duan, Z.; Fotsing, E.; Goldstein, N.; Kok, K.; et al. Comparing the input, output, and validation maps for several models of land change. Ann. Reg. Sci. 2008, 42, 11–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García, A.M.; Santé, I.; Boullón, M.; Crecente, R. A comparative analysis of cellular automata models for simulation of small urban areas in Galicia, NW Spain. Comput. Environ. Urban. Syst. 2012, 36, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Factors | Cropland | Woodland | Grassland | Water Body | Built-Up Land | Unused Land | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constrains | Water | Water | Water | Water | |||
| Driving factors | DEM (m) | monotonically decreasing; sigmoidal; c = 100, d = 900 | monotonically increasing; sigmoidal; a = 100, b = 2000 | monotonically decreasing; sigmoidal; c = 50, d = 1000 | monotonically decreasing; sigmoidal; c = 50, d = 300 | monotonically decreasing; sigmoidal; c = 50, d = 300 | |
| Slope (°) | monotonically decreasing; J-shaped; c = 2, d = 15 | monotonically increasing; J-shaped; a = 2, b = 25 | monotonically decreasing; J-shaped; c = 10, d = 30 | monotonically decreasing; J-shaped; c = 2, d = 15 | monotonically decreasing; J-shaped; c = 5, d = 15 | ||
| Aspect (°) | symmetric; sigmoidal; a = 10, b = 180, c = 210, d = 350 | symmetric; sigmoidal; a = 10, b = 180, c = 210, d = 350 | symmetric; sigmoidal; a = 10,b = 180, c = 210, d = 350 | symmetric; sigmoidal; a = 10,b = 180, c = 210, d = 350 | symmetric; sigmoidal; a = 10, b = 180, c = 210, d = 350 | ||
| Distance from the highway (m) | monotonically decreasing; sigmoidal; c = 2000, d = 50,000 | monotonically decreasing; sigmoidal; c = 500, d = 100,000 | monotonically increasing; sigmoidal; a = 2000, b = 100,000 | monotonically decreasing; sigmoidal; c = 500, d = 50,000 | monotonically increasing; sigmoidal; a = 500, b = 100,000 | ||
| Distance from the railway (m) | monotonically decreasing; sigmoidal; c = 4000, d = 100,000 | monotonically decreasing; sigmoidal; c = 500, d = 100,000 | monotonically increasing; sigmoidal; a = 2000, b = 100,000 | monotonically decreasing; sigmoidal; c = 500, d = 50,000 | monotonically increasing; sigmoidal; a = 500, b = 100,000 | ||
| Population density (people/km2) | monotonically decreasing; sigmoidal; c = 500, d = 5000 | monotonically decreasing; sigmoidal; c = 500, d = 3000 | monotonically decreasing; sigmoidal; c = 500, d = 3000 | monotonically increasing; sigmoidal; a = 100, b = 3000 | monotonically decreasing; sigmoidal; c = 100, d = 3000 | ||
| GDP (104 yuan/km2) | monotonically decreasing; sigmoidal; c = 500, d = 2000 | monotonically decreasing; sigmoidal; c = 500, d = 5000 | monotonically decreasing; sigmoidal; c = 500, d = 5000 | monotonically increasing; sigmoidal; a = 100, b = 5000 | monotonically decreasing; sigmoidal; c = 500, d = 3000 | ||
| Distance from the cities (m) | monotonically increasing; sigmoidal; a = 1000, b = 30,000 | monotonically increasing; sigmoidal; a = 1000, b = 30,000 | monotonically increasing; sigmoidal; a = 1000, b = 30,000 | monotonically increasing; sigmoidal; a = 100, b = 5000 | |||
| Distance from the villages (m) | monotonically decreasing; sigmoidal; c = 5000, d = 30,000 | monotonically increasing; sigmoidal; a = 1000, b = 20,000 | monotonically increasing; sigmoidal; a = 1000, b = 30,000 | monotonically increasing; sigmoidal; a = 1000, b = 60,000 | |||
| Driving Factors | DEM | Slope | Aspect | Distance from the Highway | Distance from the Railway | Population Density | GDP | Distance from the Cities | Distance from the Villages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cropland | 0.1519 | 0.1894 | 0.1894 | 0.0919 | 0.0919 | 0.0508 | 0.0508 | 0.0919 | 0.0919 |
| Woodland | 0.1878 | 0.1878 | 0.1292 | 0.1091 | 0.1091 | 0.0466 | 0.0466 | 0.0919 | 0.0919 |
| Grassland | 0.1878 | 0.1878 | 0.1292 | 0.1091 | 0.1091 | 0.0466 | 0.0466 | 0.0919 | 0.0919 |
| Water body | |||||||||
| Built-up land | 0.1840 | 0.1840 | 0.1385 | 0.0822 | 0.0822 | 0.1645 | 0.1645 | ||
| Unused land | 0.1831 | 0.1831 | 0.1263 | 0.1059 | 0.1059 | 0.0603 | 0.0475 | 0.0938 | 0.0938 |
| Area of Land-Use Types in 2015 (Million ha) | Initial Total Area | Gross Loss | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PF | DL | WL | GL | WB | BL | UL | ||||
| Area of land-use types in 2000 (million ha) | PF | 2.71 | 1.20 | 0.11 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.20 | 0.13 | 4.51 | 1.80 |
| 4.11 | 0.15 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.13 | 0.01 | 4.51 | 0.40 | ||
| DL | 1.95 | 23.74 | 2.63 | 1.84 | 0.40 | 1.24 | 0.84 | 32.68 | 8.94 | |
| 2.95 | 27.22 | 0.81 | 0.41 | 0.17 | 0.88 | 0.25 | 32.69 | 5.47 | ||
| WL | 0.19 | 2.78 | 42.61 | 2.68 | 0.21 | 0.17 | 1.48 | 50.11 | 7.50 | |
| 0.44 | 6.91 | 39.46 | 2.84 | 0.09 | 0.10 | 0.25 | 50.11 | 9.65 | ||
| GL | 0.16 | 2.29 | 4.67 | 12.91 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 3.55 | 23.91 | 11.02 | |
| 0.23 | 3.92 | 1.17 | 18.14 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.34 | 23.94 | 5.78 | ||
| WB | 0.10 | 0.28 | 0.13 | 0.20 | 1.68 | 0.05 | 0.53 | 2.96 | 1.28 | |
| 0.06 | 0.22 | 0.07 | 0.16 | 2.27 | 0.02 | 0.16 | 2.96 | 0.70 | ||
| BL | 0.15 | 0.92 | 0.13 | 0.11 | 0.03 | 1.24 | 0.05 | 2.63 | 1.39 | |
| 0.22 | 0.89 | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.02 | 1.33 | 0.03 | 2.63 | 2.31 | ||
| UL | 0.29 | 0.81 | 0.49 | 1.19 | 0.26 | 0.07 | 3.90 | 7.00 | 3.10 | |
| 0.39 | 0.97 | 0.20 | 0.57 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 4.79 | 7.01 | 2.21 | ||
| Final total area | 5.57 | 32.02 | 50.78 | 19.00 | 2.84 | 3.14 | 10.48 | 123.83 | 35.03 | |
| 8.40 | 40.28 | 41.82 | 22.23 | 2.70 | 2.59 | 5.82 | 123.83 | 26.52 | ||
| Gross gain | 2.86 | 8.28 | 8.16 | 6.09 | 1.16 | 1.90 | 6.58 | 35.03 | ||
| 4.29 | 13.06 | 2.36 | 4.08 | 0.43 | 1.26 | 1.03 | 26.52 | |||
| Land Use Types | 2015 | 2050 | Area Changes (Million ha) | Proportion Changes (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area (Million ha) | Proportion (%) | Area (Million ha) | Proportion (%) | |||
| PF | 5.57 | 4.50 | 7.45 | 6.01 | 1.88 | 1.52 |
| DL | 32.02 | 25.86 | 31.70 | 25.60 | −0.32 | −0.26 |
| WL | 50.78 | 41.01 | 45.64 | 36.86 | −5.14 | −4.15 |
| GL | 19.00 | 15.34 | 17.26 | 13.94 | −1.74 | −1.41 |
| WB | 2.84 | 2.29 | 3.23 | 2.61 | 0.39 | 0.32 |
| BL | 3.14 | 2.54 | 4.46 | 3.60 | 1.32 | 1.07 |
| UL | 10.48 | 8.46 | 14.09 | 11.38 | 3.61 | 2.92 |
| Land Use Types | Paddy Field | Dryland | Woodland | Grassland | Water Body | Built-Up Land | Unused Land | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kappa index | 0.61 | 0.66 | 0.85 | 0.64 | 0.73 | 0.69 | 0.57 | 0.77 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pu, L.; Yang, J.; Yu, L.; Xiong, C.; Yan, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S. Simulating Land-Use Changes and Predicting Maize Potential Yields in Northeast China for 2050. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 938. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18030938
Pu L, Yang J, Yu L, Xiong C, Yan F, Zhang Y, Zhang S. Simulating Land-Use Changes and Predicting Maize Potential Yields in Northeast China for 2050. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(3):938. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18030938
Chicago/Turabian StylePu, Luoman, Jiuchun Yang, Lingxue Yu, Changsheng Xiong, Fengqin Yan, Yubo Zhang, and Shuwen Zhang. 2021. "Simulating Land-Use Changes and Predicting Maize Potential Yields in Northeast China for 2050" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 3: 938. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18030938
APA StylePu, L., Yang, J., Yu, L., Xiong, C., Yan, F., Zhang, Y., & Zhang, S. (2021). Simulating Land-Use Changes and Predicting Maize Potential Yields in Northeast China for 2050. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(3), 938. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18030938








